INTRODUCTION
The herbaceous plant, Peperomia pellucida (L.) Kunth, is one of the Piperaceae family and is widely found in South American and Asian countries. The plant is commonly grown wildly in humid areas and yards. Empirically, this herb has been used to treat several diseases such as diabetic complications, muscular tissue discomfort, conjunctive inflammation, abscesses, fever, skin wounds, boils, headaches, aches, and convulsions [1]. Many investigations have been conducted to prove the biological activities of P. pellucida, including antihypertensive, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, analgesic, antibacterial, antiamoebic, antioxidant, gastroprotective, and other pharmacological effects [2,3].
Peperomia pellucida contains a variety of polyphenolic compounds, including pellucidin A, patuloside A, sesamin, peperomin (A, B, and C), isovitexin, isoswertisin, pellucididatin, apiole, caryatin, and 2,3,5-trimethoxy-9-(12,14,15-trimethoxybenzyl)-1H-indene [2,4]. These compounds are known for their antimicrobial, antioxidant, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor properties [2,4,5]. Therefore, polyphenols derived from P. pellucida are intriguing candidates for further research and development as raw materials for therapeutic applications.
Polyphenols frequently indicate the antioxidant content of foods and supplements. A higher polyphenol concentration is usually linked to better antioxidant activity. This means that foods or extracts that are high in polyphenols might effectively stop or lower oxidative stress and improve health [6,7].
Unfortunately, the potential of P. pellucida as a medicinal ingredient has not been fully utilized. This herbaceous plant has remained a weed for farmers, especially in oil palm cultivation. Moreover, the small amount of extraction yield has restricted its widespread application as raw material. Thus, a wide variety of organic solvents and extraction techniques have been developed by many researchers to optimize the extraction yield of the plant [8]. Cold and hot extraction techniques have been employed, including maceration and reflux, using various organic solvents, such as methanol, butanol, and ethyl acetate for the extraction process. However, the yield had remained relatively low, at approximately 3%–20% [9]. Hence, developing extraction techniques to improve the yield of P. pellucida is essential for its optimal utilization. The use of alternative solvents that have lower toxicity to the environment is a critical consideration in the development of extraction technologies.
Nowadays, environmentally friendly solvents are being developed as alternatives to organic solvents for reducing the use of toxic chemicals. Green solvents exhibit biocompatibility, non-toxicity, high selectivity, and a high degree of biodegradability [10]. Ahmad et al. [11] reported that the use of ionic liquids as a green solvent for extracting polyphenols from P. pellucida has successfully increased the amount of the yield. However, ionic liquid is considered expensive, quite difficult to produce, and lack of availability [12].
The natural deep eutectic solvent (NADES) is another green solvent that provides numerous advantages over ionic liquids. NADES is relatively simple to synthesize and inexpensive [13]. The preparation of NADES involves the combination of hydrogen-bonding acceptors (HBAs) and hydrogen-bonding donors (HBDs). Combining these two constituents in accurate molar proportions results in a liquid with a much-reduced melting point compared to the individual constituents. The application of NADES has been successfully demonstrated to extract polyphenol compounds from olive oil [14]. In addition, the use of NADES on extracting polyphenols from rosemary showed superior result compared to conventional solvents [14,15]. To our knowledge, there is no previous study on the extraction of phenolic compounds from P. pellucida using NADES. This study aims to identify the NADES solvent composition that generates the highest concentration of polyphenols. In this study, we used glucose, sorbitol, and sucrose as HBDs, and citric acid, choline chloride, and lactic acid as HBAs. A response surface methodology (RSM) approach was employed to optimize the conditions of the NADES-based microwave-assisted extraction (NADES-MAE) method used in the polyphenol extraction process.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample materials
Peperomia pellucida herb (with voucher specimen number 001/BRN/03/2024) as a sample was collected from Baras, Pasang Kayu, West Sulawesi, Indonesia, and identified at the Dendrology Laboratories, Faculty of Forestry, Universitas Mulawarman, Samarinda. The herbs were initially washed and then subjected to a wet sorting process. Subsequently, the samples were dried in an oven at 50°C–60°C for 24 hours. Thereafter, the dried samples were sorted, powdered, and put in airtight containers until further use.
Chemical materials
The chemical materials used in this study were edible glucose and non-GMO citric acid (Chlorogreen, Bandung, Indonesia), methanol, ethanol, distilled water (SmartLab, Indonesia), Folin–Ciocalteu, Na2CO3, and gallic acid (Sigma Aldrich, Germany). All chemical reagents were analytical grade.
Methods
NADES preparation and selection of NADES composition
The heating and stirring method was employed to prepare NADESs in accordance with previous research [13,16,17]. Lactic acid, citric acid, and choline chloride act as hydrogen-bond acceptors (HBAs), while sucrose, glucose, and sorbitol serve as HBDs. The selection of NADES composition was based on several previous studies on polyphenol extraction [2,16,18–20]. Initially, the NADES composition was designed with an HBA:HBD ratio of 1:1 with the addition of 30% water to reduce its viscosity. This mixture was melted using a magnetic stirrer with constant stirring at 80°C until a clear homogeneous solution was formed. All produced NADESs (choline chloride–sorbitol, lactic acid–sucrose, citric acid–glucose) were screened for their effectiveness in extracting polyphenolic compounds from the samples by determining their total phenolic content (TPC) values. The NADES composition resulting in the highest TPC level was selected to be optimized further.
Screening of single-factor
The single-factor screening process was conducted based on our previous studies [17,21]. In this case, we focused on the NADES composition that yielded the highest level of TPC value. The level of each factor in the test parameters was varied while the other parameters were held constant. We screened the effect of NADES ratios using a range ratio of Ca-Glu at 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, 4:1, and 5:1 g/g while maintaining the other parameter levels constant. The effect of microwave power was screened at 10%, 30%, 50%, and 70% watts, adjusting the tool setting conditions. As for the extraction time, it was set at 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 minutes. The solvent-to-sample ratio was screened at 3:1, 4:1, 5:1, 6:1, and 7:1 ml/g. A total of 5 g of sample was used for each screening and run in triplicate.
Extraction process
The extraction procedure was carried out using NADES-MAE based on our previous studies with some modifications [13,16,17]. Firstly, 5 g of P. pellucida herb was mixed with NADES in the round-bottom flasks and then extracted under different conditions, as shown in Table 1.
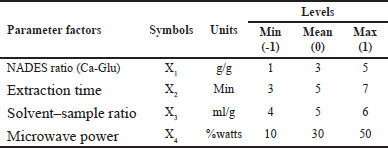 | Table 1. Extraction condition according to the different levels for each factor. [Click here to view] |
To obtain the extract solution, the mixture was subsequently filtered. The resulting extract was then subjected to a food dehydrator to reduce volume and dry. The dried or concentrated extract was stored in airtight containers until required.
Determination of TPC
The TPC value was determined through spectrophotometry in accordance with a previous study [16,22], with a few modifications. Briefly, 1 ml of each NADES extract was pipetted and diluted with aquadest in a 50 ml volumetric flask. Subsequently, 5 ml of the extract was combined with 5 ml of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent, and the mixture was incubated for 5 minutes. Following the incubation, 2 ml of NaCO3 solution was introduced into the mixture, and incubation continued for 30 minutes. Finally, the absorbance of the analytes was measured at a wavelength of 761 nm. The TPC value of the observed samples was calculated using a linear regression equation of the gallic acid as reference (Y = 0.0046X – 0.0075, with R2 = 0.99) and expressed in mg gallic acid equivalent (GAE) per gram extract.
Statistical analysis for optimization
To conduct the optimization process of the NADES-MAE, RSM was performed. Analysis of the relationship between each factor and the TPC value as the response variable was conducted for the optimization. A total of 29 experiments were conducted, comprising one block and five center points per block (four factors and three levels). These experiments were designed using the Box–Behnken design (BBD) approach to optimize the extraction conditions (Table 1). The experimental data from these various extraction conditions and TPC values were then estimated using multilinear quadratic regression models. This was conducted using licensed Design Expert (DE) v12 software (Statease Inc., Minneapolis, MN).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Selection of NADES composition
The composition of NADES has a significant effect on its physicochemical properties, including polarity, viscosity, and solubility. The efficiency of target metabolite compound extraction is directly influenced by these properties. A combination of choline chloride and sorbitol, lactic acid and sucrose, as well as citric acid and glucose, with a mass ratio of 1:1, was prepared to assess the effect of NADES compositions on their ability to attract polyphenols on the samples. During the extraction process, the microwave power (30% Watts), the extraction time (5 minutes), and the sample-solvent ratio (5 ml/g sample) were set constant. The results are presented in Figure 1.
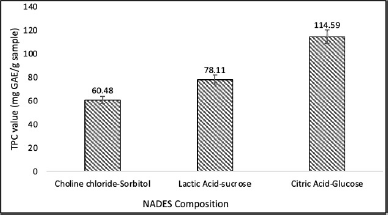 | Figure 1. TPC value of different NADES extract of P. pellucida. [Click here to view] |
Figure 1 illustrates that the extraction efficiency of target metabolite compounds, specifically the polyphenol content, is significantly affected by the composition of NADES, as indicated by the TPC. The value of TPC for the choline chloride-sorbitol with a ratio of 1:1 (w/w) was 60.48 mg GAE per gram. The lactic acid-sucrose had a TPC of 78.11 mg GAE/g, while the citric acid–glucose had a TPC of 114.59 mg GAE per gram of sample.
The results demonstrate that the citric acid-glucose was the most effective NADES composition in extracting the polyphenolic compounds. The combination of citric acid and glucose possesses numerous hydroxyl groups (-OH), which can establish hydrogen bonds to polyphenol compounds. Polyphenols interact with NADES via hydrogen bonding, increasing their solubility and resulting in the extraction of a greater quantity of polyphenol compounds. In addition, the combination of citric acid and glucose exhibits high polarity, promoting the solubility of naturally polar polyphenolic substances. High polarity facilitates the breakdown of the link between the polyphenols and the plant matrix, thus increasing the extraction efficiency. The acidic environment provided by citric acid can assist in stabilizing polyphenol compounds throughout the extraction procedure. An acidic pH can inhibit the oxidation and degradation of polyphenols, thus ensuring the quality of the extracted compounds. Therefore, the citric acid–glucose composition was employed to optimize the extraction conditions further.
One of the advantages of NADES is that it can stabilize the extracted compounds by protecting them from interacting with oxygen therefore preventing oxidative stress reactions. A study conducted by Pani? et al. [23] has shown that polyphenols extracted and stored in NADES, including those based on citric acid, generally exhibit greater stability over time compared to conventional solvents such as ethanol. The improved stability is attributed to molecular interactions between polyphenols and the NADES components, which reduce molecular mobility and prevent oxygen exposure, thereby prolonging oxidative degradation [24]. In addition, cucuminoids extracted with citric acid–glucose were found to be more stable than that of with organic solvent [25]. Spaggiari et al. [26] stated that the physicochemical properties of most NADES remain stable for at least 12 months under proper storage conditions (minimal moisture exposure and airtight containers). However, some NADES compositions may show viscosity and polarity changes over time due to moisture absorption, which could influence extraction and storage efficiency. Nevertheless, the protective effect on polyphenols generally persists as long as the NADES structure is maintained [26]. The impact of citric acid on the long-term stability of extracted polyphenols has been a subject of considerable interest. It has been demonstrated that citric acid can assist in maintaining the stability of polyphenols by preventing oxidation and enzymatic degradation [27,28]. However, it is important to note that excessive acidity can lead to the degradation of polyphenols [29], mainly if the extraction process is carried out at high temperatures or for extended periods. Therefore, finding the right balance using citric acid is vital to ensure optimal polyphenol stability [30].
In the present study, the viscosity of the mixture of citric acid–glucose was adjusted by incorporating 30% water in accordance with our previous studies [16,30]. The addition of a larger amount of water resulted in an increase in the NADES polarity, hence reducing the solubility of polyphenols [31]. However, an excessive water addition can disrupt the hydrogen bonds that bind the components of NADES, leading to the disintegration of their supramolecular structure [32].
Single factor analysis
After selecting the NADES composition, the optimum extraction conditions are subsequently determined. Several variables were examined, including microwave power, extraction time, NADES ratio, and solvent–sample ratio. The objective is to ascertain the impact of each variable on the TPC value. Figure 2 displays the findings of the analysis.
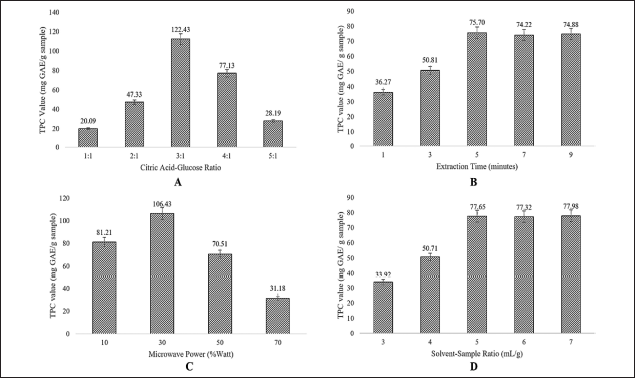 | Figure 2. The effect of different extraction conditions on the TPC values. Citric acid–glucose ratio (A), Extraction time (B), Microwave power (C), and solvent-to-sample ratio (D). [Click here to view] |
The extraction conditions were established after the selection of the NADES composition. Figure 2 illustrates that the level of TPC was influenced by parameters including microwave power, extraction duration, NADES proportion, and solvent–sample ratio.
The molar ratio of citric acid to glucose in the mixture affected the TPC of the P. pellucida herb, with specific ratios of 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, 4:1, and 5:1 (w/w) exhibiting varying effects. Figure 2A shows the variation of the citric acid and glucose combination ratio, where the proportion 3:1 obtained the highest TPC value. Citric acid acts as the HBA during extraction, while glucose functions as the HBD [11,33]. At specific ratios, the combination of HBA and HBD forms a stable solution with physicochemical properties that can be adjusted to the conditions of the target compounds in the sample. The eutectic phenomena result in the establishment of bonds of hydrogen among the constituents of NADES. This enables the optimal retrieval of the desired substance.
The effects of extraction time on TPC values are illustrated in Figure 2B, using a NADES-MAE-based citric acid–glucose composition. Various extraction times were employed, including 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 minutes. The TPC value peaked at an extraction time of 5 minutes and remained constant at 7 and 9 minutes. Figure 2B illustrates that the TPC value rises with an increase in extraction time from 1 to 5 minutes. However, the TPC value remained unchanged from minutes 5 to 9, showing a slight decrease, though not statistically significant. The observed phenomena may be due to the hydroxyl groups of polyphenols in the sample undergoing oxidation as a result of the prolonged extraction time. The utilization of NADES in the extraction procedure of polyphenols from P. pellucida herb results in a significantly reduced extraction time than that of ionic liquid, which lasts approximately 10 to 15 minutes.
The observed microwave power varied from 10% to 70%, as 90% power was not used to prevent charring or damage to the samples. High microwave power leads to elevated temperatures, potentially causing damage to the cell wall and altering the structure of the target molecule. Figure 2C illustrates the maximum TPC value at 30% microwave power, consistent with findings from previous studies, especially those using NADES as a solvent [20,34]. Consequently, the microwave power of 30% Watts was employed as the middle level in experimental design for further optimization process.
Figure 2D shows that the TPC value increased when the solvent–sample ratio rose from 3:1 to 5:1 ml/g, and then remained constant between 5:1 and 7:1 ml/g. The solvent–sample ratio of 5:1 is the most effective proportion for extracting the desired compounds from the P. pellucida herb. At this ratio, solute dissolution and mass transfer rate are maximized, hence enhancing the effectiveness of extraction [18,19,21]. However, excessive solvent use (above this ratio) may result in a wasteful and ineffective extraction process.
Optimization of the NADES-MAE method using RSM
The optimum conditions for extracting polyphenols from P. pellucida herbs were determined using RSM in DE. The BBD approach was employed to optimize the effects of four experimental variables: the ratio of citric acid: glucose (1:1, 1:3, and 1:5 w/w), microwave power (10%, 30%, and 50%), extraction time (3, 5, and 7 minutes), and solid–liquid ratio (1:4, 1:5, and 1:6 g/ml) resulted in 29 runs, as presented in Table 2.
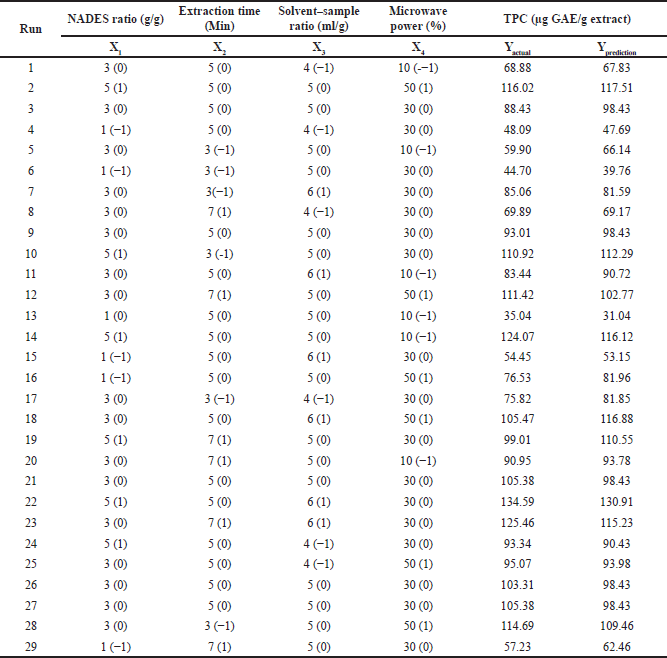 | Table 2. TPC values from P. pellucida herb experiments. [Click here to view] |
The quadratic standard modeling was chosen due to the lack of significance in the lack-of-fit p-value and a predicted R2 score of 0.74, which was lower than the adjusted R2 score (0.88). Nevertheless, the discrepancy between the predicted R2 amount and the adjusted R2 score remains within the range of less than 0.2. This signifies that the recommended equation model is compatible with both the data and the model. Consequently, these recommendations can be implemented to achieve optimal conditions by modeling equations. Furthermore, the mixed polynomial can be simplified before point selection to achieve the most optimal model design. By altering the selection variables, the quantity of coefficients can be diminished, reducing the number of necessary model points.
Table 3 shows that the predicted R2 value (0.7362) was lower than the adjusted R2 value (0.8894), leading to the recommendation of the quadratic standard model due to the lack of a significance score at the insufficient fit p-value.
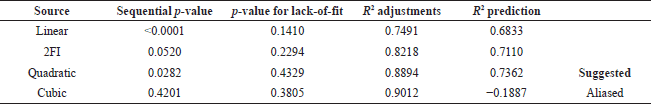 | Table 3. Summary of fit. [Click here to view] |
Based on the ANOVA results (Table 4), the independent variable of the extraction conditions optimized significantly influences the TPC value as the resulting response. In this model, two interactive coefficients (X1X3 and X2X3) and two quadratic coefficients (X32 and X42) have a p-value higher than 0.05. They are regarded as not statistically significant and, therefore, do not directly influence the TPC value but affect the validity of the recommended equation model. In addition, the F-value and p-value of lack–of-fit are 1.09 and 0.51, indicating that the model’s fit is insignificant. Hence, the suggested equation framework effectively elucidates the outcomes and precisely forecasts the optimal circumstances.
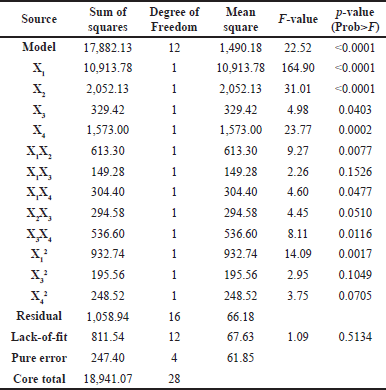 | Table 4. Response surface variance analysis by utilizing simplified quadratic regression. [Click here to view] |
The equation obtained is Y = 98.43 + 30.16X1 + 13.08X2 + 5.24X3 + 11.45X4 - 12.38X1X2 - 6.11X1X3 + 8.72X1X4 - 8.58X2X3 + 11.58X3X4 - 11.78X12 - 5.39X32 - 6.08X42. In the equation, Y is the TPC, X1 is the NADES ratio (w/w), X2 is microwave power (%watts), X3 is the extraction period, and X4 is the solvent–sample proportion (v/w). The validity of the best equation was selected based on fit statistic parameters, including the value of the correlation coefficient (R2), predicted correlation coefficient (predicted R2), and adjusted correlation coefficient (adjusted R2). The R2 score of 0.94 indicates a high degree of connection, as it is extremely close to 1. The adjusted R2 score of 0.90, derived less than 0.2 from the predicted R2 score of 0.79, indicates that the selected model is relatively stable and reliable [22,33].
The optimization condition of NADES-MAE
The interaction between each factor strongly influences the extraction efficiency. The RSM analysis determined the most favorable circumstances were a microwave power of 50%, a time of extraction of 5 minutes, a NADES ratio of 5:1 (w/w), and a solvent–sample ratio of 6:1 (ml/g). These conditions yielded a predicted TPC value of 131.60 ± 8.14 mg GAE per gram extract (95% confidence interval range at 115.19–148.01 mg GAE/g extract), as illustrated in Figure 3. It illustrates the significant interaction among factors affecting the TPC value, represented in a three-dimensional response surface, along with the slope of the surface reflecting the observable interactive effects.
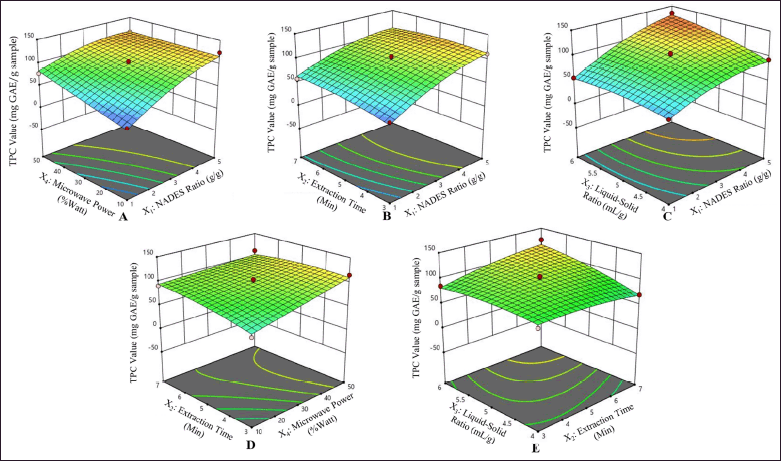 | Figure 3. Three-dimensional contour plot response surface of each factor illustrating the comprehensive effects of experimental parameter factors on the TPC value of P. pellucida. NADES ratio and microwave power (A); NADES ratio and extraction time (B); NADES ratio and solvent–sample ratio (C); extraction time and microwave power (D); extraction time and solvent–sample ratio (E). [Click here to view] |
The response surface plots in Figure 3 reveal the optimal points for the response variables (red-colored areas) seen in Figures 3A–E. However, the optimal points are not visible in Figure 3D. The obtained equation models and three-dimensional graphs can be used to navigate and get the optimum conditions. The extraction conditions proposed by RSM yielded extracts with optimal predicted TPC values. This optimal extraction condition was employed to conduct confirmation tests on three replicates, resulting in a TPC value of 138.29 ± 2.21 mg GAE/g extract.
Several investigations are currently being accomplished to extract the total polyphenolic compounds of the P. pellucida herb using microwave and analyzed by RSM. In a previous study using ionic liquid as a solvent, the highest TPC level obtained was only 33.05 µg GAE/g sample, or equivalent to 0.03 mg GAE/g sample. In contrast, the conventional maceration method resulted in the highest condition using ethyl acetate solvent of 16.15 µg GAE/g sample.
The use of ethyl acetate in the conventional method was found to be a more effective solvent compared to other conventional solvents (such as ethanol and methanol) [11,35]. Interestingly, the use of citric acid–glucose as a solvent in this study showed superior results compared to conventional solvents and ionic liquids. This suggests that NADES presents a potential method for the extraction of polyphenol-rich compounds from P. pellucida.
Due to the accessibility of components and the efficiency of the extraction method, citric acid–glucose (NADES) has a low production cost, making it highly cost-effective. In terms of environmental impact, NADES-based citric acid–glucose is environmentally friendly due to the absence of toxic substances and its easy degradation properties [11,35]. In contrast, ionic liquids pose a significant challenge due to the limited availability of raw materials. In addition, some types of ionic liquids may contain chemicals that must be managed carefully to avoid negative environmental impacts. Furthermore, most ionic liquids have poor biodegradation properties in nature.
CONCLUSION
According to the findings, NADES is an environmentally friendly solvent used to extract polyphenolic components of P. pellucida herb. The results of the RSM analysis indicate that the optimum conditions for the extraction of polyphenols from P. pellucida herb are as follows: a NADES (citric acid–glucose) ratio of 5:1 (w/w), a solvent-to-sample ratio of 6:1 ml/g, and a microwave power of 50% for 5 minutes. The study suggests that citric acid–glucose-based NADES-MAE was a green and effective method to extract targeted compounds from P. pellucida herb.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was supported by Universitas Mulawarman through Riset Kolaborasi Institusi, Konsorsium Perguruan Tinggi Negeri Kawasan Timur Indonesia collaboration with Universitas Mulawarman, Universitas Lambung Mangkurat, and Politeknik Negeri Tanah Laut (No. 472/UN17.L1/HK/07.00/2024).
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors report no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
This study does not involve experiments on animals or human subjects.
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated and analyzed are included in this research article.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used artificial intelligence (AI)-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI
REFERENCES
1. Ahmad I, Hikmawan BD, Sulistiarini R, Mun’im A. Peperomia pellucida (L.) Kunth herbs: a comprehensive review on phytochemical, pharmacological, extraction engineering development, and economic promising perspectives. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2023;13(1):1–9. CrossRef
2. Ahmad I, Ambarwati N, Elya B, Omar H, Mulia K, Yanuar A, et al. A new angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor from Peperomia pellucida (L.) Kunth. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2019;9(6):257–62. CrossRef
3. Uwaya OD, Omozuwa PO, Inegbedion RE. Evaluation of in-vitro antioxidant and antidiarrheal activities of Peperomia pellucida methanol extracts on Albino mice. J Appl Sci Environ Manag. 2021;25(9):1681–8. CrossRef
4. Alves NSF, Setzer WN, da Silva JKR. The chemistry and biological activities of Peperomia pellucida (Piperaceae): a critical review. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;232(232):90–102. CrossRef
5. Gomes PWP, Barretto H, Reis JDE, Muribeca A, Veloso A, Albuquerque C, et al. Chemical composition of leaves, stem, and roots of Peperomia pellucida (L.) Kunth. Molecules. 2022;27(6):1847. CrossRef
6. Makori SI, Mu TH, Sun HN. Total polyphenol content, antioxidant activity, and individual phenolic composition of different edible parts of 4 sweet potato cultivars. Nat Prod Comm. 2020;15(7):1934578X20936931. CrossRef
7. Vidal-Casanella O, Moreno-Merchan J, Granados M, Nuñez O, Saurina J, Sentellas S. Total polyphenol content in food samples and nutraceuticals: antioxidant indices versus high performance liquid chromatography. Antioxidants. 2022;11(2):324. CrossRef
8. Ho KL, Tan CG, Yong PH, Wang CW, Lim SH, Kuppusamy UR, et al. Extraction of phytochemicals with health benefit from Peperomia pellucida (L.) Kunth through liquid-liquid partitioning. J Appl Res Med Aromat Plants. 2022;30:100392. CrossRef
9. Phongtongpasuk S, Poadang S. Extraction of antioxidants from Peperomia pellucida L. Kunth. Sci Technol Asia. 2014;19(3):38–43.
10. Pathak M, Singh L, Kumar A, Upadhyay G. Green solvents and their importance in medicinal chemistry: an overview. Subharti J Interdisciplinary Res. 2020;3(1):4–8.
11. Ahmad I, Yanuar A, Mulia K, Mun’im A. Application of ionic liquid as a green solvent for polyphenolics content extraction of Peperomia pellucida (L) kunth herb. J Young Pharm. 2017;9(4):486–90. CrossRef
12. Laus G, Bentivoglio G, Schottenberger H, Kahlenberg V, Kopacka H, Röder T, et al. Ionic liquids: current developments, potential and drawbacks for industrial applications. Lenzinger Berichte. 2005;84(1):71–85.
13. Rijai L, Tang ST, Priastomo M, Siska S, Indriyanti N, Ambarwati NSS, et al. Microwave-assisted extraction of polypenols from Eleutherine bulbosa Mill. Urb. bulbs using choline chloride-sorbitol based natural deep eutectic solvent. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2023;13(6):217–24. CrossRef
14. Bonacci S, Di Gioia ML, Costanzo P, Maiuolo L, Tallarico S, Nardi M. Natural deep eutectic solvent as extraction media for the main phenolic compounds from olive oil processing wastes. Antioxidants. 2020;9(6):1–14. CrossRef
15. Barbieri JB, Goltz C, Batistão Cavalheiro F, Theodoro Toci A, Igarashi-Mafra L, Mafra MR. Deep eutectic solvents applied in the extraction and stabilization of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) phenolic compounds. Ind Crops Prod. 2020;144:112049. CrossRef
16. Yusuf B, Astati SJ, Ardana M, Herman H, Ibrahim A, Rijai L, et al. Optimizing natural deep eutectic solvent citric acid-glucose based microwave-assisted extraction of total polyphenols content from Eleutherine bulbosa (Mill.) bulb. Indonesian J Chem. 2021;21(4):797–805. CrossRef
17. Herman, Ibrahim A, Rahayu BP, Arifuddin M, Nur Y, Prabowo WC, et al. Single factor effect of natural deep eutectic solvent citric acid-glucose based microwave-assisted extraction on total polyphenols content from Mitragyna speciosa Korth. Havil leaves. Pharmacogn J. 2021;13(5):1109–15. CrossRef
18. Oktaviyanti ND, Kartini, Mun’im A. Application and optimization of ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent for the extraction of new skin-lightening cosmetic materials from Ixora javanica flower. Heliyon. 2019;5(11):e02950. CrossRef
19. Shang XC, Chu D, Zhang JX, Zheng YF, Li Y. Microwave-assisted extraction, partial purification and biological activity in vitro of polysaccharides from bladder-wrack (Fucus vesiculosus) by using deep eutectic solvents. Sep Purif Technol. 2021;259:118169. CrossRef
20. Hapid A, Zullaikah S, Mahfud M, Kawigraha A, Azmi MU, Haryanto I, et al. Optimization of microwave-assisted roasting: box-behnken design for oxidation of sulfide minerals and control of atmospheric sulfur in refractory gold ore pretreatment. Case Stud ChemEnviron Eng. 2024;10:100826. CrossRef
21. Simamora A, Timotius KH, Setiawan H, Saputri FC, Putri CR, Aryani D, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of xanthorrhizol from Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb. rhizomes by natural deep eutectic solvents: optimization, antioxidant activity, and toxicity profiles. Molecules. 2024;29(9):2093. CrossRef
22. Bezerra MA, Santelli RE, Oliveira EP, Villar LS, Escaleira LA. Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta. 2008;76(5):965–77. CrossRef
23. Pani? M, Gunjevi? V, Cravotto G, Radoj?i? Redovnikovi? I. Enabling technologies for the extraction of grape-pomace anthocyanins using natural deep eutectic solvents in up-to-half-litre batches extraction of grape-pomace anthocyanins using NADES. Food Chem. 2019;300:125185. CrossRef
24. Gómez-Urios C, Viñas-Ospino A, Puchades-Colera P, Lopez-Malo D, Frigola A, Esteve MJ, et al. Sustainable development and storage tability of orange by-products extract using natural deep eutectic solvents. Foods. 2022;11(16):2457. CrossRef
25. Liu Y, Li J, Fu R, Zhang L, Wang D, Wang S. Enhanced extraction of natural pigments from Curcuma longa L. using natural deep eutectic solvents. Ind Crops Prod. 2019;140:111620. CrossRef
26. Spaggiari C, Carbonell-Rozas L, Zuilhof H, Costantino G, Righetti L. Structural elucidation and long-term stability of synthesized NADES: a detailed physicochemical analysis. J Mol Liq. 2025;424:127105. CrossRef
27. Savi LK, Dias MCGC, Carpine D, Waszczynskyj N, Ribani RH, Haminiuk CWI. Natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) based on citric acid and sucrose as a potential green technology: a comprehensive study of water inclusion and its effect on thermal, physical and rheological properties. Int J Food Sci Technol. 2019;54(3):898–907. CrossRef
28. Airouyuwa JO, Mostafa H, Ranasinghe M, Maqsood S. Influence of physicochemical properties of carboxylic acid-based natural deep eutectic solvents (CA-NADES) on extraction and stability of bioactive compounds from date (Phoenix dactylifera L.) seeds: an innovative and sustainable extraction technique. J Mol Liq. 2023;388:122767 CrossRef
29. Gómez Vargas C, Ponce NMA, Stortz CA, Fossore EN, Bonelli P, González CMO, et al. Pectin obtention from agroindustrial wastes of Malus domestica using green solvents (citric acid and natural deep eutectic solvents). Chemical, thermal, and rheological characterization. Front Chem. 2025;12:1504582. CrossRef
30. Ahmad I, Shakti SOP, Prabowo WC, Hikmawan BD, Arifudin M, Angelina M, et al. Citric acid-glycerol-based NADES for microwave-assisted extraction enhances the polyphenols level of Eleutherine bulbosa mill. Urb. Bulbs. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2024;14(9):189–97. CrossRef
31. Huamán-Castilla NL, Gajardo-Parra N, Pérez-Correa JR, Canales RI, Martínez-Cifuentes M, Contreras-Contreras G, et al. Enhanced polyphenols recovery from grape pomace: a comparison of pressurized and atmospheric extractions with deep eutectic solvent aqueous mixtures. Antioxidants. 2023;12(7):1446. CrossRef
32. Grudniewska A, Pop?o?ski J. Simple and green method for the extraction of xanthohumol from spent hops using deep eutectic solvents. Sep Purif Technol. 2020;250:117196. CrossRef
33. Aung T, Kim SJ, Eun JB. A hybrid RSM-ANN-GA approach on optimisation of extraction conditions for bioactive component-rich laver (Porphyra dentata) extract. Food Chem. 2022;366:130689. CrossRef
34. Costa FS, Moreira LS, Ludovico LL, Volpe J, de Oliveira AC, Dos Santos MP, et al. Microwave-assisted extraction based on emulsion breaking with natural deep eutectic solvent for vegetable oil sample preparation prior to elemental determination by ICP OES. Talanta. 2024;266:125108. CrossRef
35. Ahmad I, Yanuar A, Mulia K, Mun’im A. Extraction of polyphenolic content from Peperomia pellucida (L) Kunth herb with 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide as a green solvent. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2017;79(6):1013–7. CrossRef