INTRODUCTION
Insulin and its analogs are commonly utilized in diabetes treatment to regulate blood glucose levels. Various hosts have been utilized for insulin production [1–4]; however, Escherichia coli and yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) have remained the dominant hosts for human diabetes therapy’s recombinant human insulin (HI) production [5]. HI is generated as inclusion bodies in E. coli, thus necessitating solubilization and oxidative refolding of inclusion bodies [6]. In comparison, yeast has been utilized for the secretion of a properly formed, soluble insulin precursor (IP) in the culture supernatant [7,8].
In addition to the S. cerevisiae system, other yeast strains, including Hansenula polymorpha and Pichia pastoris, are commonly used for recombinant protein production [9]. Pichia pastoris is a methylotrophic yeast that has gained popularity as an alternative host for heterologous protein production due to its capability of achieving high cell densities and producing a substantial amount of recombinant proteins under the robust and tightly regulated methanol-inducible alcohol oxidase 1 promoter [10]. There are numerous reports that have employed P. pastoris for IP production [5,11–15].
HI comprises 51 amino acids (aa) arranged in two polypeptide chains: A (21 aa) and B (30 aa). The A and B chains are linked by two disulfide bonds, and the A chain contains one intra-disulfide bond. Production of a DesB30 insulin analog lacking the 30th aa (Thr) commonly found in HI is a common approach for HI production. This analog can be transformed into mature HI through enzymatic reactions [14–17]. Highly efficient expression of IP in P. pastoris was attained by replacing the original C-peptide with a short linker peptide and inserting the spacer peptide (EEAEAEAEPK) between the α-factor and IP, resulting in increased yields [8,18]. Proinsulin is not readily expressed in S. cerevisiae. Nonetheless, secretion efficiency increases significantly when the smaller IP is expressed. This IP comprises the first 29 residues of the insulin B chain and the 21 residues of the insulin A chain. Both chains are linked by the peptide sequence Ala-Ala-Lys (AAK), and this fusion protein is created with an appropriate prepro-leader [11]. Using a modified expression cassette, specifically for the truncated α-factor leader peptide and the short linker peptide Asp-Gly-Lys (DGK), we generated recombinant P. pastoris strains expressing IP [19].The molecular structure of IP and its conversion process to mature HI is shown in Figure 1. We further analyzed IP expression in both flask and bioreactor settings [20,21] utilizing our best-expressing clone, CL-4 [22]. In this study, we utilized LC-MS/MS analysis to characterize the secreted IP, produced the IP using the pulse-batch method, purified it, and transformed it into mature HI. The resulting product underwent LC-MS analysis and was tested for glucose uptake activity.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strain
A recombinant strain of P. pastoris (CL-4) containing the IP expression cassette [19] was employed in this research and was obtained from the wild-type P. pastoris X-33 strain [23].
IP production in shake flask
Shake flask protein production was carried out according to our previously optimized expression conditions [20], using buffered glycerol complex medium (BMGY)/buffered methanol complex medium (BMMY). Methanol induction was accomplished in BMMY medium by adding 100% methanol at a final concentration of 2% every 24 hours to maintain induction. After 72 hours of methanol induction, the resulting supernatant was collected in a separate tube and stored at −20°C until ready for assay. The secreted IP was then analyzed by mass spectrometry (MS) to determine its properties.
IP production in a bioreactor by the pulse-batch method
A flask pre-culture was prepared by inoculating 0.5 ml of glycerol stock of recombinant P. pastoris into 10 ml of YPD medium, composed of 10 g/l of yeast extract, 20 g/l of peptone, and 20 g/l of dextrose, which contained 100 µg/ml of Zeocin™. The culture was incubated in a shaking incubator at 30°C and 250 rpm for 24 hours. The cells were subsequently collected through centrifugation at 3,000 × g for 5 minutes at room temperature. Afterward, they were resuspended in a flask containing 100 ml of 50% basal salt medium (BSM). The composition of BSM to produce IP, as described by Wu et al. [24] (with slight modification), the solution was composed of 0.435% (v/v) trace salts, 8.7 × 10−5% (w/v) biotin, and 40 g/l glycerol. After 24 hours of incubation at 30°C and 250 rpm, the culture was transferred to a 2 l bioreactor (Eppendorf BioFlo®120) medium containing 50% BSM and 60 g/l glycerol in a total volume of 1 l. Biotin, trace salts, and antifoam were added to the culture at concentrations of 8.7 × 10−5% (w/v), 0.435% (v/v), and 0.01% (v/v), respectively. Temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), aeration, and agitation were all controlled. The culture temperature was maintained at 28°C through the use of a heating plate and circulating chilled water. The pH level was maintained at pH 5.0 by adding 12.5% (v/v) liquid ammonia and 1 M phosphoric acid. The airflow rate was set to 2 l/minute. Agitation speed was set at 300–500 rpm and cascaded with DO set at a minimum of 30%. Methanol induction was initiated in pulse mode after 24 hours of fermentation. Subsequently, methanol was added at a pulse mode at 50% (v/v) every 24 hours, gradually increasing from 3% to 5% (v/v). The addition of trace salts (1.2%) and biotin (2.4 × 10−4%) to the methanol feed was at a concentration of 12 ml per liter of 100% methanol. Samples were collected at baseline and every 24 hours of methanol induction. Subsequently, the culture broth was centrifuged at 7,825 × g and 4°C for 10 minutes followed by storage of the supernatant in separate tubes at −20°C for protein assays.
Purification and quantification of IP protein
The culture supernatant from both the shake flask and the 2 l bioreactor cultivation underwent filtration through a sterile filter with a pore size of 0.2 µm. Next, the filtrate from the shake flask was diluted in 20 mM sodium acetate, pH 4.0 (buffer A), while the filtrate from the 2 l bioreactor was diluted in MilliQ water. The pH was adjusted using 85% phosphoric acid to achieve a solution pH of 3.0. The sample solution was then injected into three 5 ml HiTrap SP-HP columns that were connected in series and operated at a flow rate of 6.5 ml/minute. The purification process involved several steps: an equilibration step using buffer A at a volume of 6 column volumes (CV; 1 CV = 5.027 ml), sample loading, a washing step using buffer A at a volume of 6 CV, a first elution step using buffer B [20 mM sodium acetate, pH 4.0, containing 50% (v/v) ethanol] at a volume of 7 CV, and a second elution step using buffer C (20 mM sodium acetate, pH 4.0, containing 50% [v/v] ethanol and 500 mM NaCl) at a volume of 10 CV. The flow rate used for equilibration and washing was 5.5 ml/minute, while it was reduced to 3 ml/minute during both elution steps. The column effluent was continuously monitored at a wavelength of 280 nm, and the eluted fractions were collected for further analysis.
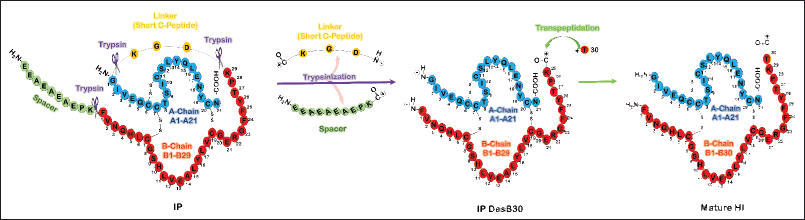 | Figure 1. Molecular structure of secreted IP produced in P. pastoris and its conversion to mature HI through transpeptidation process. The single chain IP consists of a spacer, B chain (1-29), short C peptide (DGK), and A chain (1-21). The single-chain IP fusion protein has correctly paired disulfide bonds. The intermediate product of DesB30 as a double-chain IP can be obtained from the IP fusion protein through a digestion process with trypsin that occurs at three sites. The DesB30 peptide serves as a crucial intermediate in the production of HI and its analogs. To obtain the final product of mature HI, a ThrB30 is coupled through a transpeptidation process, followed by preliminary purification, deprotection, and final purification [15]. [Click here to view] |
IP was quantified using a reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) method, equipped with an Agilent HPLC system featuring an autosampler and diode array detector (UV detector). The samples were filtered through a 0.2 µm filter and blended with an equal volume of mobile phase A [0.1% (v/v) trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) in MilliQ water]. This mixture was then loaded into a Jupiter Phenomenex C4 (300 Å, 250 mm l × 4.6 mm ID, 5 µm). Elution occurred at a flow rate of 0.8 ml/minute using mobile phases A and B, consisting of 0.1% (v/v) TFA in acetonitrile. The gradient method proceeded as follows: 15%–50% B (0–20 minutes), 50%–100% B (20–25 minutes), and 100% B (25–30 minutes). The column effluent was monitored at 214 nm while maintaining the column temperature at 25°C. A standard curve for quantification was generated utilizing bovine pancreatic insulin.
Protein analysis
The molecular weight of the elution fractions of the target IP protein purified by chromatography was determined using Tricine sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (Tricine SDS-PAGE) [25]. Electrophoresis was performed in Tris/Tricine/SDS running buffer at a constant voltage of 138 V for 120 minutes at room temperature. Separate polypeptides in the gel were stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 staining solution (Bio-Rad) for 1 hour. The gel was then destained with destaining solution I [53% (v/v) water, 40% (v/v) methanol, 7% (v/v) acetic acid] for 30 minutes, followed by destaining solution II [88% (v/v) water, 5% (v/v) methanol, 7% (v/v) acetic acid] overnight.
MS was performed for intact MS and peptide mapping analysis of IP and recombinant HI, respectively (U-Medico, Osaka University, Japan). The intact MS was performed to identify and confirm the total molecular weight of IP and HI without fragmentation. The subsequent peptide mapping analysis was performed to verify the primary structure of IP, including its aa sequence and chemical modifications. For both MS analysis, the solvent for the chromatography-purified IP target protein was replaced with 100 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.0, using Vivaspin 500 (VS0191, Sartorius). For intact MS, the sample solutions were then diluted in water containing 0.1% formic acid (FA) to a concentration of approximately 0.1 mg/ml. A 20 μl of each diluted sample solution was subjected to LC-MS. For analysis of putative recombinant HI protein, the sample was dissolved in MilliQ water, 0.01 N HCl or 0.01 N HCl containing 0.01% FA and 10% acetonitrile at a concentration of approximately 1 mg/ml in a 1.5 ml microtube. Since the samples were not completely solubilized, the supernatants were subjected to LC-MS after centrifugation (15,000 × g, 30 minutes, 5°C). The absorbance of the supernatants was confirmed using a spectrophotometer. LC (ExionLC, SCIEX) was performed under the following conditions. LC column: ACQUITY UPLC CSH C18, 1.7 μm, 130 Å, 2.1 mm × 150 mm (186005298, Waters); column temperature: 60°C; mobile phase A: 0.1% FA in water; mobile phase B: 0.1% FA in acetonitrile; flow rate: 0.3 ml/minute. The eluent was detected by a mass spectrometer (X500B QTOF system, SCIEX) equipped with an electrospray ion source in positive ion mode for m/z 350–3,000.
For peptide mapping analysis, the sample was digested with Glu-C (11420399001, Roche) overnight at 37°C, followed by adding TFA to a final concentration of 1% to complete the digestion. Approximately 3.5 μg of each digestion was subjected to LC-MS/MS. LC (ExionLC, SCIEX) was performed under the following conditions. LC column: ACQUITY UPLC CSH C18 column, 130 Å, 1.7 μm 2.1 mm × 150 mm (186005298, Waters); column temperature: 40°C; mobile phase A: 0.1% FA in water; mobile phase B: 0.1% FA in acetonitrile; flow rate: 0.3 ml/minute. In tandem MS (X500B QTOF system, SCIEX), the eluent was analyzed in positive ion mode using the SWASH method, with TOF MS scanning from 200 to 3,000 m/z followed by production scans from 100 to 1,800 m/z.
Conversion of IP to mature HI
The conversion procedures involved a transpeptidation reaction, deprotection, and purification steps following the previously reported IP conversion [15] with some modifications. The IP in the elution fraction of the cation exchange purification was subjected to a transpeptidation reaction with trypsin, H-Thr(tBu)-OtBu.AcOH, 41% (v/v) dimethylformamide, and CaCl2. The weight ratio of trypsin to IP and a molar ratio of IP to H-Thr(tBu)-OtBu.AcOH were 1:25 and 1:48, respectively. The final concentration of CaCl2 was 11 M. The solution’s pH was adjusted to pH 7.0 with Tris-base, and then MilliQ water was added to a final volume of 50 ml. The reaction was run for 24 hours at 20°C and then terminated by dilution with sodium acetate buffer to pH 5.0. In the first purification step, the transpeptidation product was applied to the reversed-phase chromatography (RPC) column (Cytiva; 3 ml CV), buffer pH 2.0 (buffer D). Protein was eluted by 0.3 ml/minute gradient elution of buffer D and E (0.1 M ammonium sulfate and 40% (v/v) 2-propanol) as follows: 0%–60% E (2.3 CV); 60% E (2.3 CV); 60%–75% E (4 CV); 75% E (0.3 CV); 75%–100% E (4.7 CV). Elution was monitored at 280 nm absorbance. The collected insulin ester fraction was crystallized by the addition of 2 mg ZnCl2 per mg IP. Crystallization was performed overnight at 4°C and pH 6.0. The insulin crystal was recovered by centrifugation at 5,000 × g and 4°C for 20 minutes. The tertiary butyl group of threonine was removed by the addition of 19 μl TFA per mg of IP. L-glutamine and L-tryptophan were each added at 0.05 mg per mg IP to prevent protein degradation and deamidation.
The mixture was incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes for a deprotection reaction. The mixture was then diluted in the second purification with 50 mM sodium sulfate buffer containing 10% (v/v) 2-propanol and 2% (v/v) acetic acid (buffer F). The solution was then applied to the RPC column (Cytiva; 3 ml CV), which was previously equilibrated with buffer F. Protein was eluted by 0.3 ml/minute gradient elution of buffer F and G (50 mM sodium sulfate; 50% (v/v) 2-propanol; 2% (v/v) acetic acid) as follows: 0%–18% G (0.1 CV); 18% G (1 CV); 18%–38% G (7.8 CV); 38%–100% G (0.5 CV). Elution was monitored at 280 nm absorbance. The collected HI fraction was stored at 4°C for further analysis and lyophilization.
In vitro study of recombinant HI
The putative recombinant HI fractions were then tested for activity against USP HI and IP using the glucose uptake assay method on C2C12 myoblast cells. The C2C12 myoblast cells were first differentiated into myotubes to perform the glucose uptake assay of HI through the following steps. The C2C12 myoblast cells maintained in the Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM)/15% fetal bovine serum (FBS) growth medium were seeded on a 24-well plate and incubated to form a confluent monolayer. The cells were induced to form myotubes by differentiation medium (DMEM/2% horse serum). On day 8 after differentiation, the cells were used for glucose uptake assays with the following treatment. First, the cells were starved in DMEM low glucose without FBS for overnight incubation. The cells were then incubated in Krebs-Ringer-Phosphate-HEPES buffer containing 2% BSA for 40 minutes and treated with 10 µM insulin. After 20 minutes of incubation, a D-glucose analog 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) was added and incubated for another 20 minutes. Cell lysates were then prepared to determine intracellular 2-DG uptake by the fluorometric method.
The activity of USP HI and 1C5 HI was also confirmed by sandwich ELISA (Elabscience) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Each of USP HI, 1C5 HI, and IP was added to an ELISA plate precoated with anti-HI antibody and incubated for 90 minutes. A biotinylated detection antibody was then added to each well and incubated for 60 minutes. Following a washing step, an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody was added. The addition of HRP substrate developed the signal from the antibody reaction. After 15 minutes of incubation and adding the stop solution, the optical density of each well was read at OD450 nm using a microplate reader. The absorbance of each well is correlated with the activity of HI.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Characterization of secreted IP by MS analysis
In the previous study, we characterized the recombinant P. pastoris clone (CL-4) harboring an IP expression cassette and IP expression in BMGY/BMMY at the flask scale. According to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis, the IP protein, secreted by the CL-4 strain, had an approximate molecular weight of 7 kDa [19,20]. Furthermore, we explored the CL-4 strain’s stability for IP expression, and the outcome revealed that the IP expression remained stable in culture media without ZeocinTM selection for over 70 generations [26]. The purified IP was analyzed using intact MS and peptide mapping techniques, supporting the SDS-PAGE and Western blot results that confirmed the molecular weight of IP (7072.10 Da) from our synthetic IP cassette in the recombinant CL-4 strain. In addition, peptide mapping revealed the correct single-chain IP aa sequence with its disulfide bridges with 100% protein sequence coverage. The findings from the flask-scale evaluation propose starting bioreactor-scale production of IP for additional analysis of IP’s purification and conversion to mature HI.
The IP protein’s molecular species, secreted by the recombinant P. pastoris strain, underwent intact MS analysis, which led to the identification. The highest intensity in the intact MS result (Fig. 2) belonged to a molecular species of 7072.10 Da, indicating dominance over the IP protein. The experiment affirmed that the IP protein produced by the recombinant P. pastoris strain corresponded to the theoretical molecular weight of the human IP aa sequence used in this study, which was calculated to be around 7072.86 Da. Besides, other IP species with a size of 7054.44 Da were also detected, corresponding to the theoretical molecular weight of the N-terminal pyro-Glu form of the IP with a molecular weight of 7054 Da.
Peptide mapping analysis identified the peptide sequence of the secreted IP, revealing two interchain disulfide bridges between the A and B chains, and one intrachain disulfide bridge in the A chain. Endoprotease Glu-C was utilized to digest the IP, and Figure 3A and B depict the simulation of the digestion results. The endoprotease Glu-C cleaves at the C-terminus of aspartic or glutamic acid residues and has seven digestion sites on a single chain IP, as shown in Figure 3A. The IP comprises three disulfide bridges, and digestion of 63 aa of IP with Glu-C produced five fragments: G1-4, G5G9, G6G10, G7, and G8, with disulfide bridges located at G5G9 and G6G10. Peptide mapping analysis using MS detected all five peptide fragments illustrated in Figure 3C, achieving complete protein sequence coverage. The peptide mapping analysis revealed the presence of both expected and scrambled disulfide bonds, as shown in Table 1.
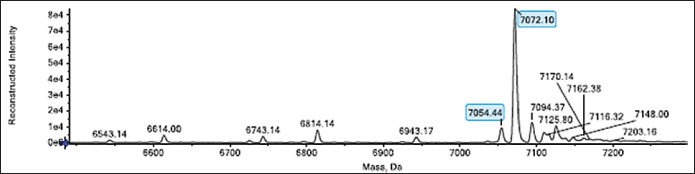 | Figure 2. Intact MS analysis of secreted IP. Molecular species of 7072.10 and 7054.44 Da are similar to the theoretical molecular weights of 7072.86 and 7054 Da corresponding to the unmodified and N-terminal pyro-Glu form, respectively, were detected. [Click here to view] |
Bioreactor production and purification of IP
After confirming the molecular mass of the secreted IP protein expressed in the shake flask to be similar to the theoretical size of IP, and confirming the aa sequence of IP via peptide mapping, we performed IP production on a larger scale using a pulse-batch method in a 2 l bioreactor (Eppendorf BioFlo-120). Previously, IP production at a bioreactor scale in 1 l culture was characterized for the CL-4 recombinant strain using a pulse-batch method [21]. A secreted IP of 0.4 g/l was achieved following 72 hours of methanol induction. To achieve high cell density cultivation, a 50% BSM growth medium was utilized in a 1 l total volume growth culture, as described by Wu et al. in [24] for the expression of IP DesB30. Methanol was added to the growth medium, and glycerol depletion occurred when the medium reached over 30% DO. After 72 hours of induction, the dry cell weight reached 161.5 g/l. The pH was maintained at 5.0 for both growth and induction cultures. Figure 4A displays the SDS-PAGE analysis of secreted IP from 0 to 72 hours post methanol induction, resulting in a single band size of approximately 7 kDa. The concentration of the IP band increased with longer induction times up to 72 hours. RP-HPLC was used to measure the amount of secreted IP, which was found to be 0.4 g/l after 72 hours of methanol induction (Fig. 4B).
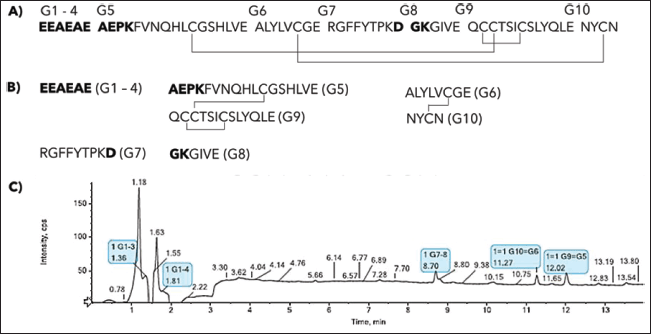 | Figure 3. Peptide mapping was performed on the secreted IP. The results include: (A) a single-chain structure of IP; (B) expected IP fragments that were digested by endoprotease Glu-C; and (C) a UV chromatogram of fragmented IP at 214 nm. The identified IP fragments are highlighted in light blue. The analysis detected peptide fragments (100% sequence coverage) and disulfide bonds of IP as expected. [Click here to view] |
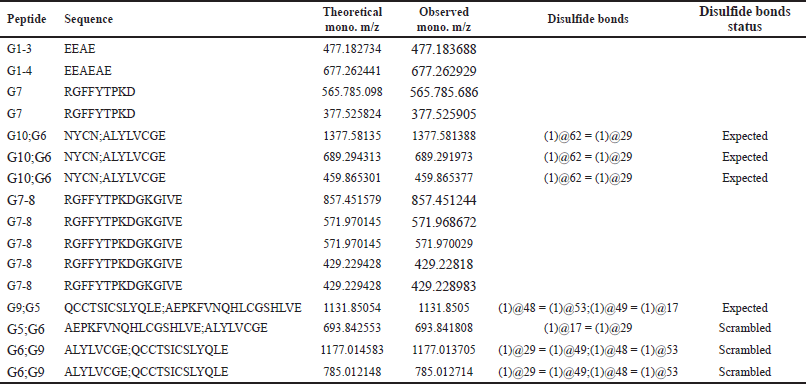 | Table 1. List of matched ions in the peptide mapping analysis of IP. [Click here to view] |
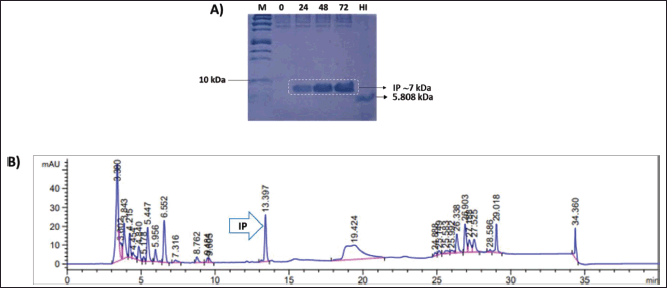 | Figure 4. (A) SDS-PAGE gel image of IP produced from bioreactor using 50% BSM medium. Samples were collected at 0, 24, 48, and 72 hours after methanol induction. M = Precision plus protein™ Dual xtra prestained protein standard (BioRad); HI = USP HI standard (MilliporeSigma; 5808 Da); (B) RP-HPLC profile of culture supernatant at 72 hours post-methanol induction. The secreted IP was found at a retention time of 13.397 minutes. [Click here to view] |
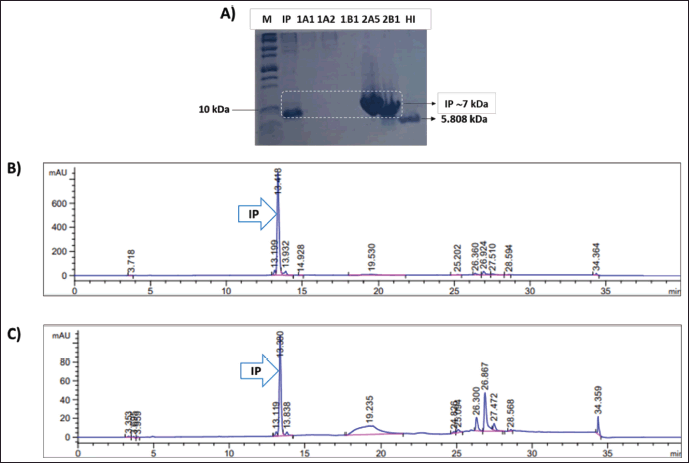 | Figure 5. (A) SDS-PAGE gel image of purified IP by cation exchange chromatography. M = Precision plus protein™ Dual xtra prestained protein standard (BioRad); IP = secreted IP 72 hours after methanol induction; 1A1, 1A2, and 1B1: flow-through fractions of IP purification; 2A5 and 2B1: elution fractions of IP purification; HI: USP HI standard (MilliporeSigma; 5808 Da); (B); and (C) RP-HPLC profiles of elution fractions 2A5 and 2B1, respectively. [Click here to view] |
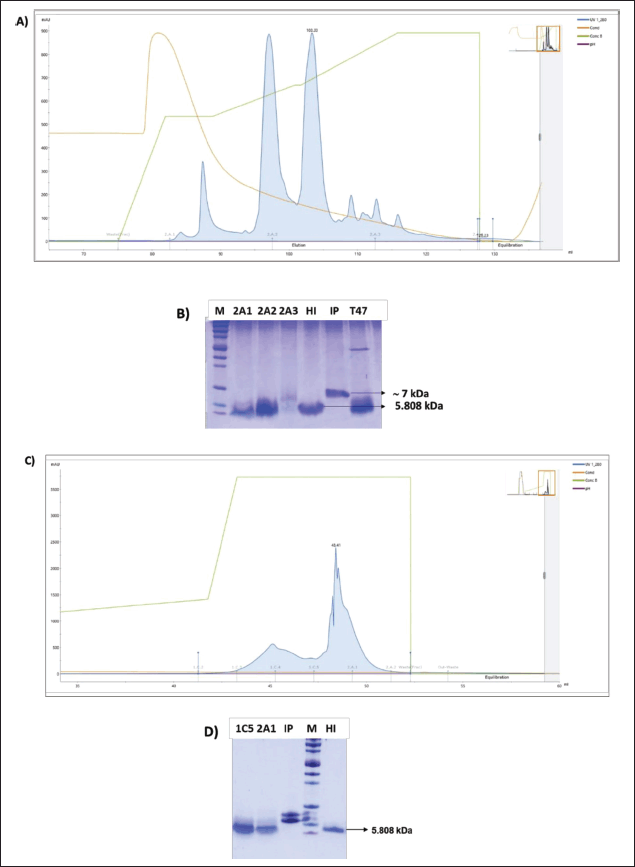 | Figure 6. (A) RPC-1 profile of IP conversion into mature HI; (B) SDS-PAGE confirmation of RPC-1 elution fractions 2A1, 2A2, and 2A3. T47: Transpeptidation reaction after 47 hours incubation; (C) RPC-2 profile of putative HI; (D) SDS-PAGE confirmation of RPC-2 elution fractions 1C5 and 2A1. M: Precision plus protein™ Dual xtra prestained protein standard (BioRad); IP: secreted IP 72 hours after methanol induction; HI: USP HI standard (MilliporeSigma; 5808 Da). [Click here to view] |
To achieve a high purification yield of IP, we optimized the purification process by evaluating various parameters, including sample loading concentration, loading flow rate, and pH of the loaded samples. The highest yield obtained was approximately 47% [27]. As part of this study, we modified the purification process by diluting with MilliQ water to lower the conductivity and pH of the loaded sample (pH 3.0) compared to our previous study, which used pH 3.0–4.0 of the loaded sample. To enhance the capture of the IP from the culture supernatant, we connected three 5 ml HiTrap SP-HP columns in series. Using the ÄKTA Avant purification system, we purified the IP protein present in the culture supernatant through cation exchange chromatography. One ion exchange chromatography method was utilized to isolate the IP protein by exploiting differences in ionic charge with respect to other proteins [15]. The culture supernatant was filtered and adjusted from pH 5.0 to pH 3.0 by adding the 85% phosphoric acid and then diluting it with MilliQ water twice to attain a positive charge state for the target IP protein. The negative-charged SP column resins capture the IP protein for purification utilizing the ÄKTA Avant purification system. The five-step procedure involves equilibration, sample loading, washing, initial elution, and elution. Collected IP proteins in a batch purification were ~255 mg from 700 ml culture supernatant with a purification recovery of ~90%. The IP protein was successfully purified, as demonstrated in Figure 5, with a retention time of 13.38 minutes and fewer nontarget proteins observed in the RP-HPLC profile when compared to the crude culture supernatant RP-HPLC profile depicted in Figure 4.
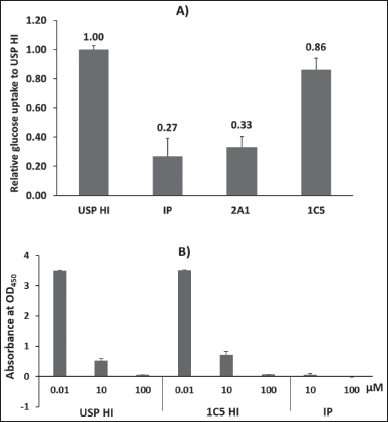 | Figure 7. (A) Glucose uptake assay of putative HIs 2A1 and 1C5 using C2C12 muscle cell myotubes. The potency of the recombinant HI was compared as its relative glucose uptake ability to USP HI; (B) ELISA analysis of 1C5 HI compared to USP HI. [Click here to view] |
A purification recovery of 90% was achieved in this study by adding ethanol to the elution buffer during cation exchange chromatography. Previous research has shown that organic solvents can prevent the formation of dimers and hexamers of IP [28] and improve the catalytic properties of enzymes [15]. Polez et al. [15] demonstrated insulin production through ethanol use during IP purification, by passing buffer exchange and lyophilization steps. However, in our study, we performed buffer exchange and lyophilization of purified IP for sufficient concentration in a one-step transpeptidation process.
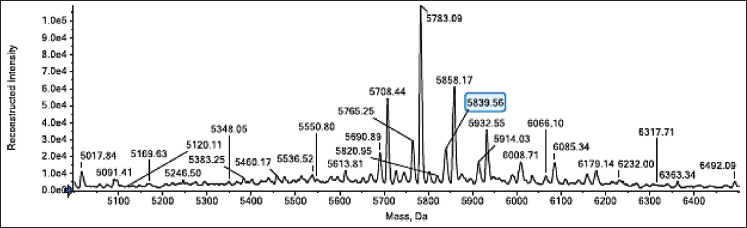 | Figure 8. Intact MS of RPC-2 elution fraction 1C5. A molecular species with a molecular weight of 5839.56 Da was detected in fraction 1C5, which is 0.02 Da less than the theoretical value of HI when two aa with a molecular weight of 5839.58 Da are oxidized. [Click here to view] |
Conversion of IP to mature HI
The IP conversion to mature HI consists of four steps: transpeptidation, preliminary purification, deprotection, and final purification. The transpeptidation reaction was
performed by reacting IP powder from purification, dialysis, and lyophilization up to 129 mg with trypsin, H-Thr(tBu)- OtBu.AcOH, dimethylformamide, and CaCl2 under excess conditions. The reaction was performed in a 15 ml centrifuge tube in a closed state and incubated on a thermal block at 20°C. The transpeptidation reaction was carried out for 47 hours, and the pH was adjusted to pH 7.0 with Tris base. The transpeptidation reaction was stopped by adding a 100 mM acetate buffer to pH 5.0. The first purification step of the 47 hours transpeptidation results (HI ester) was performed using a 3 ml RPC Resource column (Cytiva) (RPC-1) (Fig. 6A and B). The HI ester was crystallized with ZnCl2 at a pH of 6.0 and left to react overnight at 4°C. Insulin crystals were separated through centrifugation at 5,000 × g for 20 minutes at 4°C. The tertiary-butyl of threonine was removed using TFA, and L-glutamine and L-tryptophan were subsequently added to prevent protein degradation and deamidation. After deprotection, the reaction mixtures were diluted with buffer C. The sample underwent RPC-2 as shown in Figure 6C and D.
The RPC-2 fraction was dialyzed and lyophilized, resulting in a putative dry weight of 19.3 mg, which was divided between 1C5 and 2A1. Both lyophilized putative HI 1C5 and 2A1 fractions underwent in vitro glucose uptake analysis.
In vitro assay and MS analysis of the putative recombinant HI
The activity of several putative recombinant HI fractions (IC5 and 2A1) obtained from the final purification step was tested together with the USP IP using the glucose uptake fluorometric assay (GUFA). The GUFA method uses the D-glucose analog 2-DG. After entering the cell, 2-DG will undergo an enzymatic reaction with the enzyme hexokinase to produce 2-deoxy-D-glucose-6-phosphate (2DG6P), which accumulates intracellularly. Cell lysates containing 2DG6P are oxidized to produce NADPH that will couple with a fluorescence probe to produce a fluorescence signal (excitation/emission = 535/587 nm). This signal correlates directly with the amount of glucose that enters and accumulates within cells. The study assessed the biological potency of HI compared to the USP HI, based on glucose metabolism [29]. Insulin-mediated glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle is critical for maintaining glucose homeostasis, serving as an energy source for muscle contraction [30,31]. Carbohydrate molecules, including glucose, cannot pass through muscle cell membranes. Glucose entry into muscle cells is facilitated by glucose transporters, specifically GLUT1 and GLUT4 [32]. Insulin, an essential hormone, lowers blood glucose levels by inducing intracellular insulin signaling, which promotes the translocation of glucose transporters to the cell membrane. Thus, glucose uptake increases [33]. Our study evaluated the potency of putative recombinant HI activity using C2C12 myoblast cells. The C2C12 cells are adult muscle stem cells capable of proliferation, migration, and differentiation in an in vitro setting [34].
The myotube, which is produced through myoblast differentiation, serves as an in vitro model for skeletal myofibers and exhibits physiological similarity in the uptake of glucose from the extracellular environment by expressing GLUT1 and GLUT4 [32,35]. Glucose uptake analysis of the RPC-2 fractions indicates that the 1C5 fraction effectively enhances glucose uptake by muscle cells. This finding is in line with the intact MS outcome, which identifies the mature HI solely in the 1C5 fraction. The ELISA confirmed that the activity of 1C5 HI was comparable to that of USP HI. According to Figure 7A, the 1C5 fraction demonstrated a glucose uptake activity with a sequential efficacy of 0.86 when compared to the USP HI as control. In the meantime, the 2A1 fraction displayed similar activity to IP.
The ELISA analysis presented in Figure 7B shows no significant difference in the absorbance of the tested USP HI and 1C5 HI at the same concentration. On the other hand, IP demonstrated no activity. These findings were consistent with the in vitro glucose uptake data that 1C5 HI had in vitro activity comparable to USP HI.
Further analysis through intact MS was only performed for the 1C5 fraction which revealed that it contains molecular species of mature HI with a molecular weight of 5839.56 Da which is similar to the theoretical value of HI when two aa with a molecular weight of 5839.58 Da are oxidized (Fig. 8). On the other hand, the mass analysis for the 2A1 fraction was not performed due to the in vitro result showing no activity for glucose uptake.
CONCLUSION
This study attempts to address the future demand for insulin in Indonesia, where the number of people with diabetes has reached 19.5 million in 2021, according to the International Diabetes Federation data [36]. Recombinant HI is currently produced commercially using E. coli and yeast-based systems (particularly S. cerevisiae). In the E. coli system, IP is overexpressed in the form of inclusion bodies, which require solubilization and oxidative refolding [6]. In contrast, the yeast-based expression system secretes soluble IP into the culture supernatant, where it is converted into HI through enzymatic reactions. Saccharomyces cerevisiae lacks the ability to efficiently express recombinant proteins without over-glycosylation [5]. An alternative yeast expression system, P. pastoris, shares common features with eukaryotes which ensure proper protein folding, processing, and post-translational modifications. Pichia pastoris is also preferred due to its inexpensive culture medium, fast growth rate, easy purification, and high secretory ability. The P. pastoris system was utilized in this study to produce IP. The IP produced has a molecular weight of 7072.10 Da, which is similar to its theoretical molecular weight (7072.86 Da). The current yield of IP production in a 1 l bioreactor was approximately 0.4 g/l, which is lower compared to other studies at similar or larger scales. However, it is expected that the yield will improve at higher production scales. The subsequent conversion of the produced IP resulted in a small amount of mature HI. This HI was confirmed to be effective in inducing myotube cells to take up glucose.
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
BMGY: Buffered glycerol complex medium; BMMY: Buffered methanol complex medium; BSM: Basal salt medium; 2-DG: 2-deoxy-D-glucose; 2DG6P: 2-deoxy-D-glucose 6-phosphate; GUFA: Glucose uptake fluorometric assay; HI: Human insulin; IP: Insulin precursor; MS: Mass spectrometry; RP-HPLC: Reversed-phase HPLC; RPC: Reversed-phase chromatography; TFA: Trifluoroacetic acid
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors would like to thank Prof. Susumu Uchiyama (Osaka University; U-Medico, Osaka, Japan), Dr. Ayano Fukuhara (U-Medico, Osaka, Japan), Dr. Masanori Noda (U-Medico, Osaka, Japan), Dr. Kayoko Hayashihara (U-Medico, Osaka, Japan), and Dr. Masami Yokoyama (U-Medico, Osaka, Japan) for valuable discussion regarding IP purification and conversion and continuous assistance in the MS analysis.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to the conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be authors according to the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
This study was supported by RISET PRO-LPDP (No. 245/G/KPT/TAHUN 2019, Indonesia), RISPRO-LPDP Mandatory (No. KEP-32/LPDP/2020, Indonesia), and DIPA Research Organization of Life Sciences and Environment-National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN) (No. 9/III/HK/2022, Indonesia).
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors report no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICS APPROVALS
This research does not involve experiments on animals or human subjects.
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used artificial intelligence (AI)-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
REFERENCES
1. Yanagita M, Nakayama K, Takeuchi T. Processing of mutated proinsulin with tetrabasic cleavage sites to bioactive insulin in the non-endocrine cell line, COS-7. FEBS Lett. 1992;311:55–9. CrossRef
2. Arakawa T, Yu J, Chong DKX, Hough J, Engen PC, Langridge WHR. A plant-based cholera toxin B subunit-insulin fusion protein protects against the development of autoimmune diabetes. Nat Biotechnol. 1998;16:934–8. CrossRef
3. Nykiforuk CL, Boothe JG, Murray EW, Keon RG, Goren HJ, Markley NA, et al. Transgenic expression and recovery of biologically active recombinant human insulin from Arabidopsis thaliana seeds. Plant Biotechnol J. 2006;4:77–85. CrossRef
4. Boyhan D, Daniell H. Low-cost production of proinsulin in tobacco and lettuce chloroplasts for injectable or oral delivery of functional insulin and C-peptide. Plant Biotechnol J. 2011;9:585–98. CrossRef
5. Baeshen MN, Bouback TAF, Alzubaidi MA, Bora RS, Alotaibi MAT, Alabbas OTO, et al. Expression and purification of C-peptide containing insulin using Pichia pastoris expression system. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:2005–8. CrossRef
6. Nilsson J, Jonasson P, Samuelsson E, Ståhl S, Uhlén M. Integrated production of human insulin and its C-peptide. J Biotechnol. 1996;48:241–50. CrossRef
7. Thim L, Hansen MT, Norris K, Hoegh I, Boel E, Forstrom J, et al. Secretion and processing of insulin precursors in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986;83:6766–70. CrossRef
8. Kjeldsen T. Yeast secretory expression of insulin precursors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2000;54:277–86. CrossRef
9. Baeshen NA, Baeshen MN, Sheikh A, Bora RS, Ahmed MMM, Ramadan HAI, et al. Cell factories for insulin production. Microb Cell Fact. 2014;13:1–9. CrossRef
10. Ahmad M, Hirz M, Pichler H, Schwab H. Protein expression in Pichia pastoris: recent achievements and perspectives for heterologous protein production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;98:5301–17. CrossRef
11. Kjeldsen T, Pettersson AF, Hach M. Secretory expression and characterization of insulin in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1999;29(1):79–86.
12. Wang Y, Liang ZH, Zhang YS, Yao SY, Xu YG, Tang YH, et al. Human insulin from a precursor overexpressed in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris and a simple procedure for purifying the expression product. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2001;73:74–9. CrossRef
13. Xie T, Liu Q, Xie F, Liu H, Zhang Y. Secretory expression of insulin precursor in Pichia pastoris and simple procedure for producing recombinant human insulin. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2008;38:308–17. CrossRef
14. Gurramkonda C, Polez S, Skoko N, Adnan A, Gäbel T, Chugh D, et al. Application of simple fed-batch technique to high-level secretory production of insulin precursor using Pichia pastoris with subsequent purification and conversion to human insulin. Microb Cell Fact. 2010;9:1–11. CrossRef
15. Polez S, Origi D, Zahariev S, Guarnaccia C, Tisminetzky SG, Skoko N, et al. A simplified and efficient process for insulin production in Pichia pastoris. PLoS One. 2016;11:1–15. CrossRef
16. Liu H, Zhou X, Tian S, Hao X, You J, Zhang Y. Two-step transpeptidation of the insulin precursor expressed in Pichia pastoris to insulin ester via trypsin-catalyzed cleavage and coupling. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2014;61:408–17. CrossRef
17. Morihara K, Ueno Y, Sakina K. Influence of temperature on the enzymic semisynthesis of human insulin by coupling and transpeptidation methods. Biochem J. 1986;240:803–10. CrossRef
18. Kjeldsen T, Ludvigsen S, Diers I, Balschmidt P, Sorensen AR, Kaarsholm NC. Engineering-enhanced protein secretory expression in yeast with application to insulin. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:18245–8. CrossRef
19. Nurdiani D, Hariyatun H, Kusharyoto W. Secretory expression of human insulin precursor in Pichia pastoris employing truncated α-factor leader sequence and a short C-peptide. Indones J Biotechnol. 2018;23:102–8. CrossRef
20. Nurdiani D, Hariyatun H, Utami N, Putro EW, Kusharyoto W. Enhancement in human insulin precursor secretion by Pichia pastoris through modification of expression conditions. HAYATI J Biosci. 2021;29:22–30. CrossRef
21. Putro EW, Nurdiani D, Hariyatun H, Utami N, Kusharyoto W, Juanssilfero AB, et al. Evaluating pulses and modified fed-batch feeding of methanol to increase expression level of human insulin precursor in Pichia pastoris high-density cultivation. Int J Adv Sci Eng Inf Technol. 2022;12:1001–7. CrossRef
22. Nurdiani D, Hariyatun H, Utami N, Wahyu Putro E, Kusharyoto W. Selecting Pichia pastoris recombinant clones for higher secretion of human insulin precursor into the culture supernatant. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. 2020;439:012017. CrossRef
23. Invitrogen Corporation. User manual—EasySelectTM Pichia Expression Kit. Life Technol Rev. 2010; Manual part no. 25-0172: MAN0000042.
24. Wu J, Gong G, Han S, Zhang W, Hu Y, Xie L. Expression, purification, and characterization of the degludec precursor DesB30. Protein Expr Purif. 2019;161:28–39. CrossRef
25. Haider SR, Reid HJ, Sharp BL. Tricine-SDS-PAGE. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;869:81–91. CrossRef
26. Nurdiani D, Hariyatun H, Utami N, Putro EW, Kusharyoto W. Stability analysis of a Pichia pastoris recombinant clone expressing human insulin precursor. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. 2020;572:012008. CrossRef
27. Putro EW, Nurdiani D, Hariyatun H, Utami N, Kusharyoto W. Capture and intermediate purification of human insulin precursor from Pichia pastoris culture using cation exchange chromatography. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. 2021;762:012028. CrossRef
28. Liu H, Zhou X, Xie F, You J, Zhang Y. An efficient trypsin digestion strategy for improving DesB30 productivity from recombinant human insulin precursor fusion protein. Process Biochem. 2013;48:965–71. CrossRef
29. Hack R, Rueggeberg S, Schneider L, Mayert D, Tennagels N, Welte S, et al. Progress towards the replacement of the rabbit blood sugar bioidentity assay by an in vitro test for batch release of insulins in quality control. ALTEX. 2017;34:565–6. CrossRef
30. Hulett NA, Scalzo RL, Reusch JEB. Glucose uptake by skeletal muscle within the contexts of type 2 diabetes and exercise: an integrated approach. Nutrients. 2022;14. CrossRef
31. Stump CS, Henriksen EJ, Wei Y, Sowers JR. The metabolic syndrome: role of skeletal muscle metabolism. Ann Med. 2006;38:389–402. CrossRef
32. Evans PL, McMillin SL, Weyrauch LA, Witczak CA. Regulation of skeletal muscle glucose transport and glucose metabolism by exercise training. Nutrients. 2019;11:1–24. CrossRef
33. Leney SE, Tavaré JM. The molecular basis of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake: signalling, trafficking and potential drug targets. J Endocrinol. 2009;203:1–18. CrossRef
34. Wong CY, Al-Salami H, Dass CR. C2C12 Cell model: its role in understanding of insulin resistance at the molecular level and pharmaceutical development at the preclinical stage. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2020;72:1667–93. CrossRef
35. Sarabia V, Lam L, Burdett E, Leiter L, Klip A. Glucose transport in human skeletal muscle cells in culture. J Clin Invest. 1992;90:1386–95. CrossRef
36. International Diabetes Federation-IDF. Indonesia diabetes report 2000–2045. 10th ed. Brussels, Belgium: IDF Diabetes Atlas [Internet]; 2021 [updated 2022; cited 2024 Apr 01]. Available from: https://diabetesatlas.org/data/en/country/94/id.html