INTRODUCTION
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease. It is the most common form of dementia. Generally, it affects older people above 65 years of age. However, it can occur at any age. Clinical symptoms of AD include progressive loss of memory, irritability, impairment in cognitive function, and a mess in thinking and decision-making ability [1]. AD is characterized by the deposition of neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) resulting from the aggregation of hyperphosphorylated tau protein and amyloid-β (Aβ1-42) peptides. In addition, hyperactivation of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme (AChE), upregulation of glutamate transmission, glial cell activation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuro-inflammation also occur in the AD brain. There is neuronal death, loss of synaptic plasticity, and shrinkage in the hippocampal region [2]. Age, chronic diseases, cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, diabetes, genetic, and environmental changes are some triggering factors for AD [3,4,5].
Only four medications are approved by FDA for the treatment of AD. Based on the mechanism of action, they are anti-cholinesterase inhibitors (Galantamine, Donepezil, and Rivastigmine) and NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptor antagonists (Memantine). These medications only address the symptoms rather than the disease progression [6]. So, there is a need for new therapeutic approaches for AD. Again, the blood–brain barrier (BBB) plays a key role in drug delivery. Not all active drug moieties can cross BBB. So, it is necessary to target BBB during drug development against neurodegenerative diseases including AD [7].
Enormous shreds of evidence show aging and raised blood pressure are important risk factors for AD progression. The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is an endocrinal hormonal system that mediates several physiological and pathological functions by controlling salt and water retention, blood volume, and systemic vascular resistance. Hypertension arises due to an imbalance of the RAS. Hyperactivation of RAS in the brain is responsible for the induction of AD. It generates oxidative stress and neuronal inflammation. In the AD brain, there is an inadequate blood supply and insufficient clearance of metabolic waste products. So, inhibition of RAS in the brain can enhance cognition in AD patients [8,9]. The review aims to insight into the novel use of RAS inhibitors against AD. It describes all the preclinical and clinical studies using search engines such as Scopus, Google Scholar, Science Direct, and PubMed with the keywords AD, Angiotensin, ACE, and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), mainly from 2015 to 2024.
ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE
There is no exact etiology of AD established to date. However, NFTs inside neurons and amyloid plaques between neurons are the hallmarks of AD [10]. NFTs are formed by the hyperphosphorylation of Tau protein (p-tau). Tau is an important protein for stabilizing microtubules [11]. Insoluble β-Amyloid (Aβ1-42) is a neurotoxic substance produced by cleaving amyloid precursor proteins (APPs). Deposition of Aβ peptide causes the aggregation of soluble oligomers and the formation of senile plaque. In the AD brain, there is a decline in the clearance of oligomerized Aβ [12]. Aβ-oligomer is capable of producing reactive oxygen or nitrous species (ROS/RNS) by postponing scavenging activity. The presence of ROS/RNS activates the microglia cells leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and the generation of pro-inflammatory markers [13,14].
Another hypothesis is on the role of neurotransmitters in AD. Acetylcholine (ACh) is a major neurotransmitter in the hippocampal area. In AD, the amount of ACh declines due to over activity of the AChE. Less availability of ACh causes improper synaptic transmission through muscarinic and nicotinic receptors leading to cognitive impairment [15]. In a normal brain, glutamate acts as an NMDA receptor agonist and plays a role in maintaining synaptic plasticity. Excessive production and release of glutamate cause neuronal damage [16]. Genetically, AD is developing due to the mutations in Apo lipoprotein E4, presenilin-1, and presenilin-2 genes [17,18].
Brain Renin-angiotensin system and Alzheimer’s diseaseThe brain also contains the peripheral RAS components. Conversion of angiotensinogen to Ang I is done by renin-mediated cleavage. Ang I is then converted to Ang II by ACE-I. Ang II activates the angiotensin type-1 (AT1 R) receptor. RAS causes neurodegeneration through Ang II- AT1 receptor stimulation inside the brain. Ang II induces the production of neurotoxic oligomerized Aβ and hyperphosphorylated tau [19]. The activated brain RAS uplifts the production of ROS and RNS. ACE-I is associated with neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, glial cell activation, elevated γ-secretase activity, and brain atrophy [20,21]. Binding of Ang II with AT1 R activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), NRF2 and the JNK signaling pathway prompts vascular resistance, inflammation, and oxidative stress [22,23]. Hence, excessive Ang II concentrations, and up-regulation of ACE and AT1 receptors are the potential contributors (Fig. 1) to AD [9,24].
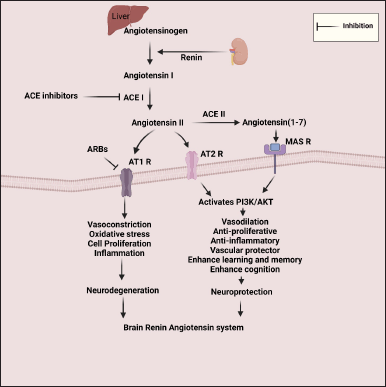 | Figure 1. RAS in neurodegeneration and neuroprotection [The neurodegenerative effects of Ang II are associated with ACE-I and AT1 receptors. The neuroprotective effects of Ang II are associated with the AT2 receptor and that of Ang 1-7 are associated with ACE-II and Mas receptor]. [Click here to view] |
On the other hand, Ang II is inactivated by ACE II to produce angiotensin 1-7, which can activate the MAS1 receptor and exert vasodilator effects. Ang II also activates the AT2 receptor. AT2 receptors mediate anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects. Mas receptors mediate anti-inflammatory effects. So, the components of the angiotensin system like ACE II, MAS1, and the AT2 receptor reverse the neurodegenerative effects of ACE and the AT1 receptor [9,25,26].
Stress, age, and chronic vascular disorders are major risk factors for up-regulating the brain RAS through the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Evidence of chronic unpredictable mild stress on a non-transgenic model found the hyperactivity of ACE protein, p-tau, and oligomerized Aβ in the hippocampal region [27]. From a meta-analysis, it is revealed that there is a synchronized correlation found between ACE 1 and ApoE ε4 allele [28]. The modified ApoE ε4 gene allele has a significant role in the development of sporadic AD due to the unbalancing lipid level in the brain [29]. An age-related cognitive impaired brain down-regulates the ACE II and AT2 receptors. Activation of AT1 and nicotinamide oxidase (NOX) activate the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB), RhoA/Rho kinase pathway and inhibit PI3K/Akt signaling and glycogen synthase kinase- 3 beta (GSK-3β). Oxidative stress is mediated by nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) NOX which further stimulates superoxide production. Free radicals cause neuronal dysfunction, and neuronal death [30] and encourage neuronal inflammation by upregulating tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), and proinflammatory cytokines like IL-1β and IL-6 [31]. Apoptosis cascade and neuronal inflammation induce neuronal death, reduction in ACh, and impaired G-protein signaling [32] (Fig. 2).
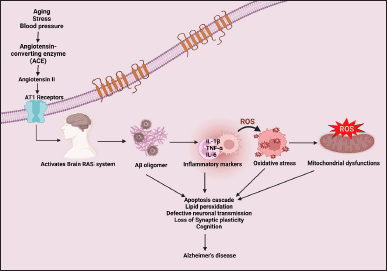 | Figure 2. Angiotensin II (Ang II) in the pathogenesis of AD [Ang II oligomerizes Aβ, encourages the inflammatory, oxidative, and apoptosis pathways thereby resulting in loss of synaptic plasticity and integrity; impaired cognition and neuronal transmission]. [Click here to view] |
RAS INHIBITORS IN AD
A lot of RAS components are altered in the AD brain. Arterial hypertension is a major contributor to the development of AD. So, anti-hypertensive drugs inhibiting RAS are now repurposed for AD management. Notably, the AD patient’s brain has a higher amount of ACE-I, which produces Ang II and aldosterone [33]. Targeting these two components can be useful in RAS-induced AD. Anti-hypertensive drugs like ACE inhibitors and Ang II receptor (AT1 receptor)ARBs are the first-line treatment options due to their indication and safety profile [34]. These two classes of drugs down-regulate the RAS. ACE inhibitors inhibit the ACE-I and ARBs block the AT1R.
The ACE inhibitors such as Benazepril, Enalapril, Moexepril, Quinapril, and Ramipril cannot cross the BBB. In contrast, Captopril, Fosinopril, Lisinopril, Perindopril, Trandolapril, and Zofenopril are the drugs that penetrate BBB [35]. Similarly, ARBs such as Eprosartan, Irbesartan, Losartan, and Olmesartan do not cross BBB whereas the drugs such as Azilsartan, Candesartan, Telmisartan, and Valsartan can cross the BBB [36].
Preclinical studies
The in-vitro and in-vivo studies on ACE inhibitors and ARBs are given in Table 1.
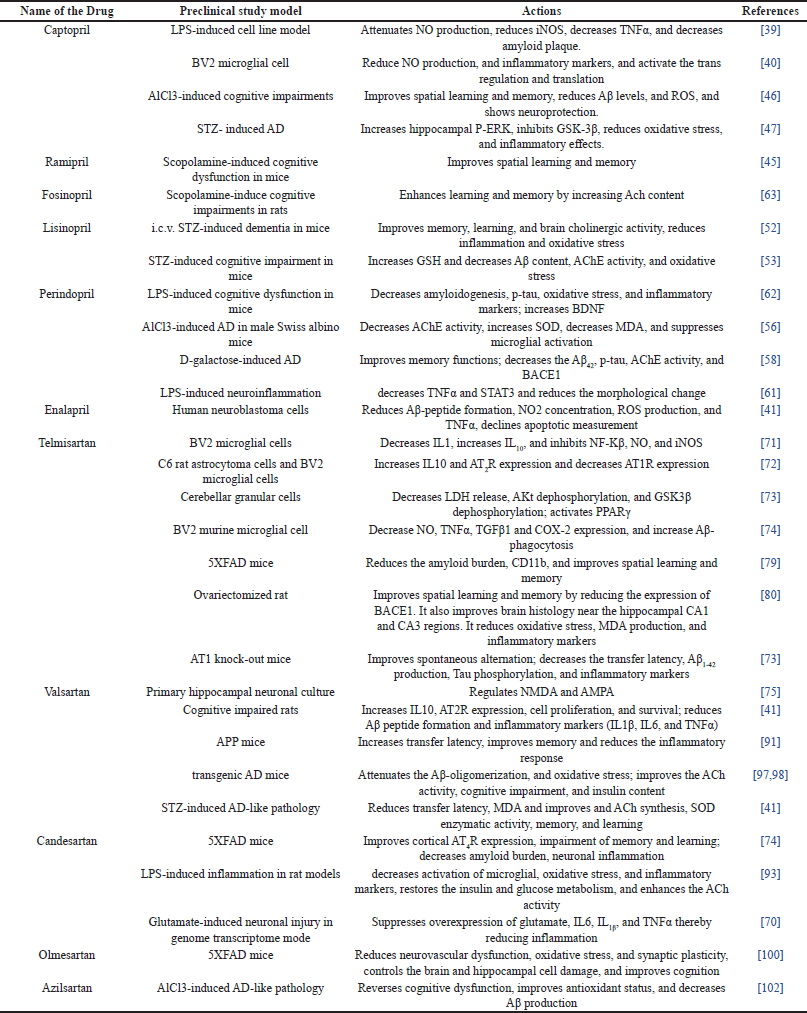 | Table 1. In vivo and In vitro pre-clinical trial outcomes of some RAS inhibitors in the management of AD. [Click here to view] |
ACE inhibitors
ACE inhibitors are structurally and chemically different. Based on the presence of different chemical groups they are classified into three groups such as sulfhydryl-containing ACE inhibitor (Captopril), dicarboxyl-containing ACE inhibitor (Enalapril), and phosphorus-containing ACE inhibitor (Fosinopril). Different ACE inhibitors have different pharmacokinetic properties and potency based on chemical structure. According to the drug bank data, lisinopril and captopril exhibit 30%–75% bioavailability, respectively. Other ACEIs are considered prodrugs due to their very low bioavailability ranging from 4% to 60%. All are orally absorbed but show different rates of crossing the BBB. Lipophilicity is denoted in log p value. This property strongly decides the BBB permeability of ACEIs. An increase in log p enhances the permeability. Fosinopril has the highest log p value (4.71) with the highest BBB permeability among ACEIs whereas Lisinopril has the lowest (−1.2) log p value [37,38].
In vitro studies
Both Perindopril and Captopril reduce NO production and activate the transregulation and translation of microglial cells. Both reduce bradykinin production, and neuronal inflammation and improve neurodegeneration [39,40]. Enalapril reduces Aβ-peptide formation, ROS production, and TNFα. It decreases the mortality of cells in human neuroblastoma cells. It declines apoptotic measurement, decreases nitrite concentration, and scavenges the activity of free radical and peroxy nitrate [41]. In an LPS-induced cell line model, Captopril attenuates NO production, reduces iNOS, decreases TNFα, and decreases amyloid plaque in the hippocampus and cortex region [39]. So, the anti-oxidant and neuroprotective effects of ACEIs may be useful in the treatment of AD and other neurodegenerative disorders.
In vivo studies
Captopril
Captopril delays neurodegeneration by reducing tau hyperphosphorylation (p-tau), and regulating the amyloidogenic process of APP [42,43]. In STZ induced cognitive impairment model, Captopril increases SOD (superoxide dismutase) and Catalase; reduces MDA (malonyl dialdehyde) and NOX [42]. It significantly suppresses the apoptotic marker Bax and the inflammatory markers such as NF-kB, IL-1 β, COX-1, and COX-2; and elevated anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 levels in H2O2-induced oxidative damage in C6 cells [44]. This shows that the anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory actions of Captopril may be attributed to its efficacy in improving learning and memory.
It remarkably improves cognition, particularly in APoE4- carriers of specific ACE genotypes [45]. In scopolamine-induced memory deficits, Captopril improves spatial learning and memory at 25 mg/kg doses in Swiss mice [46]. It reduces Aβ levels, decreases amyloidogenesis, suppresses ROS, and shows neuroprotection against the AlCl3-induced AD-like pathology [47]. It is also effective against STZ-induced AD in rats. It increases hippocampal P-ERK, inhibits GSK-3β, reduces oxidative stress, and has anti-inflammatory effects [48]. It significantly increases the hippocampal BDNF, IL-6, oxidative stress pointers, and nitric oxide in scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats [49]. So, Captopril is also improving cholinergic function.
Ramipril
Ramipril is a potent lipid-soluble anti-hypertensive drug. It improves cognition by acting on central RAS via anti-inflammatory mechanisms [50]. It declines the over-expression of ACE in myelomonocytes. It improves the immunological response and decreases cognitive deterioration by reducing the Aβ content in the AD brain [51]. Ramipril improves spatial learning and memory in scopolamine-induced cognitive dysfunction in mice at a dose of 4 mg/kg for 8 days [46]. In another experiment following the whole brain irradiation procedure in Fischer rats; Ramipril decreases the activation of microglial cells and elevates the Ang (1-7) thereby showing neuroprotective actions [52].
Lisinopril
It reduces inflammation and oxidative stress in i.c.v. STZ-induced dementia in mice. It modulates the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma PPAR-γ and has the potential to cross the BBB. It can also address Aβ proteases including insulin-degrading enzymes [52]. It increases GSH and decreases Aβ content, AChE activity, and oxidative stress in STZ-induced cognitive impairment in mice at a dose of 10 and 15 mg/kg for 18 days [53]. It significantly improves the learning and memory dysfunction in a Drosophila melanogaster model of AD [54]. It and atorvastatin significantly reduce total tau and pTau in PS19 transgenic mice [55]. It improves memory, and learning by increasing brain cholinergic, anti-oxidant, and anti-inflammatory activity.
Perindopril
It improves cognition against AlCl3 and D-galactose-induced AD in male Swiss albino mice by decreasing AChE activity, increasing SOD, decreasing MDA, and suppressing microglial activation [56,57,58]. Perindopril improves the reduced glutathione content as an anti-oxidant in the hippocampus of rats [59]. Perindopril improves cognition in a mouse model of AD by inhibiting brain ACE activity [60]. However, Perindopril is less effective than captopril in AlCl3-induced amyloidogenesis and AD-like pathology [47].
A dose of 0.5 mg/kg for 30 days, decreases the Aβ42, p-tau, AChE activity, and BACE1 in D-galactose-induced AD in rats to improve learning, memory, and cognition [61]. At a dose of 0.5 and 1 mg/kg for 7 days, it decreases amyloidogenesis, p-tau, oxidative stress, and inflammatory markers in LPS-induced cognitive dysfunction in mice. It also increases neurotrophic factors like BDNF [62]. In another study, at a dose of 0.1 mg/kg for 5 days, it decreases TNFα and STAT3 and reduces the morphological change in LPS-induced neuroinflammation [61]. Hence, the memory-enhancing effect of Perindopril may be attributed to cholinergic, anti-oxidant, and anti-inflammatory activity.
Other ACEIsFosinopril has a high lipophilicity profile. It enhances learning and memory by increasing ACh content in scopolamine-induced cognitive impairments in rats [63]. Enalapril alone ameliorates cerebrovascular dysfunctions but has no effects on amyloidosis in a mouse model of AD [64]. Imidapril and Enalapril are less potent inhibitors of brain ACE. So, they have no beneficial effect on AD [60].
Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)
ARBs are a key class of antihypertensive drugs. They are non-peptide compounds that exhibit different structures. Except for Irbesartan, all ARBs have a free carboxylic acid group. They may have a common tetrazole-biphenyl structure (Candesartan, Irbesartan, Valsartan, and Losartan) or a common benzimidazole group (Candesartan and Telmisartan). These different structures contribute to their different pharmacokinetic profiles and different affinity to the AT1R [65]. They are absorbed orally and their bioavailability ranges from 13% for Eprosartan to 60%–80% for Irbesartan. They have high protein binding properties and high polar surfaces. These properties limit the BBB permeability. Their partition coefficient (LogP) ranges from 2.98 (Olmesartan) to 6.66 (Telmisartan), with increasing permeability to the brain [37,38].
ARBs inhibit nuclear translocation of NF-kB, decrease NOX activation, reduce ROS production, decrease the activity of COX-2, and prostaglandins, halt iNOS activity, decrease pro-inflammatory cytokine production and increase neuroprotectors like IL-10 [66]. They act by blocking the AT1 receptor. They promote the conversion of Ang II to Ang IV thereby increasing the activity of AT2R or AT4R and hence are neuroprotective [67].
In vitro studies
Candesartan restores the cell proliferation of neural stem cells and inhibits Aβ-oligomerization through PI3K activation [68]. It also shows an anti-inflammatory effect through the activation of AT2 receptor [69]. It prevents overexpression of glutamate, IL6, IL1β, and TNFα thereby reducing inflammation. It has also a protective effect on glutamate-induced neuronal injury in a genome transcriptome model [70].
In BV2 microglial cells Telmisartan decreases IL1, increases IL10, and inhibits NF-Kβ, NO, and iNOS [71]. In C6 rat astrocytoma cells and BV2 microglial cells, Telmisartan increases IL10 and AT2R expression and decreases AT1R expression [72]. In cerebellar granular cells, telmisartan decreases LDH release, AKt dephosphorylation, and GSK3β dephosphorylation; and activates PPARγ [73]. Candesartan and Telmisartan decrease NO, TNFα, TGFβ1, and COX-2 expression, and increase Aβ-phagocytosis in BV2 murine microglial cells [71,74].
Valsartan regulates NMDA and AMPA receptors in primary hippocampal neuronal culture [75]. Both Valsartan and Telmisartan restore the cholinergic function [76]. Losartan increases protective signaling through Ang IV/AT4R in mice [77]. Most of the sartans (Losartan, Candesartan, and Telmisartan) have neuroprotective effects by increasing BDNF and VEGF [78]. In addition, they increase cholinergic function and show anti-inflammatory effects which may contribute to their efficacy against cognitive impairment.
In-vivo studies
Telmisartan
Telmisartan reduces amyloid burden, CD11b, and improves spatial learning and memory in 5XFAD mice at a dose of 1 mg/kg (intranasal) for 2 months [79]. It improves spontaneous alternation; and decreases the transfer latency, Aβ1-42 production, Tau phosphorylation, and inflammatory markers at a dose of 10 mg/kg p.o. [76]. It improves spatial learning and memory by reducing the expression of BACE1. It also improves brain histology near hippocampal CA1 and CA3 regions. It reduces oxidative stress, MDA production, and inflammatory markers in the ovariectomized rat model [80]. It shows neuroprotection in AT1 knock-out mice of both sexes [73].
It inhibits the neurotoxicity of microglial cells through NF-κB degradation in LPS-induced neuronal inflammation in C57BL/6 mice [81]. It reduces the expression of NF-κB as well as pro-inflammatory cytokines and upregulates the expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and the levels of heme oxygenase-1 and NADPH quinone oxidoreductase 1 enzymes in cuprizone-induced demyelination and behavioral dysfunction at a dose of 5 mg/kg, p.o. in 6 weeks old male C57BL/6 mice [82]. It alters the AMPK–mTOR–autophagy pathway and microglial viability in LPS-induced neuronal inflammation in BV2 microglial cell lines [83].
It is an FDA-approved anti-hypertensive drug. It acts as a partial agonist of PPARγ. The preclinical studies revealed that activation of PPARγ declines cognitive impairment by crossing the BBB [84]. It also reduces the accumulation of cellular Aβ, phosphorylated-Tau protein, and neuro-inflammation [85]. It also shows neuro-protection, suppresses neuronal apoptosis, and reduces oxidative stress [86]. This contributes to its efficacy against neurodegenerative diseases, particularly AD.
Losartan
It is a prototype ARB that prevents Ang II conversion centrally in mice models [87]. It increases cerebral blood flow. It reduces neuropathology and neuronal damage [88,89]. It reduces AT1R expression and improves AT4R expression [77]. When losartan is conjugated with ascorbic acid, the brain availability of Losartan carboxylic acid, a metabolite of Losartan, increases. It has a neuroprotective effect [90]. Losartan increases IL10, AT2R expression, cell proliferation, and survival; reduces Aβ peptide formation and inflammatory markers (IL1β, IL6, and TNFα) at a dose of 0.24 mg/kg administered for 35 days [78,89]. It increases transfer latency, improves memory, and reduces inflammatory response at a dose of 10 mg/kg for 4 months in APP mice [91]. Because of its low BBB permeability, Losartan can be conjugated with small molecules to improve its brain permeability and efficacy against neurodegenerative diseases.
CandesartanCandesartan controls the NADPH oxidase expression, and lipid peroxidation [92]. It improves cortical AT4R expression, impairment of memory and learning; decreases amyloid burden, and neuronal inflammation at a dose of 1 mg/kg (intranasal) in 5XFAD mice [69,74]. It decreases activation of microglial, oxidative stress, and inflammatory markers, restores insulin and glucose metabolism, and enhances the ACh activity in LPS-induced inflammation in rat models at doses of 0.1 mg/kg and 2 mg/kg for 35 days [61,93]. It increases ACh production and neuroprotective factors like BDNF and VEGF in rats [70,94].
It decreases neuronal damage and improves memory impairments by reducing the brain MDA and increasing the catalase and total thiol at a dose of 1 mg/kg, p.o. in d-galactose-induced cognitive dysfunction [95]. It inactivates the NLRP3 inflammasome, NF-kB Activation, and MAPK Phosphorylation in the mouse macrophage cell line model [96]. So, Captopril by reducing oxidative stress, neuronal inflammation, and microglial activation and improving cholinergic function has the potential to be used to improve memory functions in AD.
Valsartan
Valsartan attenuates the Aβ-oligomerization, and oxidative stress; and improves the ACh activity, cognitive impairment, and insulin content in transgenic AD mice at a dose of 10 and 40 mg/kg [97,98]. It reduces transfer latency, and MDA and improves ACh synthesis, and SOD enzymatic activity thereby improving memory, and learning in STZ-induced AD-like pathology at a dose of 30 mg/kg [41]. Like other ARBs, Valsartan also has the potential against cognitive impairment due to its cholinergic and antioxidant actions.
Olmesartan
Olmesartan is a neuroprotective agent. It prevents oligomerization of Aβ and neuronal senescence by down-regulating p16 and p21 [99]. It reduces neurovascular dysfunction, oxidative stress, and synaptic plasticity, controls brain and hippocampal cell damage, and improves cognition in 5XFAD mice [100].
Amyloid-β plaques, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation are the pathological features of AD. RAS has a role in the pathology of AD. Memory is a cholinergic function [9,101].
Inhibitors of the RAS like ACEIs and ARBs improve the cholinergic function. They show antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions. They reduce Aβ. So, ACEIs and ARBs have the potential to be repurposed against AD and other forms of dementia.
Clinical trials
After the successful outcomes from preclinical models, a lot of clinical trials were conducted on RAS inhibitors against AD. The growth of Aβ plaques and NFTs cannot be eliminated only by cholinesterase inhibitors or NMDAR antagonists. Targeting other approaches like neuronal inflammation, oxidative stress, and NMDAR activity through RAS inhibitors using anti-hypertensive drugs (ACE inhibitors and ARBs) are under clinical trial for the treatment of AD (Table 2). Retrospective cohort studies are conducted to evaluate the risk management of developing AD between RAS-acting drugs and non-RAS-acting drugs. RAS-acting drugs are more effective against AD than non-RAS-acting drugs. RAS-acting drugs can prevent AD pathology and improve cognition [103]. Phase II clinical trials are underway for several novel antihypertensive drug classes, including ACE inhibitors (Perindopril) and ARBs (Telmisartan and Candesartan) [104,105].
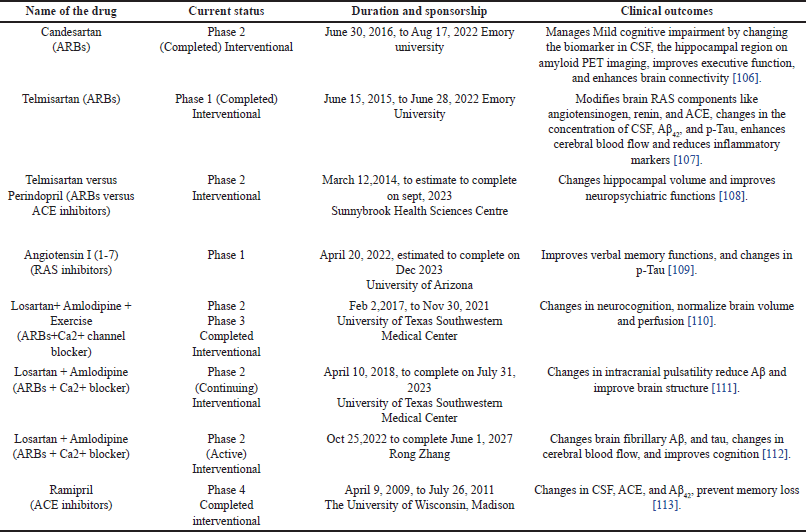 | Table 2. Clinical trial status of some RAS inhibitors and their combinations with other antihypertensive drugs in the management of Alzheimer’s disease. [Click here to view] |
CONCLUSION
RAS inhibitors (ACE inhibitors and ARBs) present a promising strategy for developing effective treatments for AD. By leveraging their mechanisms of action and established safety profiles, RAS inhibitors offer a more direct route to clinical application, potentially bypassing lengthy development processes. Pre-clinical and clinical investigations have shown that RAS inhibitors possess anti-Aβ plaque, anti-tauopathy, free radical scavenging, and anti-inflammatory activities. Furthermore, ongoing research continues to reveal the complexities of Alzheimer's pathology, suggesting that innovative drugs could provide meaningful therapeutic options for managing this devastating neurodegenerative condition. Consequently, ACE inhibitors and ARBs are considered a highly reliable and effective future therapeutic approach against AD.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors are thankful to DBT-BUILDER for providing the support.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
All authors agreed to submit the article to the current journal, gave final approval of the version to be published, made significant contributions to conception and design, data collection, analysis, and interpretation, participated in its writing or critically revised it for important intellectual content, and agreed to be responsible for all aspects of the work. According to the requirements/guidelines of the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE), all of the writers are qualified to be authors.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
There is no funding to report.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
This study does not involve experiments on animals or human subjects.
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated and analyzed are included in this research article.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
REFERENCES
1. Ramachandran AK, Das S, Joseph A, Shenoy GG, Alex AT, Mudgal J. Neurodegenerative pathways in Alzheimer’s disease: a review. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021 Apr 1;19(5):679–92.
2. Srivastava S, Ahmad R, Khare SK. Alzheimer’s disease and its treatment by different approaches: a review. Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Apr 15;216:113320.
3. Ding E, Wang Y, Liu J, Tang S, Shi X. A review on the application of the exposome paradigm to unveil the environmental determinants of age-related diseases. Hum Genomics. 2022 Dec;16(1):1–6.
4. Sahu PK, Tiwari P, Prusty SK, Subudhi BB. Past and present drug development for Alzheimer’s disease. Front Clin Drug Res Alzheimer Disord. 2018 Nov 2;7:214–53.
5. Behera A, Sa N, Pradhan SP, Swain S, Sahu PK. Metal nanoparticles in Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimer’s Dis Rep. 2023 Aug 4(Preprint):1–20.
6. Nunes D, Loureiro JA, Pereira MC. Drug delivery systems as a strategy to improve the efficacy of FDA-approved Alzheimer’s drugs. Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 26;14(11):2296.
7. Wilhelm I, Krizbai IA. In vitro models of the blood–brain barrier for the study of drug delivery to the brain. Mol Pharm. 2014 Jul 7;11(7):1949–63.
8. Loera-Valencia R, Eroli F, Garcia-Ptacek S, Maioli S. Brain renin–angiotensin system as novel and potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 20;22(18):10139.
9. Subudhi BB, Sahu PK. Targeting renin–angiotensin system: a strategy for drug development against neurological disorders. In: Pilowsky, Angiotensin. Academic Press; 202 3. pp. 107–50.
10. Moloney CM, Lowe VJ, Murray ME. Visualization of neurofibrillary tangle maturity in Alzheimer’s disease: a clinicopathologic perspective for biomarker research. Alzheimer’s Dementia. 2021 Sep;17(9):1554–74.
11. Otero-Garcia M, Mahajani SU, Wakhloo D, Tang W, Xue YQ, Morabito S, et al. Molecular signatures underlying neurofibrillary tangle susceptibility in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 2022 Sep 21;110(18):2929–48.
12. Gehlot P, Kumar S, Vyas VK, Choudhary BS, Sharma M, Malik R. Guanidine-based β amyloid precursor protein cleavage enzyme 1 (BACE-1) inhibitors for the Alzheimer’s disease (AD): a review. Bioorg Med Chem. 2022;74:117047.
13. Misrani A, Tabassum S, Yang L. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Feb 18;13:57.
14. Butterfield DA, Halliwell B. Oxidative stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019 Mar;20(3):148–60.
15. Ju Y, Tam KY. Pathological mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2022 Mar;17(3):543.
16. Andersen JV, Schousboe A, Verkhratsky A. Astrocyte energy and neurotransmitter metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease: integration of the glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle. Progress Neurobiol. 2022 Jul 21;217:102331.
17. Yamazaki Y, Zhao N, Caulfield TR, Liu CC, Bu G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: pathobiology and targeting strategies. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019 Sep;15(9):501–18.
18. Galla L, Redolfi N, Pozzan T, Pizzo P, Greotti E. Intracellular calcium dysregulation by the Alzheimer’s disease-linked protein presenilin 2. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 24;21(3):770.
19. Yasar S, Varma VR, Harris GC, Carlson MC. Associations of angiotensin converting enzyme-1 and angiotensin II blood levels and cognitive function. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018 Jan 1;63(2):655–64.
20. Gebre AK, Altaye BM, Atey TM, Tuem KB, Berhe DF. Targeting renin–angiotensin system against Alzheimer’s disease. Front Pharmacol. 2018 Apr 30;9:440.
21. Ouk M, Wu CY, Rabin JS, Edwards JD, Ramirez J, Masellis M, et al. Associations between brain amyloid accumulation and the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors versus angiotensin receptor blockers. Neurobiol Aging. 2021 Apr 1;100:22–31.
22. Labandeira-Garcia JL, Labandeira CM, Guerra MJ, Rodriguez-Perez AI. The role of the brain renin-angiotensin system in Parkinson´s disease. Translat Neurodegen. 2024 Apr 15;13(1):22.
23. Ali NH, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Albuhadily AK, Hamad RS, Alexiou A, et al. Role of brain renin–angiotensin system in depression: a new perspective. CNS Neurosci Therap. 2024 Apr;30(4):e14525.
24. Kehoe PG, Wong S, Al Mulhim N, Palmer LE, Miners JS. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is reduced in Alzheimer’s disease in association with increasing amyloid-β and tau pathology. Alzheimer’s Res Ther. 2016 Dec;8:1–0.
25. Vadhan JD, Speth RC. The role of the brain renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in mild traumatic brain injury (TBI). Pharmacol Therap. 2021 Feb 1;218:107684.
26. Mishra S, Prusty SK, Sahu PK, Das D. Irbesartan protects against aluminium chloride induced amyloidogenesis and cognitive impairment. JKIMSU. 2022 Apr 1;11(2):18–30.
27. De Dios L, Collazo C, Inostroza-Nieves Y. Renin-angiotensin-system increases phosphorylated tau and reactive oxygen species in human cortical neuron cell line. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Dec 1;32:101355.
28. Xin XY, Lai ZH, Ding KQ, Zeng LL, Ma JF. Angiotensin-converting enzyme polymorphisms and Alzheimer’s disease susceptibility: an updated meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2021 Nov 24;16(11):e0260498.
29. Xu C, Garcia D, Lu Y, Ozuna K, Adjeroh DA, Wang K. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Levels of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Apolipoproteins Are Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease and Cardiovascular Diseases. Cells. 2021 Dec 23;11(1):29.
30. Cosarderelioglu C, Nidadavolu LS, George CJ, Oh ES, Bennett DA, Walston JD, et al. Brain renin–angiotensin system at the intersect of physical and cognitive frailty. Front Neurosci. 2020 Sep 30;14:586314.
31. Torika N, Asraf K, Roasso E, Danon A, Fleisher-Berkovich S. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors ameliorate brain inflammation associated with microglial activation: possible implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;11:774–85.
32. Kirouac L, Rajic AJ, Cribbs DH, Padmanabhan J. Activation of Ras-ERK signaling and GSK-3 by amyloid precursor protein and amyloid beta facilitates neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. eNeuro. 2017 Mar 1;4(2):0149–16.
33. Quitterer U, AbdAlla S. Improvements of symptoms of Alzheimers disease by inhibition of the angiotensin system. Pharmacol Res. 2020 Apr 1;154:104230.
34. Sanchis-Gomar F, Lavie CJ, Perez-Quilis C, Henry BM, Lippi G. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and antihypertensives (angiotensin receptor blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors) in coronavirus disease 2019. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020 Jun;95(6):1222–30.
35. Fazal K, Perera G, Khondoker M, Howard R, Stewart R. Associations of centrally acting ACE inhibitors with cognitive decline and survival in Alzheimer’s disease. BJPsych Open. 2017 Jul;3(4):158–64.
36. Salim H, Jones AM. Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) and manufacturing contamination: a retrospective National Register Study into suspected associated adverse drug reactions. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022 Nov;88(11):4812–27.
37. Gouveia F, Camins A, Ettcheto M, Bicker J, Falcao A, Cruz MT, et al. Targeting brain Renin-Angiotensin System for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Past, present and future. Ageing Res Rev. 2022 May 1;77:101612.
38. Drug Bank, n.d. [cited 2021 Nov 1] Available from: https://go.drugbank.com/
39. Asraf K, Torika N, Apte RN, Fleisher-Berkovich S. Microglial activation is modulated by captopril: in vitro and in vivo studies. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 May 1;12:116.
40. Kozin SA, Polshakov VI, Mezentsev YV, Ivanov AS, Zhokhov SS, Yurinskaya MM, et al. Enalaprilat inhibits zinc-dependent oligomerization of metal-binding domain of amyloid-beta isoforms and protects human neuroblastoma cells from toxic action of these isoforms. Mol Biol. 2018 Jul;52:590–7.
41. Abbassi YA, Mohammadi MT, Foroshani MS, Sarshoori JR. Captopril and valsartan may improve cognitive function through potentiation of the brain antioxidant defense system and attenuation of oxidative/nitrosative damage in STZ-induced dementia in rat. Adv Pharm Bull. 2016 Dec;6(4):531.
42. AbdAlla S, El Hakim A, Abdelbaset A, Elfaramawy Y, Quitterer U. Inhibition of ACE retards tau hyperphosphorylation and signs of neuronal degeneration in aged rats subjected to chronic mild stress. BioMed Res Int. 2015 Oct;2015:917156.
43. Sahin B, Ergul M. Captopril exhibits protective effects through anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic pathways against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in C6 glioma cells. Metabo Brain Dis. 2022 Apr;37(4):1221–30.
44. de Oliveira FF, Chen ES, Smith MC, Bertolucci PH. Pharmacogenetics of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in patients with Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2018 Apr 1;15(4):386–98.
45. Ababei DC, Bild V, Ciobica A, Lefter RM, Rusu RN, Bild W. A Comparative study on the memory-enhancing actions of oral renin-angiotensin system altering drugs in scopolamine-treated mice. Am J Alzheimer’s Dis Other Demen. 2019 Aug;34(5):329–36.
46. Mohapatra D, Kanungo S, Pradhan SP, Jena S, Prusty SK, Sahu PK. Captopril is more effective than Perindopril against aluminium chloride induced amyloidogenesis and AD like pathology. Heliyon. 2022 Feb 1;8(2):e08935.
47. Youssef MM, Abd El-Latif HA, El-Yamany MF, Georgy GS. Aliskiren and captopril improve cognitive deficits in poorly controlled STZ-induced diabetic rats via amelioration of the hippocampal P-ERK, GSK3β, P-GSK3β pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 May 1;394:114954.
48. Beheshti F, Akbari HR, Baghcheghi Y, Mansouritorghabeh F, Mortazavi Sani SS, Hosseini M. Beneficial effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition on scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairment in rats, the roles of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, nitric oxide and neuroinflammation. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2021 Aug 18;43(6):505–15.
49. Rygiel K. Can angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors impact cognitive decline in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease? an overview of research evidence in the elderly patient population. J Postgrad Med. 2016 Oct;62(4):242.
50. Bernstein KE, Khan Z, Giani JF, Zhao T, Eriguchi M, Bernstein EA, et al. Overexpression of angiotensin-converting enzyme in myelomonocytic cells enhances the immune response. F1000Res. 2016;5:F1000.
51. Lee TC, Greene-Schloesser D, Payne V, Diz DI, Hsu FC, Kooshki M, et al. Chronic administration of the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, prevents fractionated whole-brain irradiation-induced perirhinal cortex-dependent cognitive impairment. Radiation Res. 2012 Jul 1;178(1):46–56.
52. Liu Z, Zhu H, Fang GG, Walsh K, Mwamburi M, Wolozin B, et al. Characterization of insulin degrading enzyme and other amyloid-β degrading proteases in human serum: a role in Alzheimer's disease?. J Alzheimer's Dis. 2012 Jan 1;29(2):329–40.
53. Singh B, Sharma B, Jaggi AS, Singh N. Attenuating effect of lisinopril and telmisartan in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced experimental dementia of Alzheimer’s disease type: possible involvement of PPAR-γ agonistic property. J Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2013 Jun;14(2):124–36.
54. Thomas J, Smith H, Smith CA, Coward L, Gorman G, De Luca M, et al. The angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor lisinopril mitigates memory and motor deficits in a drosophila model of alzheimer’s disease. Pathophysiology. 2021 Jun 18;28(2):307–19.
55. Collu R, Giunti E, Daley S, Chen M, Xia W. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and statins therapies-induced changes in omics profiles in humans and transgenic tau mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Dec 1;168:115756.
56. Yang WN, Han H, Hu XD, Feng GF, Qian YH. The effects of perindopril on cognitive impairment induced by d-galactose and aluminum trichloride via inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity and oxidative stress. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2013 Dec 1;114:31–6.
57. Messiha BA, Ali MR, Khattab MM, Abo-Youssef AM. Perindopril ameliorates experimental Alzheimer’s disease progression: role of amyloid β degradation, central estrogen receptor and hyperlipidemic-lipid raft signaling. Inflammopharmacology. 2020 Oct;28:1343–64.
58. Yang W, Shi L, Chen L, Zhang B, Ma K, Liu Y, et al. Protective effects of perindopril on d-galactose and aluminum trichloride induced neurotoxicity via the apoptosis of mitochondria-mediated intrinsic pathway in the hippocampus of mice. Brain Res Bull. 2014 Oct 1;109:46–53.
59. Mashhoody T, Rastegar K, Zal F. Perindopril may improve the hippocampal reduced glutathione content in rats. Adv Pharm Bull. 2014 Jun;4(2):155.
60. Yamada K, Uchida S, Takahashi S, Takayama M, Nagata Y, Suzuki N, et al. Effect of a centrally active angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, perindopril, on cognitive performance in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 2010 Sep 17;1352:176–86.
61. Bhat SA, Goel R, Shukla R, Hanif K. Angiotensin receptor blockade modulates NFκB and STAT3 signaling and inhibits glial activation and neuroinflammation better than angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition. Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Dec;53:6950–67.
62. Ali MR, Abo-Youssef AM, Messiha BA, Khattab MM. Tempol and perindopril protect against lipopolysaccharide-induced cognition impairment and amyloidogenesis by modulating brain-derived neurotropic factor, neuroinflammation and oxido-nitrosative stress. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;389:637–56.
63. Deb D, Bairy KL, Nayak V, Rao M. Comparative effect of lisinopril and fosinopril in mitigating learning and memory deficit in scopolamine-induced amnesic rats. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2015 Jan 1;2015:521718.
64. Ongali B, Nicolakakis N, Tong XK, Aboulkassim T, Imboden H, Hamel E. Enalapril alone or co-administered with losartan rescues cerebrovascular dysfunction, but not mnemonic deficits or amyloidosis in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimer's Dis. 2016 Jan 1;51(4):1183–95.
65. Israili ZH. Clinical pharmacokinetics of angiotensin II (AT1) receptor blockers in hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2000 Apr;14(1):S73–86.
66. Villapol S, Saavedra JM. Neuroprotective effects of angiotensin receptor blockers. Am J Hypertens. 2015 Mar 1;28(3):289–99.
67. Jackson L, Eldahshan W, Fagan SC, Ergul A. Within the brain: the renin angiotensin system. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 15;19(3):876.
68. Choi H, Choi NY, Lee KY, Lee YJ, Koh SH. Candesartan restores the Amyloid Beta-inhibited proliferation of neural stem cells by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. Dementia Neurocognitive Disord. 2017 Sep 1;16(3):64–71.
69. Trigiani LJ, Royea J, Lacalle-Aurioles M, Tong XK, Hamel E. Pleiotropic benefits of the angiotensin receptor blocker candesartan in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Hypertension. 2018 Nov;72(5):1217–26.
70. Elkahloun AG, Hafko R, Saavedra JM. An integrative genome-wide transcriptome reveals that candesartan is neuroprotective and a candidate therapeutic for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer's Res Therap. 2016 Dec;8:1–8.
71. Torika N, Asraf K, Danon A, Apte RN, Fleisher-Berkovich S. Telmisartan modulates glial activation: in vitro and in vivo studies. PLoS One. 2016 May 17;11(5):e0155823.
72. Wang ZF, Li J, Ma C, Huang C, Li ZQ. Telmisartan ameliorates Aβ oligomer-induced inflammation via PPARγ/PTEN pathway in BV2 microglial cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 1;171:113674.
73. Wang J, Pang T, Hafko R, Benicky J, Sanchez-Lemus E, Saavedra JM. Telmisartan ameliorates glutamate-induced neurotoxicity: roles of AT1 receptor blockade and PPARγ activation. Neuropharmacology. 2014 Apr 1;79:249–61.
74. Torika N, Asraf K, Apte RN, Fleisher-Berkovich S. Candesartan ameliorates brain inflammation associated with Alzheimer's disease. CNS Neurosci Therap. 2018 Mar;24(3):231–42.
75. Sohn YI, Lee NJ, Chung A, Saavedra JM, Turner RS, Pak DT, et al. Antihypertensive drug Valsartan promotes dendritic spine density by altering AMPA receptor trafficking. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Oct 4;439(4):464–70.
76. Khalifa M, Safar MM, Abdelsalam RM, Zaki HF. Telmisartan protects against aluminum-induced Alzheimer-like pathological changes in rats. Neurotox Res. 2020 Feb;37:275–85.
77. Ongali B, Nicolakakis N, Tong XK, Aboulkassim T, Papadopoulos P, Rosa-Neto P, et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker losartan prevents and rescues cerebrovascular, neuropathological and cognitive deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease model. Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Aug 1;68:126–36.
78. Drews HJ, Yenkoyan K, Lourhmati A, Buadze M, Kabisch D, Verleysdonk S, et al. Intranasal losartan decreases perivascular beta amyloid, inflammation, and the decline of neurogenesis in hypertensive rats. Neurotherapeutics. 2019 Jul 15;16:725–40.
79. Torika N, Asraf K, Cohen H, Fleisher-Berkovich S. Intranasal telmisartan ameliorates brain pathology in five familial Alzheimer’s disease mice. Brain, Behav Immunity. 2017 Aug 1;64:80–90.
80. Abo-Youssef AM, Khallaf WA, Khattab MM, Messiha BA. The anti-Alzheimer effect of telmisartan in a hyperglycemic ovariectomized rat model; role of central angiotensin and estrogen receptors. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020 Aug 1;142:111441.
81. Quan W, Xu CS, Li XC, Yang C, Lan T, Wang MY, et al. elmisartan inhibits microglia-induced neurotoxic A1 astrocyte conversion via PPARγ-mediated NF-κB/p65 degradation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Oct 1;123:110761.
82. Abd El Aziz AE, Sayed RH, Sallam NA, El Sayed NS. Neuroprotective effects of telmisartan and nifedipine against cuprizone-induced demyelination and behavioral dysfunction in mice: roles of NF-κB and Nrf2. Inflammation. 2021 Aug;44:1629–42.
83. Affram KO, Janatpour ZC, Shanbhag N, Villapol S, Symes AJ. Telmisartan reduces LPS-mediated inflammation and induces autophagy of microglia. Neuroglia. 2024 Jun 20;5(2):182–201.
84. Tayler HM, Skrobot OA, Baron DH, Kehoe PG, Miners JS. Dysregulation of the renin-angiotensin system in vascular dementia. Brain Pathol. 2024 Mar 7;34(4):e13251.
85. Pang T, Wang J, Benicky J, Sánchez-Lemus E, Saavedra JM. Telmisartan directly ameliorates the neuronal inflammatory response to IL-1β partly through the JNK/c-Jun and NADPH oxidase pathways. J Neuroinflamm. 2012 Dec;9:1–9.
86. Malik S, Suchal K, Gamad N, Dinda AK, Arya DS, Bhatia J. Telmisartan ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibiting MAPK mediated inflammation and apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Feb 5;748:54–60.
87. Kehoe PG, Turner N, Howden B, Jarutyte L, Clegg SL, Malone IB, et al. Safety and efficacy of losartan for the reduction of brain atrophy in clinically diagnosed Alzheimer's disease (the RADAR trial): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2021 Nov 1;20(11):895–906.
88. Liu H, Liu X, Wei X, Chen L, Xiang Y, Yi F, et al. Losartan, an angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker, ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via PI3K/Akt-mediated eNOS phosphorylation. Brain Res Bull. 2012 Oct 1;89(1-2):65–70.
89. Drews HJ, Klein R, Lourhmati A, Buadze M, Schaeffeler E, Lang T, et al. Losartan improves memory, neurogenesis and cell motility in transgenic Alzheimer’s mice. Pharmaceuticals. 2021 Feb 20;14(2):166.
90. Subudhi BB, Sahu PK, Singh VK, Prusty S. Conjugation to ascorbic acid enhances brain availability of losartan carboxylic acid and protects against parkinsonism in rats. AAPS J. 2018 Oct 22;20(6):110.
91. Royea J, Zhang L, Tong XK, Hamel E. Angiotensin IV receptors mediate the cognitive and cerebrovascular benefits of losartan in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 2017 May 31;37(22):5562–73.
92. Trofimiuk E, Wielgat P, Braszko JJ. Candesartan, angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker is able to relieve age-related cognitive impairment. Pharmacol Rep. 2018 Feb 1;70(1):87–92.
93. Bhat SA, Goel R, Shukla S, Shukla R, Hanif K. Angiotensin receptor blockade by inhibiting glial activation promotes hippocampal neurogenesis via activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in hypertension. Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Jun;55:5282–98.
94. Ishrat T, Pillai B, Soliman S, Fouda AY, Kozak A, Johnson MH, et al. Low-dose candesartan enhances molecular mediators of neuroplasticity and subsequent functional recovery after ischemic stroke in rats. Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Jun;51:1542–53.
95. Khedr NF, Werida RH, Abo-Saif MA. Candesartan protects against d-galactose induced–neurotoxicity and memory deficit via modulation of autophagy and oxidative stress. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 15;435:115827.
96. Lin WY, Li LH, Hsiao YY, Wong WT, Chiu HW, Hsu HT, et al. Repositioning of the angiotensin II receptor antagonist candesartan as an anti-inflammatory agent with NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitory activity. Front Immunol. 2022 May 20;13:870627.
97. Wang J, Ho L, Chen L, Zhao Z, Zhao W, Qian X, et al. Valsartan lowers brain β-amyloid protein levels and improves spatial learning in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Clin Investig. 2007 Nov 1;117(11):3393–402.
98. Yang WN, Hu XD, Han H, Shi LL, Feng GF, Liu Y, et al. The effects of valsartan on cognitive deficits induced by aluminum trichloride and d-galactose in mice. Neurol Res. 2014 Jul 1;36(7):651–8.
99. Wang J, Zheng B, Yang S, Zhou D, Wang J. Olmesartan prevents Oligomerized amyloid β (Aβ)-Induced cellular Senescence in neuronal cells. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021 Mar 12;12(7):1162–9.
100. Nakagawa T, Hasegawa Y, Uekawa K, Senju S, Nakagata N, Matsui K, et al. Transient mild cerebral ischemia significantly deteriorated cognitive impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease via angiotensin AT1 receptor. Am J Hypertens. 2017 Feb 1;30(2):141–50.
101. Zhong MZ, Peng T, Duarte ML, Wang M, Cai D. Updates on mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegen. 2024 Mar 11;19(1):23.
102. Mishra S, Prusty SK, Sahu PK, Das D. Azilsartan ameliorates aluminum chloride-induced Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology. Curr Issues Pharm Med Sci. 2023;36(3):151–7.
103. Yasar S, Xia J, Yao W, Furberg CD, Xue QL, Mercado CI, et al. Antihypertensive drugs decrease risk of Alzheimer disease: Ginkgo evaluation of memory study. Neurology. 2013 Sep 3;81(10):896–903.
104. Wharton W, Goldstein FC, Zhao L, Steenland K, Levey AI, Hajjar I. Modulation of renin-angiotensin system may slow conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Sep;63(9):1749–56.
105. Cummings J, Lee G, Ritter A, Sabbagh M, Zhong K. Alzheimer’s disease drug development pipeline: 2020. Alzheimer’s Dementia: Translat Res ClinInterven. 2020;6(1):e12050.
106. Hajjar I, Okafor M, Wan L, Yang Z, Nye JA, Bohsali A, et al. Safety and biomarker effects of candesartan in non-hypertensive adults with prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Commun. 2022 Dec 1;4(6):fcac270.
107. Wharton W, Goldstein FC, Tansey MG, Brown AL, Tharwani SD, Verble DD, et al. Rationale and design of the mechanistic potential of antihypertensives in preclinical Alzheimer’s (HEART) trial. J Alzheimer's Dis. 2018 Jan 1;61(2):815–24.
108. Ihara M, Saito S. Drug repositioning for Alzheimer’s disease: finding hidden clues in old drugs. J Alzheimer's Dis. 2020 Jan 1;74(4):1013–28.
109. Kehoe PG. The coming of age of the angiotensin hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease: progress toward disease prevention and treatment?. J Alzheimer's Dis. 2018 Jan 1;62(3):1443–66.
110. Szabo-Reed AN, Vidoni E, Binder EF, Burns J, Cullum CM, Gahan WP, et al. Rationale and methods for a multicenter clinical trial assessing exercise and intensive vascular risk reduction in preventing dementia (rrAD Study). Contemp Clin Trials. 2019 Apr 1;79:44–54.
111. Law CS, Yeong KY. Repurposing antihypertensive drugs for the management of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Med Chem. 2021 Mar 1;28(9):1716–30.
112. Fuller SJ, Shah T, Chatterjee P, Dias CB, Hillebrandt H, Sohrabi HR, et al. Physical activity can reduce hypertension and the long-term benefits may contribute toward a lower risk of cognitive decline and dementia. Hypertension. 2020 Jul;6(3):133–41.
113. Wharton W, Stein JH, Korcarz C, Sachs J, Olson SR, Zetterberg H, et al. The effects of ramipril in individuals at risk for Alzheimer's disease: results of a pilot clinical trial. J Alzheimer's Dis. 2012 Jan 1;32(1):147–56.