INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus is a serious worldwide prevalent chronic disease. It is characterized by remarkable elevations in blood glucose levels. Disruption of glucose metabolism in cells could be due to lack of pancreatic insulin production or lack of the ability of the cells to effectually utilize the produced insulin (Roglic, 2016). The global prevalence of diabetes in the year 2019 was estimated at 9.3% (463 million people), with expected rising to 10.2% and 10.9% affecting 578 and 700 million people by year 2030 and 2045, respectively (Saeedi et al., 2019).
According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), Egypt is listed among the top 10 countries for the number of diabetic individuals between the ages of 20 and 79 years, with a diabetes national prevalence of around 15.2%. The number of diabetic patients in 2019 was estimated at 8.9 million, and is expected to rise to 11.9 and 16.9 million by 2030 and 2045, respectively (IDF, 2019). In Egypt, diabetes is the major cause of loss of vision, with estimations of patients having diabetic retinopathy (42%), legally blind (5%), and peripheral neuropathy (22%). In addition, diabetes is the leading cause of leg amputation and end-stage renal disease in Egypt (Hegazi et al., 2015).
Despite the great global approaches for the prevention and control of diabetes, it will continue to pose a huge burden on economies and healthcare systems by 2030 (Bommer et al., 2018). Therefore, the need for effective novel therapies to control blood glucose is essential for the prevention of the complications of diabetes and improvement of the patient’s quality of life. Initial management often includes change in lifestyle, such as diet and exercise, but in many cases, drug therapy is also required with disease progress (Marín-Peñalver et al., 2016). However, many medications for diabetes are often associated with side effects, such as weight gain (Verhaegen and Van Gaal, 2019). Thus, the development of novel alternative approaches is of a great significance; also, natural products that can manage blood glucose levels in patients without remarkable side effects are receiving substantial attention.
Marine biological systems represent a huge reservoir of massive chemical entities with potential biological activities that can lead to remarkable novel bioactive candidates (Alsterberg et al., 2017).
In fact, the broad range of uses of marine fungi is ascribed to their ability to produce a tremendous number of so-called secondary metabolites with remarkable pharmacological applications (Rateb and Ebel, 2011).
Researches, in the last few years, have revealed new pharmacologically active compounds isolated from sponges and soft corals accompanying fungi secondary metabolites. They were evaluated for their antimicrobial, anticancer, and other numerous biological activities (Abd El-Hady et al., 2014; 2015)
Marine species-associated fungi produce bioactive secondary metabolites that are considered a good source for exploration of more potent marine lead drugs. The investigation of safer α-glucosidase inhibitors from marine species-associated microorganisms constitutes a source of attraction for many scientists where the inhibition of the membrane-bound α-glucosidase enzyme is considered one of the effective strategies to regulate blood sugar of diabetic patients through delaying its intestinal absorption (Liu et al., 2018).
Novel bioactive metabolites discovered from the Red Sea constitute a continuous challenge to investigate potential compounds for new medicinal products (Nadeem et al., 2015). To our knowledge, there are few researches on the investigation of diverse biological activities of the sponge-associated fungi in the Red Sea region of Egypt and their therapeutic effect, especially on diabetes.
So, the current study aimed to isolate and identify sponge-associated fungus from the Red Sea, as well as to determine the potential antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of their secondary metabolites with concomitant gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) analysis for the promising biologically active extract(s).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sponge materials
Sponge (Agelas sp.) was gathered from the coast of Hurghada, Red Sea, Egypt (Shaab al-Ariq; latitude, N 27° 25? 08.9″, E 33° 51? 0.5″) and specimens were gathered at depths of 5–8 m and kept in the refrigerator at 4°C until use. The morphological classification of sponges was determined by Mohamed Abdel Ghani, Environmental Researcher, Red Sea marine parks, Hurghada, Red Sea, Egypt.
Preparation of sponge material and isolation of fungi
The isolation of fungi from the sponge samples was carried out according to Manilal et al. (2010). Minute pieces of the inner tissue of the sponge, fresh sample, were cleaned by washing with autoclaved seawater; the sterilized sponge was divided into minor chops (0.5 cm3 each). Several parts from each sample were placed on the appropriate isolation media. Another technique used for the isolation of fungi from sponge had been achieved by aseptical homogenization and dilution of the homogenate, and each dilution was used to inoculate the appropriate fungal isolation media. The inoculated media were placed at 30°C for 7–14 days and the appeared pure fungal colonies were picked up (Subramani et al., 2013).
Molecular identification of the fungal isolates
The potent fungus was molecularly identified by the 18S rRNA technique through DNA extraction, followed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, and the sequencing was carried out through the universal fungal Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) genes (Papagianni and Mattey, 2004). The PCR primers used were ITS2 and ITS3, but primers ITS1 and ITS4 were used for sequencing.
Screening media
Three different screening liquid media were used to cultivate the selected fungus: (a) Sabouraud broth, which has dextrose (20 g/l) and peptone (10 g/l); (b) potato dextrose broth, having dextrose (20 g/l) and potato infusion from 200 chipped potatoes; and (c) malt extract broth, which has yeast extract (3 g/l) and malt extract (17 g/l). Eight conical flasks of 1 l volume, each filled with 200 ml from each broth medium, were cultivated with spore suspensions from one slant of the fungus Aspergillus unguis isolate SP51-EGY. The cultivated flasks were incubated under shake and static conditions at 30°C for 12 days.
Preparation of fungal extracts
Fungal cultures were first centrifuged at 8,000 rpm at 4°C to get rid of the mycelia using cooling centrifuge (Centurion Scientific Ltd model K2015R, UK). The culture supernatants (mycelial-free) were extracted with ethyl acetate (EtOAc) and then dried under vacuum. At the same time, acetone and ethyl acetate were used to extract the fungal mycelia (Abd El-Hady et al., 2016). The produced extracts were abbreviated as shake filtrate (Sh filtrate) extract, shake mycelia (Sh mycelia) extract, static filtrate (St filtrate) extract, and static mycelia (St mycelia) extract.
In-vitro α-glucosidase inhibition assay
The inhibitory activities of all extracts against α-glucosidase were examined in vitro using the standard method with small changes (Sancheti et al. 2011).
The inhibitory activity of α-glucosidase was calculated as follows:
% Inhibition = [(Ac–Ax)/Ac] × 100
where Ac is control absorbance and Ax is sample absorbance.
GC/MS) analysis
Dry extract (1.5 mg) and 20 μl pyridine were mixed well; then, 30 μl of N,O-bis-(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide was added and heated at 80°C for 30 min. Finally, GC/MS analysis was performed (Greenaway et al., 1991).
A mass spectrometer (Finnigan MAT SSQ 7000) was attached to a Varian 3400 gas chromatograph. The DB-5 column had an internal diameter of 30 m x 0.32 mm; the carrier gas was helium (He pressure, 20 Mpa/cm2); 310°C was the injector temperature; 85–310°C at 3°C/minute (10 minutes initial hold) was GC temperature program; and EI mode was at 70 eV. The scan repetition rate was 0.5 s over a mass range of 39–650 amu.
Computer search user-generated reference libraries (NIST and WILEY) incorporating mass spectra were used for identification. Peaks were inspected by single-ion chromatographic reconstruction to authorize their homogeneity. Occasionally, and in case if identical spectra were not created, only the structural type of the corresponding component was proposed based on its mass spectral fragmentation. Reference compounds were co-chromatographed when possible to confirm GC retention times.
In vivo pharmacological evaluation
The extracts that demonstrated the highest significant in vitro α-glucosidase inhibitory activity were used in the in vivo pharmacological studies. Therefore, Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts from medium C were further assessed for their in vivo antidiabetic potential.
Animals
Male albino mice, 25–30 g, were obtained from the National Research Centre Animal House. Mice were housed in wire mesh plastic cages and kept under standard laboratory conditions of room temperature (23 ± 2°C), relative humidity (55 ± 5%), and 12 hour light /12 hour dark cycle. Mice were fed s standard pellet diet and allowed free access to tap water. All animal experiments were carried out according to the Medical Research Ethics Committee of the National Research Centre (Decision No.: 20184).
Determination of acute toxicity
The Sh mycelia and Sh filtrate extracts were administered orally to male Albino mice in ascending and widely spaced dose ranges (100–4,000 mg/kg body weight). Each treated group was observed for clinical signs and symptoms for 14 days. Then, the mortality rate was recorded and LD50 was calculated (Litchfield and Wilcoxon, 1949)
Experimental design
Induction of diabetes
Diabetes was induced chemically in overnight food-deprived mice according to the method of Phelan et al. (1997). In three successive days, diabetes was induced using streptozotocin (STZ) (75 mg/kg) intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection in mice. STZ was dissolved in freshly prepared cold sodium citrate buffer (0.01 M, pH 4.5) and immediately used (Aboul-Enein et al., 2016). Using a glucometer (Bionime, Switzerland), the diabetic state of the mice was confirmed by measuring the fasting blood glucose levels over 250 mg/dl after 1 week.
Experimental groups
The diabetic mice were divided into seven experimental groups (n = 8). Group I received the vehicle (1% Tween 80 in distilled water) and served as diabetic control. Group II received orally (p.o.) acarbose (20 mg/kg) (Shu et al., 2009) as a reference drug. Groups III and IV received Sh mycelial extract at dose 1/20 and 1/10 of LD50 value (50 and 100 mg/kg, p.o.), respectively, dissolved in vehicle. Mice in groups V and VI received Sh filtrate extract at dose 1/20 and 1/10 of LD50 value (125 and 250 mg/kg, p.o.), respectively, dissolved in vehicle. Normal control mice (nondiabetic) received the vehicle only. All treatments were administered for 7 days. 24 hours after the last oral administration of the Sh mycelia and Sh filtrate extracts, anesthesia was carried out. Then, the blood was directly collected from the heart and centrifuged at 3,000 rpm at 4°C for 20 min using cooling centrifuge (Sigma Laborzentrifugen GmbH, Germany). Serum samples were divided into aliquots and stored at −80°C until analysis.
Determination of blood glucose level
Blood glucose level was assessed in serum samples from different groups using the glucose enzymatic colorimetric kit (Biodiagnostic, Egypt) and measured using a spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, USA) (Barham and Trinder, 1972).
Measurement of C-peptide level
The mouse C-peptide enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (ALPCO, Salem, NH, USA) is a sandwich-type immunoassay for the quantitative determination of C-peptide in mouse serum. The amount of C-peptide in the sample is directly proportional to the intensity of the color generated at 450 nm using ELISA plate reader.
Measurement of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) level
GLP-1 ELISA Kit (Fine test®, China) is a sandwich ELISA technique. The optical density absorbance of the sample and standard was read at 450 nm using the ELISA plate reader and then the concentration of GLP-1 was calculated using a standard curve of know concentrations of the GLP-1 standard.
Measurement of α-glucosidase level
The α-glucosidase level was estimated using Mouse Gaa (Lysosomal α-glucosidase) ELISA Kit (Fine test®, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The optical density absorbance was measured at 450 nm using the ELISA plate reader. The concentration of α-glucosidase enzyme in the sample was calculated using a standard curve of known concentrations of the α-glucosidase enzyme.
Measurement of adiponectin level
Mouse adiponectin ELISA Kit (LifeSpan BioSciences Inc., USA) is a sandwich ELISA assay based principle. The optical density absorbances of the sample and standard were measured at a wavelength of 450 nm using the ELISA plate reader. The concentration of adiponectin in the serum sample was calculated using a standard curve of known concentrations of the adiponectin standard.
Determination of antioxidant activities
The free radical scavenging capacity of both Sh mycelia and Sh filtrate extracts were determined using the radical 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,20-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) scavenging capacity assays (Mehaya and Mohammad, 2020).
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical analysis was carried out using a one-way analysis of variance, followed by a Student–Newman–Keuls post-hoc comparison using the Sigma stat Software. A result was considered statistically significant where p < 0.05.
RESULTS
Fungal identification
The isolated fungus (SP51-EGY) was molecularly identified using the molecular protocol (18SrRNA). The phylogenic tree was constructed to show the phylogenic relationship of the isolated strain with the reference strains (Fig. 1). The phylogeny and multiple sequence alignment analysis of isolated strain show clear similarity (100%) with the fungal strain A. unguis isolate SPMD-EGY (KM203833.1), 98.87% similarity with A. unguis voucher VG2.6 (MH655006.1), 98.7% similarity with A. unguis voucher AG1.2 (MH655000.1), and 98.69% similarity with A. unguis isolate 1038. The sequence has been deposited in GenBank with the name A. unguis isolate SP51-EGY and the accession number KM203831.1. This strain was maintained on potato dextrose agar slants and kept at 4°C for further use.
In vitro α-glucosidase inhibitory activity
The extracts from three different broth media: A, B, and C [under shake (Sh) and static (St) conditions for both filtrate and mycelia] were tested for their potentiality to improve α-glucosidase inhibitory activity for the fungus “A. unguis isolate SP51-EGY” (Fig. 2).
In medium A, the St filtrate extract showed the highest significant α-glucosidase inhibitory activity (81%), followed by Sh filtrate extract (73%) compared to the drug (acarbose, 73%), while Sh mycelia had low activity. Meanwhile, St mycelia was inactive (Fig. 2a).
Regarding medium B, the St filtrate extract showed the highest significant -glucosidase inhibitory activity (80%) compared to acarbose (73%), while the Sh filtrate extract exhibited similar α-glucosidase inhibitory activity (73%) compared to the acarbose. Sh mycelial extract had low activity, while St mycelial extract was inactive (Fig. 2b).
Furthermore, as shown in medium C, both (Sh filtrate and Sh mycelia) extracts showed the highest α-glucosidase inhibitory activity (82%) that was not statistically significant from the reference drug acarbose (73%) (Fig. 2c). St filtrate extract showed low activity, while St mycelial extract was inactive.
GC/MS analysis
The GC/MS analysis for the chemical composition of medium C extracts showed the highest α-glucosidase inhibitory activity (Sh filtrate and Sh mycelia), revealing the identification of 29 compounds in Sh filtrate extract, from which seven compounds were present with high concentration : 2-furancarboxylic acid-5-hydroxy (0.92%), 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (0.55%), 3-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzoic acid (isovanillic acid) (4.8%), ethylene glycol-o-(2-hydroxy)benzoate (2.2%), d-friedoolean-14-en-3-one (18.9%), 2,4,2’-trihydroxychalcon (0.3%), and 2(5-Hydroxy-1,6-dimethyl-4,11-dioxo-4,11-dihydro-1H-isochromano(7,6-F)indazol-8-yl)acetic acid methyl ester (69%) (Fig. 3 and Table 1).
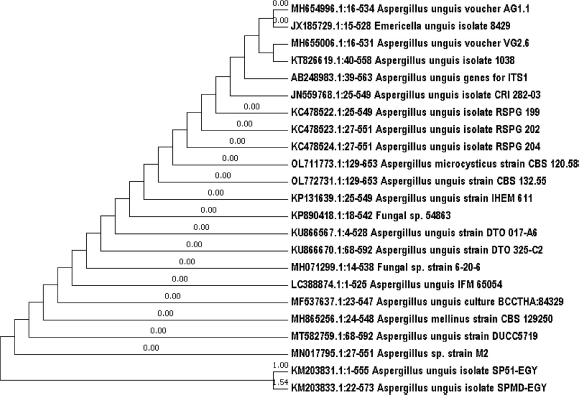 | Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship of strain SP51 with other related fungal species retrieved from GenBank based on their sequence homologies of 18SrRNA using MEGA7 program. [Click here to view] |
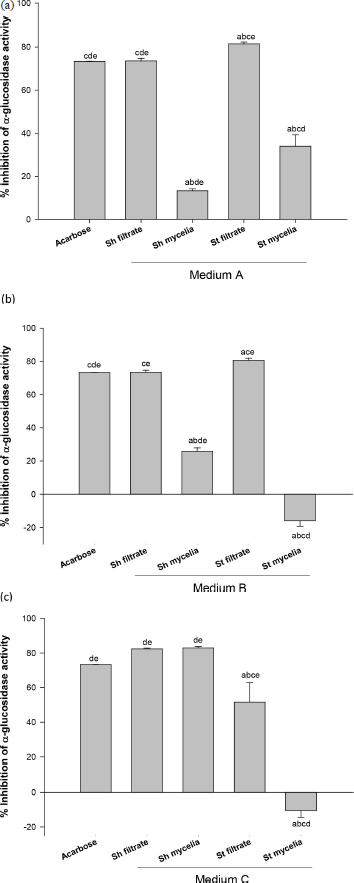 | Figure 2. % α-Glucosidase inhibitory activity of secondary metabolite extracts for media A, B, and C. The secondary metabolite extracts under shake and static conditions are expressed as shake filtrate extract (Sh filtrate), shake mycelial extract (Sh mycelia), static filtrate extract (St filtrate), and static mycelial extract (St mycelia) Values are expressed as mean ± SEM., n = 3 (200 μg/ml for all tested extracts and reference standard drug; Acarbose). aSignificantly different from acarbose at p < 0.05, bsignificantly different from Sh filtrate at p < 0.05, csignificantly different from Sh mycelia at p < 0.05, dsignificantly different from St filtrate at p < 0.05, and esignificantly different from St mycelia at p < 0.05. [Click here to view] |
In the Sh mycelial extract, 15 compounds were identified, some of them possessed high percentage:hexadecanoic acid methyl ester (palmitic acid ester) (24.5%), hexadecanoic acid (palmitic acid) (22.6%), linolenic acid esters (5,8-octadecadienoic acid, and methyl ester and 13,16-octadecadienoic acid, methyl ester) (12.3% and 5.4%, respectively) (Fig. 3 and Table 1).
In vivo pharmacology studies
Assessment of acute toxicity
The LD50 for Sh filtrate extract was 2,500 mg/kg, while the LD50 for Sh mycelial extract was 1,000 mg/kg. Therefore, 1/10 and 1/20 of this dose was chosen for the assessment of the in vivo pharmacological studies.
Effect of Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts on blood glucose level
To examine the antidiabetic effect of Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts in STZ-induced diabetic mice, the serum blood glucose level was determined at the end of the treatment period (7 days). As shown in Figure 4, the blood glucose value of the STZ-induced diabetic group reached 301.33 ± 13.3 mg/dl at the end of the treatment period, which is 166% higher than the normal control. In Sh mycelial extract treated groups (50 and 100 mg/kg), the blood glucose level was significantly lowered by 27% and 54%, respectively, compared to the diabetic group. Treatment with Sh filtrate extract at doses of 125 and 250 mg/kg demonstrated significantly higher reduction in the blood glucose level by 49% and 70%, respectively, compared to the diabetic group. The effect of Sh filtrate (250 mg/kg) was significantly higher than Sh filtrate (125 mg/kg). Treatment with the reference standard acarbose (20 mg/kg), Sh filtrate at both dose levels and Sh mycelia (100 mg/kg) reduced the blood glucose to a normal level of 113.2 ± 2.77 mg/dl, showing no significance from normal control. In addition, the effect of Sh mycelia (50 mg/kg) was statistically higher than that of Sh filtrate (125 mg/kg and 250 mg/kg), as well as mycelia (100 mg/kg).
Effect of Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts on C-peptide level
Figure 5 shows that induction of diabetes in mice using STZ exhibited 84% reduction in their serum C-peptide level (0.72 ± 0.07 ng/ml) compared to normal control mice (4.63 ± 0.18 ng/ml). This reduction was reversed by treatment with acarbose (2.96 ± 0.14 ng/ml) as well as Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts at both dose levels; however, they did not restore the C-peptide levels to normal level. Sh filtrate (250 mg/kg; 2.86 ± 0.04 ng/ml) exhibited a significant increase in C-peptide level compared to Sh filtrate (125 mg/kg; 1.86 ± 0.06 ng/ml) and Sh mycelia (50 mg/kg; 1.24 ± 0.05 ng/ml), while there were no significant differences from the reference acarbose and Sh mycelia (100 mg/kg; 2.59 ± 0.06 ng/ml).
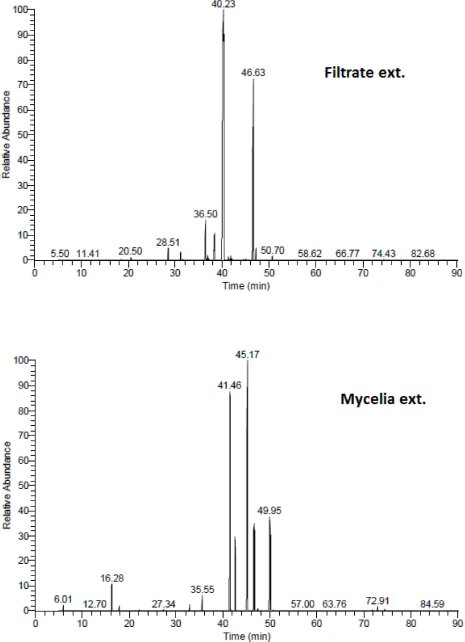 | Figure 3. GC/MS chromatograms of the Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts of A. unguis (Medium C). [Click here to view] |
Effect of Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts on GLP-1 level
Induction of diabetes in mice using STZ significantly lowered GLP-1 serum level (29.50 ± 3.02 pg/ml) by 35% (1.5-fold) compared to normal control value (45.50 ± 5.50 pg/ml) (Fig. 6). Treatment with acarbose, Sh filtrate (125 and 250 mg/kg), and Sh mycelia (50 and 100 mg/kg) extracts significantly reversed this reduction by 97, 94, 136, 48, and 75%, respectively, compared to the diabetic group. The GLP-1 levels of all the treated groups were statistically insignificant from the normal control, except for Sh filtrate (250 mg/kg) as it raised the GLP-1 level by 53% compared to the control value. In addition, treatment with Sh filtrate (250 mg/kg; 69.5±2.18 pg/ml) exhibited higher GLP-1 levels compared to Sh mycelia (50 and 100 mg/kg; reaching 43.78±5.13 pg/ml and 51.67±3.32 pg/ml, respectively).
Effect of Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts on α-glucosidase level
In an attempt to investigate the mechanism by which the extracts cause the aforementioned changes in blood glucose, C-peptide, and GLP-1 levels, the level of α-glucosidase was assessed in mice serum (Fig. 7). Inhibition of α-glucosidase enzyme is considered an effective tool for the treatment and management of diabetes (Proença et al., 2021). Initially, the diabetic group demonstrated a 3.1-fold increase in α-glucosidase level compared to the normal control value. Treatment with the Sh filtrate (125 and 250 mg/kg) and Sh mycelia (50 and 100 mg/kg) exhibited a sharp decrease in the serum α-glucosidase level by 58%, 78%, 63%, and 72%, respectively, compared to the diabetic group.
Effect of Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts on adiponectin level
To further explore the possible mechanisms of action of Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts, the adiponectin level was evaluated. STZ-induced diabetic mice showed significant reduction in serum adiponectin level by 84% (6.4-fold) compared to normal control value (Fig. 8). Both Sh filtrate (125 mg/kg; 88.40±2.72 pg/ml and 250 mg/kg; 134.50±4.28 pg/ml) and Sh mycelia (50 mg/kg; 55.20±3.31 pg/ml and 100 mg/kg; 113.07±2.28 pg/ml) extracts demonstrated a sharp significant increase in adiponectin level by 211%, 374%, 94%, and 298% compared to the diabetic control, respectively. Remarkably, this sharp increase was still significantly lower than control and acarbose values except for the treatment with Sh filtrate extract (250 mg/kg; 134.50±4.28 pg/ml) which showed the most effective increase in serum adiponectin level which was similar to that of acarbose (144.43±3.06 pg/ml).
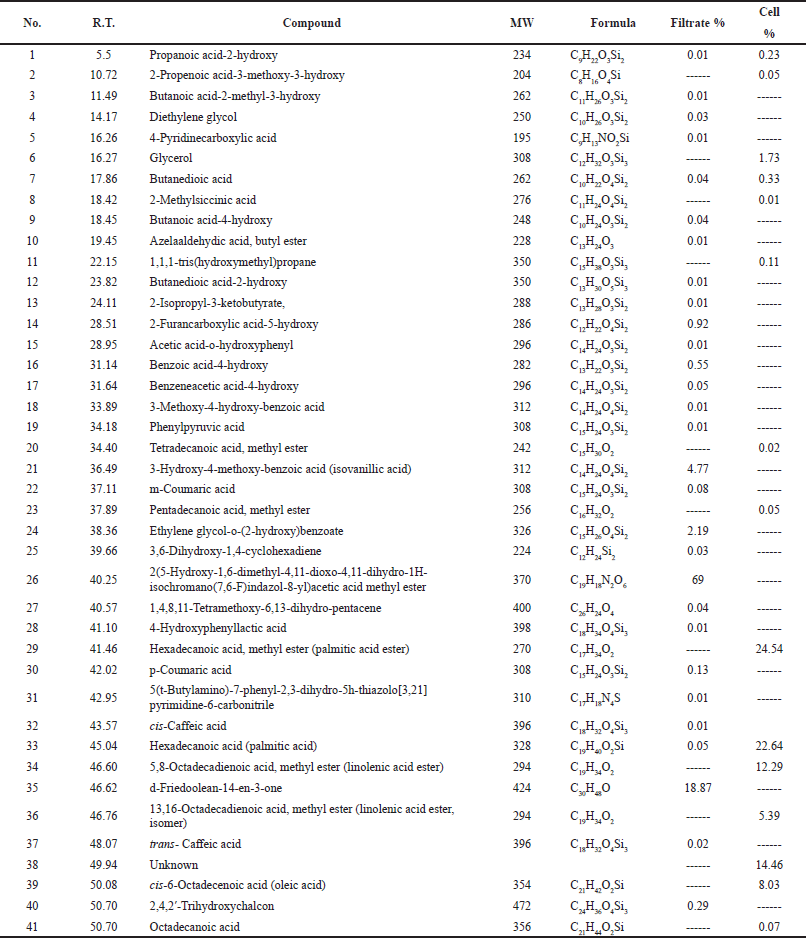 | Table 1. GC/MS analysis of Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts of A. unguis SP51-EGY. [Click here to view] |
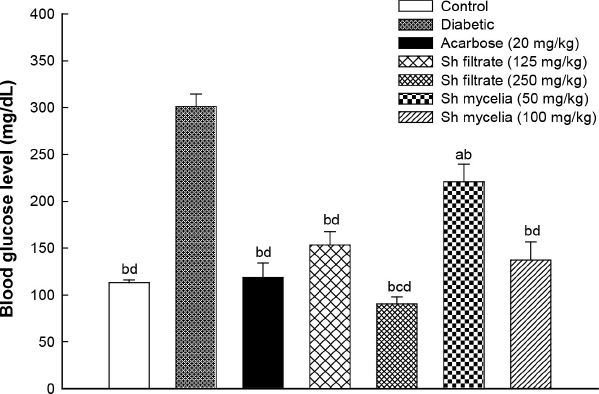 | Figure 4. Effect of the oral administration of Sh filtrate (125 and 250 mg/kg) and Sh mycelia (50 and 100 mg/kg) extracts on blood glucose level in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. aSignificantly different from control at p < 0.05, bsignificantly different from diabetic value at p < 0.05, csignificantly different from Sh filtrate (125 mg/kg) at p < 0.05, and dsignificantly different from Sh mycelia (50 mg/kg) at p < 0.05. [Click here to view] |
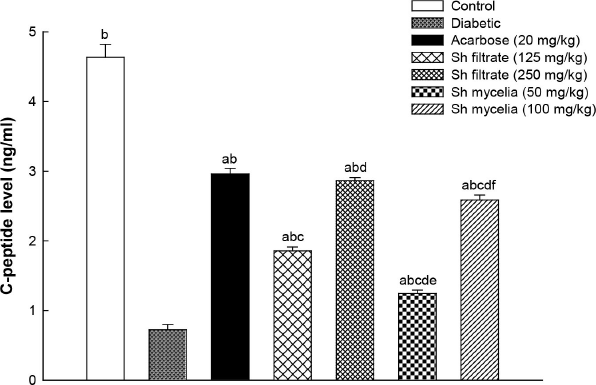 | Figure 5. Effect of the oral administration of Sh filtrate (125 and 250 mg/kg) and Sh mycelia (50 and 100 mg/kg) extracts on C-peptide level in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. aSignificantly different from control at p <0.05, bsignificantly different from diabetic value at p < 0.05, csignificantly different from acarbose at p < 0.05, dsignificantly different from Sh filtrate (125 mg/kg) at p < 0.05, esignificantly different from Sh filtrate (250 mg/kg) at p < 0.05, and fsignificantly different from Sh mycelia (50 mg/kg) at p < 0.05. [Click here to view] |
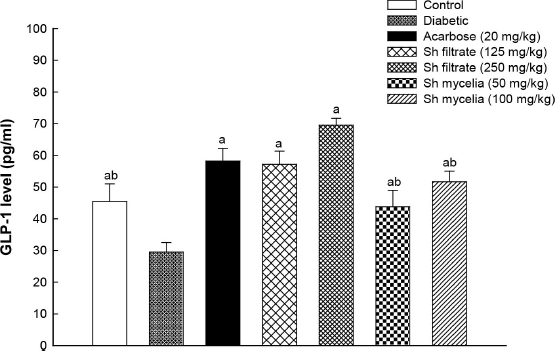 | Figure 6. Effect of the oral administration of Sh filtrate (125 and 250 mg/kg) and Sh mycelia (50 and 100 mg/kg) extracts on GLP-1 level in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. aSignificantly different from diabetic value at p < 0.05 and bSignificantly different from Sh filtrate (250 mg/kg) at p < 0.05. [Click here to view] |
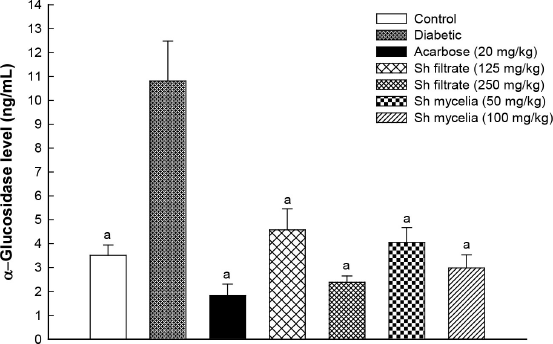 | Figure 7. Effect of the oral administration of Sh filtrate (125 and 250 mg/kg) and Sh mycelia (50 and 100 mg/kg) extracts on α-glucosidase level in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. aSignificantly different from diabetic value at p < 0.05. [Click here to view] |
Effect of Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts on antioxidant activity
The free radical scavenging activity of Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts was demonstrated using the DPPH and ABTS assays. Both extracts exhibited a free radical scavenging power; however, Sh mycelia demonstrated higher antioxidant capacity by 20.09 ± 0.15 and 66.61 ± 1.63 (mg Trolox equiv./g sample) compared to Sh filtrate showing 17.18 ± 0.08 and 23.70 ± 0.07 (mg Trolox equiv./g sample) in DPPH and ABTS assays, respectively.
DISCUSSION
In the present study, treatment with Sh mycelial and Sh filtrate extracts of the A. unguis isolate SP51-EGY showed significant antidiabetic effect demonstrated in the reduction of blood glucose level that was accompanied by elevation in C-peptide level, GLP-1, and adiponectin levels. In addition, both extracts demonstrated α-glucosidase inhibitory activity.
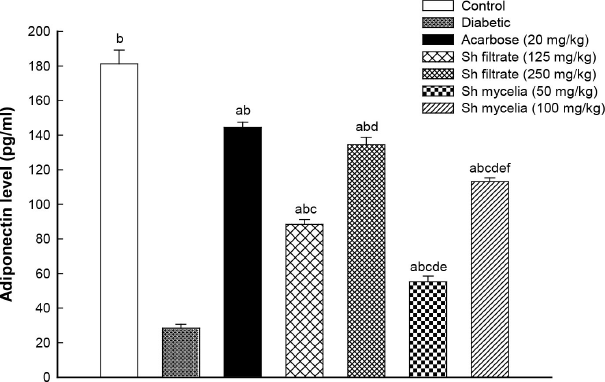 | Figure 8. Effect of the oral administration of Sh filtrate (125 and 250 mg/kg) and Sh mycelia (50 and 100 mg/kg) extracts on adiponectin level in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. aSignificantly different from control at p < 0.05, bsignificantly different from diabetic value at p < 0.05, csignificantly different from acarbose at p<0.05, dsignificantly different from Sh filtrate (125 mg/kg) at p < 0.05, esignificantly different from Sh filtrate (250 mg/kg) at p < 0.05, and fsignificantly different from Sh mycelia (50 mg/kg) at p < 0.05. [Click here to view] |
Moreover, treatment with Sh mycelia or Sh filtrate, as well as the reference standard “acarbose,” significantly reversed the C-peptide inhibition in diabetic mice. C-peptide is a well-established biomarker of functional β-cell mass where abolished or extremely reduced C-peptide levels were found in type 1 and late-stage type 2 diabetes (Luppi and Drain, 2017). It is produced as a part of the normal insulin biosynthesis in the pancreatic β-cells secretory granules and secreted in equimolar amounts with insulin in the bloodstream (Fu et al., 2013). In this study, C-peptide levels were significantly increased in the diabetic mice treated with acarbose, Sh filtrate, and Sh mycelia compared to the diabetic group. Acarbose treatment has been reported to significantly reduce the plasma glucose, C-peptide, and insulin, compared to the respective baseline values and placebo in cystic fibrosis patients with impaired glucose tolerance (Kentrup et al., 1999).
The antioxidant action of C-peptide has a dual beneficial effect on β-cells. A direct effect by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) through stimulation β-cell pathways reduces ROS caused by excess glucose or fat, as well as cytotoxic immune cell attack. Preservation of the insulin secretion via protecting β-cell insulin secretory capacity is considered an indirect pathway that leads to reduction of the hyperglycemic load and its glucotoxic consequences on β-cells (Luppi and Drain, 2017).
Interestingly, both Sh mycelia and Sh filtrate demonstrated significant inhibitions of α-glucosidase serum level compared to diabetic mice, and this inhibition was not significant from acarbose which is an α-glucosidase inhibitor. Acarbose was reported to suppresses the post-prandial elevations of blood glucose level (Ochiai et al., 2008). However, α-glucosidase enzyme functions as a digestive enzyme where it catabolizes the breakdown of complex carbohydrates into glucose intestinal lumen. The glucose is transported via sodium/glucose cotransporter-1 to the cytosol of enterocytes and then to the blood by glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) (Proença et al., 2021).
Thus, inhibition of α-glucosidase enzyme prevents the digestion of carbohydrates, such as sugar and starch; reduces postprandial hyperglycemia; and also delays the development of type 2 diabetes in patients with impaired glucose tolerance (Nakamura et al., 2014).
In the current study, inhibition of α-glucosidase enzyme was accompanied by an increase in GLP-1 serum levels in the acarbose, Sh filtrate, and Sh mycelial extracts. Moritoh et al. (2009) reported that inhibition of α-glucosidase increases plasma levels of GLP-1 in diabetic ob/ob mice. In addition, increased levels of fasting and postprandial GLP-1 were recorded in patients newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and treated with acarbose for 24 weeks (Zheng et al., 2013). GLP-1 is a gastrointestinal hormone incretin which enhances insulin, suppresses glucagon secretion, and slows the gastric emptying, leading to lowered blood glucose levels (Antony and Vijayan, 2021). Therefore, following α-glucosidase inhibitors administration, large amounts of undigested carbohydrates reach the distal small intestine, which is rich in L-cells that produce GLP-1 and accordingly stimulates GLP-1 increased long-lasting secretion (Kalra, 2014).
The results of present study showed that serum adiponectin level was significantly lower in diabetic mice compared to the control group. On the other hand, treatment with acarbose, Sh filtrate, and Sh mycelial extract significantly increased its level compared to the diabetic group. In agreement with our results, Ochiai et al. (2008) demonstrated that decreased circulating levels of adiponectin have been observed in obese and diabetic patients; however, acarbose increases the serum concentration of adiponectin in type 2 diabetics. Adiponectin improves insulin resistance through reducing inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress. The activation of adiponectin receptors, AdipoR1 or AdipoR2, stimulates adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and PPAR-α leading to improvement of insulin resistance in the liver and skeletal muscle as it increase glucose and fatty acids utilization by the skeletal muscles and reduces hepatic glucose production, hence lowering blood glucose levels. Moreover, adiponectin possesses β-cell protective effect and its levels are decreased in type 2 diabetes (Yamada et al., 2012; Yamauchi et al., 2002; Yanai and Yoshida, 2019).
The reduction of the blood glucose level in diabetic mice treated with Sh mycelial extract could be attributed to the chemical composition of the extract. Linolenic acid is one of the main components of the Sh mycelial extract and its repeated administration was reported to significantly suppress the increment of blood glucose in diabetic mice without alteration in the blood glucose level of normal mice, signifying its usefulness in the treatment of diabetes. In addition, α-linolenic acid significantly increased the protein content of GLUT4 in KK-Ay mice as an animal model for type 2 diabetes and decreased the blood glucose in insulin tolerance test, suggesting that hypoglycemic effect could be due to the decrease in insulin resistance (Kato et al., 2000; Sadiq et al., 2020).
Furthermore, conjugated linoleic acid supplementation in diet of ob/ob C57BL-6 diabetic mice resulted in a significant reduction in fasting glucose, insulin, and triacylglycerol concentrations, while significant increase in insulin receptor expression and adipose tissue plasma membrane GLUT4 compared with similarly fed control mice (Moloney et al., 2007). In addition, adiponectin plasma level was enhanced in conjugated linoleic acid-fed Zucker diabetic fatty (fa/fa) rats resulting in improved hyperinsulinemia (Nagao et al., 2003). In alloxan-induced diabetic rats, treatment with linoleic acid showed significant improvement in blood glucose level and lipid profile compared to the diabetic control rats (Srinivasan and Rayar, 2020).
In addition, oleic acid, a component of the Sh mycelial extract, was reported to possess a beneficiary effect in diabetes as it reversed the negative effects of inflammatory cytokines, produced by adipose tissue that has the capacity to decrease insulin secretion and enhance insulin resistance (Vassiliou et al., 2009). Moreover, intracerebroventricular administration of the oleic acid noticeably suppressed food intake and glucose production via a mechanism that involves ATP-sensitive K channels (Obici et al., 2002).
Palmitic acid ester is one of the chemical constituents of the Sh mycelial extract. It showed hypoglycemic activity in diabetic (db/db) mice. However, palmitic acid hypoglycemic activity was less than exendin-4 (GLP-1 receptor agonist) which is probably attributed to its substantial reduced GLP-1 receptor binding affinity (Chae et al., 2010). Interestingly, palmitic acid can play two opposing roles in skeletal muscle. In acute conditions, palmitic acid enhances glucose uptake via activation of Akt and ERK1/2 in skeletal muscle cells. In chronic administration, palmitic acid could inhibit insulin-induced glucose uptake through blocking Akt phosphorylation resulting in a Yin–Yang balance of palmitic acid in skeletal muscle (Pu et al., 2011).
In addition, one of the main components of the Sh filtrate extract is benzoic acid, 4-hydroxy. Peungvicha et al. (1998) demonstrated that its oral administration resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in plasma glucose levels in diabetic rats, while no effect was observed on liver glycogen content and serum insulin level. Moreover, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid increased glucose consumption in both normal and diabetic rats’ diaphragms, suggesting that hypoglycemic effect is due to the increase in consumption of peripheral glucose.
Furthermore, 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy benzoic acid (HMBA) treatment restored the plasma insulin, glycosylated hemoglobin, and liver glycogen levels in STZ-induced diabetes demonstrating its potential hypoglycemic effect and normalized the levels of total cholesterol, triglycerides, and low density lipoproteins (LDL)-cholesterol in STZ-induced diabetes (Gayathri and Kannabiran, 2009a). HMBA restored the antioxidant defense system in STZ-induced diabetic rats through reducing the free radical production and lipid peroxidation (Gayathri and Kannabiran, 2009b). Moreover, its oral administration significantly decreased lipid peroxidation and malondialdehyde levels in liver and kidney of STZ-induced diabetic rats (Gayathri and Kannabiran, 2010).
In the current work, we demonstrated that D-friedoolean-14-en-3-one is one of the main components of Sh filtrate extract. In vitro investigations of the cinnamoyloxy-D-friedoolean-14-en-28-oic acid derivatives exhibited high antioxidant activity using the DPPH assay that was accompanied by the inhibiting effect on the α-glycosidase enzyme (Sultanova et al., 2013). Furthermore, 21 and 29-hydroxy-D:A-friedoolean-3-one derivatives showed much stronger inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase compared to acarbose (Huang et al., 2012).
2,4,2?-trihydroxychalcon, which is a constituent of the Sh filtrate extract, is a trihydroxychalcone derivative which is found to facilitate AMPK activation and might be a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of diabetes. It improved glucose tolerance, reduced fat accumulation in the liver and skeletal muscles, and increased muscle fatty acid oxidation when administered to high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice (Shin et al., 2018). Interestingly, diet supplementation of 2,2?,5?-trihydroxychalcone (10 mg/kg, 3 times per week) was found to blunt the increase in glucose that exists with weight gain in 6-week-treated Zucker fatty (fa(-)/fa(-)) rats. In addition, 2,2?,5?-trihydroxychalcone demonstrated an excellent in vitro ROS scavenging activity in THP-1 human monocytes and L-6 myoblasts (Rossi et al., 2013).
In addition, p-coumaric acid is a component of the filtrate extract. Oral administration at dose 100 mg/kg was reported to significantly lower the blood glucose level and gluconeogenic enzymes while increasing glucose-6 phosphatase dehydrogenase, hexokinase, and GSH activities via increasing insulin level in STZ-induced diabetic rats (Amalan et al., 2016). P-coumaric acid modulated the lipid metabolism through reducing triglycerides and total cholesterol in plasma, liver, and kidney tissues. P-coumaric acid modulates lipid metabolism and glucose through activation of pancreatic GLUT2, suggesting its potential beneficial role in the management of metabolic disorders (Amalan et al., 2016). Furthermore, m-coumaric acid significantly decreased blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin levels in STZ-induced diabetic rats, which was accompanied by significant elevations of GSH level, catalase, and SOD activities, and reduction of MDA levels (Moselhy et al., 2018).
In high-fat diet/STZ-induced diabetic rats, caffeic acid intake showed marked lowering of fasting blood glucose and lipid profile. In addition, caffeic acid improved creatinine clearance and inhibited autophagy regulatory miRNAs, resulting in modulation of the autophagy pathway and suggesting its curative role in diabetic kidney disease (Matboli et al., 2017). Moreover, caffeic acid esters decreased hepatocellular glucose production, adipogenesis, and enhanced glucose transport in skeletal muscles via mechanisms involving AMPK (Eid et al., 2017). In addition, administration of caffeic acid in diabetic rats reduced oxidative stress through increasing the antioxidant enzymes, while inhibiting lipid peroxidase (Mohammed and El-Shehabi, 2015).
CONCLUSION
Red Sea marine fungi are a rich source for future discovery of new drug leads. The bioactive secondary metabolites derived from marine species-associated fungi play a promising potential role in drug discovery due to their vast range of pharmacological activities.
Globally, there is an ultimate need for the discovery of effective novel approaches to control high blood glucose level. It is an essential requirement to prevent diabetic complications and improve the patient’s quality of life. Data emerged from this study have demonstrated that Sh filtrate and Sh mycelial extracts from medium C showed the highest significant in vitro -glucosidase inhibitory activity. Both extracts exhibited a free radical scavenging power in vitro, with Sh mycelia having a higher antioxidant capacity compared to Sh filtrate. In vivo, both Sh filtrate and Sh mycelia significantly lowered the blood glucose level and increased the C-peptide, GLP-1, and adiponectin levels compared to the diabetic group. On the other hand, a significant inhibition was observed in α-glucosidase serum level compared to the diabetic value. Thus, secondary metabolites from the Red Sea sponge associated fungus “A. unguis” isolate SP51-EGY provided new insights for the development of novel strategies in the regulation of high blood glucose level.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This study was supported financially by the bilateral projects of the Executive Program of Scientific and Technological Cooperation between Egypt and Italy under Project No. A2-12-15.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTIONS
M.E.A.: wrote the manuscript, conducted pharmacological studies, and wrote the relevant sections. Y.A.M. and M.E.A: conceived, designed, analyzed and interpreted the data, and revised the pharmacology part. M.S.A.: conceived, designed, conducted the fungal preparation assays, and wrote and revised the relevant section. F.K.A.: conceived, designed, and conducted GC/MS analysis and the in vitro alpha glycosidase assay, analyzed and interpreted the data, and wrote and revised the relevant section. All authors revised and gave approval to the final version of the manuscript.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors report no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICAL APPROVAL
All animal experiments were carried out according to the Medical Research Ethics Committee of the National Research Centre (Decision No.: 20184).
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated and analyzed are included within this research article.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
REFERENCES
Abd El-Hady FK, Abdel-Aziz MS, Shaker KH, El-Shahid ZA, Ghani MA. Coral-derived fungi inhibit acetylcholinesterase, superoxide anion radical, and microbial activities. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res, 2014; 26(1):301–8.
Abd El-Hady FK, Abdel-Aziz MS, Shaker KH, El-Shahid ZA, Ibrahim LS. Antioxidant, acetylcholinesterase and α-Glucosidase potentials of metabolites from the marine fungus Aspergillus unguis RSPG_204 associated with the sponge (Agelas sp.). J Pharm Sci Rev Res, 2015; 30(1):272–8.
Abd El-Hady FK, Abdel-Aziz MS, Souleman AMA, El-Shahid ZA, Shaker KH. Enhancement of acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity for the soft coral associated fungus Aspergillus unguis SPMD-EGY by media composition. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res, 2016; 41:349–57.
Aboul-Enein MN, El-Azzouny A, Saleh O, Maklad Y, Aboutabl M, Gamal El-Din M. Synthesis, bio-evaluation and molecular modeling studies of (2S)-1-[({[1-substituted cyclohexyl] methyl} amino) acetyl] pyrrolidine-2-carbonitriles for their DPP-4 Inhibiting Activity. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res, 2016; 39(2):230–40.
Alsterberg C, Roger F, Sundbäck K, Juhanson J, Hulth S, Hallin S, Gamfeldt L. Habitat diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality-The importance of direct and indirect effects. Sci Adv, 2017; 3(2):e1601475. CrossRef
Amalan V, Vijayakumar N, Indumathi D, Ramakrishnan A. Antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic activity of p-coumaric acid in diabetic rats, role of pancreatic GLUT 2: in vivo approach. Biomed Pharmacother, 2016; 84:230–6. CrossRef
Antony P, Vijayan R. Bioactive peptides as potential nutraceuticals for diabetes therapy: a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci, 2021; 22(16):9059. CrossRef
Barham D, Trinder P. An improved colour reagent for the determination of blood glucose by the oxidase system. Analyst, 1972; 97(151):142–5. CrossRef
Bommer C, Sagalova V, Heesemann E, Manne-Goehler J, Atun R, Bärnighausen T, Davies J, Vollmer S. Global economic burden of diabetes in adults: projections from 2015 to 2030. Diabetes Care, 2018; 41(5):963.
Chae SY, Choi YG, Son S, Jung SY, Lee DS, Lee KC. The fatty acid conjugated exendin-4 analogs for type 2 antidiabetic therapeutics. J Control Release, 2010; 144(1):10–6. CrossRef
Eid HM, Thong F, Nachar A, Haddad PS. Caffeic acid methyl and ethyl esters exert potential antidiabetic effects on glucose and lipid metabolism in cultured murine insulin-sensitive cells through mechanisms implicating activation of AMPK. Pharm Biol, 2017; 55(1):2026–34. CrossRef
Fu Z, Gilbert ER, Liu D. Regulation of insulin synthesis and secretion and pancreatic Beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rev, 2013; 9(1):25–53. CrossRef
Gayathri M, Kannabiran K. Antidiabetic activity of 2-hydroxy 4-methoxy benzoic acid isolated from the roots of Hemidesmus indicus on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int J Diabetes Metab, 2009a; 17:53–7. CrossRef
Gayathri M, Kannabiran K. Effect of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy benzoic acid from the roots of Hemidesmus indicus on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Indian J Pharm Sci, 2009b; 71(5):581–5. CrossRef
Gayathri M, Kannabiran K. 2-hydroxy 4-methoxy benzoic acid isolated from roots of Hemidesmus indicus ameliorates liver, kidney and pancreas injury due to streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Indian J Exp Biol, 2010; 48(2):159–64.
Greenaway W, May J, Scaysbrook T, Whatley FR. Identification by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry of 150 compounds in propolis. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C, 1991; 46(1–2):111–21. CrossRef
Hegazi R, El-Gamal M, Abdel-Hady N, Hamdy O. Epidemiology of and risk factors for type 2 diabetes in Egypt. Ann Glob Health, 2015; 81(6):814–20. CrossRef
Huang J, Guo Z-h, Cheng P, Sun B-h, Gao H-Y. Three new triterpenoids from Salacia hainanensis Chun et How showed effective anti-α-glucosidase activity. Phytochem Lett, 2012; 5(3):432–37. CrossRef
IDF (2019) International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes atlas, 9th edition. Available via https://www.diabetesatlas.org/upload/resources/material/20200302_133351_IDFATLAS9e-final-web.pdf
Kalra S. Incretin enhancement without hyperinsulinemia: α-glucosidase inhibitors. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab, 2014; 9(5):423–5. CrossRef
Kato M, Miura T, Nakao M, Iwamoto N, Ishida T, Tanigawa K. Effect of alpha-linolenic acid on blood glucose, insulin and GLUT4 protein content of type 2 diabetic mice. J Health Sci, 2000; 46(6):489–92. CrossRef
Kentrup H, Bongers H, Spengler M, Kusenbach G, Skopnik H. Efficacy and safety of acarbose in patients with cystic fibrosis and impaired glucose tolerance. Eur J Pediatr, 1999; 158(6):455–9. CrossRef
Litchfield J, Wilcoxon F. A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 1949; 96(2):99–113.
Liu M, Qi C, Sun W, Shen L, Wang J, Liu J, Lai Y, Xue Y, Hu Z, Zhang Y. α-Glucosidase inhibitors from the coral-associated fungus Aspergillus terreus. Front Chem, 2018; 6:422. CrossRef
Luppi P, Drain P. C-peptide antioxidant adaptive pathways in β cells and diabetes. J Intern Med, 2017; 281(1):7–24. CrossRef
Manilal A, Sabarathnam B, Kiran GS, Sujith S, Shakir C, Selvin J. Antagonistic potentials of marine sponge associated fungi Aspergillus clavatus MFD15. Asian J Med Sci, 2010; 2(4):195–200.
Marín-Peñalver JJ, Martín-Timón I, Sevillano-Collantes C, Del Cañizo-Gómez FJ. Update on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes, 2016; 7(17):354–95. CrossRef
Matboli M, Eissa S, Ibrahim D, Hegazy MGA, Imam SS, Habib EK. Caffeic acid attenuates diabetic kidney disease via modulation of autophagy in a high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Sci Rep, 2017; 7(1):2263. CrossRef
Mehaya FM, Mohammad AA. Thermostability of bioactive compounds during roasting process of coffee beans. Heliyon, 2020; 6(11):e05508. CrossRef
Mohammed FZ, El-Shehabi M. Antidiabetic activity of caffeic acid and 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid and its relationship with the antioxidant property. Asian J Pharm Clin Res, 2015; 8:229–35.
Moloney F, Toomey S, Noone E, Nugent A, Allan B, Loscher CE, Roche HM. Antidiabetic effects of cis-9, trans-11-conjugated linoleic acid may be mediated via anti-inflammatory effects in white adipose tissue. Diabetes, 2007; 56(3):574–82. CrossRef
Moritoh Y, Takeuchi K, Hazama M. Chronic administration of voglibose, an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, increases active glucagon-like peptide-1 levels by increasing its secretion and decreasing dipeptidyl peptidase-4 activity in ob/ob mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2009; 329(2):669–76. CrossRef
Moselhy SS, Razvi SS, Alshibili FA, Kuerban A, Hasan MN, Balamash KS, Huwait EA, Abdulaal WH, Al-Ghamdi MA, Kumosani TA. m-Coumaric acid attenuates non-catalytic protein glycosylation in the retinas of diabetic rats. J Pesticide Sci, 2018; 43(3):180–5. CrossRef
Nadeem F, Oves M, Qari H, Ismail I. Red sea microbial diversity for antimicrobial and anticancer agents. J Mol Biomark Diagn, 2015; 7(267):2.
Nagao K, Inoue N, Wang YM, Yanagita T. Conjugated linoleic acid enhances plasma adiponectin level and alleviates hyperinsulinemia and hypertension in Zucker diabetic fatty (fa/fa) rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2003; 310(2):562–6. CrossRef
Nakamura K, Oe H, Kihara H, Shimada K, Fukuda S, Watanabe K, Takagi T, Yunoki K, Miyoshi T, Hirata K, Yoshikawa J, Ito H. DPP-4 inhibitor and alpha-glucosidase inhibitor equally improve endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes: EDGE study. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2014; 13:110. CrossRef
Obici S, Feng Z, Morgan K, Stein D, Karkanias G, Rossetti L. Central administration of oleic acid inhibits glucose production and food intake. Diabetes, 2002; 51(2):271. CrossRef
Ochiai H, Ooka H, Shida C, Ishikawa T, Inoue D, Okazaki R. Acarbose treatment increases serum total adiponectin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocr J, 2008; 55(3):549–56. CrossRef
Papagianni M and Mattey M. Physiological aspects of free and immobilized Aspergillus niger cultures producing citric acid under various glucose concentrations. Process Biochem, 2004; 39(12):1963–70. CrossRef
Peungvicha P, Thirawarapan SS, Watanabe H. Possible mechanism of hypoglycemic effect of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, a constituent of Pandanus odorus root. Jpn J Pharmacol, 1998; 78(3):395–8. CrossRef
Phelan SA, Ito M, Loeken MR. Neural tube defects in embryos of diabetic mice: role of the Pax-3 gene and apoptosis. Diabetes, 1997; 46(7):1189–97. CrossRef
Proença C, Ribeiro D, Freitas M, Fernandes E. Flavonoids as potential agents in the management of type 2 diabetes through the modulation of α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2021; 1–71. CrossRef
Pu J, Peng G, Li L, Na H, Liu Y, Liu P. Palmitic acid acutely stimulates glucose uptake via activation of Akt and ERK1/2 in skeletal muscle cells. J Lipid Res, 2011; 52(7):1319–27. CrossRef
Rateb ME, Ebel R. Secondary metabolites of fungi from marine habitats. Nat Prod Rep, 2011; 28(2):290–344. CrossRef
Roglic G. WHO global report on diabetes: a summary. Int J Noncommun Dis, 2016; 1(1):3. CrossRef
Rossi M, Caruso F, Crespi EJ, Pedersen JZ, Nakano G, Duong M, McKee C, Lee S, Jiwrajka M, Caldwell C, Baffour F, Karlin DA, Lidoff G, Leone S, Balducci V, Miler J, Incerpi S. Probing antioxidant activity of 2′-hydroxychalcones: crystal and molecular structures, in vitro antiproliferative studies and in vivo effects on glucose regulation. Biochimie, 2013; 95(10):1954–963. CrossRef
Sadiq A, Rashid U, Ahmad S, Zahoor M, AlAjmi MF, Ullah R, Noman OM, Ullah F, Ayaz M, Khan I, Islam Z-U, Ali W. Treating hyperglycemia from Eryngium caeruleum M. Bieb: in-vitro α-glucosidase, antioxidant, in-vivo antidiabetic and molecular docking-based approaches. Front Chem, 2020; 8:1064. CrossRef
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA, Ogurtsova K, Shaw JE, Bright D, Williams R. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2019; 157:107843. CrossRef
Sancheti S, Sancheti S, Lee SH, Lee JE, Seo SY. Screening of Korean medicinal plant extracts for α-glucosidase inhibitory activities. Iran J Pharm Res, 2011; 10(2):261–4.
Shin J, Jang MG, Park JC, Koo YD, Lee JY, Park KS, Chung SS, Park K. Antidiabetic effects of trihydroxychalcone derivatives via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. J Indus Eng Chem, 2018; 60:177–84. CrossRef
Shu X-S, Lv J-H, Tao J, Li G-M, Li H-D, Ma N. Antihyperglycemic effects of total flavonoids from Polygonatum odoratum in STZ and alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol, 2009; 124(3):539–43. CrossRef
Srinivasan S, Rayar A. Isolation and identification of linoleic acid as an antidiabetic agent from the dry walnuts. Int J Recent Sci Res, 2020; 11(12):40213–6.
Subramani R, Kumar R, Prasad P, Aalbersberg W. Cytotoxic and antibacterial substances against multi-drug resistant pathogens from marine sponge symbiont: citrinin, a secondary metabolite of Penicillium sp. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed, 2013; 3(4):291–6. CrossRef
Sultanova NA, Abilov ZA, Umbetova AK, Choudhary MI. Biologically Active terpenoids from Tamarix species. Eurasian Chem-Technol J, 2013; 15(3):219–26. CrossRef
Vassiliou EK, Gonzalez A, Garcia C, Tadros JH, Chakraborty G, Toney JH. Oleic acid and peanut oil high in oleic acid reverse the inhibitory effect of insulin production of the inflammatory cytokine TNF-α both in vitro and in vivo systems. Lipids Health Dis, 2009; 8(1):25. CrossRef
Verhaegen AA, Van Gaal LF. Drugs that affect body weight, body fat distribution, and metabolism. In: Feingold KR, Editor-in-chief, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hershman JM, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, Morley JE, New M, Purnell J, Sahay R, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL Wilson DP. (eds.). Endotext [Internet], 2019; South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537590/
Yamada Y, Muraki A, Oie M, Kanegawa N, Oda A, Sawashi Y, Kaneko K, Yoshikawa M, Goto T, Takahashi N, Kawada T, Ohinata K. Soymorphin-5, a soy-derived μ-opioid peptide, decreases glucose and triglyceride levels through activating adiponectin and PPARα systems in diabetic KKAy mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2012; 302(4):E433–40. CrossRef
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y, Waki H, Uchida S, Yamashita S, Noda M, Kita S, Ueki K, Eto K, Akanuma Y, Froguel P, Foufelle F, Ferre P, Carling D, Kimura S, Nagai R, Kahn BB, Kadowaki T. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med, 2002; 8(11):1288–95. CrossRef
Yanai H, Yoshida H. Beneficial Effects of Adiponectin on glucose and lipid metabolism and atherosclerotic progression: mechanisms and perspectives. Int J Mol Sci, 2019; 20(5):1190. CrossRef
Zheng MY, Yang JH, Shan CY, Zhou HT, Xu YG, Wang Y, Ren HZ, Chang BC, Chen LM. Effects of 24-week treatment with acarbose on glucagon-like peptide 1 in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients: a preliminary report. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2013; 12:73. CrossRef