INTRODUCTION
Microfluidics is one such field that has seen tremendous growth in the past decade and has revolutionized various aspects of the pharmaceutical industry, including drug discovery, development, and analysis. This notable advancement is due to the development and exploration of technologies that help to analyze, manipulate, and move small quantities of fluid [1]. Microfluidics considerably newer branch of science and technology that involves systems that use channels with sizes ranging from tens to a few hundreds of micrometers to process small (10-9 to 10-18 l) volumes of fluid [2]. In other words, microfluidics involves the strategic manipulation of fluids in a small-scale system that is competent in dealing with the organic/biological environment at the microscale and throws light on a variety of cellular processes. This technology is used in various fields of the pharmaceutical industry, for instance, and has transformed how biologists examine cells and tissues by allowing them to conduct extremely precise experiments and evaluate biological samples with unmatched precision [3]. Microfluidics has transformed the way chemists synthesize and study molecules by enabling the execution of complex chemical reactions in a small, portable device. In the field of environmental monitoring, where it is being used to evaluate water, air, and soil samples with great precision and accuracy, microfluidics has also created new opportunities [4]. Microfluidics has transformed the way scientists investigate the behavior of fluids in the discipline of physics by enabling them to conduct experiments on small-scale systems that are not practical in bigger ones [1, 5]. Among many applications, lab-on-chip (LOC), which is also referred to as the “micro-total analysis systems” (TAS) system, is the most prominent use of microfluidics technology [6]. The LOC technology has seen a dramatic development after the introduction of micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) in the early 1990s owing to its huge potential in various fields, including diagnostic, point-of-care testing, medical, and a spectrum of other healthcare applications [7]. The primary goal of LOC technology at its inception was the downsizing of laboratory processes for handling fluids (gases and liquids). A collection of microfluidic devices, each with a specific purpose, such as controlling flow, mixing fluids, preparing samples, and detecting them on a tiny, miniaturized chip, make up an integrated LOC device. Due to its versatility, controllability, and scalability, LOC technology has attracted a lot of interest from the scientific fraternity [8]. Additionally, it could be effectively applied to the development of straightforward diagnostic systems and personalized medical care [9, 10]. Our review mainly emphasizes on integration of operational parameter optimization using advanced design of experiment (DoE) approaches, as well as in-depth analytical performance evaluation specific to API detection. Additionally, while earlier literature primarily discusses fabrication techniques and basic applications, this review fills the gap by critically analyzing the interplay of device design, reaction conditions, and quantitative performance metrics, such as sensitivity, precision, and validation against standard methods. This comprehensive approach offers new insights and practical guidelines for optimizing paper-based microfluidic analytical devices, thereby advancing the field toward more reliable and efficient point-of-care applications.
DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF MICROFLUIDIC SYSTEMS
The microfluidic system is inclusive of a wide array of devices that range from the simplest microneedles (MNs) used for drug delivery purposes to the complex organ-on-chip (OOC) or LOC. The design, components, and technology used for fabrication vary based on the complexity of the system. In the preparation of simple microfluidics, just polymers along with drugs are sufficient to serve the purpose. For advanced systems, the number of components and critical parameters increases with an increase in the complexity of the device. While designing advanced systems, the mixing of the fluids inside the device is one important parameter that requires a lot of attention. In the case of several physical properties, such as heat and mass fluxes, as well as other chemical processes, the mixing phase is crucial [11]. The goal of mixing in microfluidics is to efficiently and quickly combine different samples at a very low volume (micro- or pico) scale to provide the largest possible interfacial area along with using the least amount of energy possible [12]. The overall efficiency of the mixing process can be enhanced by including baffles within microchannels carrying the fluid. In contrast to the inertial forces, viscous forces are more dominant in the capillary microenvironment. There are two major types of mixing processes, namely active and passive. Active mixing involves the use of an external agent such as temperature or magnetic field causing a disturbance in the flow of fluid resulting in efficient mixing [13]. Even though active mixing results in good mixing, it cannot be used always, especially while dealing with biological samples due to the stability problems arising from magnetic or electrical interventions [14].
In contrast to this, passive mixing uses the energy of the fluid flow to power the mixing process, which depends on the geometry of the microfluidic device along with other physicochemical aspects of fluid flow. As the sample passes along the microfluidic chip, the time and area with which the fluid is in contact are specifically specified within the microchannel designs. Given that it increases the diffusion of the samples, passive mixing is regarded as an effective strategy for sample mixing [15]. There are two major types of flow designs one of which is T-junction channels and another Y-junction channels. Both have two different flow channels having fluids with/without solutes finally intersect at a point. The major difference between the two designs is that in the Y-junction channel, the two fluid channels intersect each other at an angle resulting in a sigmoid diffusion profile. Among the two designs, the T-junction design has been studied extensively. However, both the designs include following components (except in the case of microfluidics used in drug delivery). The general components of a microfluidic system are given in Figure 1.
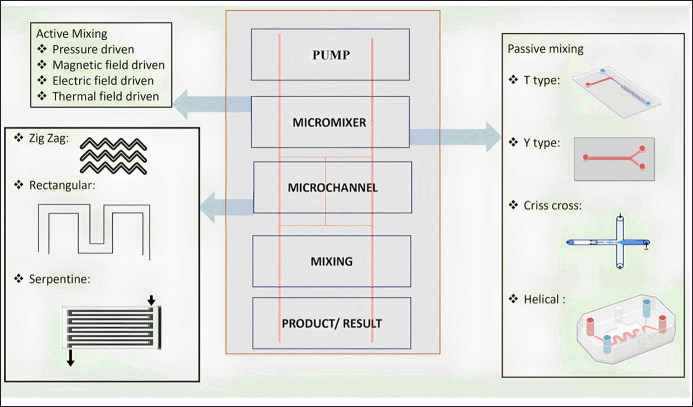 | Figure 1. General components of a microfluidic system [Click here to view] |
MICROFLUIDICS IN DRUG DISCOVERY AND SCREENING
Microfluidics has emerged as a breakthrough technique in drug discovery, modifying how researchers conduct tests and speeding up the drug development process. Microfluidic devices provide unparalleled control over experimental settings by manipulating small quantities of fluids within microscale channels and chambers, enabling high-throughput screening (HTS), precision dosing, and the production of physiologically realistic microenvironments for cells and tissues. This provides more precise and effective frameworks for different phases of the drug development pipeline, which have considerably aided drug discovery activities [16]. Microfluidics in HTS represents one of its most important contributions to drug development. Traditional drug screening methods are frequently time-consuming and arduous, whereas microfluidic devices can test numerous substances or conditions in tandem, substantially lowering experimental time and resource usage. This quick screening capability expedites the discovery of promising hit molecules and the initial phases of drug development [17].
Microfluidics in drug delivery
Ideal therapy involves delivering the right dose of the drug at the correct site (target) at the correct time. Advances in microfluidic technology have enabled considerably increasing bioavailability as well as bioaccessibility along with reducing the side effects [18]. Using microfluidics, it is possible to develop a system with a high state of control and reproducibility. This technology is especially leveraged in the delivery of nanoparticles [19]. It allows accurate liquid management and rapid fluid movement in micrometer-scale channels. Microfluidic devices are employed for direct delivery of biologically active compounds in addition to the ability to create sophisticated drug carriers [20]. In this review, we have tried to explore two major applications of microfluidics in drug delivery.
Drug carriers
Preparation for drug carriers
The ideal goal of incorporating drug carriers in therapy is to have greater control over the release rate and site and also to deliver the active ingredient at the desired site thereby reducing the side effects and improving the overall efficacy of therapy [21]. In this regard, nanodrug carriers have gained attention of the scientists in this field. However, precise fabrication of such nanoparticles is a herculean task. This has resulted in researchers using microfluidic technology for the fabrication of nanocarriers from lipids, polymers, and inorganic materials [22]. Lipid-based nanoparticles have a structure that resembles that of a cell membrane and have been widely used in DDSs thereby having an array of advantages including biocompatibility, penetrating ability, simplicity of superficial modification, and considerably superior drug-loading capacity. The effectiveness of drug distribution and therapeutic efficacy is significantly influenced by the size of lipid-based nanoparticles. Conventional investigations, however, are hampered by the challenging procedures involved in creating liposomes because multiple steps after processing are necessary to keep liposomes homogeneous. To overcome these drawbacks, microfluidic platforms have drawn a lot of attention [23, 24]. Microfluidic reactors as the name itself suggests are small in size; this, however, has restrictions that have limited its industrial utilization. These drawbacks include poor manufacturing rates, condensed equipment life, and high costs. Larger-scale reactions were required to overcome these obstacles. Formulation of nanoparticles using microfluidics technology is given in Figure 2.
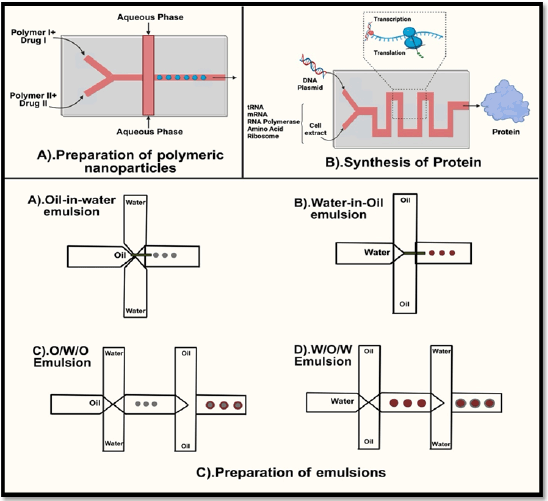 | Figure 2. Formulation of nanoparticles using microfluidics technology. [Click here to view] |
A drug delivery device
The advent of microfluidic technology and different fabrication techniques have resulted in several drug delivery opportunities. Among all the available options, MNs top the hierarchy. Therefore, in this review, more focus is given to MNs as a drug delivery device [25]. MNs as the name itself signifies MNs involve micronized needles which are used especially for drug delivery purposes. In recent times, MNs have been combined with microfluidic devices for both drug delivery and analytical purposes [26, 27]. There are different types of MNs which are given in the following.
Microneedles
Solid MNs: The use of solid MNs for pore-creating skin preparation was originally described in 1971. A sharp needle punctures the skin to administer medication through tiny channels that are then taken up by capillaries [26]. Easy medication loading and delivery mechanisms can be delivered by integrating solid MNs in microfluidic channels. These manufactured advanced devices have shown their utility as delivery vehicles using a variety of material chips and MNs consisting of silicon, tungsten, SU-8, and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) [28, 29]. Coated MNs: As the name itself signifies these MNs include a drug coated over the miniature needles [30]. Different MNs used in drug delivery are given in Table 1.
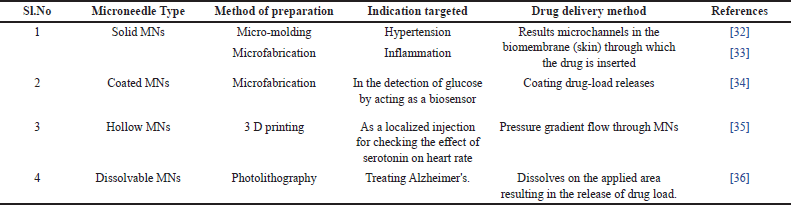 | Table 1. Different MNs used in drug delivery. [Click here to view] |
Yeung et al. [31] developed a novel stereolithography-based 3D printing technique to fabricate integrated microfluidic-enabled hollow MNs in a single step. This approach overcomes previous limitations of high cost, low versatility, and limited throughput. The method achieves high-resolution printing beyond conventional limits, enabling the creation of complex microfluidic and MN architectures with enhanced efficiency. A prototype device demonstrated hydrodynamic mixing and transdermal drug delivery, showcasing the system’s potential for advanced biomedical applications. These architectures offer promising capabilities for future transdermal therapies, including combinational drug delivery and preclinical testing of biologics, providing a customizable and cost-effective platform for innovative drug delivery systems. The drug delivery method using microfluidic-based MNs is depicted in Figure 3.
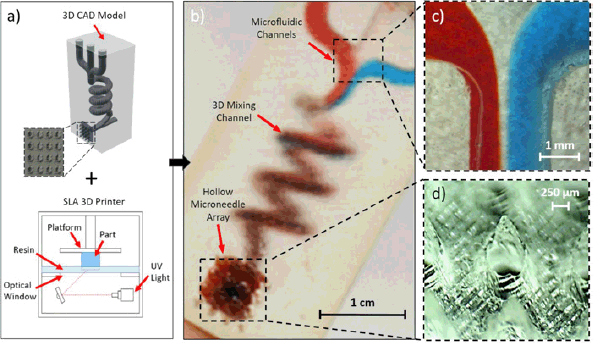 | Figure 3. Drug delivery method using microfluidic-based microneedles. Reproduced with permission [31]. [Click here to view] |
Mansor et al. [37] proposed a cost-effective and simplified method for cell detection using an integrated dual MN-microfluidic impedance flow cytometry system. This approach replaces conventional embedded electrodes with removable tungsten MNs positioned at half the microchannel height, enabling efficient electrical impedance measurement of yeast cells. The reusable MNs simplify cleaning and reduce fabrication complexity and cost. Despite its low cost, the system effectively detects cells passing through the sensing zone, maintaining essential sensor functionality. This design offers a practical solution for medical diagnostics and food safety screening, especially in resource-limited settings, where affordability and ease of use are critical.
Trautmann et al. [38] presented a hybrid system integrating femtosecond laser-fabricated microfluidic channels with direct laser-written hollow MN arrays, aiming to develop efficient point-of-care devices. Using a single laser system, MNs were produced through two-photon polymerization, and 3-dimensional microchannels were created in PMMA material. Compression tests confirmed that the MNs had sufficient strength for skin insertion. The unified fabrication method simplifies production by avoiding complex multi-step processes. A flow test using rhodamine B dye validated the system’s ability for fluid injection and extraction. This integrated platform shows promise for painless drug delivery and lab-on-a-chip diagnostic applications in clinical settings.
MICROFLUIDICS IN BIOANALYTICAL APPLICATIONS
In the past decade, rapid growth and continued research on microfluidics have brought about a revolutionary change in the field of bioanalytical sciences. This union of microfluidics with bioanalysis has given rise to a spectrum of cutting-edge uses that go beyond the limitations of traditional approaches [39]. Scientists have redefined the field of bioanalytical activities by unlocking new dimensions in precision, automation, and integration by utilizing the extraordinary capabilities of microfluidic systems. Microfluidics has established itself as a dynamic catalyst driving improvements in healthcare, diagnostics, and biological research. It has done this by developing small “lab-on-a-chip” platforms and streamlining complex sample preparation procedures [14].
Lab-on-chip
Microfluidic platforms, also known as “lab-on-a-chip” devices, merge various analytical processes onto a unit microscale chip [40]. These tools are capable of carrying out operations such as sample preparation, separation, reaction, and detection in a very regulated and effective way. In the case of point-of-care diagnostics, where quick and precise analysis of small sample volumes is essential, lab-on-a-chip devices are very useful [41]. A recent study by Pablo Rodriguez-Mateo et al. [42] explored LOC platforms by combining RNA extraction and SARS-CoV-2 detection processes. The lab-on-a-chip platform described in the work offers a promising alternative for resource-constrained environments. This cutting-edge technology accelerates the diagnostic process (470 pairs of genomic RNA per hour) while solving the infrastructure and skilled people issues that are frequently present in such situations. The platform improves efficiency and lowers the danger of contamination by combining two different steps one being sample preparation and the other involving detection in a single device. This development helps to manage and control the continuing epidemic in resource-constrained locations by speeding up the testing procedure and improving the accessibility of reliable SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection [42].
Murphy et al. created cellulose filter paper-based microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for the electrochemical detection of dopamine (DA) and ascorbic acid (AA) as well as chromatographic separation. They investigated the ion-exchange capabilities and physical characteristics of different filter sheets and discovered that these elements had a big impact on separation performance. VWR 413 accomplished baseline separation of AA and DA, but Whatman grade P81, a strong cation exchange paper, completely retained DA. The study showed that changes in ion-exchange capacity were caused by carboxyl groups on cellulose fibers. A DA detection limit of 3.41 μM in the presence of 1 mM AA was achieved by enhanced resolution through eluent ionic strength and pH optimization, suggesting the device’s potential for biological sample analysis [43]. Using chiral and reversed-phase columns, Lotter et al. [44] created the first chip-integrated 2-dimensional HPLC system for enantioselective micro-flow synthesis real-time monitoring. By facilitating heart-cut analyte transport between columns, this microfluidic system makes it possible to determine enantiomeric excess precisely using mass spectrometry. The technology was shown to be faster and more efficient than conventional techniques in the asymmetric synthesis of warfarin. Despite the technological difficulties in integrating packed columns on-chip, this method combines reaction and analytical processes in a single device, offering extensive applicability for complex separations and advancing automated chemical synthesis. The first high-performance chiral liquid chromatography employing packed microfluidic glass chips has been demonstrated by Thurmann et al. Cellulose tris(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate) was packed into the chip-integrated columns using 5-μm silica as the chiral stationary phase. The adaptability of the chip was demonstrated by the baseline separation of a variety of racemic substances, including medicines, into enantiomers under reversed-phase, polar organic, and normal-phase conditions. A lower plate height of 2.2 and better mass transfer at low retention were revealed by Van Deemter analysis. Ultrafast enantioseparations were accomplished in as low as 5 seconds using extremely short columns (down to 12 mm) [45, 46]
Organ-on-chip (OOC)
It is an emerging technology that has been in focus for the past several years as a result of a confluence of cell biology (stem cell) and microfluidics technologies [47]. The main goal of developing these systems is to simulate the physiological conditions of the host. In other words, these systems allow scientists to experiment in vitro (i.e., outside the living organisms) and still obtain results that relate to the host in the study [48, 49]. The examples of novel OOC platforms include heart-on-chip, kidney-on-chip, bone-on-chip [50], lung-on-chip, and liver-on-chip [51]. Various in vitro models of cardiac diseases have been created using heart-on-a-chip technology. These models can be employed to investigate various disease mechanisms and treatment approaches. The most important elements of the heart that are responsible for keeping it pumping include cardiomyocytes (CMs), cardiac fibroblasts, and endothelial cells, among various other cardiac cells [52]. Since CMs beat rhythmically and react to various stimuli, such as external force and pulses of electricity, they are frequently employed as components of heart-on-a-chip devices [53].
None of the 22 research on bioprinting for OOC systems employed laser-based techniques: instead, 16 used extrusion-based bioprinting, 4 used inkjet, and 1 used stereolithography. Although extrusion-based bioprinting is simple to use and versatile with a range of biomaterials, it has drawbacks, such as nozzle clogging and low resolution. Only low-viscosity bioinks can be used with inkjet printing, which offers excellent resolution and cell survival. Although stereolithography guarantees excellent precision, the process is slow, and exposure to UV light may weaken cell viability. The biocompatibility, ECM mimicking, and printability of hydrogels—both natural and synthetic—make them popular bioinks for OOC applications [54, 55].
The drawbacks of non-vascularized organoids, which frequently experience inadequate oxygen supply and waste accumulation that results in necrosis, are being addressed by vascularized OOC models. OOCs improve drug screening and disease modeling by more accurately simulating in vivo tissue conditions with the integration of microvascular networks. Research on metabolism and toxicity is aided by liver-on-a-chip systems, which coculture hepatocytes with endothelium and other liver-specific cells in a perfusable microenvironment to imitate liver function and structure. While heart-on-a-chip devices use CMs derived from induced pluripotent stem cells to replicate the myocardium, allowing for drug testing and modeling of heart conditions, vascularized lung-on-a-chip models replicate the alveolar-capillary interface, which is useful in the study of respiratory infections, such as COVID-19. Additional examples include neurovascular units for researching the blood–brain barrier and vascularized bone marrow and kidney chips for nephrotoxicity and cancer research.
These systems offer platforms that are physiologically appropriate and help close the gap between intricate in vivo models and conventional 2D cultures. Gut-on-chip model microfluidic device is depicted in Figure 4 [56]. In addition, different types of microfluidic designs consisting of different organ models are given in Table 2.
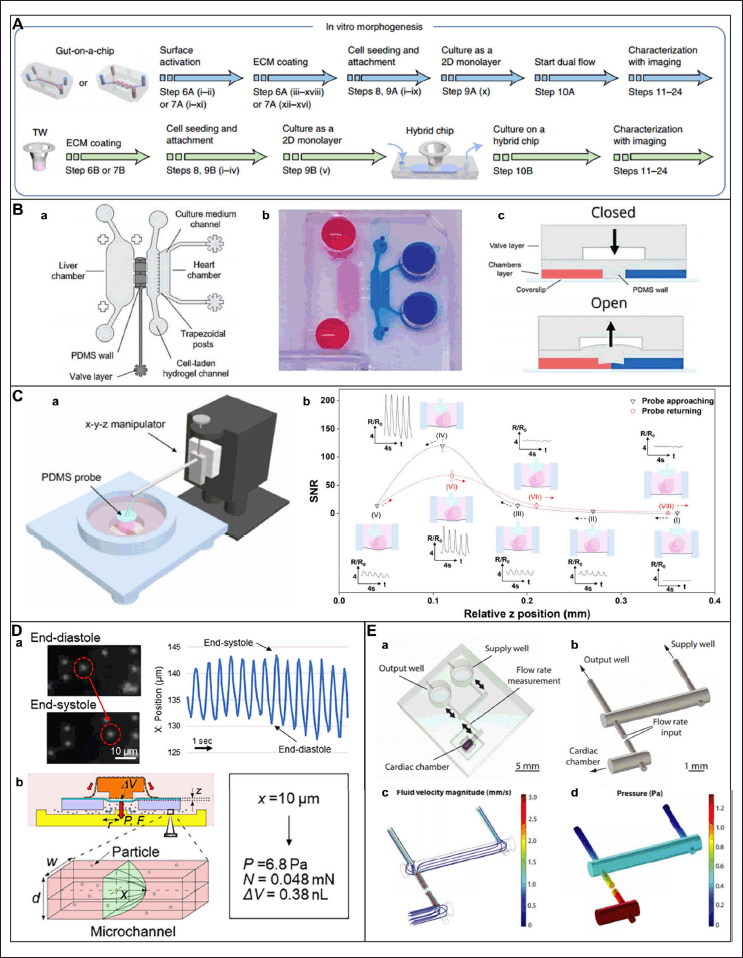 | Figure 4. Gut on chip model microfluidic device. Reproduced with permission [56]. [Click here to view] |
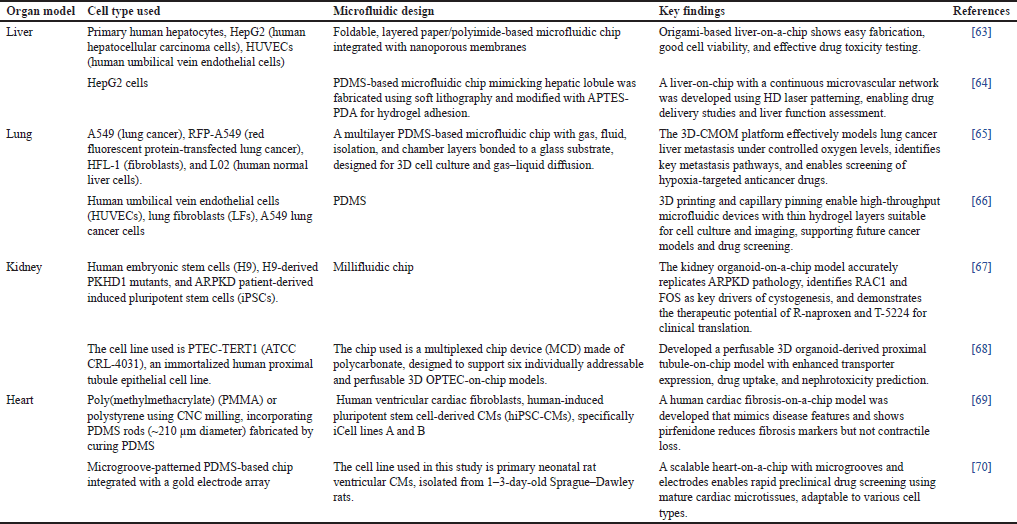 | Table 2. Different types of microfluidic design consisting of different organ models. [Click here to view] |
Integration of OOC with AI
OOC technology and artificial intelligence (AI), especially deep learning (DL), are fast-evolving technologies with high potential when combined, especially for drug evaluation. OOCs represent great preclinical models but are hindered by limitations in scalability and throughput, which restrict their general application to drug screening [57]. Recent advancements involve high-throughput microfluidic platforms where experiments can be conducted in parallel with real-time sensing and imaging, and large datasets are produced. Examples include devices with 36 to 384 devices to model sophisticated tissues and disease conditions, greatly expanding experimental capacity and data quantities [58].
However, processing and analyzing this massive amount of data become a labour-intensive and time-consuming task, which leads to a snag in data interpretation. AI—more especially, machine learning and DL—can help automate data analysis, reduce human bias, and accelerate insights. Without the need for explicit software coding, machine learning (ML) uses supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, and reinforcement learning techniques to identify patterns and provide predictions. As a branch of machine learning that uses deep neural networks, DL excels at processing raw, complex data to extract features more accurately and efficiently. In order to reduce computing demands, transfer learning in DL also makes it easier to reuse previously trained models for related tasks. With the integration of high-throughput OOCs and AI, scientists are able to efficiently process large multidimensional data sets, enhancing drug discovery and testing protocols. The fusion is accomplished through accurate measurement equipment, stable data acquisition and storage infrastructure, sophisticated ML software for data retrieval, and insightful result interpretation. This combination holds the potential for better, faster, and more scalable drug development pipelines that can revolutionize pharmacological studies, particularly for complicated drugs and personalized medicine [59,60].
Emerging frontiers (2024–2025)
Microfluidic rheology
Zsófia Vilimi et al. studied the viscosity of various pharmaceutical products such as gel, solutions, injections, and excipients using two instruments: the Kinexus Pro+ rotational rheometer and the FluidicamTM RHEO microfluidic viscometer. These were selected based on the formulation type and route of administration. The Kinexus Pro+ measured flow properties across a broad viscosity range (1 mPa.s to 10,000 Pa.s) using cone–plate or plate–plate geometries, with shear rates and temperatures adjusted to simulate actual usage conditions. The FluidicamTM RHEO, ideal for fluid or shear-thinning semisolid formulations, used laminar flow and reference liquids (5, 50, 500 mPa.s at 25 °C) to determine viscosity, particularly under high shear conditions such as blinking or injection. Nozzle and applicator dimensions were measured using a digital caliper (±0.02 mm accuracy) to estimate shear rates during application. Extrudability was assessed using a handheld hardness tester to determine the force needed to dispense vaginal gel: Klysma. Shear stress and shear rate calculations were based on standard fluid mechanics equations considering viscosity, flow rate, nozzle size, and applied force. The results revealed that the rotational rheometer works well for gel-based formulations across a wide shear range but is less effective for low-viscosity samples. It allows partial sample recovery. The microfluidic rheometer suits high-shear applications such as injections and eye drops but is destructive. Both methods gave similar results in overlapping ranges, with the microfluidic device offering faster analysis and minimal preparation. Each method has specific uses and benefits [61].
Modular microfluidic chip
Lambert et al. [62] investigated the polymorphic forms of drugs including Rimonabant, Sulfathiazole, Aripiprazole, and Irbesartan using a custom-built microfluidic platform. The setup includes components for droplet generation, temperature control, and real-time characterization via UV, optical microscopy, and Raman spectroscopy. Saturated drug solutions are prepared by flowing solvent through a powder-filled column, and droplets are formed using a fluorinated oil. Droplets are cooled to induce crystallization, and their polymorphic forms are analyzed. The platform uses chemically resistant materials and 3D-printed holders. Interfacial energy is measured by the pendent drop method, with solubility also confirmed using traditional millivials. Solubility and crystallization of Irbesartan, Rimonabant, Aripiprazole, and Sulfathiazole were studied using microfluidics. Results showed form-specific solubility differences, phase transitions, and nucleation influenced by cooling rates and solvents. A new Sulfathiazole polymorph (U1) with unique properties was discovered, highlighting microfluidics’ effectiveness for polymorph screening.
Instant topical drug quantification with 3D microfluidics
Benjamin A. Kuzma et al. investigated the permeability of Ruxolitinib formulations by applying it onto the mouse ear skin using a 3D-printed applicator. Stimulated Raman scattering microscopy was employed to track the drug penetration over 2 hours. Drug concentrations in lipid-rich and lipid-poor skin regions were analyzed, and pharmacokinetic parameters were compared using statistical tests. The study developed a 3D-printed applicator enabling precise, low-volume (20 µl) topical drug delivery and real-time imaging of early drug permeation into mouse skin. The study revealed that PEG enhanced rapid drug uptake, while DGME provided sustained release, highlighting formulation impacts on skin pharmacokinetics and potential for screening excipients [71].
Flexible microfluidic sensor
Ractopamine is illegally used in food, which can harm health, so quick and low-cost testing is needed. The study developed a cost-effective colorimetric chemosensing platform using modified paper-based microfluidic devices (mPCD) and various gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) to detect ractopamine (RAC) in chicken meat. Four types of AuNPs—AuNPs-CysA, AuNPs-DDT, positively charged AuNPs, and gold nanostars (GNSs)—were synthesized, with AuNPs-CysA and AuNPs-DDT showing significant colorimetric changes upon RAC interaction. The device design included hydrophilic and semi-hydrophilic zones formed by paraffin treatment. Characterization via FE-SEM, TEM, AFM, EDS, UV-Vis, and zeta potential confirmed the successful synthesis and stability of AuNPs. The Instant Eyedropper tool and Colorxs software were used for digital color analysis, enhancing detection accuracy. The sensor with cysteamine showed good detection from 0.1 mM to 0.01 M with a detection limit of 0.001 mM. Another sensor with dodecanethiol was even more sensitive, detecting as low as 1 nM. These sensors were easy to make, stable, and worked well. Finally, the system was combined with a simple glass fiber device to allow on-site food testing [72].
CHALLENGES AND LIMITATIONS OF OOC
It is inherently difficult to accurately replicate the multilayered architecture and multifunctionality of human tissues. Each organ has a unique cellular composition, mechanical property, and microenvironment that is hard to reproduce in vitro. Compounding the issue of complexity, there is the requirement to physically replicate the size and number of cells in each organ to reach physiologically relevant levels; this is important to produce meaningful experimental results. A common and routine fabrication method used in the development of OOC devices is soft lithography; this requires cleanroom facilities and specialized equipment that do not exist in all laboratories. Moreover, even alternative, lower-resolution methods of fabrication still add complexity when integrating parts and the combined assembly and operations of devices. PDMS remains widely accepted as a material for OOC devices; however, PDMS has limitations including adsorption of hydrophobic drugs, leaching of uncrosslinked oligomers, and restrictions on the dimensions within the channels; each of these factors can affect experimental outcomes and drug testing reliability. As substitute materials, such as PMMA polymers, are developed and has unique fabrication and performance benefits
CONCLUSION
This review paper explores the field of microfluidics, a technology that involves controlling the flow of fluids at the microscale. We delve into various methods used to fabricate complex mPCD, including photolithography, soft lithography, and 3D printing. The underlying principles of microfluidics are discussed, with a focus on the unique characteristics of fluid behavior at the microscale, such as the dominance of surface tension and laminar flow. Recent advancements in microfluidics are highlighted, including the integration of microfluidics with other technologies such as optics, electronics, and nanotechnology. These advancements have led to innovative applications in diverse fields, including drug delivery, diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and energy production. As the field continues to progress, future research efforts will likely focus on developing scalable, cost-effective, and user-friendly microfluidic systems. Overcoming challenges related to scalability, cost, and user experience will be crucial to fully harness the potential of microfluidics. With ongoing innovation and interdisciplinary collaborations, microfluidics is poised to revolutionize various industries and improve our quality of life.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors would like to thank Department of Pharmaceutics, Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Manipal Academy of Higher Education for their support in providing infrastructure for the review work.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
There is no funding to report.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors report no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICS APPROVAL
This study does not involve experiments on animals or human subjects.
INFORMED CONSENT
This review has not involved studies on the human participants.
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated and analyzed are included in this research article.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used artificial intelligence (AI)-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
REFERENCES
1. Thimmaraju MK, Trivedi R, Hemalatha G, Thirupathy B, Billah AM. Microfluidic revolution and its impact on pharmaceutical materials: a review. Mater Today Proc. 2023.. CrossRef
2. Pattanayak P, Singh SK, Gulati M, Vishwas S, Kapoor B, Chellappan DK, et al. Microfluidic chips: recent advances, critical strategies in design, applications and future perspectives. Vol. 25, Microfluidics and Nanofluidics. Berlin: Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH; 2021. CrossRef
3. Fallahi H, Zhang J, Phan HP, Nguyen NT. Flexible microfluidics: fundamentals, recent developments, and applications. Vol. 10, Micromachines. Basel, Switzerland: MDPI AG; 2019. CrossRef
4. Liao CC, Chen YZ, Lin SJ, Cheng HW, Wang JK, Wang YL, et al. A microfluidic microwell device operated by the automated microfluidic control system for surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021;191:113483. CrossRef
5. Azizipour N, Avazpour R, Rosenzweig DH, Sawan M, Ajji A. Evolution of biochip technology: a review from lab-on-a-chip to organ-on-a-chip. Micromachines (Basel). 2020;11(6):1–15. CrossRef
6. Lang P, Liu Y. Soft matter at aqueous interfaces. Lecture notes in physics. 2015. CrossRef
7. Jung W, Han J, Choi JW, Ahn CH. Point-of-care testing (POCT) diagnostic systems using microfluidic lab-on-a-chip technologies. Vol. 132, Microelectronic Engineering. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier B.V.; 2015. pp: 46–57. CrossRef
8. Kung CT, Gao H, Lee CY, Wang YN, Dong W, Ko CH, et al. Microfluidic synthesis control technology and its application in drug delivery, bioimaging, biosensing, environmental analysis and cell analysis. Vol. 399, Chemical Engineering Journal. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier B.V.; 2020. CrossRef
9. Yaman G. A suggestion of standard and optimized steps in the LOC (Lab on a Chip), LOD (Lab on a Disc), and POC (Point of Care) development process for biomedical applications: a case study about ESR. J Comput Appl Math. 2023;417:114626. CrossRef
10. Pradeep A, Raveendran J, Babu TGS. Chapter five¾Design, fabrication and assembly of lab-on-a-chip and its uses. In: Pandya A, Singh V, editors. Micro/nanofluidics and lab-on-chip based emerging technologies for biomedical and translational research applications - Part B [Internet]. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press; 2022. p. 121–62. CrossRef
11. Al-wdan OA, Sharallah OA, Abdelwahab NA, Mohammed AO, Elmowafy E, Soliman ME. Insights into microfabrication and implementation of microfluidics in pharmaceutical drug delivery and analysis. OpenNano. 2023;12:100156. CrossRef
12. Sun K, Wang Z, Jiang X. Modular microfluidics for gradient generation. Lab Chip. 2008;8(9):1536–43. CrossRef
13. Shanko ES, van de Burgt Y, Anderson PD, den Toonder JMJ. Microfluidic magnetic mixing at low reynolds numbers and in stagnant fluids. Micromachines (Basel). 2019;10(11):731. CrossRef
14. Berlanda SF, Breitfeld M, Dietsche CL, Dittrich PS. Recent advances in microfluidic technology for bioanalysis and diagnostics. Vol. 93, Analytical chemistry. Washington, DC: American Chemical Society; 2021. pp: 311–31. CrossRef
15. Bringer MR, Gerdts CJ, Song H, Tice JD, Ismagilov RF. Microfluidic systems for chemical kinetics that rely on chaotic mixing in droplets. Philos Trans R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2004;362(1818):1087–104. CrossRef
16. Maurya R, Gohil N, Bhattacharjee G, Alzahrani KJ, Ramakrishna S, Singh V. Chapter Twelve - Microfluidics device for drug discovery, screening and delivery. In: Pandya A, Singh V, editors. Progress in molecular biology and translational science [Internet]. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press; 2022. pp: 335–46. CrossRef
17. Qing LS, Wang TT, Luo HY, Du JL, Wang RY, Luo P. Microfluidic strategies for natural products in drug discovery: current status and future perspectives. TrAC Trends Analy Chem [Internet]. 2023;158:116832. CrossRef
18. Ejeta F. Recent advances of microfluidic platforms for controlled drug delivery in nanomedicine. Vol. 15, Drug design, development and therapy. Macclesfield, United Kingdom: Dove Medical Press Ltd; 2021. pp: 3881–91. CrossRef
19. Ahn J, Ko J, Lee S, Yu J, Kim YT, Jeon NL. Microfluidics in nanoparticle drug delivery; From synthesis to pre-clinical screening. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;128:29–53. CrossRef
20. Wongkaew N, Simsek M, Griesche C, Baeumner AJ. Functional nanomaterials and nanostructures enhancing electrochemical biosensors and lab-on-a-chip performances: recent progress, applications, and future perspective. Chem Rev [Internet]. 2019;119(1):120–94. CrossRef
21. Ma Z, Li B, Peng J, Gao D. Recent development of drug delivery systems through microfluidics: from synthesis to evaluation. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(2):434. CrossRef
22. Rossow T, Heyman JA, Ehrlicher AJ, Langhoff A, Weitz DA, Haag R, et al. Controlled synthesis of cell-laden microgels by radical-free gelation in droplet microfluidics. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134(10):4983–9. CrossRef
23. Forbes N, Hussain MT, Briuglia ML, Edwards DP, Horst JH ter, Szita N, et al. Rapid and scale-independent microfluidic manufacture of liposomes entrapping protein incorporating in-line purification and at-line size monitoring. Int J Pharm. 2019;556:68–81. CrossRef
24. Hamano N, Böttger R, Lee SE, Yang Y, Kulkarni JA, Ip S, et al. Robust microfluidic technology and new lipid composition for fabrication of curcumin-loaded liposomes: effect on the anticancer activity and safety of cisplatin. Mol Pharm. 2019;16(9):3957–67. CrossRef
25. Waghule T, Singhvi G, Dubey SK, Pandey MM, Gupta G, Singh M, et al. Microneedles: a smart approach and increasing potential for transdermal drug delivery system. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:1249–58. CrossRef
26. Maia R, Carvalho V, Lima R, Minas G, Rodrigues RO. Microneedles in advanced microfluidic systems: a systematic review throughout lab and organ-on-a-chip applications. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(3):792. CrossRef
27. Tariq N, Ashraf MW, Tayyaba S. A review on solid microneedles for biomedical applications. J Pharm Innov. 2022;17:1464–83. CrossRef
28. Hao Y, Li W, Zhou XL, Yang F, Qian ZY. Microneedles-based transdermal drug delivery systems: a review. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2017;13:1581–97. CrossRef
29. Hoang MT, Ita KB, Bair DA. Solid microneedles for transdermal delivery of amantadine hydrochloride and pramipexole dihydrochloride. Pharmaceutics. 2015;7(4):379–96. CrossRef
30. Chen BZ, He MC, Zhang XP, Fei WM, Cui Y, Guo XD. A novel method for fabrication of coated microneedles with homogeneous and controllable drug dosage for transdermal drug delivery. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022;12(11):2730–9. CrossRef
31. Yeung C, Chen S, King B, Lin H, King K, Akhtar F, et al. A 3D-printed microfluidic-enabled hollow microneedle architecture for transdermal drug delivery. Biomicrofluidics. 2019;13(6):064125. CrossRef
32. Kolli CS, Banga AK. Characterization of solid maltose microneedles and their use for transdermal delivery. Pharm Res. 2008;25(1):104–13. CrossRef
33. Xiang Z, Wang H, Pastorin G, Lee C. Development of a flexible and disposable microneedle-fluidic-system with finger-driven drug loading and delivery functions for inflammation treatment. J Microelectromech Syst. 2015;24(3):565–574. CrossRef
34. Trzebinski J, Sharma S, Radomska-Botelho Moniz A, Michelakis K, Zhang Y, Cass AEG. Microfluidic device to investigate factors affecting performance in biosensors designed for transdermal applications. Lab Chip [Internet]. 2012;12(2):348–52. CrossRef
35. Zabihihesari A, Hilliker AJ, Rezai P. Localized microinjection of intact Drosophila melanogaster larva to investigate the effect of serotonin on heart rate. Lab Chip [Internet]. 2020;20(2):343–55. CrossRef
36. Yan Q, Wang W, Weng J, Zhang Z, Yin L, Yang Q, et al. Dissolving microneedles for transdermal delivery of huperzine A for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Deliv. 2020;27(1):1147–55. CrossRef
37. Mansor MA, Takeuchi M, Nakajima M, Hasegawa Y, Ahmad MR. A novel integrated dual microneedle-microfluidic impedance flow cytometry for cells detection in suspensions. Int J Electric Comput Eng. 2017;7(3):1513–21. CrossRef
38. Trautmann A, Roth GL, Nujiqi B, Walther T, Hellmann R. Towards a versatile point-of-care system combining femtosecond laser generated microfluidic channels and direct laser written microneedle arrays. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2019;5(1):6. CrossRef
39. Gomez FA. Bioanalytical applications in microfluidics. Vol. 2, Bioanalysis. London, UK: Wiley-Interscience; 2010. pp: 1661–2. CrossRef
40. Bahnemann J, Grünberger A. Microfluidics in biotechnology. Vol. 179, Advances in biochemical engineering/biotechnology. Berlin: Springer-Verlag Berlin and Heidelberg GmbH & Co. K.
41. Liu X, Fang J, Huang S, Wu X, Xie X, Wang J, et al. Tumor-on-a-chip: from bioinspired design to biomedical application. Vol. 7, Microsystems and nanoengineering. Berlin: Springer Nature; 2021. CrossRef
42. Rodriguez-Mateos P, Ngamsom B, Walter C, Dyer CE, Gitaka J, Iles A, et al. A lab-on-a-chip platform for integrated extraction and detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in resource-limited settings. Anal Chim Acta. 2021;1177:338758. CrossRef
43. Murphy A, Gorey B, De Guzman K, Kelly N, Nesterenko EP, Morrin A. Microfluidic paper analytical device for the chromatographic separation of ascorbic acid and dopamine. RSC Adv. 2015;5(113):93162–9. CrossRef
44. Lotter C, Poehler E, Heiland JJ, Mauritz L, Belder D. Enantioselective reaction monitoring utilizing two-dimensional heart-cut liquid chromatography on an integrated microfluidic chip. Lab Chip. 2016;16(24):4648–52. CrossRef
45. Thurmann S, Lotter C, Heiland JJ, Chankvetadze B, Belder D. Chip-based high-performance liquid chromatography for high-speed enantioseparations. Anal Chem. 2015;87(11):5568–76. CrossRef
46. Ai Y, Zhang F, Wang C, Xie R, Liang Q. Recent progress in lab-on-a-chip for pharmaceutical analysis and pharmacological/toxicological test. TrAC¾Trends Analy Chem. 2019;117:215–30. CrossRef
47. Koyilot MC, Natarajan P, Hunt CR, Sivarajkumar S, Roy R, Joglekar S, et al. Breakthroughs and applications of organ-on-a-chip technology. Vol. 11, Cells. Basel, Switzerland: MDPI; 2022. CrossRef
48. Mastrangeli M, van den Eijnden-van Raaij J. Organs-on-chip: the way forward. Vol. 16, Stem cell reports. Cambridge, MA: Cell Press; 2021. pp: 2037–43. CrossRef
49. Chen H, Luo Z, Lin X, Zhu Y, Zhao Y. Sensors-integrated organ-on-a-chip for biomedical applications. Nano research. Beijing, China: Tsinghua University; 2023. CrossRef
50. Hu Y, Zhang H, Wang S, Cao L, Zhou F, Jing Y, et al. Bone/cartilage organoid on-chip: construction strategy and application. Vol. 25, Bioactive materials. Beijing, China: KeAi Communications Co.; 2023. pp: 29–41. CrossRef
51. Hassan S, Sebastian S, Maharjan S, Lesha A, Carpenter AM, Liu X, et al. Liver-on-a-chip models of fatty liver disease. Vol. 71, Hepatology. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons Inc.; 2020. pp: 733–40. CrossRef
52. Zhang F, Qu KY, Zhou B, Luo Y, Zhu Z, Pan DJ, et al. Design and fabrication of an integrated heart-on-a-chip platform for construction of cardiac tissue from human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes and in situ evaluation of physiological function. Biosens Bioelectron [Internet]. 2021;179:113080. CrossRef
53. Yang Q, Xiao Z, Lv X, Zhang T, Liu H. Fabrication and biomedical applications of heart-on-a-chip. Int J Bioprint. 2021;7(3):54–70. CrossRef
54. Chen S, Jang TS, Pan HM, Jung H Do, Sia MW, Xie S, et al. 3D freeform printing of nanocomposite hydrogels through in situ precipitation in reactive Viscous fluid. Int J Bioprint. 2020;6(2):1–21. CrossRef
55. Emmermacher J, Spura D, Cziommer J, Kilian D, Wollborn T, Fritsching U, et al. Engineering considerations on extrusion-based bioprinting: interactions of material behavior, mechanical forces and cells in the printing needle. Biofabrication. 2020;12(2):ab7553. CrossRef
56. Huang Y, Liu T, Huang Q, Wang Y. From organ-on-a-chip to human-on-a-chip: a review of research progress and latest applications. ACS Sens. 2024;9(7):3466–88. CrossRef
57. Criscione J, Rezaei Z, Hernandez Cantu CM, Murphy S, Shin SR, Kim DH. Heart-on-a-chip platforms and biosensor integration for disease modeling and phenotypic drug screening. Biosens Bioelectron. 2023;220:114840. CrossRef
58. Azizgolshani H, Coppeta JR, Vedula EM, Marr EE, Cain BP, Luu RJ, et al. High-throughput organ-on-chip platform with integrated programmable fluid flow and real-time sensing for complex tissue models in drug development workflows. Lab Chip. 2021;21(8):1454–74. CrossRef
59. Halagali P, Nayak D, Seenivasan R, Manikkath J, Rathnanand M, Tippavajhala VK. Artificial intelligence revolution in pharmaceutical sciences: advancements, clinical impacts, and applications. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025;26. CrossRef
60. Raagul Seenivasan, Anitha Marimuthu, Jey Kumar Pachiyappan GG. Integrating organ-on-chip models in drug discovery: a comprehensive review on innovations and implications. Curr Pharm Anal. 2024;20: 953–65. CrossRef
61. Vilimi Z, Pápay ZE, Basa B, Orekhova X, Kállai-Szabó N, Antal I. Microfluidic rheology: an innovative method for viscosity measurement of gels and various pharmaceuticals. Gels. 2024;10(7):464. CrossRef
62. Lambert M, Grossier R, Lagaize M, Bactivelane T, Heresanu V, Robert B, et al. Modular microfluidic platform for solubility measurement, nucleation statistics and polymorph screening of active pharmaceutical ingredients: Irbesartan, Rimonabant, Aripiprazole and Sulfathiazole. J Cryst Growth. 2023;616:127252. CrossRef
63. Xie X, Maharjan S, Kelly C, Liu T, Lang RJ, Alperin R, et al. Customizable microfluidic origami liver-on-a-chip (oLOC). Adv Mater Technol. 2022;7(5):2100677. CrossRef
64. Watanabe M, Salvadori A, Markovic M, Sudo R, Ovsianikov A. Advanced liver-on-chip model mimicking hepatic lobule with continuous microvascular network via high-definition laser patterning. Mater Today Bio. 2025;32:101643. CrossRef
65. Zheng L, Wang B, Sun Y, Dai B, Fu Y, Zhang Y, et al. An oxygen-concentration-controllable multiorgan microfluidic platform for studying hypoxia-induced lung cancer-liver metastasis and screening drugs. ACS Sens. 2021;6(3):823–32. CrossRef
66. Nguyen TTY, Lee J, Choi S, Jeon NL. Surface tension-based open microfluidic platform using micropillars to recreate the 3D lung cellular microenvironment. Biochip J. 2024;18:589–600. CrossRef
67. Hiratsuka K, Miyoshi T, Kroll KT, Gupta NR, Valerius MT, Ferrante T, et al. Organoid-on-a-chip model of human ARPKD reveals mechanosensing pathomechanisms for drug discovery. Sci Adv. 2022;8(38):eabq0866. CrossRef
68. Aceves JO, Heja S, Kobayashi K, Robinson SS, Miyoshi T, Matsumoto T, et al. 3D proximal tubule-on-chip model derived from kidney organoids with improved drug uptake. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):14997. CrossRef
69. Mastikhina O, Moon BU, Williams K, Hatkar R, Gustafson D, Mourad O, et al. Human cardiac fibrosis-on-a-chip model recapitulates disease hallmarks and can serve as a platform for drug testing. Biomaterials. 2020;233:119741. CrossRef
70. Ren L, Zhou X, Nasiri R, Fang J, Jiang X, Wang C, et al. Combined effects of electric stimulation and microgrooves in cardiac tissue-on-a-chip for drug screening. Small Methods. 2020;4(10):2000438. CrossRef
71. Kuzma BA, Tu D, Goss A, Iliopoulos F, Slade JB, Wiatrowski A, et al. Instantaneous topical drug quantification using a 3D printed microfluidic device and coherent Raman imaging. OpenNano. 2023;12:100151. CrossRef
72. Baghban HN, Hasanzadeh M. Multifunctional one-droplet microfluidic chemosensing of ractopamine in real samples: a user-oriented flexible nano-architecture for on-site food and pharmaceutical analysis using optical sensors. Analyt Methods. 2023;15(35):4506–17. CrossRef