INTRODUCTION
Hydrogels are polymer networks capable of carrying more water or biological fluid that are hydrophilic in nature. Due to the existence of physical or chemical crosslinks, polymer networks are formed by homopolymers or copolymers of an insoluble nature. These hydrogels have a thermodynamic affinity for water, which allows them to expand in an aqueous solution (Peppas and Khare, 1993). These hydrogels have a broader range of applications, especially in the medical and pharmaceutical fields (Peppas and Langer, 1994; Ratner and Hoffman, 1976; Varaprasad et al., 2017). The presence of extra water content and softness in the hydrogel is similar to the natural living tissue than any other synthetic biomaterial (Ratner and Hoffman, 1976). Also, because of the presence of extra water content, hydrogels have a biocompatibility quality. Hydrogels can also be used as biosensor membranes, drug delivery systems, artificial skin fabrics, linings for artificial hearts, and contact lenses (Moghimi and Hunter, 2000; Peppas, 1997).
In response to slight changes in environmental parameters such as ionic pressure, pH, and temperature, hydrogels can show rapid volume changes known as stimuli-responsive materials. In smart hydrogels, stimulus-responsive polymers play a major role, and these hydrogels are used in separation processes for industrial applications as potential economic alternatives to conventional separation processes (Shah and Patel, 2014). Regulated permeability variations of sensitive gels may accomplish the charge or size-selective separations. The magnetic or electric field reveals powerful improvements in their swelling behavior, in addition to the temperature and pH sensitivity of the swelling behavior.
The copolymer, which consists of acrylic acid (AAC) and acrylamide (AAM) units, is poly(AAM-co-AAC). A charge, hydrogen-bonding capacity, and adequate polarity for hydration are provided by the hydrophilic carboxylic acid and amide moieties in the polymer backbone. The copolymer is very sensitive to pH and temperature; so, in response to changes in pH and temperature, this hydrogel shows a shift in swelling behavior (Vinu and Madras, 2008).
Moxifloxacin is classified as a Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) class I drug due to its high solubility and high permeability. If a drug substance has an absorption rate of 85% in humans, it is characterized as “highly permeable”. We chose moxifloxacin as a model drug because it has a rapid and nearly complete absorption in humans, with an absolute bioavailability of around 90% (Charoo et al., 2020).
A class of fourth-generation fluoroquinolone antibiotic drugs is moxifloxacin hydrochloride (Fig. 1). A bulk side chain in the C-7 position and a methoxy group in the C-8 position is present in the structure (Biedenbach and Jones, 1996; Dalhoff et al., 1996; Davis and Bryson, 1994). This antibiotic property is effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The mechanism of action of moxifloxacin is involved in the inhibition of topoisomerase IV and DNA gyrase enzymes essential for the replication, repair, and transcription of bacterial DNA (Imming et al., 2006; Reece and Maxwell, 1991; Pestova et al., 2000).
The current study targeted the synthesis of poly(AAM-co-AAC) hydrogels by using AAM and AAC as monomers for varying crosslinkers with sodium metabisulfite (SMBS) and potassium persulfate as initiators. AAC allows water to swell further and AAM increases the hydrogel mechanical strength, so these hydrogels have strong mechanical and swelling potential. The presence of amide and acidic groups causes pH sensitivity in the polymer chain. As a model drug, the drug release analysis was carried out using moxifloxacin hydrochloride. In this study, the synthesized hydrogel is used to controlled release of the moxifloxacin drug.
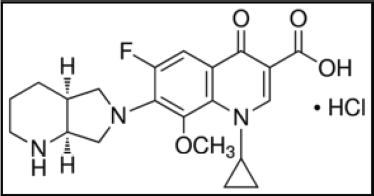 | Figure 1. Molecular composition of moxifloxacin hydrochloride. [Click here to view] |
Materials and Methods
Materials
AAC, MBA, potassium persulfate (PPS), AAM, sodium hydroxide, and potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate were received from Sd Fine Chem Limited (SDFCL), Mumbai, India. Hydrochloric acid and disodium hydrogen phosphate anhydrous were from Merck, Mumbai, India. SMBS was obtained from Avra Synthesis Pvt Ltd, Hyderabad, India. Moxifloxacin hydrochloride was received as a gift sample from Micro Labs Limited, Bangalore, India.
Hydrogel synthesis
The poly(AAM-co-AAC) hydrogel was synthesized in a glass vial using free radical initiators of SMBS and PPS by dissolving in distilled water to generate free radicals. Then, AAC and AAM monomers were added and allowed to blend for 10 minutes at an ambient temperature; then crosslinker MBA was added with uniform stirring. Then, this blend was placed in a water bath (80°C) for 1 hour until gel formation. After gel formation, it was washed with distilled water for 24 hours to eliminate unreacted constituents and eventually dried for 24 hours in the hot air oven at 50°C and stored in a closed container to avoid moisture absorbance.
Characterization
FTIR analysis
To determine the molecular interactions and structure, moxifloxacin hydrochloride, synthesized hydrogel, and moxifloxacin-loaded hydrogel samples were analyzed using the Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) instrument (Shimadzu, IRAffinity 1S FTIR, Japan).
TGA analysis
In a thermogravimetric analyzer (Perkin Elmer, STA 6000, USA), Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of the synthesized hydrogel was carried out. TGA was carried out by increasing the heat flow rate under the nitrogen atmosphere to 20°C/minute.
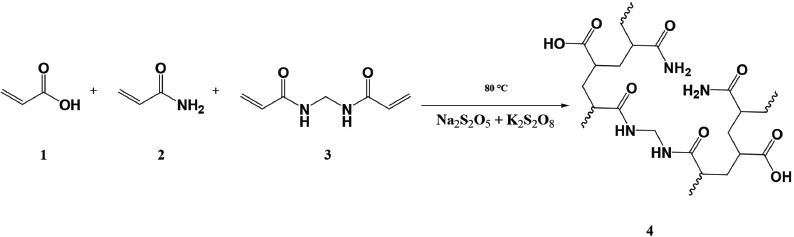 | Scheme 1. Hydrogel synthesis. (1) AAC, (2) AAM, (3) MBA, and (4) poly(AAM-co-AAC) hydrogels. [Click here to view] |
SEM study
To study the surface morphology of dried hydrogels, a scanning electron microscope was used. Using an Scanning electron microscope (SEM) (Zeiss, LS15, Germany) instrument, the hydrogel composites were exposed and imaged.
Swelling study
The swelling ratio was measured over time periods at various temperatures and pH solutions. Using HCl and NaOH solutions, the pH solutions were prepared. The pH solutions for swelling were applied to a known mass of hydrogel samples. The wet mass of the swollen samples was removed at particular time intervals and the surface water was absorbed with filter paper to eliminate excess outer surface droplets, and then the swelling ratio was weighed and measured using Equation 1.
where W1 and W2 are the initial and final weights of the hydrogel.
Preparation of calibration curve
The calibration curve was prepared using 100 mg/100 ml of moxifloxacin hydrochloride stock solution. The stock solution was formulated using a phosphate buffer solution of pH 7.4; then the solutions of 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 mg/l were prepared using the stock solution. The solutions from 200 to 400 nm were scanned using a spectrophotometer (Metash, UV-9000, China) and maximum absorption at λmax 288 nm was reported to prepare a calibration curve.
Drug-loading and drug release studies
By soaking the dry hydrogel in the presence of a drug-carrying solution, the drug would be loaded into the hydrogel. Moxifloxacin hydrochloride was selected as a model drug for the study of drug release. To 100 ml of moxifloxacin solution (1 mg/ml) in water, 0.1 g of dry hydrogel was added for drug loading. After 48 hours, the loaded hydrogels were weighed, and to prevent burst release, the loaded hydrogel was washed with ethanol and then placed in the vacuum oven for 24 hours to dry completely. The dried hydrogels were then weighed and the drug load was determined by using Equation (2). The in-vitro release efficiency of drug-loaded hydrogel in an acid buffer solution of pH 1.2 and phosphate buffer solution of pH 7.4 was evaluated at 37°C and 27°C using paddle method in dissolution test apparatus (LabIndia, DS-8000, India), respectively. The release solution was withdrawn at regular time intervals (30 minutes) with a sufficient dilution scanning the solutions between 200 and 400 nm and λmax absorbance at 288 nm using a UV-Visible spectrophotometer was reported. The release percentage was determined and the zero-order, first-order, Higuchi, Korsmeyer–Peppas, and Hixson–Crowell models were used to measure the statistical kinetic model of drug release (Baishya et al., 2017; Peppas et al., 2000).
 | Figure 2. Preparation stages of hydrogel. (a) Initial stage in solution. (b) Gel shape. (c) Dryness. (d) Swelling. [Click here to view] |
where W0 is the initial weight of the hydrogel and WD is the weight of the drug-loaded hydrogel.
Results and Discussion
Using AAM and AAC as a monomer with MBA as a crosslinker, hydrogels were prepared. As free radical generators, potassium persulfate and SMBS are used (Mahdavinia et al., 2004; Thippeswamy et al., 2021). The mechanism of the reaction is shown in Scheme 1 and the hydrogel formulations are given in Table 1.
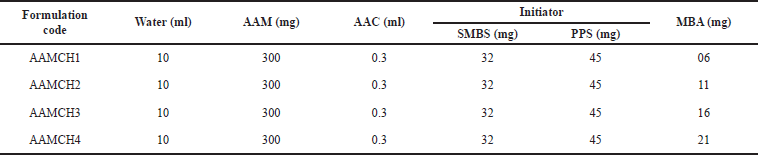 | Table 1. Schemes for the synthesis of hydrogels. [Click here to view] |
Hydrogel preparation
Figure 2 shows the hydrogel preparation steps. The swelling analysis was conducted after gel preparation (Isik and Kis, 2004; Madhusudana et al., 2021; Teo et al., 2008).
FTIR analysis
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride FTIR spectra (Fig. 3a) showed aromatic C=C stretching at 1,619 cm–1 and also demonstrated carboxylic acid C=O stretching at 1,703 cm−1, C-N stretching at 1,315 cm−1, and monofluorobenzene stretching at 1,044 cm−1. The poly(AAM-co-AAC) hydrogel spectra (Fig. 3b) showed carboxylic acid stretching at 3,213 cm−1, corresponding to the –OH. CH2 groups provided absorption at 1,450 cm−1 on the chain. The 2,925 cm−1 absorbance is the acrylate unit C-H stretching. The absorption can be attributed to the C=O group at 1,681 cm−1. The drug-loaded hydrogel peaks (Fig. 3c) observed were 3,203 cm−1, corresponding to the carboxylic acid -OH stretching. The 2,934 cm−1 absorbance is the C-H stretching and C=O group at 1,666 cm−1. Aromatic C=C stretching was at 1,615 cm−1 and monofluorobenzene stretching was at 1,044 cm−1 (Pravin et al., 2012; Tomar et al., 2007).
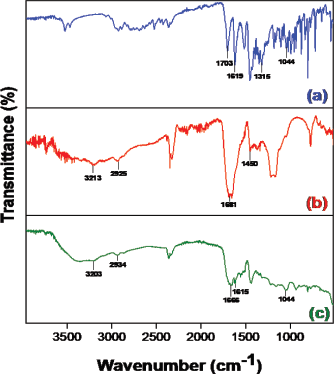 | Figure 3. FTIR spectrum of (a) moxifloxacin, (b) poly(AAM-co-AAC) hydrogel, and (c) moxifloxacin-loaded hydrogel. [Click here to view] |
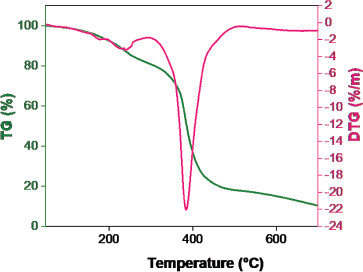 | Figure 4. Poly(AAM-co-AAC) hydrogel TGA graph. [Click here to view] |
TGA analysis
TGA has analyzed the thermal stability of the prepared hydrogel and the results are shown in Figure 4. Owing to the presence of moisture content in the hydrogel, the primary weight loss was absorbed. The poly(AAM-co-AAC) hydrogel was thermally unstable and degradation started at 240°C with a weight loss of 3.2% and a high mass loss was observed at 384°C with a weight loss of 22.0% due to breaking of crosslinking chain. This reduction has continued up to 700°C with a lesser amount (Ebrahimi and Salavaty, 2018).
SEM Study
The synthesized hydrogel micrographs (Fig. 5) were analyzed by SEM. The SEM Figures indicate that the surface is hard and it has been found to be slightly porous (Aouada et al., 2009; Chen et al., 2009).
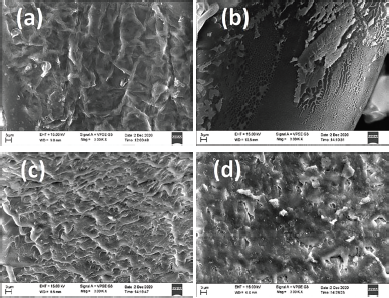 | Figure 5. SEM images of the dried hydrogels. (a) AAMCH1. (b) AAMCH2. (c) AAMCH3. (d) AAMCH4. [Click here to view] |
 | Figure 6. Images of (a) dried and (b) swollen hydrogels on a digital camera. [Click here to view] |
Swelling study
The swelling efficiency (Fig. 6) of the prepared hydrogel was studied using pH 1–10 solutions. The swelling ratio decreased when the crosslinker increased the maximum swelling observed in AAMCH1 (Fig. 7). Hence, due to the maximum swelling ratio observed, we chose AAMCH1 for further swelling and drug release study. The swelling ratio of the hydrogel in pH 1.2 and 7.4 buffer solutions similar to gastrointestinal fluids is shown in Figure 9. The results showed a high swelling ratio (7258%), observed in pH 7.4 compared to the solution at pH 1.2 (115%). The –CONH2 groups are protonated at a lower pH to create NH3+–NH3+ electrostatic repulsion swelling, but its swelling will be decreased by the presence of chloride ions. Carboxylic acid –COOH groups are deprotonated (–COO−) at higher pH and create electrostatic swelling repulsions, but the presence of more sodium ions (Na+) in pH 9 and pH 10 solutions reduces the swelling ratio compared to pH 8 by forming –COONa group (Fig. 8) (Pourjavadi and Mahdavinia, 2006; Wu et al., 2001).
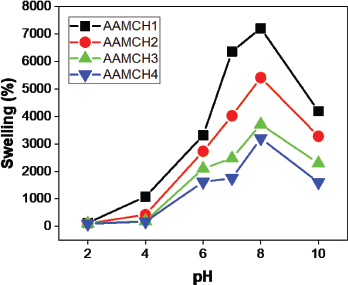 | Figure 7. Hydrogel swelling ratio of different formulations. [Click here to view] |
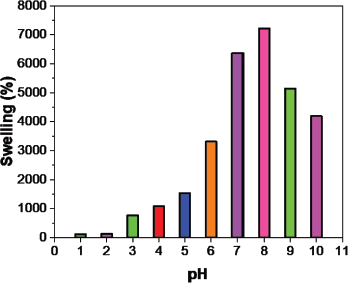 | Figure 8. Hydrogel swelling ratio at pH 1–10. [Click here to view] |
Drug selection
The selection of the drug for the release of the drug is most critical because to avoid λmax change, the drug should not react with solvents and hydrogels. Moxifloxacin drug has excellent content since no difference in λmax has been observed as time shifts. In order to assess maximal absorption at λmax 288 nm, solutions were scanned between 200 and 400 nm from the UV-Visible spectrophotometer. The calibration curve (Figs. 12 and 13) shows that R2 is 0.999 (coefficient of correlation).
Drug release
Drug release with time
The outcome of the swelling analysis helps assess the study of drug release. In acid and alkaline pH, the swelling ratio in pH 1.2 and 7.4 solutions (Fig. 9) suggest maximum swelling at alkaline pH 7.4 compared to pH 1.2 solutions similar to gastrointestinal fluid-like solutions. The drug release percentage of moxifloxacin is maximum (99%) at pH 7.4 than at pH 1.2 (18%) due to the swelling ratio maximum at pH 7.4. The hydrogel induces pH-sensitive drug release at maximum pH of 7.4 than pH 1.2 (Fig. 14).
Drug release with temperatures
The swelling ratio increased with increased temperature as compared to 27°C and 37°C (Fig. 10). To determine the temperature sensitivity of the hydrogel in drug release, we measured the pH 7.4 solution at 27°C and 37°C temperatures over time (Fig. 15). The outcome indicates that drug release has increased with temperature changes. The minimum amount (71%) of drug release was observed at 27°C and the maximum amount (99%) of drug release was observed at 37°C. The swelling ratio increases as the temperature increases due to the versatile nature produced in the polymer network, so water quickly enters the hydrogel network and swells. Similarly, the buffer solution enters the hydrogel polymer network and contributes to the increases in swelling and drug release.
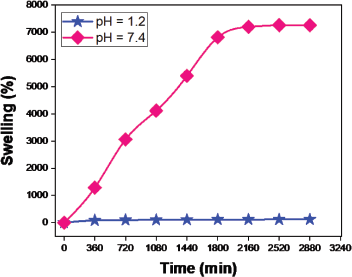 | Figure 9. Hydrogel swelling ratio at pH 1.2 and pH 7.4. [Click here to view] |
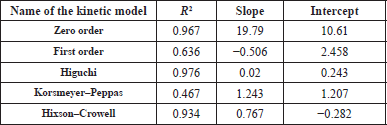 | Table 2. Drug release results in terms of R2, slope, and intercept of the different kinetic models. [Click here to view] |
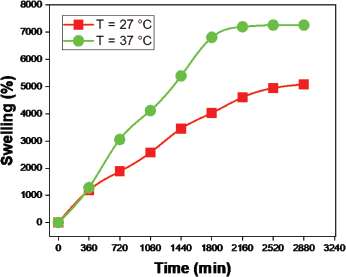 | Figure 10. Hydrogel swelling ratio at temperatures of 27°C and 37°C in pH 7.4 solution. [Click here to view] |
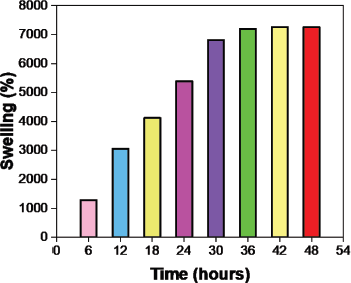 | Figure 11. Changes in the swelling ratio over time in pH 7.4. [Click here to view] |
Kinetic model drug release
The in-vitro release of the drug was estimated using different mathematical models and the effects of the correlation coefficient (R2) shown in Table 2 were evaluated. The maximum degree of the coefficient of correlation contributes to finding a suitable mathematical model that fits the kinetics of release. The result shows that the highest correlation coefficient (R2) is 0.976, so the hydrogel fits the Higuchi model drug release.
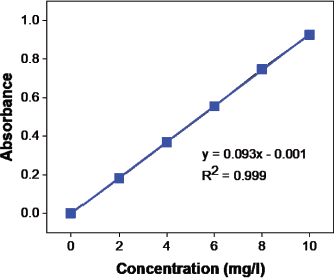 | Figure 12. Moxifloxacin calibration curve (absorbance vs. concentration). [Click here to view] |
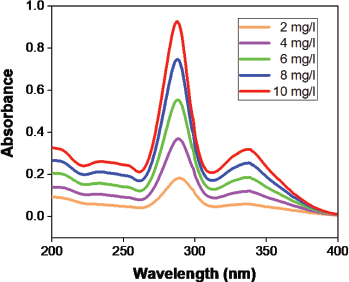 | Figure 13. Moxifloxacin calibration curve spectral graph. [Click here to view] |
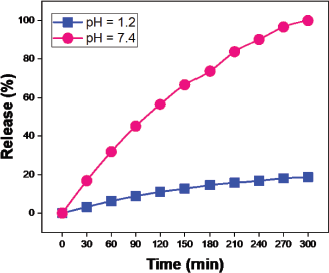 | Figure 14. Release of moxifloxacin drug at pH 1.2 and pH 7.4 solutions over time. [Click here to view] |
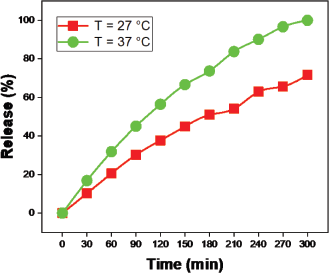 | Figure 15. Release of moxifloxacin drug at varying temperatures over time. [Click here to view] |