INTRODUCTION
Invasive aspergillosis (IA) is an opportunistic infectious disease that contributes to significant morbidity and mortality rates, especially in immunocompromised hosts [1,2]. Most IA infections are caused by the Aspergillus fumigatus (A. fumigatus) complex members [2]. The balance between exposure and host defense determines the tendency of Aspergillus to develop into IA. Prolonged neutropenia, hematology malignancy, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), solid organ transplantation, patients with a history of using immunosuppressive drugs including corticosteroid, critical illness, chronic lung disease, other pathogens, e.g., severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and Cytomegalovirus infection are risk factors for IA [2–6]. It is estimated that more than 85% of IA cases occur in patients with hematological malignancies and recipients of HSCT or organ transplantation [2]. According to 2017 global estimates, the annual incidence of IA is anticipated to be more than 300 thousand among 10 million people at risk [6,7].
The treatment modalities for IA include a variety of antifungal agents, such as spectrum azoles, polyenes, and echinocandins. For decades, polyene macrolides such as amphotericin B have been the standard therapy for IA, starting with conventional deoxycholates, which were later replaced by safer lipid formulations [8,9]. After its approval by the Food and Drug Administration in the 2000s, an extended-spectrum triazole voriconazole is recommended as IA therapy by The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) guidelines [7]. Later, other triazoles and echinocandins alone or in combination were used as treatment of IA, either as primary or salvage therapy [10,11].
Each reported drug has a specific action. Broad-spectrum triazoles disrupt ergosterol biosynthesis in fungal membranes, resulting in cell death. Voriconazole has a favorable response in more than 50% of the treatment of IA but has adverse effects, including hepatotoxicity, visual disturbances, and disruption of potassium channels of cardiac muscles, which cause prolongation of the QT interval. Several new generation triazoles, such as posaconazole and isavuconazole have been studied as alternatives to existing standard treatments, with a lower toxicity profile (4%–13%) compared to 22% in voriconazole [12,13]. Amphotericin B is a polyene that binds to ergosterol in the fungal membrane, causing perforations and cell death. It has shown a good correlation between in vitro susceptibility testing and positive clinical outcomes in patients with IA, though it has some adverse events in kidney function and gastrointestinal disorders [12]. Echinocandins inhibit the biosynthesis of β-(1,3)-d-glucan in the fungal cell wall, which causes structural abnormalities; thus, growth is inhibited, or cell death occurs due to osmotic pressure imbalance. However, echinocandins are difficult to absorb in the digestive tract, so they can only be given intravenously [14].
Small- to large-scale randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and cohort studies have been conducted to compare several drug classes and discover the best management strategy for IA. The presence of adverse effects, interactions between drugs, and the emergence of antifungal resistance also increase the need for better IA treatment options. This systematic review aims to evaluate studies regarding the comparative effectiveness of azoles, amphotericin B, and echinocandins in the treatment of IA as a primary treatment or salvage therapy, thus providing clinicians with insights to guide treatment decisions for this critical condition.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study protocol
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to compare the effectiveness of antifungal drugs in the class of azoles and echinocandins against existing guidelines for IA therapy. The IA diagnostic criteria used when reviewing the articles are from the consensus of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer and the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium published in 2002 [15], 2008 [16], and 2020 [17], depending on the year the article was issued. The protocol of this systematic review was conducted following the Preferred Reported Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines and checklists for selection studies [18]. This systematic review is registered with PROSPERO (CRD420251004440).
Eligibility criteria
We have enrolled RCT and cohort studies with defined Population, Intervention, Comparison, and Outcome (PICO) criteria in which patients were treated for IA. We reported mortality or survival, or response rates to evaluate interventions including new generation triazoles (posaconazole or isavuconazole) and echinocandins either as monotherapy or in combination, and the control group was voriconazole or amphotericin B as monotherapy. The detail of PICO is mentioned in Supplementary Table 1.
Search strategy and study selection
A comprehensive electronic search was conducted using three databases from PubMed, Scopus, and ProQuest, according to predetermined eligibility criteria with a publication year limit of over 2000. We identified relevant keywords and synonyms based on the determined PICO to maximize the retrieval of appropriate studies from each database. The details of the search strategy used in this study are shown in Supplementary Table 2. We excluded case reports, comments, consensus/guidelines, review articles, and animal studies. The Mendeley Reference Manager v2.129.0 (Elsevier) program was used to manage study results obtained based on PICO searches in all databases. At the initial selection stage, the program removed various study titles identified as duplicates for subsequent screening. In the first phase, two independent reviewers (M.V. and M.G.A.K.) screened articles based on titles and abstracts regarding inclusion and exclusion criteria. In the second phase, the selected articles were screened in full text by two investigators (M.W and R.K) and then excluded if they were not available in a full-text English version and were not comparative studies. We also conducted a review based on research references that met the criteria to ascertain whether other studies were potentially eligible. Any discrepancies found were determined by a third investigator (D.E). All studies excluded in phases 1 and 2 were recorded along with the reasons.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two evaluators (M.W and R.K) extracted data from each article in the study for qualitative synthesis and put it into a spreadsheet data. Extracted data includes the first author’s name, year of publication, study type, setting, total sample size, sample basic demographic characteristics, underlying condition, indication for treatment (whether primary or salvage), IA definition guidelines used, duration of follow-up, drugs comparison with their doses, mortality rate, and response rate. Any disputes that arise in the extracted variable data are resolved through discussion to reach an agreement. Two individual reviewers (M.W and R.K) conducted an independent risk of bias assessment using the Cochrane methods tools: Risk of Bias 2.0 (RoB 2) tool for RCT [19] and Risk of Bias in Non-randomized Studies - of Interventions (ROBINS-I) V2 tool for non-RCT/cohort studies [20]. No studies were excluded based on the risk of bias results.
Data analysis
We conducted a meta-analysis of all extracted data and disaggregated them based on therapeutic indications, either primary or salvage. The odds ratio (OR) of mortality rate and response rate with 95% CI was analyzed by comparing voriconazole, posaconazole, amphotericin B, and echinocandins with their controls. Meta-analyses were performed using Mantel-Haenszel analysis to limit the bias caused by drastically different group sizes between studies. These results are visualized in the form of a forest plot. Data analyses were performed using RevMan for Windows (v.5.4, Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Center, The Cochrane Collaboration). Heterogeneity between studies was evaluated quantitatively using the I2 estimate statistic, and an I2 estimate ≥50% was considered significant heterogeneity.
RESULTS
A search strategy based on appropriate keywords from three databases produced 264 hits. After removing duplicates, 246 studies remained in which titles and abstracts were screened. In total, 43 studies met the requirements for full-text relevance checking. In the end, 10 studies will be analyzed further in qualitative synthesis and quantitative meta-analysis (Fig. 1).
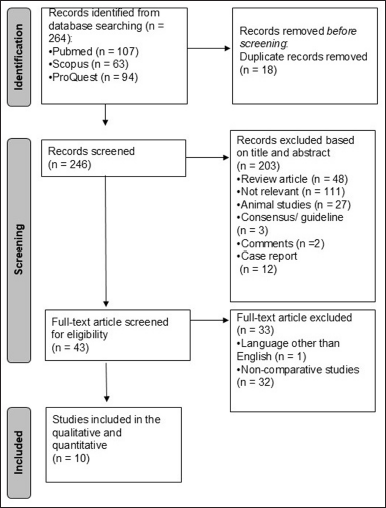 | Figure 1. PRISMA flow diagram for the study selection process. [Click here to view] |
Characteristic findings of the 10 included studies are summarized in Table 1. Following a full-text review, six RCTs, one non-RCT, two prospective cohort studies, and one retrospective cohort study were included, with a total of 2,162 patients between 1997 and 2019. Of these, 1,677 patients were assessed for their responses and survival after triazoles, echinocandins, or amphotericin B treatment. The majority of patients received voriconazole, followed by posaconazole and amphotericin B. Six studies assessed antifungal as primary treatment, and four studies as salvage treatment. The age range of the studies reviewed was 12–83 years, with predominantly male patients at 60.1%. The most common underlying conditions for IA in the study population were allogeneic HCT, acute leukemia, and neutropenia.
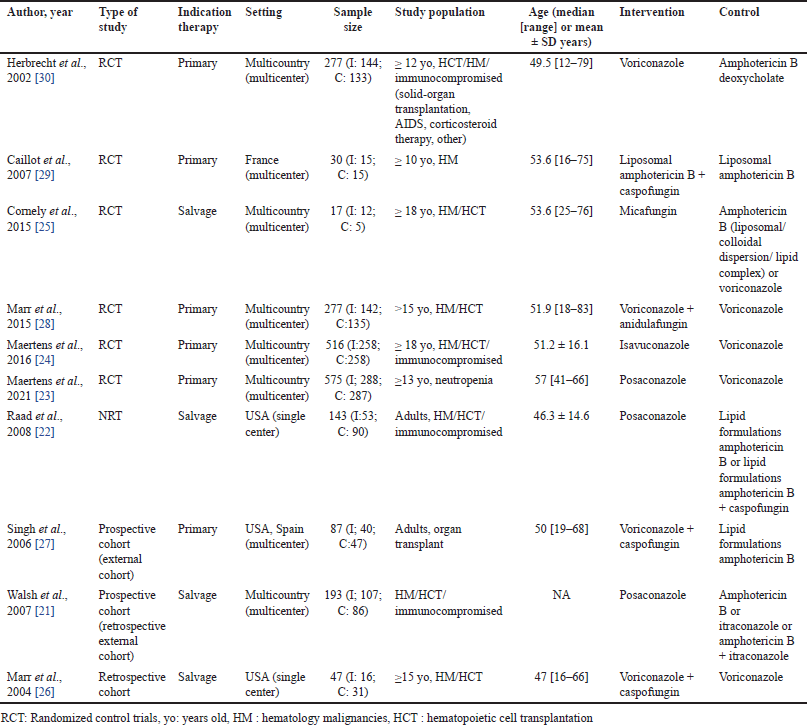 | Table 1. Summary characteristic of included studies for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis. [Click here to view] |
The comparative studies were divided into patients who had new triazoles group with posaconazole [21–23] or isavuconazole [24], echinocandin monotherapy [25], and echinocandin combinations group [22,26–29]. Subsequent analyses of each control antifungal further divide the comparative studies into the voriconazole group [23,24,26,28,30] and the amphotericin B group [21,22,27,29,30]. The regimens and delivery methods of each drug are mentioned in the supplementary files.
Quality assessment of included RCT studies with RoB 2 showed overall good results. However, one study [25] has a high risk of bias due to open-label, premature discontinuation leading to fewer participants and less rigorous statistical analysis; the reason for the discontinuation of participants was not explained. Another study [30] showed some concern about bias due to some patients not receiving any treatment without explanation and a lack of confirmation from radiologists on the data review committee to measure the outcomes. Overall, bias for non-RCT studies showed a moderate risk due to confounding factors, and one study showed a serious risk. The summary results of the quality assessment of included RCT studies can be found in Figure 2A, and non-RCT studies in Figure 2B.
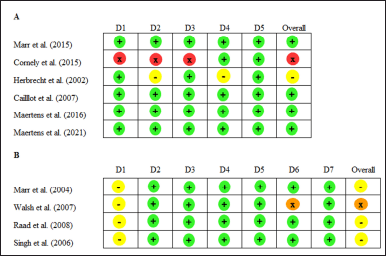 | Figure 2. Risk of bias assessment for the included studies. Risk of Bias 2.0 (RoB 2) for RCT (A) and ROBINS-I V2 for non-RCT/cohort studies (B). Notes: Domains for RoB2: D1: Bias arising from the randomization process D2: Bias due to deviations from intended intervention D3: Bias due to missing outcome data D4: Bias in measurement of the outcome D5: Bias in selection of the reporting results (+ = low risk; − = some concerns; x = high risk). Domain for ROBINS-I: D1: Bias arising from bias due to confounding D2: Bias due to selection of participants into the study D3: Bias due to classification of interventions D4: Bias due to deviations from the intended intervention D5: Bias due to missing data D6: Bias in measurement of outcomes D7: Bias in selection of the reported results (+ = low risk; − = moderate risk; x = serious risk; ! = critical risk). [Click here to view] |
The results of favorable response and survival rate were categorized by the use of new triazoles and echinocandins as primary or salvage treatment (Fig. 3). Based on the overall OR comparison for the favorable response primary treatment, both new triazoles and echinocandins do not pose superiority against control variables. New triazoles exhibit a better chance of favorable response as primary treatment with OR 0.95 (95% CI: 0.69–1.32, p = 0.780) and salvage treatment with OR 2.31 (95% CI: 1.33–4.01, p = 0.003). Echinocandins or their combinations did not show the superiority of their responses against control in both primary and salvage treatment with OR 0.89 (95% CI: 0.60–9.62, p = 0.560). These findings are confirmed by separate analyses of the control variables in the supplementary files.
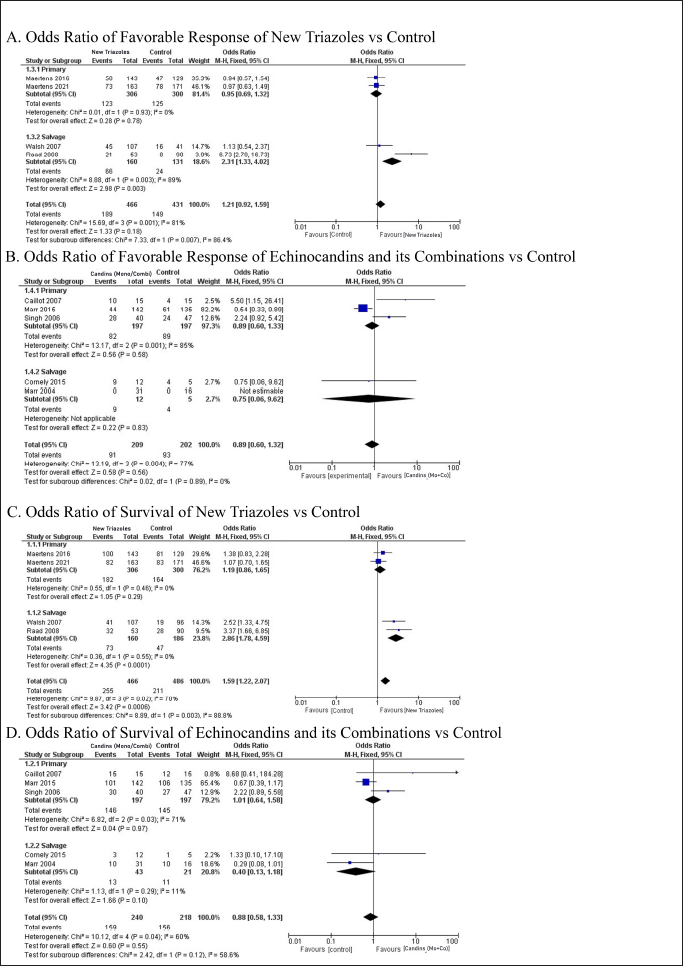 | Figure 3. Forest plots displaying the ORs for favorable response (A and B) and survival (C and D) in patients treated with new triazoles and echinocandins compared to control groups. Heterogeneity analyses show that the studies involved have high heterogeneity. [Click here to view] |
New triazoles showed a superior chance of survival after 6–12 weeks of treatment, better than control of voriconazole and amphotericin B in primary and salvage treatment, with overall OR 1.59 (95% CI: 1.22–2.07, p < 0.001). On the other hand, echinocandins did not exhibit any superiority against control variables in primary and salvage treatment, with an overall OR analysis of 0.88 (95% CI: 0.58–1.33, p =0.550). The separate analyses of control variables confirmed the findings, as shown in the supplementary files.
All analyses show that I2 is above 40% for the analyses of responses and survival, indicating the high heterogeneity of the studies involved. The funnel plot analysis (Fig. 4) indicates asymmetry within the plots. The asymmetry suggests heterogeneity of the sample sizes among the studies, meaning that studies with negative or non-significant findings might be underrepresented.
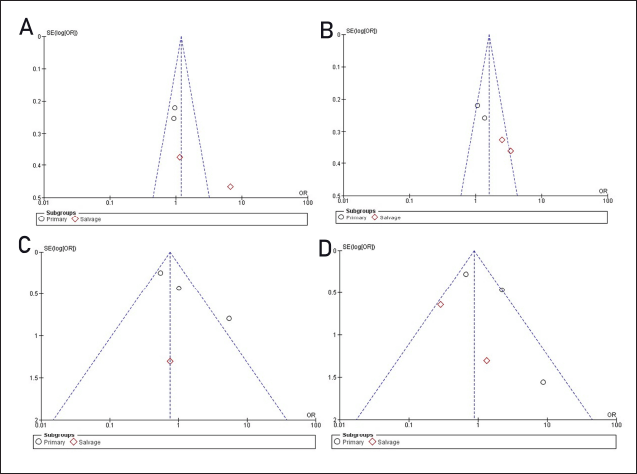 | Figure 4. Funnel plots. Panels A and B correspond to favorable response and survival with new triazoles, while panels C and D represent favorable response and survival for echinocandins and their combinations. Asymmetry suggests potential publication bias or heterogeneity among studies. [Click here to view] |
DISCUSSION
IA is a serious infection caused by Aspergillus spp. with a high mortality rate, particularly in individuals with compromised immune systems. Underlying immunocompromising conditions that are often found based on this qualitative analysis are those suffering from blood malignancies, such as acute leukemia, patients undergoing HSCT, and neutropenia [31–34]. Patients undergoing HSCT are at high risk due to the use of immunosuppressive drugs that decrease their immune response [31]. Patients with hematological malignancies and chemotherapy frequently have prolonged neutropenia (<500 cells/μl for >20 days), which makes them very susceptible to this infection [32]. From the studies we systematically reviewed, males dominate more than females; this follows global data; one of the predictors is male sex [35]. The average age of those experiencing IA is mainly in their 50s, consistent with the results of a meta-analysis study by Shekhova et al. [36].
In IA therapy, an appropriate selection of antifungal drugs is necessary to determine the success of both primary and salvage treatment. In principle, primary therapy is the administration of the first antifungal drug when the patient is diagnosed with IA. Salvage therapy is the administration of an alternative antifungal used after the failure of the first therapy [37,38]. Analyses of these studies suggest voriconazole is still superior for the primary treatment of IA as recommended by guidelines from the IDSA [39] and Douglas et al. [40], although the favorable response is statistically insignificant. Otherwise, new triazole, especially posaconazole, is significantly superior in salvage treatment. These findings support its inclusion in antifungal treatment guidelines for first-line salvage therapy if not used in primary therapy. A study in Germany [41] has also demonstrated posaconazole’s superior efficacy in salvage therapy, aligning with this review’s findings. The study found that posaconazole salvage therapy was effective in 72.2% of IA cases after failed voriconazole treatment. Posaconazole improved the response and, subsequently, the survival rate. Meanwhile, isavuconazole is in second place after posaconazole as a salvage therapy option. However, some studies found that isavuconazole showed fewer adverse events than posaconzole and voriconazole, such as hepatobiliary dysfunction and prolonged QT interval [42,43].
Amphotericin B also showed good efficacy in primary or salvage treatment, although lower than the new triazole group in this analytical review. Most included studies used amphotericin B in a lipid formulation rather than the classic deoxycholate. Amphotericin B is currently available as lipid formulations consisting of lipid complex and liposomal amphotericin B. Amphotericin B colloidal dispersion has been discontinued since 2011 due to the high rate of infusion-related incidents. The toxic effects of these polyene drugs, such as infusion-related reactions and decreased kidney function with the parameter of increased serum creatinine, are less in lipid formulations than in deoxycholate [44,45]. Despite these adverse events, several studies recommend the administration of high-dose liposomal amphotericin B because it is well tolerated and shows benefits as an alternative or concomitant therapy as needed in cases of difficult-to-treat fungal infections, with clinicians closely monitoring renal function and electrolyte changes [46–48].
The most widely used echinocandin antifungal drug class in this analysis is caspofungin, followed by anidulafungin and micafungin. The use of caspofungin is mostly in combination with voriconazole or amphotericin B lipid formulation. Echinocandins did not demonstrate superiority over control variables in primary or salvage treatment, except for one study by Caillot et al. [29], suggesting their use should be considered case-by-case, like treatment of suspected or documented azole-resistant Aspergillus. The non-superiority of echinocandins in the treatment of IA may be due to various in vitro and in vivo study results, which show that these antifungals only act as fungistatic against Aspergillus spp. and do not have a fungicidal effect [49]. There is one newest study from Lamberink et al. [50] that investigated anidulafungin in combination with an azole, but it was not included in the analysis because the azole as a combination with and as a comparator did not mention the name of the drug. A higher response rate and better survival are the clinical outcomes that would be anticipated if antifungal combination treatment (ACT) truly offered an additional advantage. Unfortunately, few human observational studies and small-scale clinical trials have been published to support this practice. It also should be noted that ACT may result in increased toxicity and substantial cost increases, and assessment of its efficacy in clinical practice is somewhat difficult due to the many potential confounding factors [49,51].
Our study has several limitations. First, the number of studies that fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria is highly variable in sample size. The heterogeneity of the sample sizes among the studies means that studies with negative or non-significant findings might be underrepresented. Another important source of heterogeneity in this meta-analysis is the wide variation in sample sizes across included studies. Smaller studies may be more prone to exaggerated effect estimates due to random error, while larger studies typically yield more stable results. When combined, these discrepancies can introduce statistical heterogeneity and skew the pooled effect size., but not responses. This leads to a lack of analyses for the response rate for that intervention group. Third, this study combines the analyses of various amphotericin B preparations, which might underrepresent the differences of action for each preparation. Fourth, specific comorbidities and immunosuppressive regiments are not included in the sub-analyses. This study only analyses the superiority of each regiment based on the outcomes of each study. The contribution of comorbidities and other medications might lead to decision bias due to the variabilities of the outcome measurement. Finally, the dose and duration of each treatment are limited to the recapitulation written in the studies. Comorbidities, antifungal resistance, and treatment regimens data are inconsistent and incompletely reported across studies. Although some variation existed even among studies using the same antifungal agents, our analysis focused on drug class comparisons to maintain consistency and interpretability within the constraints of the available data. The overall treatment course cannot be defined from this study. Hence, the findings in this study should be interpreted with caution when selecting a regimen for the first line, given the limitations of this review.
CONCLUSION
This review suggests that new triazoles (especially posaconazole) perform better in salvage treatment than primary treatment. Posaconazole salvage treatment exhibits superior efficacy and survival benefits over voriconazole and amphotericin B. Echinocandins do not show superiority over other antifungal treatments. In the control group, voriconazole performed better in primary treatment, and amphotericin B remains a strong option for salvage therapy. Further prospective randomized trials are necessary to validate these findings in diverse clinical environments.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
There is no funding to report.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors report no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
Not applicable.
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated and analyzed are included in this research article.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used artificial intelligence (AI)-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
REFERENCES
1. Zaragoza R, Sole-Violan J, Cusack R, Rodriguez A, Reyes LF, Martin-Loeches I. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: not only a disease affecting immunosuppressed patients. Diagnostics. 2023;13(3):440. CrossRef
2. Ledoux MP, Herbrecht R. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. J Fungi (Basel). 2023;9(2):131. CrossRef
3. Song L, Qiu L, Wang G, Zou W, Zhang S, Sai L. Investigation of risk factors for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis among patients with COVID-19. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):1–8. CrossRef
4. Kuo CW, Wang SY, Tsai HP, Su PL, Cia CT, Lai CH, et al. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis is associated with cytomegalovirus viremia in critically ill patients - A retrospective cohort study. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2022;55(2):291–9. CrossRef
5. Marr KA, Carter RA, Boeckh M, Martin P, Corey L. Invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: changes in epidemiology and risk factors. Blood. 2002;100(13):4358–66. CrossRef
6. Firacative C. Invasive fungal disease in humans: are we aware of the real impact? Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2020;115(9):e200430. CrossRef
7. Bongomin F, Gago S, Oladele RO, Denning DW. Global and multi-national prevalence of fungal diseases—estimate precision. J Fungi (Basel). 2017;3(4):57. CrossRef
8. Chandrasekar P. Riches usher dilemmas: antifungal therapy in invasive aspergillosis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005;11(2):77–84. CrossRef
9. Cavassin FB, Baú-Carneiro JL, Vilas-Boas RR, Queiroz-Telles F. Sixty years of amphotericin B: an overview of the main antifungal agent used to treat invasive fungal infections. Infect Dis Ther. 2021;10(1):115–47. CrossRef
10. Boyer J, Feys S, Zsifkovits I, Hoenigl M, Egger M. Treatment of invasive aspergillosis: how it’s going, where it’s heading. Mycopathologia. 2023;188(5):667–81. CrossRef
11. Aruanno M, Glampedakis E, Lamoth F. Echinocandins for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis: from laboratory to bedside. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63(8):e00399–19. CrossRef
12. Jenks JD, Hoenigl M. Treatment of aspergillosis. J Fungi (Basel). 2018;4(3):98. CrossRef
13. Cheng MP, Orejas JL, Arbona-Haddad E, Bold TD, Solomon IH, Chen K, et al. Use of triazoles for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis: a three-year cohort analysis. Mycoses. 2020;63(1):58–64. CrossRef
14. Szymanski M, Chmielewska S, Czyzewska U, Malinowska M, Tylicki A. Echinocandins – structure, mechanism of action and use in antifungal therapy. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022;37(1):876. CrossRef
15. Ascioglu S, Rex JH, De Pauw B, Bennett JE, Bille J, Crokaert F, et al. Defining opportunistic invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients with cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplants: an international consensus. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34(1):7–14. CrossRef
16. De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, et al. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European organization for research and treatment of cancer/invasive fungal infections cooperative group and the national institute of allergy and infectious diseases mycoses study group (EORTC/MSG) consensus group. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46(12):1813. CrossRef
17. Donnelly JP, Chen SC, Kauffman CA, Steinbach WJ, Baddley JW, Verweij PE, et al. Revision and update of the consensus definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer and the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(6):1367–76. CrossRef
18. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71. CrossRef
19. Sterne JAC, Savovic J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2019;366:l4898. CrossRef
20. Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savovic J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. 2016;355:i4919. CrossRef
21. Walsh TJ, Raad I, Patterson TF, Chandrasekar P, Donowitz GR, Graybill R, et al. Treatment of invasive aspergillosis with posaconazole in patients who are refractory to or intolerant of conventional therapy: an externally controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44(1):2–12. CrossRef
22. Raad II, Hanna HA, Boktour M, Jiang Y, Torres HA, Afif C, et al. Novel antifungal agents as salvage therapy for invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies: posaconazole compared with high-dose lipid formulations of amphotericin B alone or in combination with caspofungin. Leukemia. 2008;22(3):496–503. CrossRef
23. Maertens JA, Rahav G, Lee DG, Ponce-de-León A, Ramírez Sánchez IC, Klimko N, et al. Posaconazole versus voriconazole for primary treatment of invasive aspergillosis: a phase 3, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2021;397(10273):499–509. CrossRef
24. Maertens JA, Raad II, Marr KA, Patterson TF, Kontoyiannis DP, Cornely OA, et al. Isavuconazole versus voriconazole for primary treatment of invasive mould disease caused by Aspergillus and other filamentous fungi (SECURE): a phase 3, randomised-controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2016;387(10020):760–9. CrossRef
25. Cornely OA, Meems L, Herbrecht R, Viscoli C, van Amsterdam RGM, Ruhnke M. Randomised, multicentre trial of micafungin vs. an institutional standard regimen for salvage treatment of invasive aspergillosis. Mycoses. 2015;58(1):58–64. CrossRef
26. Marr KA, Boeckh M, Carter RA, Hyung WK, Corey L. Combination antifungal therapy for invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39(6):797–802. CrossRef
27. Singh N, Limaye AP, Forrest G, Safdar N, Muñoz P, Pursell K, et al. Combination of voriconazole and caspofungin as primary therapy for invasive aspergillosis in solid organ transplant recipients: a prospective, multicenter, observational study. Transplantation. 2006;81(3):320–6. CrossRef
28. Marr KA, Schlamm HT, Herbrecht R, Rottinghaus ST, Bow EJ, Cornely OA, et al. Combination antifungal therapy for invasive aspergillosis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162(2):81–9. CrossRef
29. Caillot D, Thiébaut A, Herbrecht R, De Botton S, Pigneux A, Bernard F, et al. Liposomal amphotericin B in combination with caspofungin for invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies: a randomized pilot study (Combistrat trial). Cancer. 2007;110(12):2740–6. CrossRef
30. Herbrecht R, Denning DW, Patterson TF, Bennett JE, Greene RE, Oestmann J-W, et al. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(6):408–15. CrossRef
31. Rogacheva YA, Markelov VV, Popova MO, Volkova AG, Nikolaev IY, Pinegina ON, et al. Invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients: a large cohort single-center study. Blood. 2021;138(Supplement 1):1801. CrossRef
32. Reichenberger F, Habicht JM, Gratwohl A, Tamm M. Diagnosis and treatment of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in neutropenic patients. Eur Respir J. 2001;19(4):743–55. CrossRef
33. Stafylidis C, Diamantopoulos P, Athanasoula E, Solomou E, Anastasopoulou A. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia and invasive mold infections: a challenging field. J Fungi (Basel). 2022;8(11):1127. CrossRef
34. Colombo AL, Bergamasco MD, Nouér SA, Oliveira e Castro P de T, Pasqualotto AC, de Queiroz-Telles F, et al. Invasive aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia: comparison between acute myeloid and acute lymphoid leukemia. Mycopathologia. 2022;188(1–2):1–8. CrossRef
35. Egger M, Hoenigl M, Thompson GR, Carvalho A, Jenks JD. Let’s talk about sex characteristics—As a risk factor for invasive fungal diseases. Mycoses. 2022;65(6):599–612. CrossRef
36. Shekhova E, Salazar F, Da Silva Dantas A, Chakraborty T, Wooding EL, White PL, et al. Age difference of patients with and without invasive aspergillosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis. 2024;24(1):220. CrossRef
37. Lee SO. Diagnosis and treatment of invasive mold diseases. Infect Chemother. 2023;55(1):10–21. CrossRef
38. Douglas AP, Smibert OC, Bajel A, Halliday CL, Lavee O, McMullan B, et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of invasive aspergillosis, 2021. Intern Med J. 2021;51(S7):143–76. CrossRef
39. Patterson TF, Thompson GR, Denning DW, Fishman JA, Hadley S, Herbrecht R, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aspergillosis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63(4):e1–60. CrossRef
40. Douglas AP, Smibert OC, Bajel A, Halliday CL, Lavee O, McMullan B, et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of invasive aspergillosis, 2021. Intern Med J. 2021;51(S7):143–76. CrossRef
41. Heinz WJ, Egerer G, Lellek H, Boehme A, Greiner J. Posaconazole after previous antifungal therapy with voriconazole for therapy of invasive aspergillus disease, a retrospective analysis. Mycoses. 2013;56(3):304–10. CrossRef
42. Van Matre ET, Evans SL, Mueller SW, MacLaren R, Fish DN, Kiser TH. Comparative evaluation of isavuconazonium sulfate, voriconazole, and posaconazole for the management of invasive fungal infections in an academic medical center. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2019;18(1):13. CrossRef
43. Batista MV, Ussetti MP, Jiang Y, Neofytos D, Cortez AC, Feriani D, et al. Comparing the real-world use of isavuconazole to other anti-fungal therapy for invasive fungal infections in patients with and without underlying disparities: a multi-center retrospective study. J Fungi (Basel). 2023;9(2):166. CrossRef
44. Cavassin FB, Baú-Carneiro JL, Vilas-Boas RR, Queiroz-Telles F. Sixty years of amphotericin b: an overview of the main antifungal agent used to treat invasive fungal infections. Infect Dis Ther. 10(1):115–47. CrossRef
45. Aguirre B, Restrepo JP, Am H, Aguirrejp B, Restrepo H. Amphotericin B deoxycholate versus liposomal amphotericin B: effects on kidney function. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;2015(11):CD010481. CrossRef
46. Martín MT, Gavaldà J, López P, Gomis X, Ramírez JL, Rodríguez D, et al. Efficacy of high doses of liposomal amphotericin B in the treatment of experimental aspergillosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003;52(6):1032–4. CrossRef
47. Alabdullah MN, Yousfan A. Is low dose of liposomal amphotericin B effective in management of acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis? Our conclusions from Al-Mowassat University Hospital, Syria: a prospective observational study. BMC Infect Dis. 2023;23(1):1–14. CrossRef
48. Stover KR, Jordan TE, Wagner JL, Barber KE. High-dose amphotericin: yay or nay? A case series and literature review. Drugs Context. 2024;13:2023-9-1. CrossRef
49. Aruanno M, Glampedakis E, Lamoth F. Echinocandins for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis: from laboratory to bedside. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63(8):e00399–19. CrossRef
50. Lamberink H, Huygens S, Aerts R, Lagrou K, Van Leeuwen-Segarceanu E, Lodewyck T, et al. Superiority trials in invasive aspergillosis: a harsh reality check with the ia-duet (HOVON502) trial. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2025;80(2):367–70. CrossRef
51. Jacobs SE, Chaturvedi V. CAF to the rescue! potential and challenges of combination antifungal therapy for reducing morbidity and mortality in hospitalized patients with serious fungal infections. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024;11(11):ofae646. CrossRef
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
The supplementary material can be accessed at the link here: [https://japsonline.com/admin/php/uploadss/4607_pdf.pdf]