INTRODUCTION
Niacinamide, (NA, nicotinamide, 3-pyridinecarboxamide), a derivative of niacin (vitamin B3) that acts as the precursor of the cofactors NA adenosine dinucleotide phosphate and NA adenosine dinucleotide (NAD), and possesses numerous functions in more than 35 cellular biochemical reactions in the skin. In fact, NA has been topically utilized in various medical and cosmeceutical applications including antioxidant [1], photo-immunosuppression prevention [2], acne post-inflammation treatment [3], collagen production enhancement [4], sebum production reduction [4], pigment reduction [5], andintercellular lipid synthesis increment [6]. NA is chemically stable to oxidation and photolysis, which is beneficial for its formula developments [7]. Moreover, compared to another biologically active form of niacin, nicotinic acid, NA does not activate skin flushing and variation in blood pressure and body temperature [8]. Therefore, NA is one of the best-investigated ingredients in cosmeceutical areas, especially for the skin anti-aging and whitening action.
Nevertheless, due to its inherent hydrophilicity, topical application of NA is limited, with poor skin penetration. The stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the skin, mainly consists of corneocytes and intercellular hydrophobic lipid lamellae, which prevent harmful substances from entering the body [9]. Unfortunately, these hydrophobic lipids also significantly limit the skin penetration of hydrophilic compounds [10]. In fact, the NA skin absorption is generally <3% of the total applied dose of 4 μg/cm2 after 24 hours [11]. Consequently, although proving effectiveness on the enhanced NAD levels in skin cells, NA needs to be used in high dose, and thus, potentially causes side effects to the skin [12]. Therefore, a novel approach is necessary to improve the skin penetration of NA.
To this end, one potential approach is nanocarriers, since they have been progressively employed as delivery systems for numerous pharmaceutical and cosmetics compounds [13–17]. Among various types of nanocarriers, liposomes show much benefits for transepidermal delivery of NA, since they could effectively encapsulate both hydrophobic and hydrophilic compounds [18]. However, owing to the skin barrier, conventional liposomes are limited to lipophilic drugs with respective molecular weights of <500 Da. Thus, a more deformable type of liposome, called elastic liposomes (EL) has been formulated to increase the transepidermal delivery of hydrophilic drugs [19]. EL exhibits lipid bilayers, similar to the conventional liposomes, but with the inclusion of a compound known as edge activator to enhance the vesicle deformability. Thus, they are considered as a safe delivery system that can penetrate the skin integrity, while maintaining their intact vesicles via the hydrophilic channel in the epidermis lipid lamellar regions and shunt pathways [20]. Therefore, due to their excellent biocompatibility and deformability, EL could be a promising strategy to enhance transepidermal delivery of NA. To the best of our knowledge, only one study has been reported on this issue, however, the total NA cumulative amount permeated through the skin over 24 hours of the presented NA-loaded EL was only ~2.5 times higher than that of the 2% NA solution [9]. This value might not be sufficient to enhance NA skin absorption. Thus, novel systems are necessary.
Hence, this study developed and characterized novel NA-loaded EL, with high skin permeability as a potential transepidermal delivery system for hydrophilic compounds. In addition, the effects of different types of semi-permeable membrane used in in-vitro permeation studies were evaluated. The particles were developed using the reverse phase evaporation technique and physico-chemically characterized in terms of phase transition, mean particle size, zeta potential, drug entrapment efficiency (EE%), and particle deformability. Finally, in-vitro skin permeations of the formulations were conducted on both the porcine ear epidermis skin and synthetic polycarbonate artificial skin, using Franz diffusion cell.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
NA was bought from Phitsanuchemical (Phitsanulok, Thailand). Cholesterol (CH) was imported from Sigma Chemical (Steinheim, Germany). Lipoid S100-3 (Hydrogenated phosphatidylcholine, HPC) was imported from Lipoid GmbH Co., Ltd. (Ludwigshafen, Germany). Chloroform and ethanol were purchased from RCI Labscan (Bangkok, Thailand). All other utilized chemicals and solvents were analytical grade or higher. Polycarbonate membranes, diameter of 19 mm, with 0.4- and 0.1-μm pore size (NucleporeTM, Whatman®), were bought from Whatman International Ltd. (New York, USA).
Preparation of the blank EL
The blank EL (unloaded EL) was prepared by the reverse phase evaporation technique. To this end, the organic phase containing HPC, CH, and Span 80 (Table 1), was dissolved in an ethanol-chloroform mixture (5.3:1 v/v), followed by stirring (750 rpm) at 60ºC to form a clear solution. Then, deionized (DI) water (the aqueous phase) was added to the prepared organic phase to a final volume of 20 ml and stirred (750 rpm) at 60ºC. Finally, the organic solvent was removed using a rotavapor (R153, Buchi, Switzerland) and the particles were extruded 10 times through a 0.45-μm membrane to ensure uniform particle sizes and consistency of the final obtained EL product [19]. The particle size was then measured following “Physico-chemical characterizations”, and the formula possessing the smallest size was considered optimal and selected for the preparation of NA-loaded EL.
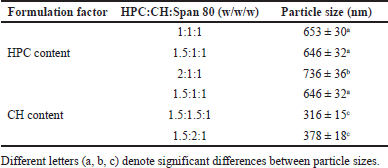 | Table 1. Effect of HPC and CH content on the mean sizes of the blank EL. [Click here to view] |
Preparation of NA-loaded EL
The optimal blank EL formulation was utilized to fabricate NA-loaded EL, following the same method. Briefly, the aqueous phase containing different NA amounts of 100, 150, and 200 mg, were respectively mixed with the organic phase. Then, the EL was obtained by evaporating the organic solvents, followed by extrusion (10 times) through a 0.45-μm membrane. Finally, the formulations were stored at 4ºC for further experiments.
Physico-chemical characterizations
Size, zeta potential, and morphology
The EL mean size (hydrodynamic diameter) and polydispersity index (PDI) were determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS) using the ZetaPALS® analyzer (Brookhaven Instrument Corporation, Holtsville, USA) equipped with a 35-mW Helium-Neon laser diode (632.8 nm) and a goniometer (BI-200SM) coupled with a digital correlator (BI-9010AT). Samples were dispersed in DI water and measured for five cycles by the auto-measuring mode.
The zeta potential was determined by the phase analysis light scattering method with the ZetaPALS®. Measurements were conducted at room temperature and an angle of 14.8o to the incident light. Samples were dispersed in DI water and measured for 10 cycles.
The EL shapes were observed using polarized optical microscopy (Olympus, USA), with a microscope attached to a 530-nm full wavelength retardation wave plate.
Drug EE%
The ability to encapsulate the NA of the EL was determined by the drug EE% values using the indirect method. For this, 10 mg of the freeze-dried NA-loaded EL was weighed and dispersed in 1 ml of DI water, followed by centrifugation at 17,000 rpm for 30 minutes. The supernatant containing the non-entrapped NA was collected, and diluted with methanol, and the non-entrapped NA amount was determined using UV-Vis spectroscopy at 262 nm (standard curve equation of y = 0.0268x – 0.0002 (R2 = 0.999)). The EE% of the encapsulated NA was then calculated using equation (1).
EE% = [1 - (amount of non-entrapped NA)/ (initial amount of NA)] × 100% (1)
Deformability measurement
The elasticity of the EL liposomal membrane was measured based on the alteration of the vesicle size while passing through the 100-nm polycarbonate membrane, using a manual mini-extruder (Avanti Polar Lipid Inc., Alabaster, AL) [21]. The EL was subjected into the syringe, followed by the extrusion process (manually by hand). The EL initial mean sizes and their respective sizes after extrusion were determined by the DLS method. The EL elasticity, demonstrating by the deformability percentage, was calculated following equation (2).
Deformability (%) = [Initial EL size (nm) – EL size after extrusion (nm)] x 100/[Initial EL size (nm)] (2)
In-vitro permeation study
To investigate the EL ability to deliver NA transepidermally, in-vitro permeation study was performed using a Franz diffusion cell (PermeGear, Hellertown, USA). For comparison purposes, 2 different kinds of membranes were utilized, namely natural porcine ear epidermis and synthetic 0.2-μm polycarbonate membrane (Nucleopore®, Whatman, Costar GmbH, Bo-denim, Germany). To get the porcine ear epidermis, pig ear skin was obtained from the slaughterhouse, subcutaneous-fat-tissue removed, immersed in hot water at 60ºC for 2 minutes, and the epidermis was separated from the dermis using a heat separation technique. Then, the trans-epidermal water loss (TEWL) value of the separated epidermis was measured by a tewameter (Model TM 300, Courage and Khazaka electronic GmbH, Germany). A TEWL value of less than 15 g/m2h indicates the undamaged epidermis [14]. The experiments were conducted with the ethical approval of the Naresuan University Animal Ethics Committee, Phitsanulok, Thailand (NU-AEE610504).
For the in-vitro permeation test, both membranes (diffusion area of 2.46 cm2) were individually fitted between the Franz cell donor and receptor chambers, followed by stabilization for 30 minutes. The receptor chamber contained 6 ml of DI water as a permeation medium, and the medium was maintained at a temperature of 32ºC ± 0.5ºC, simulating the skin normal temperature. The samples (freshly prepared following the protocol described in “Preparation of NA loaded EL”) were evenly subjected and spread on the membrane. These samples were not subjected to centrifugation, thus, both the non-entrapped NA and the encapsulated NA inside the EL were present. The tested samples included NA loaded EL 1%, 1.5%, and 2%, which contained 3, 4.5, and 6 mg NA, respectively. The 2% NA cream was used as a control (6 mg NA mixed with a cream base to get a 300 mg sample). At each pre-determined time interval of 30, 60, 120, 240, and 480 minutes, 500 μl of the medium in the receptor chamber was withdrawn and fresh-medium replaced. The withdrawal samples were then measured by UV-Vis spectroscopy (Genesys-10 Series, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., USA) at 262 nm (standard curve equation of y = 0.0268x – 0.0002 (R2 = 0.999)) to determine the permeated NA amount.
Statistical analysis
The experiments were carried out in triplicate and demonstrated in terms of mean ± standard deviation (SD). The Student’s t-test and ANOVA were utilized to denote the differences between samples, with 95% confidence intervals and a significant level of p < 0.05. Tukey’s post-hoc test was used to address multiple comparisons, where necessary. Tukey’s test is appropriate for identifying significant differences between groups while controlling for type-I errors.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Preparation of the blank EL
A report on the NA-loaded EL for transepidermal delivery has been published in the literature, nevertheless, the total NA amount permeated through the skin of that study was only ~2.5 times higher than that of the 2% NA solution [9]. Herein, we aimed to develop novel EL to significantly enhance the NA transepidermal delivery, as well as to compare the effect of membrane choice (i.e., natural vs. synthetic type) on the in-vitro drug penetration. To this end, we first preliminary formulated the unloaded/blank EL with different amounts of HPC and CH, to obtain the optimal formula.
Regarding the EL preparation method, the reverse phase evaporation technique was utilized due to the fact that this method produces EL with relatively small particle sizes that are suitable for topical administration. More importantly, the EL formulated by the reverse phase evaporation technique attained higher drug EE% (39.51% ± 3.38%) for hydrophilic drugs (i.e., NA) compared to the conventional method (30.0% ± 3.8%) such as the film hydration technique [22]. Nevertheless, this EE% value was not optimal. Further improvements may be achieved through optimizations of (1) preparation methods (the rotary evaporation-sonication method could be more effective than the vortexing-sonication method [23]), (2) lipid compositions and drugs/lipids ratios (HPC and CH show superior properties compared to other lipids [19]), (3) edge activator types and concentrations (the effectiveness of edge activator follows Span 85 > Span 80 > Sodium cholate > Sodium deoxycholate > Tween 80 [23]), and (4) other formulation factors such as charge-inducing agents and sonication addition.
Table 1 shows that the amount of HPC and CH significantly affected the EL sizes. The particle sizes tended to increase as the amount of HPC increased. On the other hand, when the CH amount increased, the mean vesicle sizes decreased. This could be because HPC, a phospholipid, is the main backbone of the EL outer membranes, while CH influences the membrane’s mechanical properties by increasing their mechanical strength and enhancing the lipids packing density [24,25]. Thus, an increase of CH enhances the EL rigidity, consequently decreases their particle sizes. Generally, liposomes with a size of >600 nm cannot penetrate deeply through the skin and stuck in the stratum corneum, while vesicles with a size of ≤300 nm are ideal for transepidermal delivery [21]. Moreover, span 80 acts as a non-ionic surfactant and an edge activator that enhances vesicle deformability. The effect of its concentration on the liposome properties has been investigated elsewhere, and thus, was fixed in this study [13,14]. Conclusively, formulation with a HPC:CH:Span 80 ratio of 1.5:1.5:1 w/w/w (formulation 4), which possessed the smallest size of 316 ± 15 nm, was selected to encapsulate the NA.
Preparation and characterizations of the NA-loaded EL
The optimal formulation was used to encapsulate NA at 3 different amounts of 100, 150, and 200 mg, corresponding to the percentage of NA content of 1%, 1.5%, and 2% w/w, respectively. The particle properties are shown in Table 2 and Figure 1. Obviously, all 3 formulas demonstrated a mean particle size of ~300 nm, similar to that of the blank EL, indicating that the NA encapsulation did not affect the EL size. Additionally, a low PDI of less than 0.3 was observed, suggesting a narrow size distribution between EL particles [19]. It is worth to notice that although the EL was extruded 10 times through a 0.45-μm membrane, the PDI was still higher than 0.2, possibly due to the particle interactions and system behaviors. The system negatively surface charge of ~-20 mV, which comes from HPC, could enhance the EL stability [26]. Moreover, under polarized light microscope, all formulations proved the liposome lamellarity by illustrating Maltese cross-like structures, which confirms the success of EL fabrication (Fig. 1) [27].
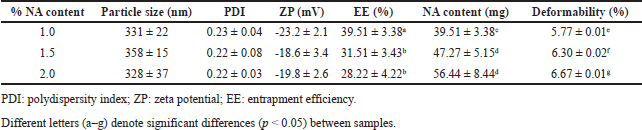 | Table 2. Physico-chemical characteristics of NA loaded EL composed of HPC:CH:Span 80 at the weight ratio of 1.5:1.5:1, with different NA content of 1%, 1.5%, and 2%. Data are shown as mean ± SD. [Click here to view] |
 | Figure 1. Optical micrographs of NA loaded EL composed of HPC:CH:Span 80 at the ratio of 1.5:1.5:1 w/w/w. Scale bar: 10 μm. [Click here to view] |
Interestingly, the NA initial amount was a parameter influencing the EE% (Table 2). As the initial amount of NA increased from 100 to 200 mg, the EE% significantly decreased from ~39.5% to ~30%. Correspondingly, the particle NA content (i.e., the amount of NA entrapped in the EL) increased from ~40 to ~50 mg. Noticeably, no significant difference was found between the 150- and 200-mg formulations, in terms of EE% and NA content, indicating the EL vesicles have reached their encapsulation limit for NA at the initial loading amount of 150 mg. Noticeably, the low EE% of NA in EL can be attributed to several factors, including the lipid compositions of EL, the inherent partitioning behavior of the particles, the EL sizes, and, especially, the hydrophilic nature of NA. Nevertheless, in this study, the EL formulated by the reverse phase evaporation technique attained higher NA EE% compared to the conventional method such as the film hydration technique [22].
The NA-loaded EL elasticity was revealed in terms of the deformability percentage. For this, the particle deformability significantly increased from 5.77% to 6.67% as the initial NA amount increased from 100 to 200 mg. A high deformability value (> 10%) indicates large differences in the liposome sizes prior and after extruding through a 100-nm membrane, possibly due to breaking and fragmentation into smaller particles. Thus, low deformability percentages, as shown in our results, are considered great elastic property, and appropriate for EL. Additionally, our data demonstrate that EL with higher NA contents possessed higher deformability index. This might be explained that the NA had some interactions with the EL lipid components, consequently making the membranes less elastic. Last but not least, the particles still preserved their physicochemical properties (i.e., size, PDI, zeta potential, EE%, and deformability) for 1-month storage at room temperature, indicating appropriate short-term stability.
In-vitro permeation study
Since NA is a hydrophilic compound [10] with inadequate skin permeation and absorption [11], we developed novel NA-loaded EL to potentially enhance NA skin permeability. To this end, three NA-loaded EL formulations, with different NA content, 1%, 1.5%, and 2%, were tested, in comparison with the control, 2% NA cream.
Two kinds of in-vitro permeation-test membranes, a synthetic 0.2-μm polycarbonate membrane and a natural porcine ear epidermis, were utilized and compared. The porcine tissues were selected because they have been confirmed to be similar with human skin [28]. For instance, the stratum corneum of both tissues composes of orthokeratotic stratified squamous epithelium with similar thickness of ~20 μm; the epidermis layers consist of basal keratinocytes with a thickness of ~72 μm; and the subcutis layers contain fat cells. Moreover, the hair follicles, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands are also very comparable between the porcine and human tissues [28]. This information suggests the study reliability and suitability as a model for human skin permeation test.
In both membranes, no significant burst release and permeation was observed, possibly due to the fact that NA has been incorporated into the EL, whereas the NA cream could not penetrate well into the skin tissue. For the synthetic membrane (Fig. 2A), the 1% NA-loaded EL formulation possessed a less NA content at the receptor chamber compared to the 1.5% and 2% NA-loaded EL, as well as the 2% NA cream. The results suggested a simple passive diffusion transport of NA through the membrane, which commonly depend on the drug concentration. The EL systems, with mean sizes of ~300 nm, could not squeeze through the 200-nm synthetic membrane. Thus, the detected NA was the NA released from the particles and passed through the membrane, but not the intact NA that was residing inside the EL. Consequently, the permeation data using the synthetic membrane were not reliable. Our data further contributed to the literature, which has demonstrated that the silicone synthetic membrane is not a predictive material of skin permeation in mammalian tissues [29].
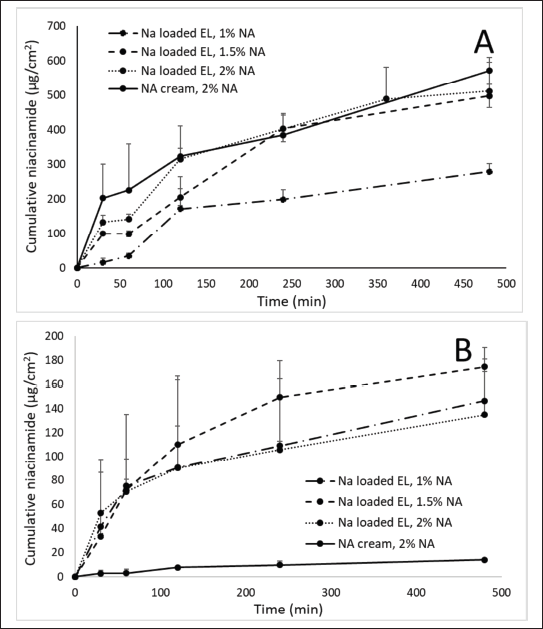 | Figure 2. In-vitro permeation profiles of 2% NA cream and NA loaded EL at different NA content of 1%, 1.5%, and 2%, using (A) synthetic 0.2-μm polycarbonate membrane and (B) natural porcine ear epidermis. Error bars show SD for n = 3. [Click here to view] |
Interestingly, when using the natural porcine epidermis, the 2% NA cream demonstrated almost no NA permeation (Fig. 2B), indicating that the free NA could not penetrate these layers due to its inherent hydrophilicity. On the other hand, all NA-loaded EL formulations showed >100-fold higher NA permeation than the 2% NA cream (the cumulative permeated NA of 2% NA cream and NA loaded EL 1%, 1.5%, and 2%, was averaged at 14.11, 146.25, 174.59, and 134.76 μg/cm2, respectively). For comparison, only one study has been reported on this issue, however, in that study, the total cumulative NA amount from NA-loaded EL permeated through the skin over 24 hours was only ~2.5 times higher than that of the 2% NA solution [9]. Hence, our formulation could better enhance the NA skin permeation and absorption. The result confirmed that 300-nm NA-loaded EL could be transported through the porcine epidermis, despites the fact that this epidermis having a pore-size of 0.4–100 nm [30]. The transepidermal penetration of EL could be explained by two possible pathways, the intercellular and the shunt pathway. The EL could squeeze intercellularly through the hydrophilic channels existed in the epidermis layers due to their high elasticity and deformability [31,32]. Moreover, owing to their nano-size, the increased drug transepidermal penetration could also be attributed to the delivery of intact NA-loaded EL via sweat glands and hair follicles that known as the shunt pathway [33,34].
Moreover, when fitted with the release and permeation of EL samples with various common models of zero-order, first-order, Higuchi, Hixson-Crowell, and Korsmeyer-Peppas (Table 3), the Higuchi model showed the highest R2 values of more than 0.9. A linear fit to the Higuchi model implies that the drug release is diffusion-controlled, which is often the case in topical formulations like creams and emulsions, as in our samples. Additionally, the steady-state flux (Js, calculated as Js = Qr/At, where Qr is the amount of permeated NA at steady state, A is the membrane area, and t is the permeation time at steady state) of the 2% NA cream, NA loaded EL 1%, 1.5%, and 2% was 1.760, 75.242, 71.744, and 70.520 μg/cm2h. The permeability coefficient (Kp, calculated as Kp = Js/C0, where C0 is the initial total NA concentration at the donor site) of these formulas was 0.088 × 10−3, 7.524 × 10−3, 4.783 × 10−3, and 3.526 × 10−3 cm/h, respectively. Indeed, both the Js and Kp of all EL formulas surpassed those of 2% NA cream, indicating the effective permeability of the particles across the epidermis layer. Interestingly, when compared between EL formulas with different NA amount (1%, 1.5%, and 2%), the Kp was independent with the drug concentration, while Js showed similar value. This could be explained by vesicle penetration via intercellular and shunt pathways may become saturated.
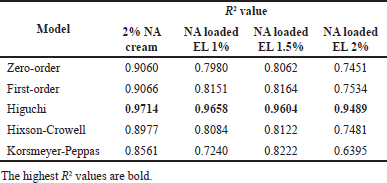 | Table 3. Fitted data on various models of the NA release and permeability on the porcine ear epidermis from NA cream and NA loaded EL samples. [Click here to view] |
Study limitations
The present study, although demonstrating interesting results, still has some limitations. First, the EE% values observed for NA (28%–39.5%) were relatively low. NA is a hydrophilic compound, thus, low lipid solubility inherently limits its entrapment within the lipid bilayers. Further improvements may be achieved through optimizations of (1) preparation methods, (2) lipid compositions and drugs/lipids ratios, (3) edge activator types and concentrations, and (4) other formulation factors such as charge-inducing agents and sonication addition. Second, stability is a key factor in the development of effective pharmaceutical formulations, especially for vesicular systems. Future research could incorporate long-term stability testing to assess the impact of various storage conditions, including different temperatures (i.e., 4ºC, 25ºC, and 40ºC) and freeze-thaw cycles, on vesicle integrity, EE%, and drug release/permeability characteristics. Third, although the porcine skin tissue closely mimics human skin morphology and permeability, its adsorption characteristics may still differ from human skin. Therefore, further validation with human skin models will be necessary for more accurate predictions of in-vivo performance. Finally, clinical studies on human skin and safety testing (i.e., irritability test, biocompatibility test) could be considered in future works, with required ethical clearance from an institutional review board and the collection of informed consent from all participants, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
CONCLUSION
In this study, novel NA-loaded EL were successfully prepared, physico-chemically characterized, and in-vitro permeability investigated. The optimal formulation possessed spherical shape particles with a mean size of ~300 nm, a zeta potential of ~-20 mV, an EE% of ~40%, and a deformability value of < 10%. Regarding the membrane suitability, the natural porcine ear epidermis closely resembled the human skin and was an ideal choice for the permeability test, whereas the synthetic 0.2-μm polycarbonate membrane was not appropriate. The NA-loaded EL showed more than 100-fold enhancement of NA in-vitro transepidermal delivery compared to the NA cream, at the same NA concentration. Conclusively, the newly developed EL demonstrate much potential in delivery hydrophilic molecules across skin.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
This work was financially supported by Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Naresuan University, Phitsanulok 65000, Thailand.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors reports no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
This study does not involve experiments on animals or human subjects.
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated and analyzed are included in this research article.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used artificial intelligence (AI)-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
REFERENCES
1. Bowes J, Piper J, Thiemermann C. Inhibitors of the activity of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase reduce the cell death caused by hydrogen peroxide in human cardiac myoblasts. Br J Pharmacol. 1998;124:1760–6. CrossRef
2. Gensler HL. Prevention of photoimmunosuppression and photocarcinogenesis by topical nicotinamide. Nutr Cancer. 1997;29:157–62. CrossRef
3. Shalita AR, Smith JG, Parish LC, Sofman MS, Chalker DK. Topical nicotinamide compared with clindamycin gel in the treatment on inflammatory acne vulgaris. Pharmacol Therap. 1995;34:434–7. CrossRef
4. Levin J, Momin SB. How much do we really know about our favorite cosmeceutical ingredients? J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010;3:22–41.
5. Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, Chhoa M, Matsubara A, Miyamoto K, et al. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:20–31. CrossRef
6. Tanno O, Ota Y, Kitamura N, Katsube T, Inoue SNicotinamide increases biosynthesis of ceramides as well as other stratum corneum lipids to improve the epidermal permeability barrier. Br J Dermatol. 2000;143:524–31. CrossRef
7. Matts PJ, Oblong JE, Bissett DL. A review of the range of effects of nacinamide in human skin. IFSCC Mag. 2016;5:285–9.
8. Namazi MR. Nicotinamide as a potential addition to the anti-atopic dermatitis armamentarium. Int Immunopharmacol. 2004;4:709–12. CrossRef
9. Lee MH, Lee KK, Park MH, Hyun SS, Kahn SY, Joo KS, et al. In vivo anti-melanogenesis activity and in vitro skin permeability of niacinamide-loaded flexible liposomes (bounsphere™). J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2016;31:147–52. CrossRef
10. Manela-Azulay M, Bagatin E. Cosmeceuticals vitamins. Clin Dermatol. 2009;27(5):469–74. CrossRef
11. Feldmann RJ, Maibach HI. Absorption of some organic compounds through the skin in man. J Invest Dermatol. 1970;54:399–404. CrossRef
12. Boo YC. Mechanistic basis and clinical evidence for the applications of nicotinamide (niacinamide) to control skin aging and pigmentation. Antioxidants. 2021;10:1–24. CrossRef
13. Kasetvatin C, Rujivipat S, Tiyaboonchai W. Combination of elastic liposomes and low frequency ultrasound for skin permeation enhancement of hyaluronic acid. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;135:458–64. CrossRef
14. Pan-On S, Rujivipat S, Ounaroon A, Kongkaew C, Tiyaboonchai W. Development, characterization and skin irritation of mangosteen peel extract solid dispersion containing clay facial mask. Int J Appl Pharm. 2018;10:202–7. CrossRef
15. Pham DT, Chokamonsirikun A, Phattaravorakarn V, Tiyaboonchai W. Polymeric micelles for pulmonary drug delivery: a comprehensive review. J Mater Sci. 2020a;56:2016–36. CrossRef
16. Pham DT, Saelim N, Tiyaboonchai W. Paclitaxel loaded EDC-crosslinked fibroin nanoparticles: a potential approach for colon cancer treatment. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2020b;10:413–24. CrossRef
17. Pham DT, Tiyaboonchai W. Fibroin nanoparticles: a promising drug delivery system. Drug Deliv. 2020c;27:431–48. CrossRef
18. Akbarzadeh A, Rezaei-Sadabady R, Davaran S, Joo SW, Zarghami N, Hanifehpour Y, et al. Liposome: classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013;8:1–9. CrossRef
19. Hussain A, Singh S, Sharma D, Webster TJ, Shafaat K, Faruk A. Elastic liposomes as novel carriers: recent advances in drug delivery. Int J Nanomed. 2017;12:5087–108. CrossRef
20. Benson HA. Elastic liposomes for topical and transdermal drug delivery. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;605:77–86. CrossRef
21. Iqbal B, Ali J, Baboota S. Recent advances and development in epidermal and dermaldrug deposition enhancement technology. Int Soc Dermatol. 2018;57:646–60. CrossRef
22. Chen G, Li D, Jin Y, Zhang W, Teng L, Bunt C, et al. Deformable liposomes by reverse-phase evaporation method for an enhanced skin delivery of (+)-catechin. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2014;40(2):260–5. CrossRef
23. El Zaafarany GM, Awad GA, Holayel SM, Mortada ND. Role of edge activators and surface charge in developing ultradeformable vesicles with enhanced skin delivery. Int J Pharm. 2010;397(1-2):164–72. CrossRef
24. Léonard A, Dufourc EJ. Interactions of cholesterol with the membrane lipid matrix. A solid state NMR approach. Biochimie. 1991;73:1295–302. CrossRef
25. Magarkar A, Dhawan V, Kallinteri P, Viitala T, Elmowafy M, Róg T, et al. Cholesterol level affects surface charge of lipid membranes in saline solution. Sci Rep. 2014;4:1–5. CrossRef
26. Moore TL, Rodriguez-Lorenzo L, Hirsch V, Balog S, Urban D, Jud C, et al. Nanoparticle colloidal stability in cell culture media and impact on cellular interactions. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44:6287–305. CrossRef
27. Vicit Rizal ES, Chung I, Misran M. Pegylated oleic acid-lecithin liposomes (poll) for anticancer drug delivery. Sains Malays. 2020;49:19–27. CrossRef
28. Jacobi U, Kaiser M, Toll R, Mangelsdorf S, Audring H, Otberg N, et al. Porcine ear skin: an in vitro model for human skin. Skin Res Technol. 2007;13:19–24. CrossRef
29. Haque T, Lane ME, Sil BC, Crowther JM, Moore DJ. In vitro permeation and disposition of niacinamidein silicone and porcine skin of skin barrier-mimetic formulations. Int J Pharm. 2017;30:158–62. CrossRef
30. Cevc G. Lipid vesicles and other colloids as drug carriers on the skin. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004;56:675–711. CrossRef
31. van den Bergh BA, Bouwstra JA, Junginger HE, Wertz PW. Elasticity of vesicles affects hairless mouse skin structure and permeability. J Control Release. 1999a;62:367–79. CrossRef
32. van den Bergh BA, Vroom J, Gerritsen H, Junginger HE, Bouwstra JA. Interactions of elastic and rigid vesicles with human skin in vitro: electron microscopy and two-photon excitation microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999b;1461:155–73. CrossRef
33. Verma A, Jain A, Hurkat P, Jain SK. Transfollicular drug delivery: current perspectives. Res Rep Transdermal Drug Deliv. 2016;5:1–17. CrossRef
34. Subongkot T, Wonglertnirant N, Songprakhon P, Rojanarata T, Opanasopit P, Ngawhirunpat T. Visualization of ultradeformable liposomes penetration pathways and their skin interaction by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Int J Pharm. 2013;441:151–61. CrossRef