INTRODUCTION
There are several combination drugs in the market formulated to meet multiple disorders that are associated with a disease. Etoricoxib (60 mg) and Thiocolchicoside (4 mg) are one such combination medicine. Etoricoxib is a nonsteroidal inflammatory drug with and aim to relieve pain and swelling of the skeleton muscles, whereas Thiocolchicoside is a muscle relaxant and is used as an add-on treatment for pain due to permanent tightening of muscles. Etoricoxib (Fig. 1) chemically is 5-chloro-2-(6-methylpyridin-3-yl)-3-[4-(trideuteriomethylsulfonyl)phenyl]pyridine and Thiocolchicoside (Fig. 2) chemically is N-[(7S)-1,2-dimethoxy-10-methylsulfanyl-9-oxo-3-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-6,7-dihydro-5H-benzo[a]heptalen-7-yl]acetamide. The literature reveals the availability of several techniques and methods for the simultaneous estimation of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside like UV spectroscopy, High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC), and High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) methods (Gulhane et al., 2021; Palte and Kondalkar, 2015; Sujit and Nitin, 2016). With the advent of lean laboratories, there is a strong need to develop methods which are quick as well as cost-competitive. Published methods in the literature provide several HPLC methods which require about 30 minutes of HPLC run time. However, there is no published data on the use of the ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) method for simultaneous estimation of both Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside. From an operations point of view, both HPLC and UPLC work on the same principle. HPLCs utilize columns with particle sizes of about 5 μ, while the UPLCs utilize 2-μ particles. Due to this, the HPLC systems can work with pressures ranging up to 6,000 psi, whereas the UPLC systems can handle pressures ranging up to 15,000 psi. The van Deemter equation states that the chromatographic process efficiency increases with a decrease in column particle size. When the particle size is lower, the height equivalent to theoretical plates reduces significantly. Both HPLC and UPLC offer precision and accuracy levels which are comparable. However, UPLC provides a major advantage with improved sensitivity, faster run time, and less solvent consumption. These advantages make UPLC the preferred technique in quality control laboratories. The objective of this study is to develop and validate a simple, sensitive, accurate, stability-indicating, and rapid RP-UPLC method for the simultaneous estimation of Thiocolchicoside and Etoricoxib in tablet formulation, so that it can be applied for routine analysis in testing laboratories.
 | Figure 1. Structure of Etoricoxib. [Click here to view] |
EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES
Materials
Etoricoxib (purity: 99.6%) and Thiocolchicoside (purity: 99.4%) drugs [Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)] and Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside tablets (Retoz MR 4) were obtained from Dr. Reddy’s laboratories as gift samples. Potassium dihydrogen phosphate, acetonitrile, methanol, orthophosphoric acid, and glacial acetic acid were of analytical reagent grade and procured from Rankem. Purified water for UPLC was obtained through Milli-Q water generation system. 0.45 μ Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) filters of Millipore make were used for sample solution filtrations.
EQUIPMENT
Waters Acquity UPLC system with an Auto Injector and Tunable UV Detector was used; the software used is Empower 2. Sonicator (Ultrasonic), pH meter (Thermo Scientific); micro balance (Sartorius); and vacuum filter pump (Labdeal) were also used.
 | Figure 2. Structure of Thiocolchicoside. [Click here to view] |
METHOD
Chromatographic conditions
The Waters Acquity UPLC chromatographic system with Hibar, C18 column of dimension 100 × 2.1 mm, 1.8 μm, was used. The mobile phase was a mixture of 0.1% orthophosphoric acid (pH 2.5) and acetonitrile in the ratio of 90:10 (v/v). The flow rate was 0.3 ml/minute, with 2 μl injection volume, column oven temperature of 30°C, and detection at 256 nm using Acquity Tunable UV detector. Instrument operation and data collation and processing were carried out using Waters Empower 2 software.
Mobile phase and solution preparation
Mobile phase. Mixture of 0.1% phosphate buffer solution (pH 2.5) and acetonitrile in the ratio of 90:10 (v/v).
Preparation of 0.1% phosphate buffer (pH 2.5). 1 ml of orthophosphoric acid is diluted to 1,000 ml with purified water. pH was adjusted to 2.5, if necessary, with glacial acetic acid.
Preparation of diluent. Based up on the solubility of the drug, the diluent was selected as phosphate buffer and acetonitrile taken in the ratio of 50:50 (v/v).
Standard preparation
Thiocolchicoside stock solution (40 μg/ml). Accurately weigh 2 mg of Thiocolchicoside standard in a 50 ml volumetric flask. Add three-quarters of the diluent and sonicate for 10 minutes. Make up the volume with the diluent and mix.
Etoricoxib stock solution (600 μg/ml). Accurately weigh 30 mg of Etoricoxib standard in a 50 ml volumetric flask. Add three-quarters of diluents and sonicate for 10 minutes. Make up the volume with diluent and mix.
Standard working solution (4 μg/ml of Thiocolchicoside and 60 μg/ml of Etoricoxib). Pipette 1 ml of Thiocolchicoside stock and 1 ml of Etoricoxib stock into a 10 ml volumetric flask. Dilute up to the mark with diluent and mix.
Test preparation
10 tablets were weighed, and the average weight of each tablet was calculated. The tablets were then finely powdered. Weight equivalent to 1 tablet (325 mg) was transferred into a 100 ml volumetric flask; 50 ml of the diluent was added and sonicated for 25 minutes; furthermore, the volume was made up with the diluent and mixed. The solution was then filtered using 0.45 μ PVDF filters to get solutions of concentration of 40 μg/ml Thiocolchicoside and 600 μg/ml Etoricoxib. 1.0 ml of the filtered sample solution was transferred to a 10 ml volumetric flask and made up with the diluent and mixed to obtain solutions of 4 μg/ml Thiocolchicoside and 60 μg/ml Etoricoxib.
Stability
Studies of the stability indicating capability of the method and degradation were conducted. These studies were conducted by exposing the Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside tablet powder to degradation conditions in accordance with the International Council of Harmonization (ICH) guidance. Samples of the Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside formulation and the degradant samples were injected and separated using the optimized method as detailed below.
Oxidation. To 1 ml of stock solution of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside, 1 ml of 20% hydrogen peroxide was added separately. The solutions were kept for 30 minutes at 60°C. For UPLC study, the resultant solution was diluted to obtain (60 and 4 μg/ml) solutions and 10 μl was injected into the system and the chromatograms were recorded to assess the stability of the sample.
Acid degradation studies. To 1 ml of stock solution of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside, 1 ml of 2 N hydrochloric acid was added and refluxed for 30 minutes at 60°C. The resultant solution was diluted to obtain (60 and 4 μg/ml) solutions and 10 μl was injected into the system and the chromatograms were recorded to assess the stability of the sample.
Alkali degradation studies. To 1 ml of stock solution of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside, 1 ml of 2 N sodium hydroxide was added and refluxed for 30 minutes at 60°C. The resultant solution was diluted to obtain (60 and 4 μg/ml) solutions and 10 μl was injected into the system and the chromatograms were recorded to assess the stability of the sample.
Dry heat degradation studies. The standard drug solution was placed in an oven at 105°C for 6 hours to study dry heat degradation. For UPLC study, the resultant solution was diluted to get (60 and 4 μg/ml) solutions and 10 μl was injected into the system and the chromatograms were recorded to assess the stability of the sample.
Photo stability studies. The photochemical stability of the drug was also studied by exposing the (600 and 40 μg/ml) solution to UV light by keeping the beaker in a UV chamber for 7 days or 200-Watthours/m2 in a photo stability chamber.. For UPLC study, the resultant solution was diluted to obtain (60 and 4 μg/ml) solutions and 10 μl was injected into the system and the chromatograms were recorded to assess the stability of the sample.
Neutral degradation studies. Stress testing under neutral conditions was studied by refluxing the drug in water for 6 hours at a temperature of 60°C. For UPLC study, the resultant solution was diluted to get (60 and 4 μg/ml) solutions and 10 μl was injected into the system and the chromatograms were recorded to assess the stability of the sample.
Method validation
For the developed RP-UPLC method, validation was carried out according to the ICH Q2R1 guideline for the analytical parameters, such as system suitability test, specificity through the degradation study of Thiocolchicoside and Etoricoxib tablets and placebo, linearity and range, precision, accuracy, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantitation (LOQ), and robustness, to demonstrate the adequacy of the method.
System suitability. A standard solution of Thiocolchicoside and Etoricoxib working standard (4 μg/ml of Thiocolchicoside and 60 μg/ml of Etoricoxib) was prepared and five replicates were injected into the UPLC system. The system suitability parameters of retention time, resolution, plate count, and relative standard deviations and variation were evaluated from standard chromatograms.
Specificity. Specificity for the RP-UPLC method was demonstrated by injecting blank, formulation placebo, and potential degradation impurities from the degradation study conducted in line with the ICH guidance.
Precision. The method precision of the RP-UPLC assay method as part of the repeatability was checked by injecting six replicates of Thiocolchicoside and Etoricoxib solutions of concentration (4 μg/ml of Thiocolchicoside and 60 μg/ml of Etoricoxib). Intermediate precision was established by injecting five sample solutions of concentration (4 μg/ml of Thiocolchicoside and 60 μg/ml of Etoricoxib) into the chromatograph after 24 hours of preparation. The %amount of Thiocolchicoside and Etoricoxib was calculated, and relative standard deviation (RSD) was determined.
Linearity and range. To demonstrate the linearity and range of the RP-UPLC assay method, six standard solutions with concentrations of about 1–6 μg/ml of Thiocolchicoside and 15–90 μg/ml of Etoricoxib were prepared corresponding to 25%, 50%, 75%, 100%, 125%, and 150%. These solutions were injected in the chromatographic system and concentration versus peak area plots were made to find the correlation coefficient.
Accuracy. To demonstrate the accuracy of the Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside RP-UPLC assay method, sample solutions of concentration 4 μg/ml Thiocolchicoside and 60 μg/ml Etoricoxib were prepared by taking one tablet equivalent to the powdered Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside tablet, followed by sonication with the diluent and filtration. Known quantities of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside standard stock solution were spiked on to the sample solution at levels of 50%, 100%, and 150%. Each of the sample solution spiked with a known concentration of the standard (50%, 100%, and 150% each of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside) was injected in triplicate.
LOQ and LOD. For LOD, diluted solutions of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside standard were prepared with concentrations of 0.15 and 0.01 μg/ml, respectively. LOD was obtained by using the regression analysis and calculated using the following equation:
LOD = 3.3 σ / S
For LOQ, diluted solutions of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside standard were prepared with concentrations of 0.45 and 0.03 μg/ml, respectively. LOQ was obtained by using the regression analysis and calculated using the following equation:
LOQ = 10 σ / S
where,
σ = Standard deviation of intercepts of calibration curves;
S = Mean of slopes of the calibration curves.
Robustness. Robustness of the Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside RP-UPLC assay method was demonstrated by deliberate changes in the method which could potentially occur in a laboratory environment by going on either side of the chromatographic parameters like flow (+0.3 ml/minute), mobile phase composition (+2%), and temperature (+5°C). Under each of these conditions, sample preparations were injected in duplicate into the optimized chromatographic conditions with the above changes. The system suitability parameters and the amount of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside content were calculated.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Optimization of sample preparation
The sample preparation technique is critical and has a significant impact on the precision and accuracy of the method. Tablets were finely powdered. Based on the solubility of Thiocolchicoside and Etoricoxib, acetonitrile and orthophosphoric acid combination were assessed and optimized for efficient extraction. The filter used was the standard 0.45 μ PVDF filter which did not show any retention of the drug on the filter.
Optimization of chromatographic conditions
The sensitivity of the UPLC method depends upon the selection of detection wavelength. An ideal wavelength is one that gives good response for all impurities and analyte peak to be detected. Wavelength was set at 256 nm by considering the UV maxima of Thiocolchicoside and UV minima of Etoricoxib. The superimposed UV spectrum is shown in Figure 3.
UPLC columns like HSS, Hibar, and BEH were evaluated along with 0.01 N potassium dihydrogen phosphate and 0.1% orthophosphoric acid (pH 2.5) buffer and acetonitrile combinations. The High Strength Silica (HSS) column with 0.1% orthophosphoric acid (pH 2.5)/0.01 N potassium hydrogen phosphate buffer and acetonitrile were checked. With 0.1% orthophosphoric acid, the (pH 2.5) peaks were merging, and with 0.01 N potassium hydrogen phosphate, the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) plate count was inadequate. The Ethylene Bridged Hybrid (BEH) column was evaluated with 0.1% orthophosphoric acid (pH 2.5) and acetonitrile mix. But resolutions were not satisfactory. Hibar column was evaluated with 0.1% orthophosphoric acid (pH 2.5) and acetonitrile. The resolution was promising but peak splitting was observed for Thiocolchicoside peak. This was further optimized by increasing the ratio of the buffer to solvent mix. With 0.1% orthophosphoric acid (pH 2.5) and acetonitrile at 90:10 (v/v), the combination worked well with quick elution, good separation, and peak shapes.
Final optimized condition was achieved using Waters Acquity Hibar, C18 column of dimensions 100 × 2.1 mm, 1.8 μm, with a flow rate of 0.3 ml/minute, column oven temperature of 30°C, and mobile phase consisting of 0.1% orthophosphoric acid (pH 2.5) and acetonitrile in the ratio of 90:10 (v/v).
Both Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside peaks eluted within 2 minutes, thus making it a quick method and hence the possibility to run multiple samples in a short time.
Stability
The stability-indicating capability of the method was demonstrated by degradation studies in accordance with the ICH guidance. Maximum degradation for Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside was observed in exposure to acidic conditions to an extent of 5.17% and 5.83%, respectively. Least degradation was observed in conditions of exposure to water to the extent of about 0.9% in both Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside. Under each condition of degradation, there were no interferences at the retention time of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside. The details of degradation under various stress conditions are detailed in Tables 1 and 2 for Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside, respectively. A chromatogram for acid degradation condition, which showed maximum degradation, is shown in Figure 4.
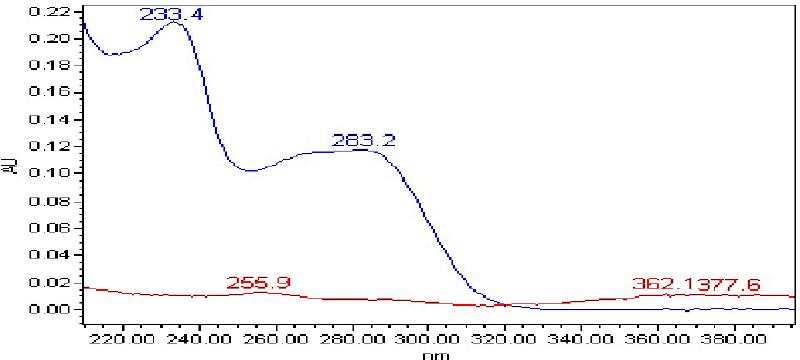 | Figure 3. UV overlay spectrum (Etoricoxib—In blue; Thiocolchicoside—In red). [Click here to view] |
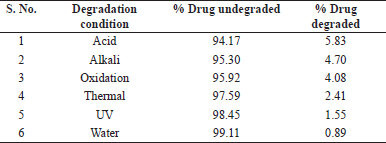 | Table 1. Degradation data for Etoricoxib. [Click here to view] |
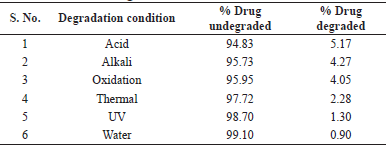 | Table 2. Degradation data for Thiocolchicoside. [Click here to view] |
Method validation
For the developed RP-UPLC method, validation was carried out according to the ICH Q2R1 guideline for the analytical parameters, such as system suitability test, specificity through degradation study of Thiocolchicoside and Etoricoxib tablets and placebo, linearity and range, precision, accuracy, LOD, LOQ, and robustness, to demonstrate the adequacy of the method.
System suitability
The system suitability parameters were evaluated from five replicate injections of the standard chromatogram. Retention time was observed to be 0.875 minutes for Thiocolchicoside and 1.498 minutes for Etoricoxib. Resolution was observed to be 6.9. Tailing was observed to be 1.49 for Thiocolchicoside and 1.05 for Etoricoxib. Plate count was consistent with 2,414 for Thiocolchicoside and 3,580 for Etoricoxib. The %RSD of retention time, tailing factor, and plate count was well within 2% variation. System suitability details are presented in Table 3. A typical chromatogram of the standard for system suitability is shown in Figure 5.
Specificity
Specificity for the RP-UPLC method was demonstrated by no interference from the blank, formulation placebo, and potential degradation impurities from the degradation study conducted in line with the ICH guidance. Chromatogram was reviewed for any interference from the blank, placebo, and potential degradation impurities. There were no interferences at the retention time of the Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside peak. To demonstrate specificity, the overlayed chromatogram for the blank, placebo, standard, and sample is shown in Figure 6.
Precision
The method precision of the RP-UPLC assay method as part of repeatability was checked and the percentage relative standard deviations for Thiocolchicoside and Etoricoxib were observed to be 0.9% and 0.7%, respectively. As part of intermediate precision, the percentage amount of Thiocolchicoside and Etoricoxib was calculated, and RSD was found to be 1.1% and 1.4%, respectively. Details of the precision method and intermediate precision are summarized in Table 4.
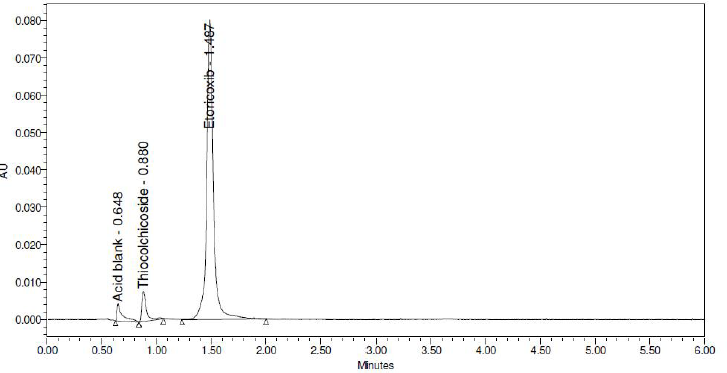 | Figure 4. Acid degradation chromatogram. [Click here to view] |
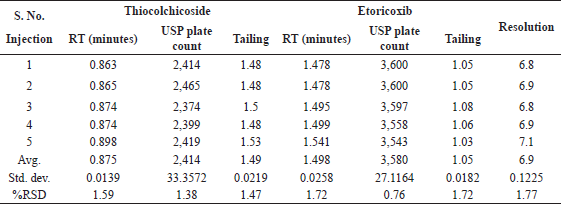 | Table 3. System suitability parameters. [Click here to view] |
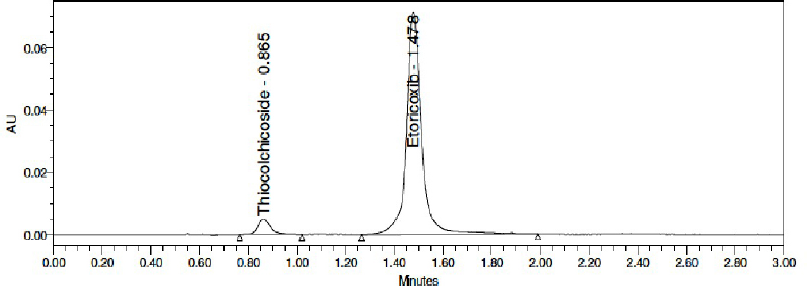 | Figure 5. Typical standard chromatogram. [Click here to view] |
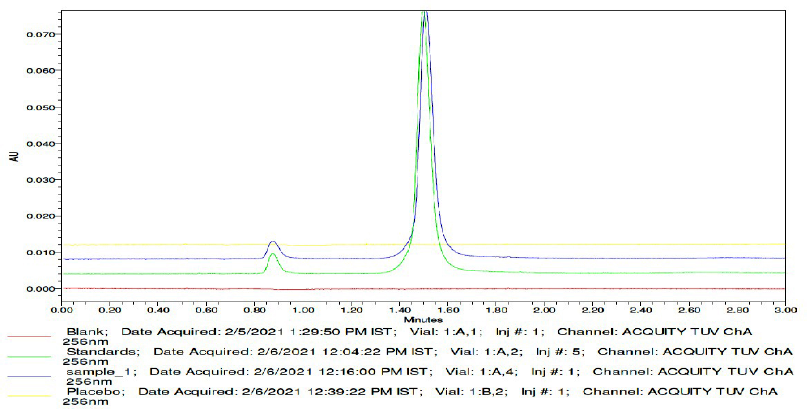 | Figure 6. Specificity—overlayed chromatogram of blank, placebo, standard, and sample. [Click here to view] |
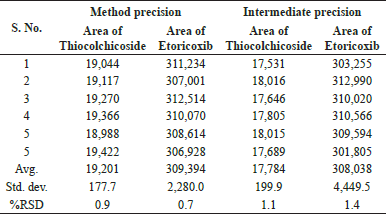 | Table 4. Data for method and intermediate precision. [Click here to view] |
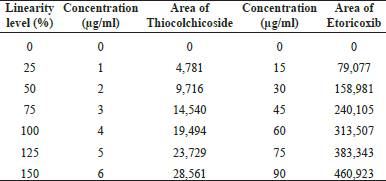 | Table 5. Linearity level, concentration, and area response. [Click here to view] |
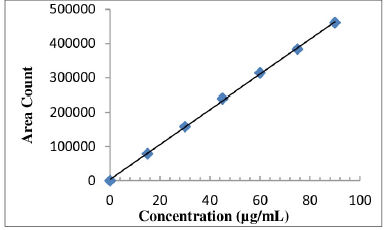 | Figure 7. Linearity plot of Etoricoxib. [Click here to view] |
Linearity and range
Linearity and range of the RP-UPLC assay method were demonstrated by the concentration versus peak area plots.
Linearity equations obtained for Thiocolchicoside: y = 4,762.8x + 114.71, and
Linearity equations obtained for Etoricoxib: y = 5,109.1x + 3,795.1
Correlation coefficient obtained was greater than 0.999 for both the drugs. This shows that the method is linear in the range of 25%–150%. Linearity level details are presented in Table 5. The linearity plot of Etoricoxib is shown in Figure 7 and that of Thiocolchicoside is shown in Figure 8.
Accuracy
Accuracy of the Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside RP-UPLC assay method was demonstrated with mean recovery observed to be 99.71% for Etoricoxib and 99.99% for Thiocolchicoside. The detailed percent recovery for Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside is presented in Table 6.
LOQ and LOD
LOD and LOQ were obtained by using regression analysis. The LOD values were observed to be at 0.64 and 0.04 μg/ml for Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside, respectively. Similarly, the LOQ values were observed to be 1.93 and 0.11 μg/ml for Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside, respectively.
Robustness
Robustness of the Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside RP-UPLC Assay method was demonstrated by deliberate changes in the method which could potentially occur in a laboratory environment. The system suitability parameters and amount of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside content were calculated and found comparable. The RSD was in the range of 0.7%–1.6% for Etoricoxib and 1.1%–1.9% for Thiocolchicoside which is well below 2% RSD. Details of the robustness data are presented in Table 7.
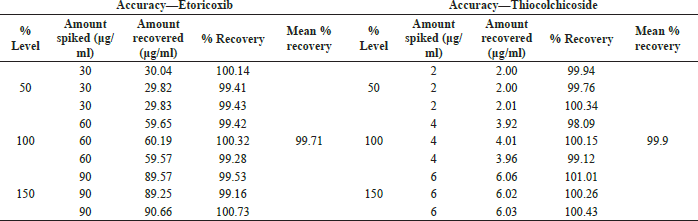 | Table 6. Accuracy % recovery of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside. [Click here to view] |
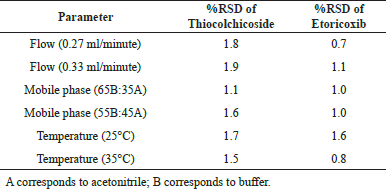 | Table 7. Robustness data for deliberate changes. [Click here to view] |
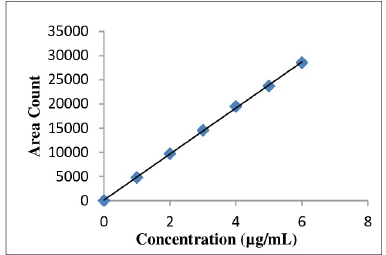 | Figure 8. Linearity plot of Thiocolchicoside. [Click here to view] |
Assay of Marketed Formulation
The assay of the marketed formulation of Etoricoxib (60 mg) and Thiocolchicoside (4 mg) tablets batch was carried out in line with the RP-UPLC assay method. Six sample sets were prepared and assayed. The assay results were observed to be 99.38% with RSD of 0.74% for Etoricoxib and 100.04% with RSD of 0.93% for Thiocolchicoside.
CONCLUSION
A sensitive, accurate, stability-indicating, and quick RP-UPLC method was developed and validated for the simultaneous estimation of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside in and Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside tablet formulation. The method demonstrated linearity in the range 25%–150% for both Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside with an R2 value greater than 0.999. Precision and accuracy were well within the 2% RSD. Both Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside were well separated and eluted well within 3 minutes, thus making this estimation quick and at the same time avoiding solvent wastage. Degradation studies reiterate that there is no interference from any of the potential impurities arising out of exposure to conditions as specified in the ICH Q2 R1; hence, the method can easily be applied to in-process, routine, and stability monitoring in the laboratory. In addition, the low levels of LOD and LOQ extend the possibility of using the same method for monitoring of cleaning residues after equipment cleaning in production shop floor.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories for providing gift samples of Etoricoxib, Thiocolchicoside active ingredient, and Etoricoxib (60 mg) and Thiocolchicoside (4 mg) tablets.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in the submission of this article.
FUNDING
There is no funding to report.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the international committee of medical journal editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
This study does not involve experiments on animals or human subjects.
DATA AVAILABILITY
The study data is available with authors.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
REFERENCES
Gulhane CA, Panchale WA, Manwar JV, Bakal RL. Liquid chromatographic method for simultaneous estimation of Thiocolchicoside and Etoricoxib from tablet formulation. Asian J Pharm Anal, 2021; 11(2):118–20. CrossRef
Palte D, Kondalkar A. Stability studies in combine dosage form of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside using RP-HPLC. Int J Res Stud Biosci, 2015; 3(9):163–70.
Sujit P, Nitin D. RP-HPLC method for estimation of Etoricoxib and Thiocolchicoside from tablet dosage form. World J Pharm Pharm Sci, 2016; 5(3):1499–505.