INTRODUCTION
Pometia genus belongs to the Sapindaceae family. This genus comprises 10 species that are distpersed from Malaysia to India (Jayasinghe et al., 2000). Pometia pinnata is one of the interesting species among Pometia genus. This plant has been traditionally used as a therapeutic agent for burns and wounds in Indonesia (Lense, 2012). Previously, the biological activities of P. pinnata extracts were reported. The methanol extract of the bark revealed antioxidant and antifungal activities (Kawamura et al., 2010). The ethanol extract of the bark also was reported to have α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitory activities (Elya et al., 2015). Recently, the tyrosinase inhibitory activities from the ethanol extract of the bark and leaves were studied (Sauriasari et al., 2017). Furthermore, the ethanol extract of the leaves and proanthocyanidin A2 from P. pinnata leaves indicated strong anti-HIV activity (Suedee et al., 2013). Nevertheless, there are no reported flavonol glycosides isolated from P. pinnata leaves as α-glucosidase inhibition. The aims of this research are to isolate secondary metabolites of P. pinnata leaves and to evaluate the α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of flavonol derivatives.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
General
All solvents and reagents were purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd (Osaka, Japan) and used without further purification. Silica gel for column chromatography (CC) was performed on silica gel N60 (Wakogel 60N, 38–100 μm) and TLC plates pre-coated with silica gel 70 F254 (60–200 mesh Wako gel) were purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd (Osaka, Japan). The separation spots of CC were monitored under the UV lamp (254 and 365 nm) and also by spraying with 10% CeSO4 followed by heating. IR spectra were measured on a PerkinElmer FT-IR/FIR Spectrometer 400. 1H, 13C, heteronuclear multiple-quantum correlation (HMQC), heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC), and 1H-1H-correlation spectroscopy (1H-1H-COSY) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra were recorded with JEOL JNM-ECS 400 spectrometer using tetramethylsilane (TMS) as an internal standard. MS spectra were recorded using the Waters UPLC-ESI-TOFMS system (Aquity UPLC XevoQTof) (Waters Corporation, Milford).
Plant material
The fresh leaves of P. pinnata (12 kg) were collected from the environment of Limau Manis, Padang, West Sumatera, Indonesia in June 2017 and later identified at Herbarium of Universitas Andalas, Padang, West Sumatera, Indonesia.
Extraction and isolation of secondary metabolites
The dried leaves (4 kg) were extracted using MeOH (12 L) at room temperature for 3 days, after that filtered and evaporated under vacuum. Afterward, the crude MeOH extract was partitioned subsequently to yield n-hexane fraction (45.5 g), dichloromethane (DCM) fraction (25.4 g), and EtOAc fraction (48.7 g), respectively.
EtOAc fraction of P. pinnata leaves (40.0 g) was separated by SiO2 CC eluting with mixtures of n-hexane/EtOAc (100:0-0:100 v/v), EtOAc/MeOH (100:0-0:100 v/v) to obtain 15 fractions (Fr. A to Fr. O). Fraction D (14.1 g) was performed on silica gel CC using a mixture of n-hexane/EtOAc (9:1 v/v) to yield five sub-fractions (D1–D5). Fraction D4 (1.1 g) was separated by CC using EtOAc to give three sub-fractions (D4.1–D4.3). Fraction D4.1 (361.2 mg) was purified by recrystallization to obtain compound 1 (211.7 mg). Fraction D4.2 (188.9 mg) was purified by CC using CHCl3/MeOH (5:1 v/v) to yield compounds 2 (17.4 mg) and also 1 (39.0 mg).
Identification of secondary metabolites
According to the analysis of spectroscopic data, including IR, NMR (1D, 2D), and MS, the structures of compounds (1–2) were determined. The NMR spectroscopic data were recorded at 400 MHz for 1H and 100 MHz for 13C using TMS as an internal standard.
Kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside (1)
Yellow amorphous powder. IR Vmax 3253, 2956, 1651, 1361, 1171, and 828 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, (CD3)2CO (ppm): δ 7.84 (2H, dd, J = 8.7, 2.8 Hz, H-2ʹ and H-6ʹ), 7.01 (2H, dd, J = 8.7, 2.8 Hz, H-3ʹ and H-5ʹ), 6.45 (1H, d, J = 2.3 Hz, H-8), 6.25 (1H, d, J = 1.8 Hz, H-6), 5.52 (1H, d, J = 1.4 Hz, H-1″), 4.20 (1H, d, J = 1.4 Hz, H-2″), 3.70 (1H, dd, J = 3.7, 8.7 Hz, H-3″), 3.30 (2H, m, H-4″ and H-5″), and 0.90 (3H, d, J = 6.0 Hz, Me-6″). 13C NMR (100 MHz, (CD3)2CO, ppm): δ 178.4 (C-4), 164.3 (C-7), 162.3 (C-5), 160.1 (C-9), 157.7 (C-4ʹ), 157.1 (C-2), 134.9 (C-3), 130.9 (C-2ʹ and C-6ʹ), 121.6 (C-1ʹ), 115.5 (C-3ʹ and C-5ʹ), 104.9 (C-10), 101.9 (C-1″), 98.8 (C-6), 93.8 (C-8), 72.0 (C-4″), 71.0 (C-2″), 70.7 (C-3″), 70.6 (C-5″), 17.0 (Me-6″). HRESITOFMS: m/z 455.0944 [M+Na]+ (calcd. for C21H20O10Na, 455.0954; error: 2.2 ppm).
Quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside (2)
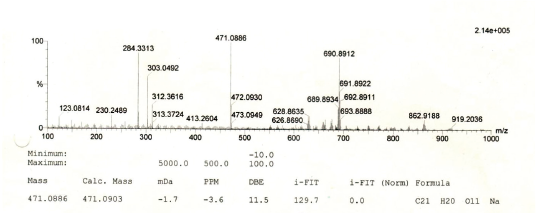
Yellow amorphous powder. IR Vmax 3198, 2923, 1652, 1354, 1195, 808 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD, ppm): δ 7.33 (1H, d, J = 1.9 Hz, H-2ʹ), 7.30 (1H, dd, J = 8.2, 2.3 Hz, H-6ʹ), 6.91 (1H, d, J = 8.2 Hz, H-5ʹ), 6.36 (1H, d, J = 1.8 Hz, H-8), 6.20 (1H, d, J = 1.8 Hz, H-6), 5.30 (1H, d, J = 1.4 Hz, H-1″), 4.20 (1H, dd, J = 3.2, 1.4 Hz, H-2″), 3.70 (1H, dd, J = 9.1, 3.7 Hz, H-3″), 3.40 (1H, dd, J = 5.9, 9.6 Hz, H-5″), 3.30 (1H, dd, J = 5.9, 9.6 Hz, H-4″), 0.90 (3H, d, J = 6.0 Hz, Me-6″). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CD3OD, ppm): δ 178.3 (C-4), 164.6 (C-7), 161.9 (C-5), 158.0 (C-9), 157.2 (C-2), 148,5 (C-4ʹ), 145.1 (C-3ʹ), 134.9 (C-3), 121.6 (C-1ʹ), 121.5 (C-6ʹ), 115.6 (C-5ʹ), 115.0 (C-2ʹ), 104.6 (C-10), 102.2 (C-1″), 98.4 (C-6), 93.4 (C-8), 71.9 (C-4″), 70.8 (C-2″), 70.7 (C-3″), 70.6 (C-5″), 16.3 (Me-6″). HRESITOFMS: m/z 471.0886 [M+Na]+ (calcd. for C21H20O11Na, 471.0903; error: 3.7 ppm).
Determination of α-glucosidase inhibitory activity
Chemical reagents
α-Glucosidase [(EC 3.2.1.20)] from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, p-nitrophenyl α-D-glucopyranoside (pNPG) and quercetin (8) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Co. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd (Japan). Three compounds, astragalin (3), isoquercetin (4), and nicotiflorin (5) were isolated from Eleutherococcus sieboldianus leaves (Nishina et al., 2017). Rutin (6) and kaempferol (7) were purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry, Ltd (Tokyo, Japan). A 96-well microtiter plate was purchased from Corning Inc. (Corning Costar, Cambridge, MA).
α-Glucosidase inhibitory assay
α-Glucosidase inhibitory activity was evaluated according to the previous method (Dewi et al., 2015). α-Glucosidase (50 μl, 0.5 ~ Unit/mg) and 2 μl of various concentrations of the sample in DMSO were poured into 96-well microplate, and then pre-incubated at 37°C for 5 minutes. The reaction was started by the addition of 50 μl of pNPG (5 mM). The mixture was later incubated at 37°C for 5 minutes. The α-glucosidase activity was measured by using a microplate reader (Emax precision microplate reader, Molecular Devices Japan, Tokyo, Japan) at 405 nm. The % inhibition value expressed α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of each sample and calculated as follows (Eq. 1):
where the control represents the assay in which the sample is replaced by the solvent used in its preparation.
UPLC-ESI-TOFMS analysis
The EtOAc fraction of P. pinnata leaves was dissolved in DMSO/H2O (1/1) at 20 mg/ml and filtered across 0.45 μm membrane filter (ADVANTEC®, Japan). An aliquot (5 μl) of the sample was injected in the Waters UPLC system (Aquity UPLC XevoQTof). Analysis was carried out by UPLC system using a UPLC BEH C18 analytical column (1.7 μm, ø 2.1 x 100 mm). The mobile phase contained solvent A (distilled water) and solvent B (MeOH). The condition of linear gradient system: 0–30 minutes (90% to 70% solvent A and 10% to 30% solvent B); was kept for 5 min; 35–45 minutes (70% to 50% solvent A and 30% to 50% solvent B). The column eluate was monitored at 260 nm UV absorbance. The negative mode was employed in ESI-TOFMS (Pardede and Koketsu, 2017).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
α-Glucosidase inhibitory activity of Pometia pinnata fractions
Fractions of n-hexane (45.5 g), DCM (25.4 g), and EtOAc (48.7 g) were obtained by successively fractionation of MeOH extract of P. pinnata leaves. As preliminary screening, we evaluated in vitro inhibitory activity of three fractions of P. pinnata leaves against α-glucosidase of S. cerevisiae with slight modification (Dewi et. al., 2015). In this study, the EtOAc fraction of P. pinnata leaves showed the strongest inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase (percent inhibition = 95.5% ± 0.7) at 100 μg/ml. DCM fraction had inhibitory activity (percent inhibition = 84.7% ± 0.1) at the same concentration, while n-hexane fraction showed poor inhibitory activity (percent inhibition = 38.7% ± 1.9) (Fig. 1). According to this result, the compounds from EtOAc fraction of P. pinnata leaves must be isolated.
Characterization of isolated compounds
To ascertain the potential compounds with respect to these properties, the EtOAc fraction of P. pinnata leaves was separated by CC on silica gel (SiO2) and later purified by CC and recrystallization to obtain two flavonol rhamnoside compounds, namely, compound 1 (146.5 mg) and compound 2 (17.4 mg). The chemical structure of isolated compounds was elucidated based on spectroscopic data, including IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, 2D NMR, and HRESITOFMS. Compound 1 was obtained as a yellow amorphous powder. IR data exhibited the presence of hydroxyl and carbonyl functional groups at 3253 and 1651 cm-1, C-H stretching at 2956 cm-1, C=C olefin ring at 1361 cm-1, asymmetric C-O-C stretching at 1171 cm-1, and substituted benzene at 828 cm−1. The 1H NMR spectrum (see Supplementary Data) of 1 showed four aromatic hydrogen signals containing six protons (Table 1). Two protons at 7.84 ppm (2H, dd, J = 8.7, 2.8 Hz, H-2ʹ and H-6ʹ) and two protons at 7.01 ppm (2H, dd, J = 8.7, 2.8 Hz, H-3ʹand H-5ʹ) assigned symmetric pattern with substitution at 1 and 4 positions. 1H-1H COSY correlation showed two set of ortho-coupled aromatic protons at 7.84 ppm (H-2ʹ/H-6ʹ) and 7.01 ppm (H-3ʹ/H-5ʹ) with coupling constant as J = 8.7 Hz. Furthermore, the proton at H-2ʹ had meta-coupled with H-6ʹ, and H-3ʹ with H-5ʹ (J = 2.8 Hz) of B ring of the flavone skeleton. A remaining two aromatic proton signals at 6.45 ppm (1H, d, J = 2.3 Hz) and 6.25 ppm (1H, d, J = 1.8 Hz) were assigned at H-8 and H-6 positions. Accordingly, this compound was predicted to have trihydroxyl substitutions at C-5 (162.3 ppm), C-7 (164.3 ppm), and C-4ʹ (157.7 ppm) in flavone skeleton. The 13C NMR spectrum indicated 19 carbon signals. The correlation between proton and carbon in HMQC showed six methines aromatic at H-6 (6.25 ppm)/C-6 (98.8 ppm), H-8 (6.45 ppm)/C-8 (93.8 ppm), H-2ʹ or H-6ʹ (7.84 ppm)/C-2ʹ and or C-6ʹ (130.9 ppm), H-3ʹ or H-5ʹ (7.01 ppm)/C-3ʹ and or C-5ʹ (115.5 ppm). According to HMQC correlation, the remaining of annomeric proton located at 5.52 ppm (1H, d, J = 1.4 Hz), four oxygenated methines at 4.20 ppm (1H, d, J = 1.4 Hz, H-2″), 3.70 ppm (1H, dd, J = 3.7, 8.7 Hz, H-3″), 3.33 ppm (2H, m, H-4″ and H-5″), and one methyl at 0.90 ppm (3H, d, J = 5.9 Hz, Me-6″) indicated the occurrence of rhamnosyl unit in this compound. HMBC correlation of the annomeric proton at 5.52 ppm with the annomeric carbon at 134.9 ppm confirmed that sugar moiety was bound to the C-3 hydroxyl group. The HRESITOFMS data showed the molecular formula was established as C21H20O10 for the peak at m/z 455.0944 [M+Na]+ (calcd. for C21H20O10Na, 455.0954; error 2.2 ppm). Compared the spectral data of the isolated compound with literature, we confirmed this isolated compound 1 as kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside (afzelin) (Suedee et al., 2013).
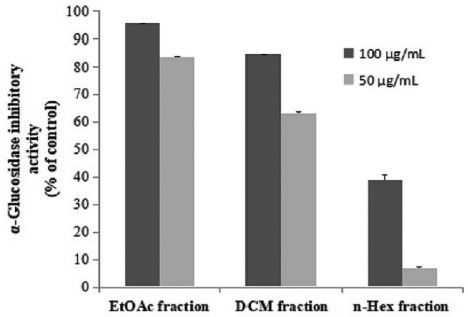 | Figure 1. α-Glucosidase inhibitory activity of Pometia pinnata leaves fractions (mean ± SEM; n = 5). [Click here to view] |
Compound 2 was obtained as a yellow amorphous powder. On the TLC, the spot of compound 2 was active under UV lamp 254 and 365 nm and came out yellow after spraying with 10% CeSO4, which was characteristic of flavone compound. The IR data of compound 2 indicated to bear the similar functional groups as similar as to compound 1, which were the vibrations of hydroxyl group, C-H stretching, carbonyl functional group, C=C olefin ring, asymmetric C-O-C stretching, and substituted benzene at 3198, 3002, 1652, 1354, 1195, and 808 cm−1, respectively. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of the compound 2 were also similar to the spectra of compound 1. The 1H NMR spectrum showed five aromatic proton signals at 7.33 ppm (1H, d, J = 1.9 Hz, H-2ʹ), 7.30 (1H, dd, J = 8.2, 2.3 Hz, H-6ʹ), 6.91 (1H, d, J = 8.2 Hz, H-5ʹ), 6.36 (1H, d, J = 1.8 Hz, H-8), 6.20 (1H, d, J = 1.8 Hz, H-6). One set of meta-coupled aromatic protons appeared at 7.33 ppm (d, J = 1.9 Hz) and 7.30 ppm (dd, J = 2.3 Hz), in other than proton at 7.30 ppm (dd) also had ortho coupling with proton at 6.91 ppm (d) with coupling constant of J = 8.2 Hz. We confirmed the presence of three substitutions in B ring. Remaining two meta-coupled aromatic protons at 6.25 and 6.36 ppm (J = 1.8 Hz) indicated dihydroxyl substitutions in A ring of flavone skeleton. The 13C NMR spectrum showed 21 signals, containing 6 rhamnosyl carbon signals (102.2, 70.8, 70.7, 71.9, 70.6, and16.3 ppm) in Table 1. The molecular formula was established as C21H20O11 for the peak at m/z 471.0886 [M+Na]+ (calcd. for C21H20O11Na; error: 3.7 ppm) from HRESITOFMS. Comparing the spectral data of the isolated compound with related literature, we confirmed this isolated compound 2 as quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside (quercitrin) (Gopi et al., 2016).
UPLC-ESI-TOFMS analysis
The EtOAc fraction and isolated kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside (1) and quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside (2) were analyzed by UPLC-ESI-TOFMS. The chromatogram of the EtOAc fraction revealed two major peaks at retention time 34.16 and 41.23 min (Fig. 2A). Figure 2B shows the peak of kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside (1) which was detected at the retention time of 41.05 min, while the peak of quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside (2) revealed at the retention time 34.13 min (Fig 2C). Furthermore, a minor peak at retention time 28.92 min from EtOAc fraction of this plant also appeared (Fig 2A). Compared with the previously isolated compound, quercetin-3-O-glucoside (isoquercetin), appeared at retention time 28.54 min (Fig 2D). The minor peak at retention time 28.92 min in EtOAc fraction of P. pinnata leaves was confirmed to be quercetin-3-O-glucoside (Nishina et al., 2017).
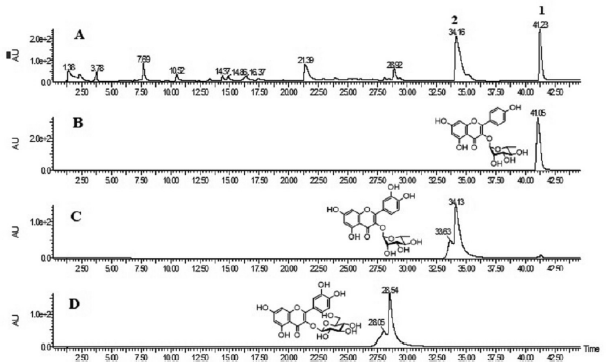 | Figure 2. UPLC-ESI-TOFMS analyses of (A) EtOAc fraction of P. pinnata leaves, (B) Kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside, (C) Quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside, and (D) Quercetin-3-O-glucoside. [Click here to view] |
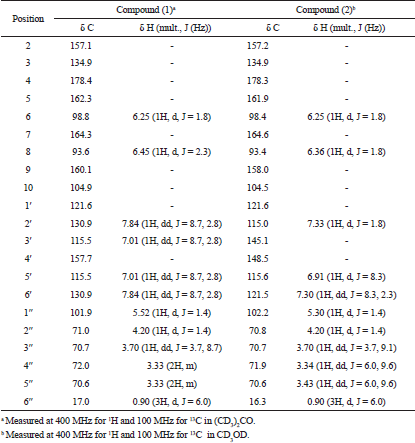 | Table 1. 1H and 13C NMR data of isolated compounds. [Click here to view] |
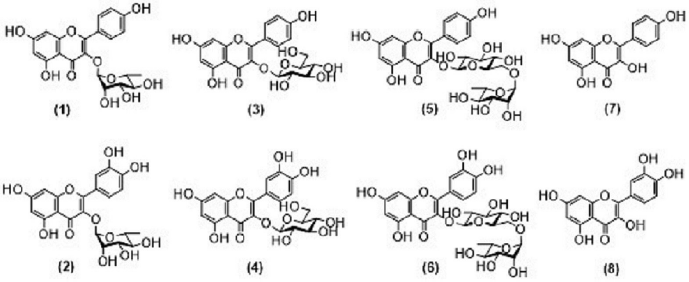 | Figure 3. Chemical structures of flavonols and their derivatives compounds: Kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside (afzelin) (1), Quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside (quercitrin) (2), Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside (astragalin) (3), Quercetin-3-O-glucoside (isoquercetin), (4), Kaempferol-3-O-glucosyl-(1→4)-rhamnoside (nicotiflorin) (5), Quercetin-3-O-glucosyl-(1→4)-rhamnoside (rutin) (6), Kaempferol (7), and Quercetin (8). [Click here to view] |
α-Glucosidase inhibitory activity of isolated compounds
In this study, two flavonol compounds kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside (1) and quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside (2) were isolated. The authors are interested in the structure–activity relationship of kaempferol derivatives and quercetin derivatives for α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. Four kaempferol derivatives and four quercetin derivatives were chosen, which include eight derivatives, including kaempferol (7) and quercetin (8) and their derivatives, bearing sugar moiety into the C-3 position, such as kaempferol-3-O-glucoside (3), quercetin-3-O-glucoside (4), kaempferol-3-O-glucosyl-(1→4)-rhamnoside (5), and quercetin-3-O-glucosyl-(1→4)-rhamnoside (6) for this assay (Fig. 3).
The α-glucosidase inhibitory activities all of the compounds (1–8) were evaluated according to the previous method with slight modification (Dewi et al., 2015). The % inhibitions of compounds 1–8 are summarized in Table 2. The results showed that quercetin 8 had the strongest α-glucosidase inhibitory activity among all the tested eight compounds (1–8). The % inhibition of compounds 1 and 2 at final concentration 50 μM were 45.06% ± 0.22 and 34.83% ± 0.59 against α-glucosidase, respectively, which were lower than that of kaempferol (7) and quercetin (8) with percent inhibition 82.93% ± 0.37 and 80.10% ± 0.76, respectively. We confirmed that the introduction of sugar moiety at the C-3 position in the flavonol structure reduced α-glucosidase inhibitory activity and that the hydroxyl group at the C-3 position was an essential requirement for the activity. Similar results have been reported, the hydroxyl group at the C-3 and C-5 positions on the A and C rings of flavones enhancing the α-glucosidase inhibitory activity (Tadera et al., 2006). Compounds 1, 3, and 5 possessed the same aglycone as kaempferol. Compound 1 had a stronger inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase than that against of compounds 3 (percent inhibition = 37.18% ± 0.62) and 5 (% I = 26.38% ± 0.63). Quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside (2) had a stronger inhibitory effect among quercetin derivatives (2, 4, and 6). The flavonol rhamnosides (1 and 2) were stronger than flavonol glucosides (3 and 4) and flavonol rutinosides (5 and 6). According to the literature data, kaempferol and quercetin showed stronger α-glucosidase inhibitory activity than that positive control (acarbose) (Abbasi et al., 2014; Proenca et al., 2017; Sheng et al., 2017). Kaempferol and quercetin from C. asiatica showed strong α-glucosidase inhibitory with IC50 16~22 μg/ml (Dewi and Faiza, 2015). Both compounds also were reported to inhibit the rat small intestinal α-glucosidase (Tadera et al., 2006). On the other hand, the inhibitory activity of flavonoid glycosides is usually lower than that the aglycones (Sarian et al., 2017). The mechanism of kaempferol and quercetin as an antidiabetic treatment showed that they were competitive inhibitors for inhibitory α-glucosidase (Proenca et al., 2017; Sheng et al., 2017).
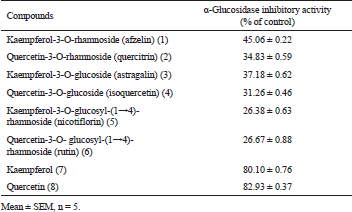 | Table 2. α-Glucosidase inhibitory activity of flavonols and their derivatives at the final concentration of 50 μM. [Click here to view] |
CONCLUSION
The EtOAc fraction from P. pinnata leaves contained the highest α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. This result was obtained after the isolation of two flavonol rhamnosides, such as kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside (1) and quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside (2), from the EtOAc fraction of P. pinnata leaves. Based on the structure–activity relationship among tested compounds (1–2 from P. pinnata leaves, 3–5 from Eleutherococcus sieboldianus leaves, and 6–8 from commercial available), the quercetin (8) showed the highest α-glucosidase inhibitory activity among eight flavonol derivatives. Compound 1 had stronger inhibitory activity than that of compound 2. In the flavonol structure, the occurrence of sugar moiety at C-3 position reduced the α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. Among flavonol derivatives, the rhamnoside moiety bound to flavonol structure (1 and 2) was stronger than flavonol glucoside (3 and 4) and flavonol rutinoside (5 and 6) against α-glucosidase.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was financially funded by The Ministry of Research and Technology of Republic of Indonesia through “Master Program of Education Leading to Doctoral Degree for Excellent Graduate (PMDSU)” scholarship (Grant number: 059/SP2H/LT/DRPM/IV/2017). The authors would also like to thank to Mr. Daiki Kaneko and Mr. Eito Horiyama for their fruitful assistance.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
Abbasi MA, Ghulam H, Aziz-ur-Rahman, Viqar UA. Flavonoids from Rhynchosia pseudo-cajan as suitable α-glucosidase inhibitors and free radical scavengers. Int Res J Pharm, 2014; 5:636–41. CrossRef
Dewi RT, Faiza M. Antioxidant and α-Glucosidase inhibitory compounds of Centella asiatica. Procedia Chem, 2015; 17:147–52. CrossRef
Dewi RT, Tachibana S, Fajriah S, Hanaf M. α-Glucosidase inhibitor compounds from Aspergillus terreus RCC1 and their antioxidant activity. Med Chem Res, 2015; 24:737–43. CrossRef
Elya B, Handayani R, Sauriasari R, Azizahwati, Hasyyati US, Permana IT, Permatasari YI. Antidiabetic activity and phytochemical screening of extracts from Indonesian plants by inhibition of α-amylase, α-glucosidase and dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Pak J Biol Sci, 2015; 18:279–84. CrossRef
Gopi K, Anbarasu K, Renu K, Jayanthi S, Vishwanath BS, Jayaraman G. Quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside from Euphorbia hirta protects against snake Venom induced toxicity. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2016; 1860:1528–40. CrossRef
Jayasinghe ULB, Wannigama GP, Fujimoto Y. Chemistry and bioactivity of saponins from some Sri Lankan plants. In: Oleszek W, Marston A (eds.). Saponins in food, Feedstuffs and Medicinal Plants, Kluwer Academic, The Netherlands, 2000; 45:113–9. CrossRef
Kawamura F, Shaharuddin NA, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ohara S. Evaluation antioxidant activity, antifungal activity and total phenols of 11 selected commercial Malaysian timber species. Jpn Agr Res Quart, 2010; 44:319–24 CrossRef
Lense O. The wild plants used as traditional medicines by indigenous people of Manokwari, West Papua. Biodiversitas, 2012; 13:98–106. CrossRef
Nishina A, Itagaki M, Suzuki Y, Koketsu M, Ninomiya M, Sato D, Suzuki T, Hayakawa S, Kuroda M, Kimura H. Effects of flavonoids and triterpene analogues from leaves of Eleutherococcus sieboldianus (Makino) Koidz. ‘Himeukogi’ in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Molecules, 2017; 22:671–9. CrossRef
Pardede A, Koketsu M. Antioxidant and antileukemic activity of chemical compounds from bark of Mangifera casturi. Comp Clin Pathol, 2017; 26:499–504. CrossRef
Pereira DF, Cazarolli LH, Lavado C, Mengatto V, Figueiredo MSRB, Guedes A, Pizzolatti MG, Silva FRMB. Effects of flavonoids on α-glucosidase activity: potential targets for glucose Homeostasis. Nutrition, 2011; 27:1161–7. CrossRef
Proenca C, Freitas M, Ribeiro D, Oliveira EFT, Sousa JLC, Tome SM, Ramos MJ, Silva AMS, Fernandes PA, Fernandes E. α-Glucosidase inhibition by flavonoids: an in vitro and in silico structure–activity relationship study. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem, 2017; 32:1216–28. CrossRef
Sarian MN, Ahmed QU, So’ad SZM, Alhassan MA, Murugesu S, Perumal V, Mohamad SNAS, Khatib A, Latip J. Antioxidant and antidiabetic effects of flavonoids: a structure-activity relationship based study. BioMed Res Int, 2017; 2017:1-14. CrossRef
Sauriasari R, Azizah N, Basah K. Tyrosinase inhibition, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging activity, and phytochemical screening of fractions and ethanol extract from leaves and stem bark of matoa (Pometia pinnata). Asian J Pharm Clin Res, 2017; 10:85–9. CrossRef
Sheng Z, Ai B, Zheng L, Zheng X, Xu Z, Shen Y, Jin Z. Inhibitory activities of kaempferol, galangin, carnosic acid and polydatin against glycation and α-amylase and α-glucosidase enzymes. Int J Food Sci Technol, 2017; 53:755–66. CrossRef
Suedee A, Tewtrakul S, Panichayupakaranant P. Anti-HIV-1 integrase compound from Pometia pinnata leaves. Pharm Biol, 2013; 51:1256–61. CrossRef
Tadera K, Minami Y, Takamatsu K, Matsuoka T. Inhibition of α-glucosidase and α-amylase by flavonoids. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol, 2006; 52:149–53. CrossRef
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Compound 1
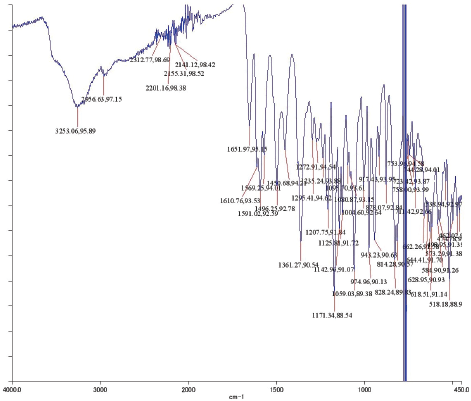 | IR Spectrum of Compound 1 [Click here to view] |
.png) | 1H-NMR Spectrum of Compound 1 [Click here to view] |
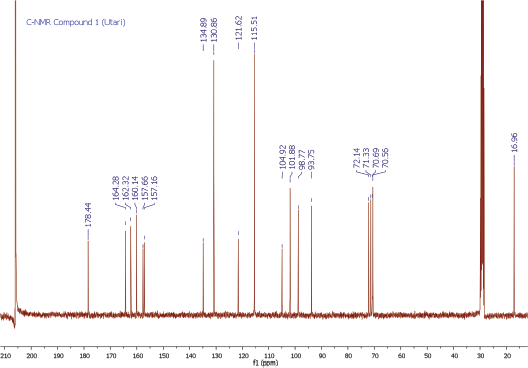 | 13C-NMR Spectrum of Compound 1 [Click here to view] |
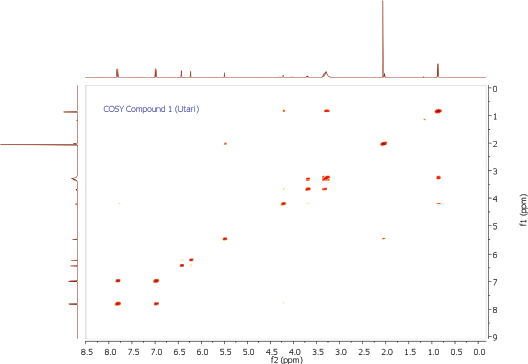 | COSY Spectrum of Compound 1 [Click here to view] |
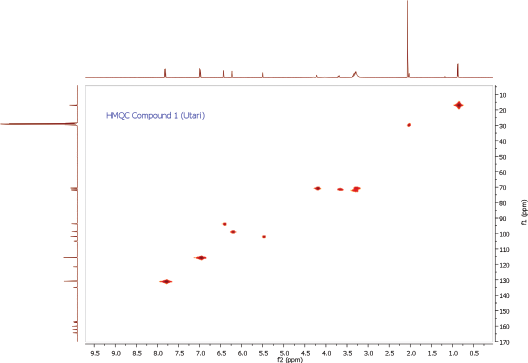 | HMQC Spectrum of Compound 1 [Click here to view] |
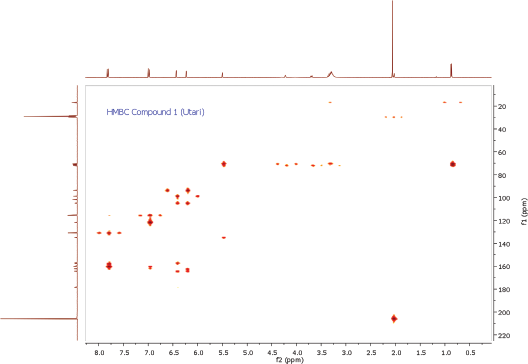 | HMBC Spectrum of Compound 1 [Click here to view] |
 | MS Spectrum of Compound 1 [Click here to view] |
Compound 2
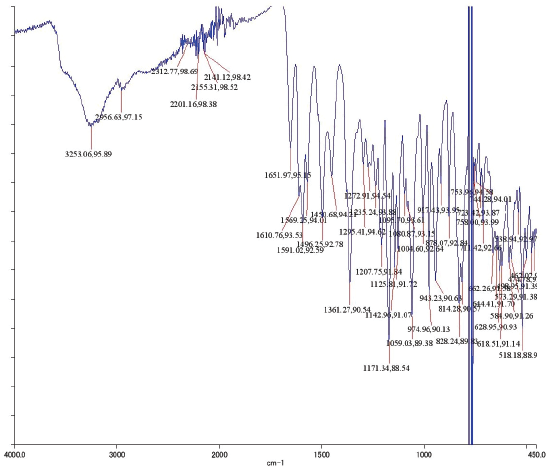 | IR Spectrum of Compound 1 [Click here to view] |
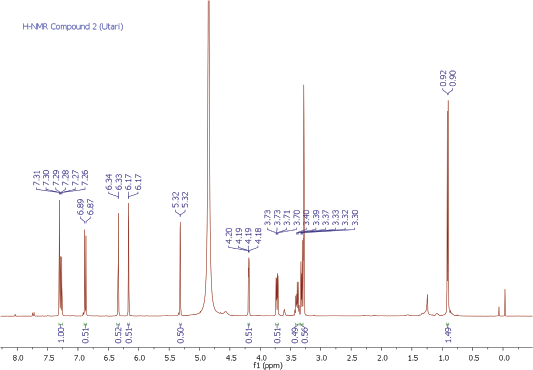 | 1H-NMR Spectrum of Compound 2 [Click here to view] |
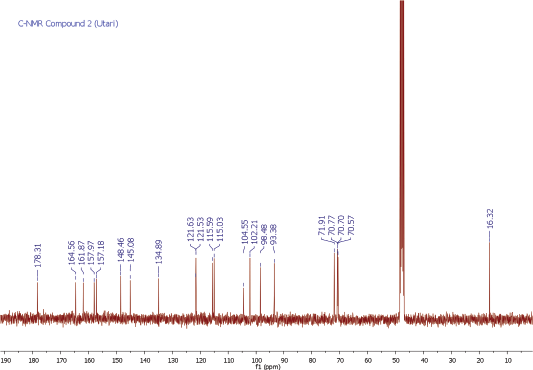 | 13C-NMR Spectrum of Compound 2 [Click here to view] |
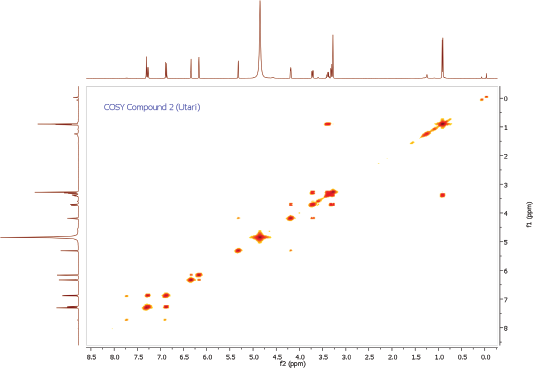 | COSY Spectrum of Compound 2 [Click here to view] |
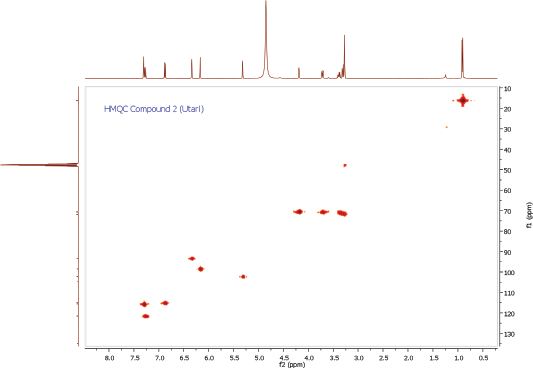 | HMQC Spectrum of Compound 2 [Click here to view] |
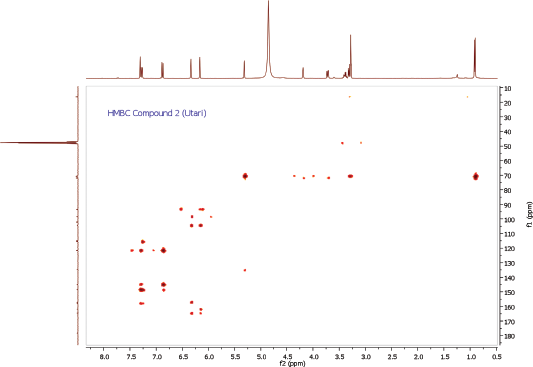 | HMBC Spectrum of Compound 2 [Click here to view] |
 | MS Spectrum of Compound 2 [Click here to view] |