INTRODUCTION
As part of ongoing efforts to enhance the healthcare system, implementing the “five rights” strategy—the right patient, right drug, right time, right dose, and right route—is crucial for achieving effective and safe clinical outcomes [1,2]. The “five rights” become particularly important when dealing with drugs having low therapeutic windows, drug/metabolite toxicity, development of treatment resistance, and therapy in specific patient populations. To get the right dose, it is imperative to assess the pharmacokinetics (PK) of drugs in the targeted patient population. In recent years, neonatal pharmacotherapy has gained significant attention as healthcare professionals and regulatory agencies strive to optimize drug dosing and improve therapeutic outcomes in this vulnerable patient population. The challenges associated with administering medications to neonates are multifaceted, ranging from the unique physiological characteristics of neonates to the limited availability of PK data for many drugs in this population. This leads to off-label prescriptions and incorrect dosing in the neonatal population preventing the implementation of the five rights [3–10].
Antibiotics are lifesaving medicines for all classes of the population irrespective of their age. Neonates are very vulnerable to infections and need to be treated with the right antibiotics at the right dose to prevent death and lifelong complications arising out of infection [11–14]. The choice of antibiotics depends on the suspected pathogens and the clinical condition of the patients. In neonatal care, antibiotics such as ampicillin (AMPI), amikacin (AMK), gentamicin (GTN), cefotaxime (CXIME), ceftriaxone (CXONE), piperacillin (PIP)-tazobactam (TAZ), cefoperazone (CFPZ)-sulbactam (SUL), cefuroxime (CFUME), meropenem (MERO), vancomycin (VCN), and so on, are the preferred choices [47,48]. Given the significance of prudent antibiotic use in preventing antibiotic resistance, neonatal care providers must practice antibiotic stewardship. This involves choosing the most appropriate antibiotic, administering the correct dosage, and limiting the duration of treatment in order to avoid superfluous exposure and reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic-treated neonates are closely monitored for treatment response. This includes monitoring clinical signs, laboratory results (such as blood cultures and inflammatory markers), and any potential antibiotic adverse effects. In addition to treatment, infection prevention is a primary focus for premature neonates who are particularly susceptible to infection [49]. Premature infants may also be given prophylactic doses of antibiotics to reduce the risk of early-onset sepsis, particularly if their mothers have risk factors for transmitting infections. The dosage, Cmax, and half of the commonly used antibiotics in pediatric care are given in Table 1.
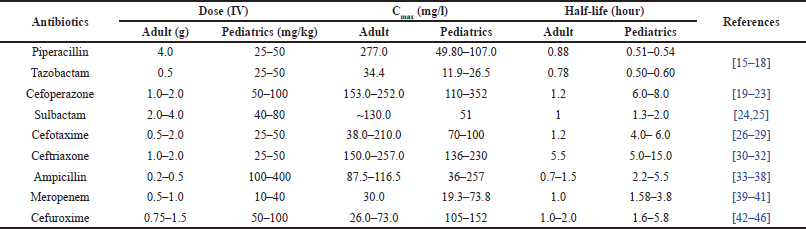 | Table 1. Dosage, Cmax, and half-life of the commonly used antibiotics in neonatal intensive care. [Click here to view] |
Although antibiotics are being extensively used in the neonatal intensive care unit, the current practice of determining the neonatal dose is by extrapolation from the pediatric dose. However, the direct extrapolation of the adult dose is not suggestive because newborns and infants have highly dynamic body physiology. Precision dosing of these antibiotics is not possible because of the lack of comprehensive PK data in the newborn population. One of the reasons for this is the difficulties encountered in designing PK studies in newborns. Population pharmacokinetic (PopPK) studies can be utilized in PK evaluations to overcome the limitations of traditional individual-based PK studies in neonates. By utilizing data from a large patient population, PopPK modeling and simulation enables the estimation of drug disposition parameters and the exploration of various factors influencing drug exposure in neonates [50,51]. Knowledge gained from population PK studies can inform evidence-based dosing guidelines, aid in preventing drug-related adverse events, and guide therapeutic drug monitoring strategies. There is an urgent need to establish the PK profile of neonates so that precise dosing is possible.
The first and foremost requirement for a PK evaluation is a sensitive analytical technique that can quantify minute quantities of drugs from complex matrices such as blood [52–54]. The volume of blood samples, the procedure used for collection, and lack of sensitive analytical techniques are a few of the several problems. It is essential to have a sensitive analytical technique that can quantify the said antibiotics from neonatal blood samples. The LC-MS/MS technique can overcome the resolution issues particularly observed with polar and multi-ionic antibiotics with poor chromatographic retention [55–62]. Sampling is always a concern in the vulnerable neonatal population. Dried blood spot (DBS) sampling is the preferred choice in neonates in comparison to traditional venous sampling because of its non-invasive nature. In this work, we explore the capability of LC-MS/MS in analyzing the nine antibiotics from minute quantities of plasma and DBS samples.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Reference standards, reagents, and biological sample
Secondary Pharmaceutical Standards: Ampicillin, Cefoperazone, Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone, Cefuroxime, Meropenem, Piperacillin, Sulbactam, Tazobactam, and Ceftiofur (Internal standard) were procured from Sigma-Aldrich. LC-MS/MS grade acetonitrile was supplied by Merck, India. Type-I water for all the analysis was produced in-house in the Merck Millipore Direct Q-3 UV water purification system. Clinical samples were collected after informed consent from patients meeting the inclusion criteria. The Institutional Ethical Committee approval was obtained from Kasturba Medical College and Kasturba Hospital Institutional Ethics Committee (Registration No. ECR/146/Inst/KA/2013/RR19), Manipal dated August 13, 2019 (certificate number 558/209) and Clinical Trials Registry, India, dated October 22, 2019 (CTRI/2019/10/021750), respectively. Whole blood and plasma samples from healthy adult human volunteers were used for method development and validation.
Instruments
Dionex Ultimate-3000 HPLC system hyphenated with LTQ-XL linear ion-trap mass spectrometer, Thermo Fisher Scientific LLC was used for the LC-MS/MS analysis. Ryan Labs, an Indian company, provided autosampler recovery vials. The blood samples were collected in 0.5 ml K2 EDTA tubes, CML Biotech Private Limited, India. The DBS samples were collected in Whatman903®paper. The clinical and long-term stability samples were stored in Sanyo MDF-U32V Ultra-Low temperature freezer China. For 2°C to 8°C storage conditions, Godrej Eon refrigerator, India, was used. A REMI C24 cooling centrifuge with an R-248 M (24 1.5 ml) rotor head was used to centrifuge the samples at multiple points in the sample preparation process.
Chromatographic conditions
The chromatographic separation was obtained using Acclaim120 C18 (150 × 4.6) mm, 3 µ column, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA, in gradient elution using acetonitrile (A) and 2 mM ammonium acetate buffer pH adjusted at 6.40 with dilute ammonia solution. The gradient programming started with 76% B, linearly reducing to 40%B in 4 minutes, holding for 1 minute and returning to the initial condition in 1 minute and 5 minutes conditioning with a total run time of 11 minutes at 0.4 ml/minute flow. The column oven was maintained at 35°C and autosampler at 10°C. The autosampler injection volume was set to 1µl for the plasma sample and 5µl for the DBS sample.
Mass spectrometry
Ionization in the mass spectrometer was accomplished with a heated electrospray ionization source operated at capillary temperature 350°C, source heater temperature 420°C, sheath gas flow 50 arb, auxiliary gas flow 16 arb, sweep gas flow 0 arb, source voltage 4.0 kV, source current 100 uA and capillary voltage 47/-2 in positive and negative polarity. The detailed mass spectrometric scan event is presented in Table 2 and Table S1.
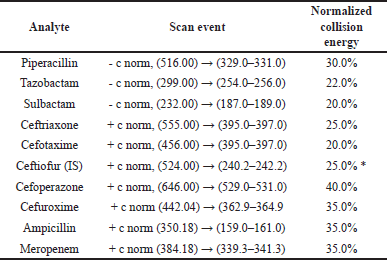 | Table 2. Mass spectrometric scan events. [Click here to view] |
Clinical sample collection
A total of 53 plasma samples from the 46 subjects receiving Piperacillin/Tazobactam as the standard care plan of the hospital were collected into 0.5 ml K2 EDTA tube between 0.25 and 12 hours after the 15 minutes intravenous infusion, centrifuged to 7,000 rpm at 4°C to separate out the plasma and stored at −70°C in deep freezer until the analysis. The clinical DBS samples were not collected as the method performance was not optimized for the use.
Calibration standards
The calibrators and QCs for the plasma and DBS matrix were prepared by spiking 3.33% and 5% working standard solution to blank plasma and blank whole blood (adjusted 40%v/v hematocrit). The 40 µl of the spiked whole blood was applied over Whatman903®paper for preparing calibrators and QCs of DBS. The concentration of calibrators and QCs is presented in Table 3 and Table S2.
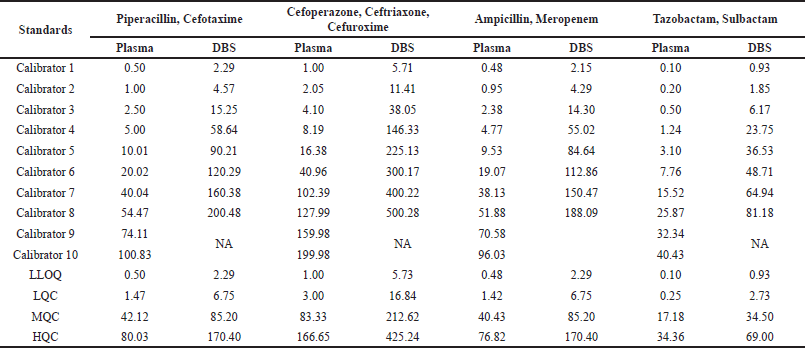 | Table 3. Calibration curve range for nine antibiotics in plasma and DBS. [Click here to view] |
Sample preparation
To clean up the plasma and DBS, the protein precipitation technique using cold acetonitrile was used. The workflow for the plasma and DBS sample preparation is depicted in Figure 1. For all the processes, the low retention type microcentrifuge tube and pipette tips were used to reduce the pipetting error.
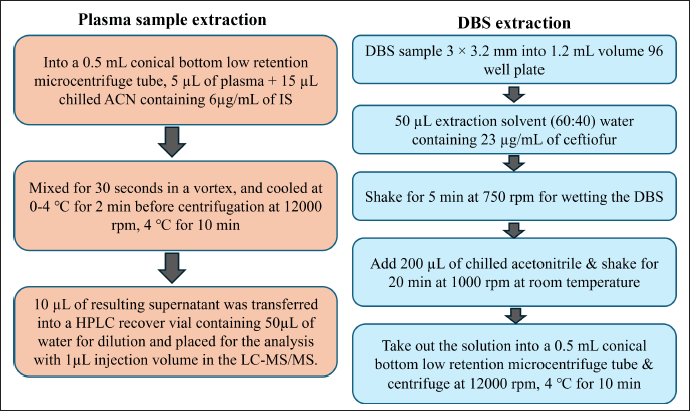 | Figure 1. Plasma and DBS sample extraction flow chart. [Click here to view] |
Method validation
Validation of the method was performed adhering to bioanalytical method validation guideline- ICH-M10 [63,64]. The plasma and DBS methods were evaluated for their selectivity, specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, recovery, dilution integrity (DI), and stability. Additional parameters like the effect of hematocrit and blood volume effects also were explored in the case of the DBS method.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Method development strategy
During method development, we took into consideration various aspects that can affect the analysis, as summarized in Table 4 and Figure 2 [65]. As the sample dilution was involved, the pipetting and micro-centrifuge tube with low retention were selected to avoid errors during sample handling. As there were nine analytes, making individual stocks, working solution, and spiking could exceed the limit of 5% spiking in the blank matrix, leading to precipitation of the matrix. Therefore, stock and working solutions of analytes were set in such a way that the calibrator does not exceed the 5% spiking limit. For the optimization of chromatographic separation, the LogP and pKa of analytes were considered. Various buffers such as 0.1% formic acid in water, 2–5 mM ammonium acetate, 2–5 mM ammonium format, and 2–5 mM ammonium bicarbonate along with acetonitrile and methanol at various isocratic and gradient elution were explored in Kinetex C18 (50 × 3) mm, 2.6 µ; Kinetex F5 (50 × 3) mm, 2.6 µ; HypersilGold (100 × 4.6) mm, 3 µ and Acclaim 120 C18 (150 × 4.6) mm, and 3 µ column with 0.2–0.6 ml flow rate. The retention of the analytes sulbactam, tazobactam, and ceftriaxone was challenging with short columns. Along with chromatographic separation, the ion suppression due to co-elution of analytes, change in mass response with solvent and their ratio, and peak shape of all nine analytes were taken into consideration. Finally, a gradient elution with acetonitrile and 2 mM ammonium acetate buffer pH 6.40 at a flow rate of 0.4 ml/minute was found to be most optimal. For the mass spectrometer optimization (tuning), 500 ng/ml of each analyte was infused with direct injection and the precursor ion was identified to obtain a prominent fragment ion with optimal normalized collision energy. The H-ESI ion source parameters, such as heater temperature, sheath gas, auxiliary gas, capillary temperature, voltage, and so on, were optimized to attain the maximum sensitivity required for analytes of interest in this study. The injection volume for both plasma and DBS samples were explored based on the LLOQ requirement, linearity of response, and peak shape. The method showed linearity in the proposed range with 2 µl injection volume for the plasma sample and 5 µl for the DBS sample. During sample extraction from the DBS matrix, a single common procedure for all the nine analytes was explored, considering the use of this method for simultaneous estimation of selected nine antibiotics. The extraction parameters in different steps such as punch size, extraction solvent addition steps, ratio of solvent, time of extraction, pH of extraction solvent, and so on, also were optimized. The representative chromatogram of the simultaneous estimation of nine antibiotics at LLOQ in LC-MS/MS is shown in Figure 3.
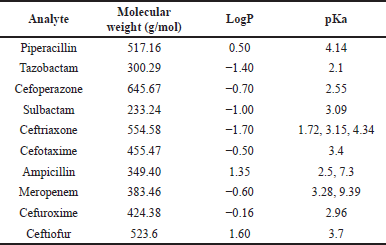 | Table 4. Physiochemical properties of analytes selected for method development. [Click here to view] |
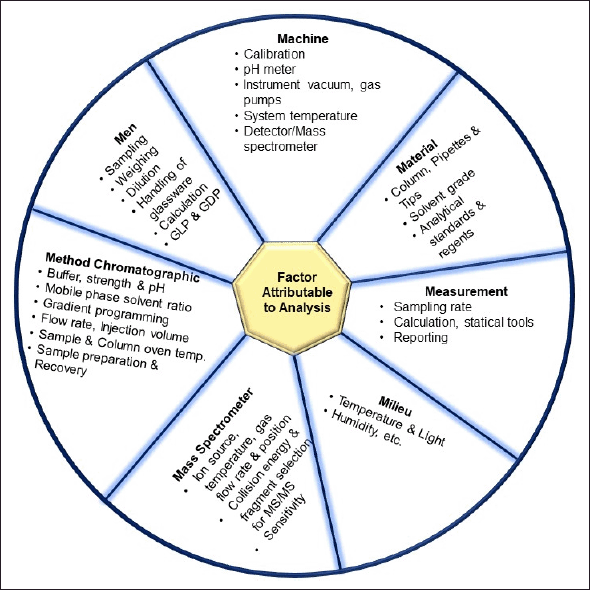 | Figure 2. Factors attributable to LC-MS/MS analysis. [Click here to view] |
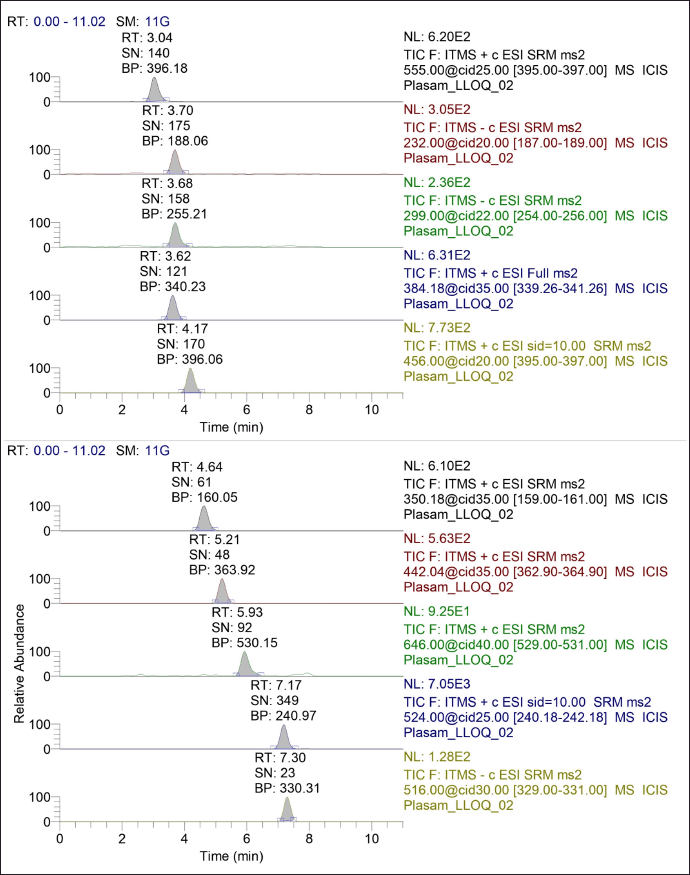 | Figure 3. Representative chromatogram of simultaneous estimation of nine antibiotics at LLOQ in LC-MS/MS. [Click here to view] |
Results of validation
Selectivity
To ensure the ability of the method to differentiate and measure the analyte in the presence of potential interfering substances in the blank plasma and DBS matrix, six blank samples from 6 different individuals and two hemolyzed blood samples (prepared by spiking 2% v/v of hemolysed blood in non-hemolyzed whole blood).
The selectivity run showed the absence of response in blank plasma matrix, plasma matrix from a hemolyzed blood sample, and DBS matrix mimicked by spotting whole blood, showing the method is selective to antibiotics of interest.
Specificity
This study spiked a blank matrix with eight antibiotics, skipping one antibiotic and IS. The response at the retention time of skipped antibiotics was evaluated. The interference of the concomitant medications such as caffeine, amikacin, and gentamicin was also evaluated by spiking in the blank matrix. The effect of EDTA in the plasma matrix and interference of the DBS card for the DBS matrix-based analysis was also evaluated.
There was no response at the retention time of the skipped antibiotic in the presence of other antibiotics and concomitantly administered amikacin, gentamicin, and caffeine, demonstrating the ability of the method to detect and differentiate the analyte from concomitant medications during simultaneous analysis.
Matrix effect
The matrix effect was evaluated by analyzing three replicates of low and high QCs; each prepared using a matrix from 6 different individuals. For each matrix source considered, the accuracy was within ± 15% of the nominal concentration, and the precision (percent coefficient of variation (%CV)) was not more than (NMT) 15%.
Carryover
The carryover was evaluated by injecting six sets of LLOQ, ULOQ, and Matrix Blank. There was no response in any matrix blank samples run after ULOQ at the retention of any analytes, meeting the criteria of NMT 20% response of analytes and NMT 5% response of IS in blank compared to LLOQ.
Linearity
The linearity of the method in the concentration range, as depicted in Table 5, was evaluated by analyzing three independent sets of calibrator solutions with known concentrations of antibiotics of interest that cover the expected concentration of the samples over three different days. The back-calculation was performed as a quantitative area ratio method, Quadratic, 1/X^2 weighing factor using Quan browser, Xcalibur software tool. The intercept, slope, weighing factor, R2 values, and calibration curve plots of three calibration curves for each analyte are provided in Supplementary data. All the LLOQ levels of analytes were within 20% of the respective nominal concentration, and other calibrators were within 15% of the respective nominal concentration. The correlation coefficient of all the analytes was NLT 0.99, indicating the method was linear at a defined concentration range. The Intercept, Slope, X-value, and R2 values of three calibration curves in the plasma matrix are shown in Table S1. The calculated % recovery after back calculation from the linearity plot for each calibrator in the plasma matrix is shown in Table S2. The calibration curves of all antibiotics are shown in Figure S1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9, respectively.
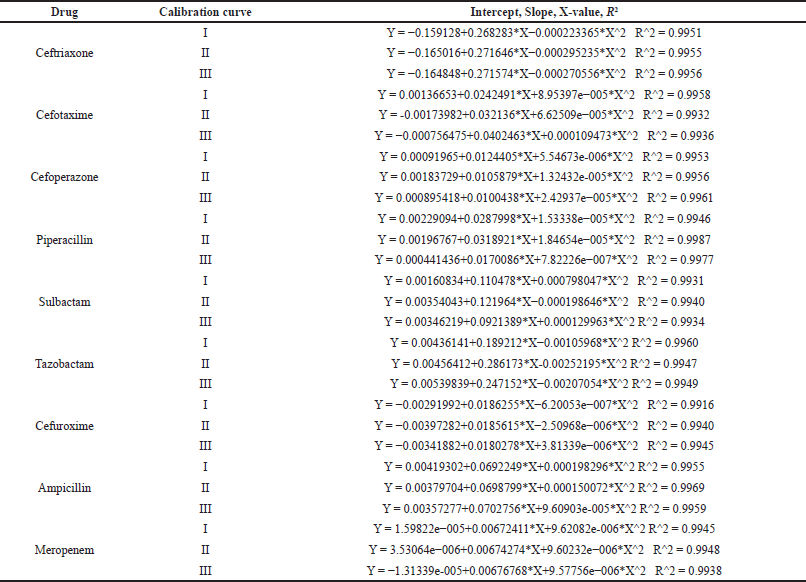 | Table 5. Intercept, Slope, X-value, and R2 values of three calibration curves in plasma matrix. [Click here to view] |
Accuracy and precision
Within-run accuracy and precision in plasma were evaluated by analyzing six replicates at LLOQ, LQC, MQC, and HQC concentration levels in each analytical run. The accuracy and precision across runs were assessed by examining the QC concentration levels in three separate analytical runs conducted over 3 days. The data from all runs were combined to establish the overall accuracy and precision. The accuracy ranged from 87.87% to 116.50%, within the acceptable range of ±15% at LQC, MQC, and HQC, and within ±20% at LLOQ, relative to the nominal concentration and coefficient of variance (CV) 1.68%–11.17%. The detailed accuracy and precision are represented in Figure 4, Figure 5, and Table S3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11, respectively.
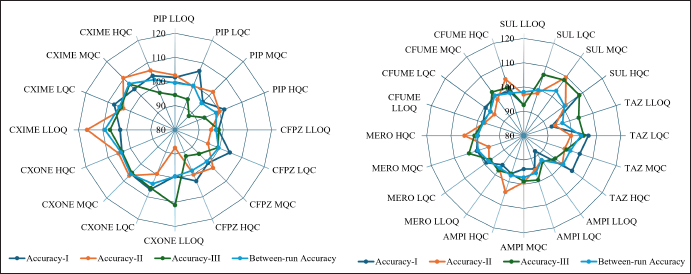 | Figure 4. Accuracy results of plasma LC-MS/MS method (PIP: Piperacillin, CFPZ: Cefoperazone, CXONE: Ceftriaxone, CXIME: Cefotaxime, SUL: Sulbactam, TAZ: Tazobactam, AMPI: Ampicillin, MERO: Meropenem, CFUME: Cefuroxime). [Click here to view] |
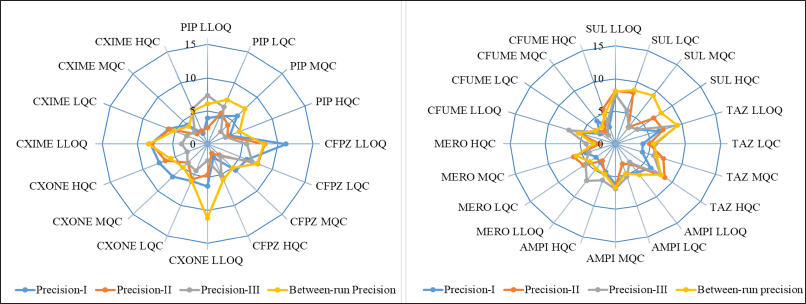 | Figure 5. Precision results of plasma LC-MS/MS method. [Click here to view] |
Recovery
Recovery experiments were conducted for each analyte in five replicates at the LQC, MQC, and HQC levels using plasma and DBS (40% v/v HCT) matrices. The recovery of all analytes from the plasma matrix exceeded 85%, with less than 15% CV, indicating consistent and reproducible recovery. The recovery from the DBS matrix was comparatively lower, with variable recovery surpassing the acceptability limit, as seen in Figure 6 and Table S12. The failure in the precision during recovery (>15%CV) from the DBS matrix resulted due to the varying physicochemical properties of the analytes, which impacts the extraction process. This suggests that achieving the extraction may be challenging with a single standard extraction method.
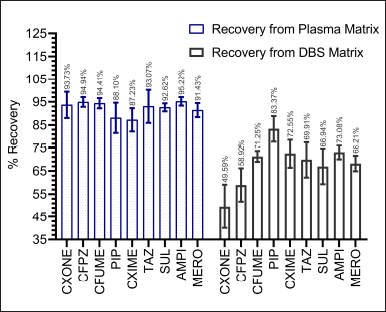 | Figure 6. Recovery results of plasma and DBS LC-MS/MS method. [Click here to view] |
It is worth noting here that the choice of solvent and extraction process for analytes from DBSs depends on several critical factors related to the chemical properties such as polarity, solubility, ionization, matrix properties (DBS filter paper), protein binding, porosity of the paper, blood components, and analyte stability. The presence of co-extracted matrix interferences and the choice of extraction method also have an effect on the recovery. The extraction process becomes complex, when there are multiple analytes, and achieving good recovery and consistency in extraction is difficult. Therefore, choosing an extraction solvent (or mixture of solvents) suitable for all analytes is practically impossible. However, procedures like adjusting the pH to match with the analyte pKa, use of additives such as surfactants (e.g., triton X-100, SLS) to improve solubility, use of sonication or vortex mixing, and so on, could be tried to enhance extraction recovery and thus the linearity.
Dilution integrity (DI)
The DI working standard was prepared in such a way that 5% spiking into blank plasma resulted in two times the ULOQ of the respective analyte. Two dilution factors, 1:3 and 1:4, in five replicate samples, were performed, and the accuracy and precision of analytes from nominal concentration were evaluated. The DI samples for all analytes demonstrated accuracy within ±15% of the expected concentration and precision below 15% CV. The DI samples exhibited an accuracy ranging from 89.54%–110.80% and a precision ranging from 2.05%–6.89 %CV, shown in Figure 7 and Table S13.
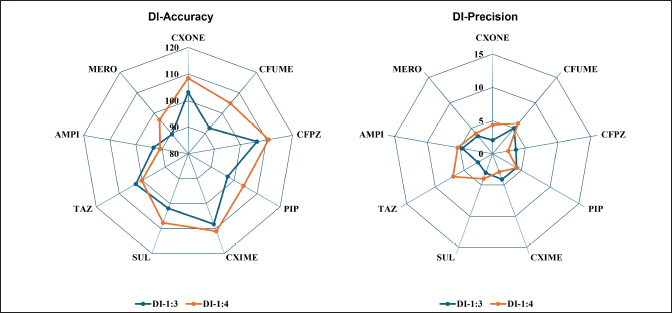 | Figure 7. Dilution integrity accuracy and precision for selected nine antibiotics. [Click here to view] |
Hematocrit and blood volume effect (Piperacillin)
The DBS calibrators were prepared by spiking whole blood with 40%v/v hematocrit. The recovery from DBS with 60%v/v exceeded the accuracy limit of ±15%, Figure 8. Critically ill neonates enrolled in this study showed a wide range (26%–67% v/v) of hematocrit, Figure 9. Therefore, calibrators with a 40%v/v hematocrit level cannot be considered valid.
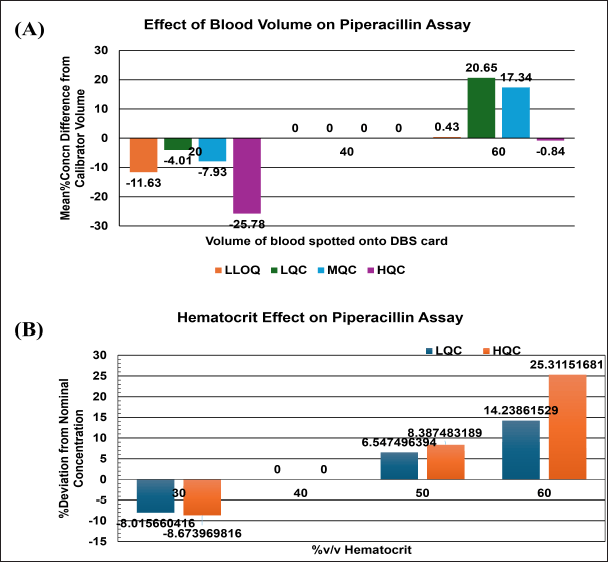 | Figure 8. (A) Effect of blood volume on piperacillin assay, (B) Effect of hematocrit on piperacillin assay. [Click here to view] |
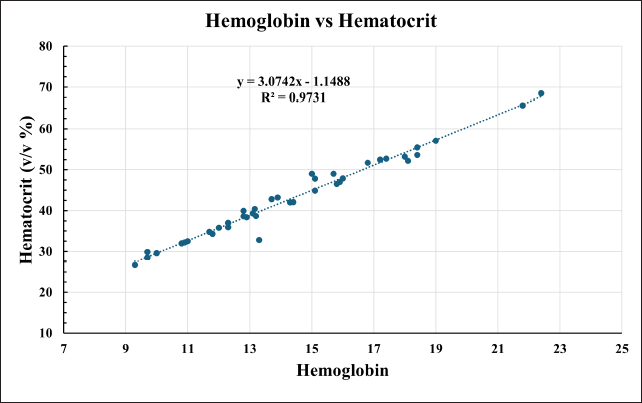 | Figure 9. Distribution of Hematocrit and Hemoglobin in Neonates recruited in this study. [Click here to view] |
Short-term stability study in plasma matrix
The stability study of standard stock solution, and internal standard solution at 2°C–8°C were evaluated for up to 30 days. All the stability studies were evaluated at LQC and HQC in five replicates. Bench-top stability in the plasma matrix was evaluated up to 24 hours at room temperature, autosampler stability at 10°C up to 36 hours, processed sample at 2°C–8°C for 72 hours, and at three freeze-thaw cycles for samples stored at −70°C were evaluated. The short-time stability studies demonstrated good stability (decay less than 10%) over the study period. The detailed short-term stability study results are shown in Figure 10 and Table S14.
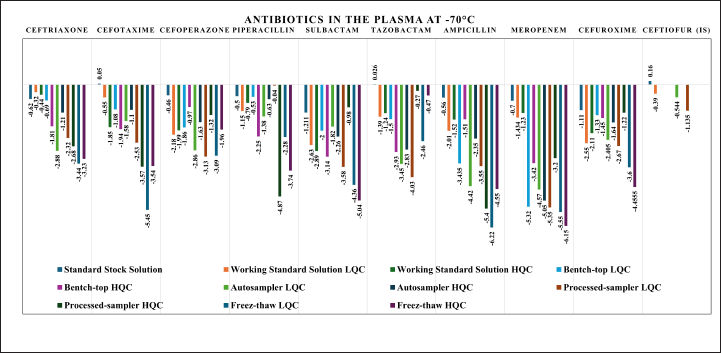 | Figure 10. Short-term stability study results for selected antibiotics at the last time-point of the study period. [Click here to view] |
Long-term stability study in plasma matrix
The LQC and HQC level long-term stability study plasma samples stored at −70° were evaluated for up to 60 days. The decay of antibiotics in the plasma at −70°C was not more than 10% demonstration of storability up to 60 days before the analysis of the sample. The stability study data is presented in Figure 11 and Table S15.
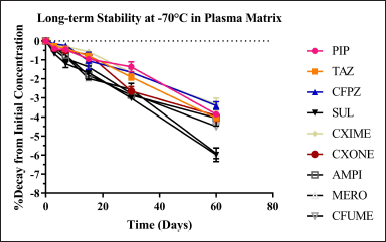 | Figure 11. Representation of decay of antibiotics in the plasma at −70°C. [Click here to view] |
Real sample analysis results
A total of 53 plasma samples from the 46 subjects were collected between 0.25 and 12 hours after the 15 minutes intravenous infusion and processed for the quantitative analysis of Piperacillin/Tazobactam. The plasma concentration of piperacillin and tazobactam ranged from 8.03–295.50 mg/l and 0.73–33.54 mg/l, respectively. The concentration distribution over time is presented as a time versus concentration plot in Figure 12.
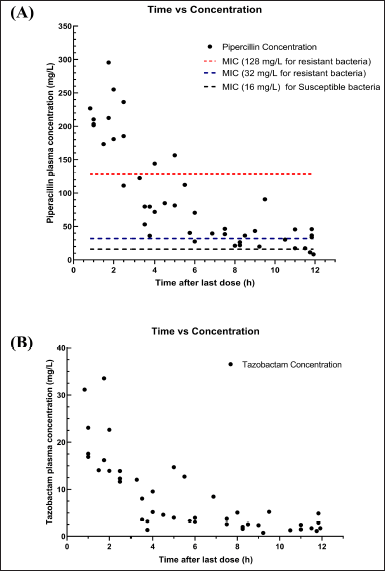 | Figure 12. Time versus plasma concentration in 53 plasma samples collected from the 46 neonates enrolled in this study: (A) Piperacillin and (B)Tazobactam. [Click here to view] |
CONCLUSION
A robust LC-MS/MS method was developed and fully validated for the simultaneous quantification of nine antibiotics from the neonatal plasma samples. The method utilizes only 5 µl of plasma sample, and hence, can decrease the duration of waiting for sample numbers for batch analysis and minimize the need to run standard plots for different analytes independently. As a result, daily sample analysis for therapeutic drug monitoring and precise dosing will be facilitated. Implementing this approach for sample analysis in a hospital setting for PK investigations will enhance sample processing efficiency and support PopPK and physiologically based PK studies. In contrast to the plasma method, the DBS method failed the linearity evaluation in the expected concentration range and was not validated further. As a future scope of the work, as an application of this validated method, a study can be undertaken to evaluate the drug interactions as well as the effect of disease conditions on the bioavailability of these antibiotics.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge Department of Biochemistry, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal, Karnataka, India, for providing instrumental facility for punching dried blood spot card. We are thankful to Mr S Yadav, Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd, New Delhi, India, and Dr AS Chauhan, Panacea Biotec. Ltd, Punjab, India, for technical suggestions during analysis. The authors are also grateful to Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, for providing the facilities.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
This work was supported by the All-India Council for Technical Education, New Delhi, India, under National Doctoral Fellowship Scheme (AICTE/NDF/PhD/2019/1-6389564801).
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors state that the manuscript does not include any conflicts of interest.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
The Institutional Ethical Committee (IEC) approval was obtained from Kasturba Medical College and Kasturba Hospital Institutional Ethics Committee (Registration No. ECR/146/Inst/KA/2013/RR19), Manipal dated August 13, 2019 (certificate number 558/209) and Clinical Trials Registry, India dated October 22, 2019 (CTRI/2019/10/021750).
DATA AVAILABILITY
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used artificial intelligence (AI)-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
REFERENCES
1. Grissinger M. The five rights. Pharm Ther. 2010 Oct;35(10):542.
2. Smeulers M, Verweij L, Maaskant JM, de Boer M, Krediet CTP, Nieveen van Dijkum EJM, et al. Quality indicators for safe medication preparation and administration: a systematic review. PLoS One 2015 Apr 17;10(4):e0122695.
3. Costa HT, Costa TX, Martins RR, Oliveira AG. Use of off-label and unlicensed medicines in neonatal intensive care. PLoS One 2018 Sep 25;13(9):e0204427.
4. Galande AD, Khurana NA, Mutalik S. Pediatric dosage forms—challenges and recent developments: a critical review. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2020;155–66.
5. O’Hara K, Wright IMR, Schneider JJ, Jones AL, Martin JH. Pharmacokinetics in neonatal prescribing: evidence base, paradigms and the future. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Dec;80(6):1281–8.
6. O’Hara K, Martin JH, Schneider JJ. Barriers and challenges in performing pharmacokinetic studies to inform dosing in the neonatal population. Pharm J Pharm Educ Pract. 2020 Feb 5;8(1):16.
7. Chen N, Aleksa K, Woodland C, Rieder M, Koren G. Ontogeny of drug elimination by the human kidney. Pediatr Nephrol Berl Ger. 2006 Feb;21(2):160–8.
8. Cheung KWK, van Groen BD, Spaans E, van Borselen MD, de Bruijn ACJM, Simons-Oosterhuis Y, et al. A comprehensive analysis of ontogeny of renal drug transporters: mRNA analyses, quantitative proteomics, and localization. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2019;106(5):1083–92.
9. van Groen BD, Nicolaï J, Kuik AC, Van Cruchten S, van Peer E, Smits A, et al. Ontogeny of hepatic transporters and drug-metabolizing enzymes in humans and in nonclinical species. Pharmacol Rev. 2021 Apr;73(2):597–678.
10. Hines RN. Ontogeny of human hepatic cytochromes P450. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. [Internet]. [cited 2023 Aug 16]. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jbt.20179
11. Barker CIS, Standing JF, Kelly LE, Hanly Faught L, Needham AC, Rieder MJ, et al. Pharmacokinetic studies in children: recommendations for practice and research. Arch Dis Child. 2018 Jul;103(7):695–702.
12. Bansal N, Momin S, Bansal R, Gurram Venkata SKR, Ruser L, Yusuf K. Pharmacokinetics of drugs: newborn perspective. Pediatr Med. 2023 Jan;0:0–0.
13. Parker SL, Abdul-Aziz MH, Roberts JA. The role of antibiotic pharmacokinetic studies performed post-licensing. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Dec 1;56(6):106165.
14. Kang JS, Lee MH. Overview of therapeutic drug monitoring. Korean J Intern Med. 2009 Mar;24(1):1–10.
15. Hayashi Y, Roberts JA, Paterson DL, Lipman J. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of piperacillin-tazobactam. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2010;6(8):1017–31.
16. Wolf MF, Simon A. The use of piperacillin—tazobactam in neonatal and paediatric patients. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2009;5(1):57–69.
17. Sdrgel F, Kinzig M. The chemistry, pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of piperatillin/tazobactam. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993;31(Suppl.A):39–60.
18. Toyonaga Y, Ishihara T, Tezuka T, Nakamura H. Pharmacokinetic and clinical evaluation of tazobactam/piperacillin in the pediatric field. Jpn J Antibiot. 1998;51(5):325–45.
19. Boscia JA, Korzeniowski OM, Snepar R, Kobasa WD, Levison ME, Kaye D. Cefoperazone pharmacokinetics in normal subjects and patients with cirrhosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983;23(3):385–9.
20. Bolton WK, Scheld WM, Spyker DA, Sande MA. Pharmacokinetics of cefoperazone in normal volunteers and subjects with renal insufficiency. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981;19(5):821–5.
21. Varghese M, Khan AJ, Kumar K, Rosenfeld W, Schaeffer HA, Evans HE. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of cefoperazone in infants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985;28(1):149–50.
22. Rosenfeld WN, Evans HE, Batheja R, Jhaveri RC, Vohra K, Khan AJ. Pharmacokinetics of cefoperazone in full-term and premature neonates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983;23(6):866–9.
23. Philips JB, Braune K, Ravis W, Cassady G, Dillon H. Pharmacokinetics of cefoperazone in newborn infants. Pediatr Phamecology. 1984;4(3):193–7.
24. Toyonaga Y, Kurosu Y, Nakamura H, Sugita M, Takahashi T, Hori M. Basic and clinical study of sulbactam/cefbpera zone in pediatrics. Jpn J Antibiot. 1984;37(12):2457–77.
25. Foulds G, Stankewich JP, Marshall DC, O’Brien MM, Hayes SL, Weidler DJ, et al. Pharmacokinetics of sulbactam in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):692–9.
26. Patel KB, Nicolau DP, Nightingale CH, Quintiliani R. Pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime in healthy volunteers and patients. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1995;22(1–2):49–55.
27. Esmieu F, Guibert J, Rosenkilde HC, Ho I, Le Go A. Pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime in normal human volunteers. 1980;83–92.
28. Claforan [Package Insert]. Bridgewater (NJ): Sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC. 2011.
29. Kearns GL, Young RA. Pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime and desacetylcefotaxime in the young. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1995;22(1–2):97–104.
30. Steele RW, Eyre LB, Bradsher RW, Weinfeld RE, Patel IH, Spicehandler J. Pharmacokinetics of ceftriaxone in pediatric patients with meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983;23(2):191–4.
31. Hayton WL, Stoeckel K. Age-associated changes in ceftriaxone pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1986;11(1):76–86.
32. Martin E, Koup JR, Paravicini U, Stoeckel K. Pediatric pharmacology pharmacokinetics of ceftriaxone in neonates and infants with meningitis. J Pediatr. 1984;105:475.
33. Wildfeuer A, Rühle KH, Bölcskei PL, Springsklee M. Concentrations of ampicillin and sulbactam in serum and in various compartments of the respiratory tract of patients. Infection. 1994;22(2):149–51.
34. Tremoulet A, Le J, Poindexter B, Sullivan JE, Laughon M, Delmore P, et al. Characterization of the population pharmacokinetics of ampicillin in neonates using an opportunistic study design. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Jun;58(6):3013–20.
35. Le J, Greenberg RG, Yoo Y, Clark RH, Benjamin DK, Zimmerman KO, et al. Ampicillin dosing in premature infants for early-onset sepsis: exposure-driven efficacy, safety, and stewardship. J Perinatol Off J Calif Perinat Assoc. 2022 Jul;42(7):959–64.
36. Peechakara BV, Basit H, Gupta M. Ampicillin. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 [cited 2023 Oct 12]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519569/
37. Kaplan JM, McCracken GH, Horton LJ, Thomas ML, Davis N. Pharmacologic studies in neonates given large dosages of ampicillin. J Pediatr. 1974 Apr;84(4):571–7.
38. Pacifici GM, Labatia J, Mulla H, Choonara I. Clinical pharmacokinetics of penicillins in the neonate: a review of the literature. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Feb;65(2):191–8.
39. Mouton JW, van den Anker JN. Meropenem clinical pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1995 Apr;28(4):275–86.
40. van den Anker JN, Pokorna P, Kinzig-Schippers M, Martinkova J, de Groot R, Drusano GL, et al. Meropenem pharmacokinetics in the newborn. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Sep;53(9):3871–9.
41. 050706s037lbl.pdf [Internet]. [cited 2023 Oct 12]. Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/050706s037lbl.pdf
42. Thønnings S, Jensen KS, Nielsen NB, Skjønnemand M, Hansen DS, Lange KHW, et al. Cefuroxime pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics for intravenous dosage regimens with 750 mg or 1500 mg doses in healthy young volunteers. J Med Microbiol. 2020;69(3):387–95.
43. de Louvois J, Mulhall A, Hurley R. Cefuroxime in the treatment of neonates. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Jan;57(1):59–62.
44. Brogden RN, Heel RC, Speight TM, Avery GS. Cefuroxime: a review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacological properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1979 Apr 1;17(4):233–66.
45. Gertler R, Gruber M, Wiesner G, Grassin-Delyle S, Urien S, Tassani-Prell P, et al. Pharmacokinetics of cefuroxime in infants and neonates undergoing cardiac surgery. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;84(9):2020–8.
46. del Rio M de los A, Chrane DF, Shelton S, McCracken GH, Nelson JD. Pharmacokinetics of cefuroxime in infants and children with bacterial meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):990–4.
47. Jain A, Dhir S, Sandhu SK. Use of off-label drugs in the neonatal intensive care unit in India. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 27;12(3):481–8.
48. Hsia Y, Lee BR, Versporten A, Yang Y, Bielicki J, Jackson C, et al. Use of the WHO access, watch, and reserve classification to define patterns of hospital antibiotic use (AWaRe): an analysis of paediatric survey data from 56 countries. Lancet Glob Health. 2019 Jul;7(7):e861–71.
49. Johnson J, Akinboyo IC, Schaffzin JK. Infection prevention in the neonatal intensive care unit. Clin Perinatol. 2021 Jun;48(2):413–29.
50. Mould DR, Upton RN. Basic concepts in population modeling, simulation, and model-based drug development. CPT Pharmacomet Syst Pharmacol. 2012 Sep;1(9):e6.
51. Ei E, Pj W. Population pharmacokinetics I: background, concepts, and models. Ann Pharmacother [Internet]. 2004 Oct [cited 2023 Aug 16];38(10):1702–6. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15328391/
52. Korfmacher WA. Foundation review: principles and applications of LC-MS in new drug discovery. Drug Discov Today. 2005 Oct 15;10(20):1357–67.
53. Seger C, Salzmann L. After another decade: LC–MS/MS became routine in clinical diagnostics. Clin Biochem. 2020 Aug;82:2–11.
54. Rizk M, Zou L, Savic R, Dooley K. Importance of drug pharmacokinetics at the site of action. Clin Transl Sci. 2017 May;10(3):133–42.
55. Popowicz ND, O’Halloran SJ, Fitzgerald D, Lee YCG, Joyce DA. A rapid, LC-MS/MS assay for quantification of piperacillin and tazobactam in human plasma and pleural fluid; application to a clinical pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2018 Apr 1;1081–1082:58–66.
56. Barco S, Risso FM, Bruschettini M, Bandettini R, Ramenghi LA, Tripodi G, et al. A validated LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of piperacillin/tazobactam on dried blood spot. Bioanalysis. 2014;6(21):2795–802.
57. Barco S, Bandettini R, Maffia A, Tripodi G, Castagnola E, Cangemi G. Quantification of piperacillin, tazobactam, meropenem, ceftazidime, and linezolid in human plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J Chemother. 2015 Nov 2;27(6):343–7.
58. Cohen-Wolkowiez M, White NR, Bridges A, Benjamin DK, Kashuba ADM. Development of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay of six antimicrobials in plasma for pharmacokinetic studies in premature infants. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2011 Nov 15;879(30):3497–506.
59. Kan M, Wu YE, Li X, Dong YN, Du B, Guo ZX, et al. An adapted LC-MS/MS method for the determination of free plasma concentration of cefoperazone in children: Age-dependent protein binding. J Chromatogr B. 2020 May 1;1144:122081.
60. Wu XJ, Huang X, Shi HY, Chen XK, Dong Q, Hao GX, et al. Determination of cefoperazone and sulbactam in serum by HPLC-MS/MS: An adapted method for therapeutic drug monitoring in children. Biomed Chromatogr BMC. 2018 Apr;32(4).
61. Zhou Y, Zhang J, Guo B, Yu J, Shi Y, Wang M, et al. Liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry assay for the simultaneous determination of cefoperazone and sulbactam in plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010 Nov 15;878(30):3119–24.
62. Ohmori T, Suzuki A, Niwa T, Ushikoshi H, Shirai K, Yoshida S, et al. Simultaneous determination of eight β-lactam antibiotics in human serum by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B. 2011 May 1;879(15):1038–42.
63. M10_Guideline_Step4_2022_0524.pdf [Internet]. [cited 2023 Oct 14]. Available from: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/M10_Guideline_Step4_2022_0524.pdf
64. Raveendran A, Gupta A, Lewis LE, Prabhu K, Moorkoth S. A comprehensive approach for detection of biotin deficiency from dried blood spot samples using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Future Sci OA. 2024 Dec 31;10(1):2355038.
65. AMC LCMS Guide_tcm18-240030.pdf [Internet]. [cited 2023 Oct 14]. Available from: https://www.rsc.org/images/AMC%20LCMS%20Guide_tcm18-240030.pdf
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
The supplementary material can be accessed at the journals website link here: [https://japsonline.com/admin/php/uploadss/4468_pdf.pdf]