INTRODUCTION
At the global level, now the third leading cause of demise is cancer (Harris et al., 2013), and it has been estimated that within 20 years there will be approximately 26 million new cases of cancer and 17 million deaths will occur per annum (Thun et al., 2010). A series of cumulative genetic and epigenetic modification that occur in healthy cells initiates cancer and characterize by many distinct behaviors (Kreeger and Lauffenburger, 2010). Cancer cells generate signals of their own growth (Marusyk and Polyak, 2010), insensitive to growth suppressive signals, stave off cell death, rampant replication (Brooks et al., 2010), capability to stimulate angiogenesis and ability to invade tissues via basement membrane and walls of capillary (Sung et al., 2007).
Most widely used treatment for metastatic cancer is chemotherapy which works by targeting rapidly dividing cells (Donnelly, 2004). As a result, chemotherapy fails to differentiate cancer cells from normal cells and is unable to target dormant cancer (Naumov et al., 2003). In order to overcome this problem, valuable efforts have been made to develop a new class of anticancer drugs which have potential to selectively kill cancer cells while sparing healthy cells, regardless of their growth rate (Bush and Li, 2002). Various natural or synthetic cationic peptides alternative to conventional chemotherapy have been studied that exhibit anticancer activity with ability to kill target cells rapidly and specifically (Dennison et al., 2006).
In hunting for new anticancer agents, host defense peptides are promising alternative anticancer therapeutics that can contribute various benefits over other treatments (Hoskin and Ramamoorthy, 2008). Due to their activity and exclusivity on cancer cell membrane, there are less chance of toxicity to normal cells (Riedl et al., 2011).
Cationic antimicrobial peptides are small proteins, usually less than 40 amino acids in length, which are mainly made of basic (e.g., lysine and arginine) and hydrophobic (e.g., tryptophan) amino acids (Mader and Hoskin, 2006). A class of antimicrobial peptide Cecropins was first described in insects and the giant silk moth Hyalophora cecropia but later also reported in mammals. Cecropin A (KWKLFKKIEKVGQNIRDGIIKAGPAVAVVGQATQIAK) and Cecropin B (KWKVFKKIEKMGRNIRNGIVKAGPAIAVLGEAKAL) exhibit anticancer activity against various human cancer cell lines like lymphoma and leukemia cells without affecting the normal cells at peptide concentrations that are fatal to the transformed cells (Hui et al., 2002; Srisailam et al., 2000).
In the present work, we have designed, synthesized, and evaluated short chain α-helical linear and cyclic peptide from cecropin B having same charge, hydrophobicity, and helicity.
DESIGNING
It is clear from the fact that anticancer peptides (ACPs) obtained from different sources have very low similarity; nevertheless, they have some common characteristics, such as an amphipathic nature, a positive charge, the ability to possesses secondary structure (α-helical or β-sheet) in a hydrophobic environment and broad spectrum anticancer activity (Zelezetsky and Tossi, 2006).
The main class of cationic ACPs has α-helical structure and exhibit following properties:
(1) They retain basic amino acids, like arginine and lysine in their chain which revealed net positive charge of peptides from +2 to +9 in neutral pH; (2) Generally peptide chain is of 5–40 amino acid long with more than 30% hydrophobic residues; (3) They have amphipathic conformation (Liberio et al., 2013). Various physicochemical parameters of peptides, such as net charge, helicity, and hydrophobicity, have been signified to play principal roles in the selectivity and activity of α-helical ACPs against tumor cells (Huang et al., 2015).
In the present work, short chain peptides were designed by utilizing template-assisted approach based on structural parameters (charge, hydrophobicity, and helicity) from naturally occurring ACP cecropin B (KWKVFKKIEKMGRNI RNGIVKAGPAIAVLGEAK AL) (Chou et al., 2008) by removing amino acids in such a manner that it retains same or more cationic charge and hydrophobicity (Table 1). Hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity, and Charge of peptide were achieved by software package provided by Genscript. The amino acids sequence of Cecropin B, linear and cyclic compounds were designed as following:
Cecropin B: KWKVFKKIEKMGRNIRNGIVKAGPAIAVLGEAKAL
Designed Linear Compound: KKVKKIKRVKIAVLA
Designed Cyclic Compound: KKVKKIKRVKIAVLA
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Melting points were determined by open capillary method. Amino acids, di-tertbutylpyrocarbonate (Boc2O), triethylamine (TEA), trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC), N-methylmorpholine (NMM), p-nitrophenol (PNP), tetrahydrofuran (THF), and pyridine were procured from Spectro Chem Limited (Mumbai, India). Determination of purity of synthesized peptide was accompanied by thin layer chromatography using chloroform & methanol as eluent. IR spectra were recorded on Perkin Elmer Spectrum RX-1 FTIR. 13C NMR and Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) spectra were recorded on Bruker AC NMR spectrometer (300 MHz), using CDCl3 as a solvent and TMS as a internal reference. A fast atom bombardment mass spectrum was recorded on JMS-DX 303 Mass spectrometer. For elemental analysis of all the synthesized compounds, Vario EL III elemental analyzer was used.
Method for protection and deprotection of amino acid/peptide units (amino terminal)
For the protection of free α-amino group, 20 mmol of amino acid/peptide dissolved in 1N NaOH (40 ml) and isopropanol (30 ml) was added to 6 ml (2.6 mmol) Boc2O with stirring for 2.5 hours at RT, followed by washing with 20 ml of light petroleum ether (b.p. 40ºC–60ºC). The above solution was acidified to pH 3.0 using 2N H2SO4 and then finally extracted by 60 ml of chloroform. Anhydrous Na2SO4 was used for drying the organic layer and resulting solution was evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain the crude product. The crude product was crystallized from petroleum ether and chloroform mixture (3:7).
For amino terminal deprotection, the solution of 10 mmol Boc peptide methyl ester and 2.28 g (20 mmol) of CF3COOH in 15 ml CHCl3 was stirred for 1 hour at room temperature. The solution was washed with 25 ml of saturated NaHCO3 solution. The organic layer was dried by using anhydrous Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product was crystallized with petroleum ether and CHCl3 mixture (1:9) producing deprotected peptide units (Dahiya and Pathak, 2007).
Method for protection and deprotection of amino acid/peptide units at carboxyl terminal
For protection of carboxyl group, 20 mmol of amino acid was dissolved in mixture of 100 ml methanol having 1.4 ml (20 mmol) thionyl chloride and then refluxed for 10 hours at 65°C. After evaporating the solvent, the residue was triturated with ether at 0ºC followed by crystallization of the crude product for purification from methanol/ether mixture (8:2).
For carboxyl terminal deprotection, 10 mmol of Boc-peptide methyl ester was dissolved in 36 ml of THF: H2O (1:1),), and then 0.36 g (15 mmol) lithium hydroxide was added. The resulting mixture was stirred for 1 hour at room temperature followed by acidification with 1 N H2SO4 to pH 3.5. The aqueous layer was extracted with 100 ml of diethyl ether and then combined organic extract was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. The organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure and crystallized with methanol/ether mixture (8:2) (Dahiya and Sharma, 2008).
.png) | Table 1. Physical characteristics of cecropin B and designed compounds. [Click here to view] |
Method for coupling
To the solution of 10 mmol amino acid methyl ester/peptide methyl ester dissolved in 20 ml chloroform, 2.3 ml (21 mmol) of N-methylmorpholine was added at 0°C followed by stirring for 15 minutes. Then after, a solution of 2.1 gm 10 mmol of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 10 mmol of Boc-amino acid/peptide dissolved in chloroform (20 ml) was added to the previous mixture with stirring for 36 hours and then filtered followed by washing with 30 ml of chloroform. The resulting filtrate was washed with 25 ml of sodium bicarbonate (5%) and 25 ml of saturated sodium chloride solution. Anhydrous Sodium sulfate was used for drying organic layer, filtered and evaporated under vacuum. Crystallization of the crude product was accomplished by a mixture of light petroleum ether and chloroform mixture (2:8) (Dahiya et al., 2010).
Procedure for Synthesis of KKVKKIKRVKIAVLA (10)
To the solution of 4.48 g (5 mmol) of compound 6 in 20 ml of chloroform, 1.1 ml (10.5 mmol) of N-methylmorpholine was added at 0°C, followed by stirring for 15 minutes. Then after, a solution of 1.06 g, 5 mmol of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 9.84 g, 5 mmol of compound 5 in 20 ml of chloroform was added into the previous solution with stirring for 36 hours and then filtered followed by washing the residue with 30 ml of chloroform. The resulting filtrate was washed with 25 ml of sodium bicarbonate (5%) and 25 ml of saturated sodium chloride solution and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and evaporated under vacuum. The crude product was crystallized from a mixture of light petroleum ether and chloroform producing a pure Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)- K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-V-L-AOCH3 compound 7.
To the solution of 7.10g, 2.5 mmol of compound 7 dissolved in 36 ml THF:H2O (1:1), 0.09g, 3.75 mmol lithium hydroxide was added. The resulting mixture was stirred for 1h at room temperature followed by acidification with 1N H2SO4 to pH 3.5. The aqueous layer was extracted with 100 ml diethyl ether and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, then concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product was crystallized with methanol/ether (8:2) to get pure Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)- K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-V-L-AOH compound 8.
At room temperature, the solution of 2.83 g, 1 mmol of compound 8 and 0.228 g, 2 mmol CF3COOH in 15 ml CHCl3 was stirred for 1 hour. The previous solution was washed with saturated 25 ml of NaHCO3 solution. The organic layer was dried by using anhydrous Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crystallization of crude product was accomplished by petroleum ether and CHCl3(2:8) producing a pure K(2-Cl-Z)- K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-V-L-AOH compound 9 (Dahiya et al., 2009).
Deprotection of 2-Cl-benzyloxycarbonyl (2-Cl-Z) of peptide units
A mixture of 5 g, 36% solution of dry hydrogen bromide in glacial acetic acid (20 ml) and 2.46 g, 0.9 mmol of compound 9 in a flask protected with a calcium chloride was allowed to stand at room temperature with occasional shaking for 0.5 hours. Then 150 ml of dry ether was added to precipitate the desired compound. The produced solid was triturated with ether and filtered followed by washing with ether. The crude product was crystallized with methanol/ether mixture (8:2) yielding pure compound 10 (Ben-Ishai and Berger, 1952; Kosaku et al., 1970).
HPLC (125 mm Nucleodur 100-5 C-18, 4.0 mm, Methanol: Water = 70:30, 0.8 ml/minutes, 220 nm, 9.3 MPa, 308 K): tR = 11.21 minutes (72.5% peak area).
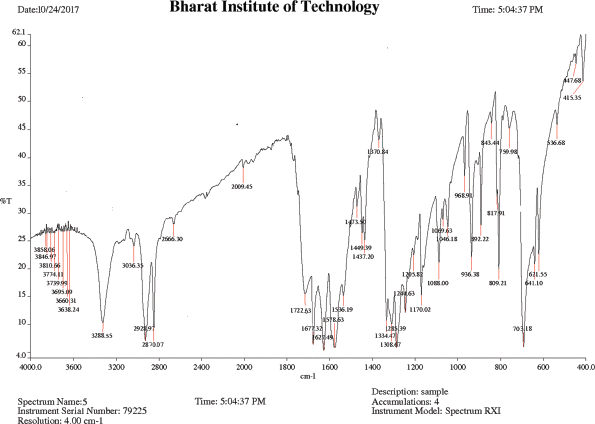
IR (KBr), cm−1: 3,410–3,230 (O–H stretching COOH), 3,288.55 (N–H stretching amide), 2,928.97 (C−H asym. stretching CH2), 2,870.07 (C−H sym. stretching CH2), 1,722.63 (C=O stretching acid), 1,677.32 (C=O stretching amide), 1,627.49 (N−H bend amine), 1,578.63 (N−H bend 2° amide), 1,308.67 (O−H bend COOH), and 703.18 (C−N bending 2° amide).
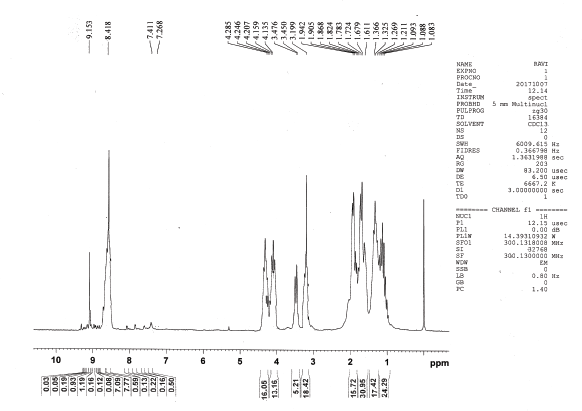
1H NMR (CDCl3), δ: 1.088 (t, 6H, J = 6.0 Hz, γ-H, Ile), 1.240 (d, 18H, J = 17.4 Hz, ββ′-H, Val), 1.346 (d, 18H, J = 12.3 Hz, α-H, Ala, γγ′-H, Leu, β′-H, Ile) 1.611–1.824 (m, 31H, β-H, γ-H, Lys, β-H, Ile, β-H Arg, β-H Leu), 1.905 (t, 16H, J= 11.1Hz, α-H, Lys, α-H Arg, α-H, Leu), 3.199 (s, 18H, NH2, Lys, NH2, NH, Arg), 3.450–3.476 (m, 5H, α-H, Ile, α-H, Val), 4.147 (t, 14H, J = 3.6Hz, γ-H, Arg, δ-H, Lys), 4.207–4.285 (m, 15H, NH-CH-CO), 8.418 (s, 14H, NH , amide), and 9.153 ppm (s, 1H, COOH, Ala).
Synthesis of Cyclic KKVKKIKRVKIAVLA (12)
The solution of 2.83 g, 1 mmol of compound 8, 0.188 g, 1.34 mmol of p-nitrophenol and 0.212 g, 1 mmol dicyclohexylcarbodiimide dissolved in 45 ml chloroform at 0°C was stirred for 12 hours at room temperature and then filtered. The filtrate was washed with 45 ml NaHCO3 (10 %) and 10 ml HCl (5 %). The organic layer was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure to get the compound 8a. To solution of 2.95 g, 1 mmol of compound 8a in 35 ml chloroform, 0.182 g, 1.6 mmol CF3COOH was added and stirred for 1 hour at room temperature. The previous solution was washed with 25 ml of NaHCO3 solution (10%). Anhydrous Na2SO4 was used for drying organic layer and concentrated under reduced pressure to get the compound 8b. To the solution of 2.85 g, 1 mmol of compound 8b in 25 ml chloroform, 0.56 ml, 4.2 mmol N-Methyylmorpholine was added. After that whole contents were allowed to stand at 0°C (7 days) followed by washing with 50 ml NaHCO3 solution (10 %) and finally washed with 75 ml HCl (5 %). Anhydrous Na2SO4 was used for drying organic layer and concentrated under reduced pressure. Pure cyclicpeptide 11 was crystallized from chloroform/n-hexane (6:4) (Dahiya et al., 2009).
Deprotection of 2-Cl-benzyloxycarbonyl(Z) of peptide units
A mixture of 5 g, 36% solution of dry hydrogen bromide in (20 ml) glacial acetic acid and 2.72 g, 1 mmol of compound 11 in a flask protected with calcium chloride at room temperature with occasional shaking for 0.5 hour. Nearly, 150 ml of dry ether was added for the formation of precipitate. After that, supernatant was decanted and solid was triturated with ether followed by filtration, and washing with ether. The crude product was crystallized with methanol/ether to get pure compound 12 (Ben-Ishai and Berger, 1952; Kosaku et al., 1970).
HPLC (125 mm Nucleodur 100-5 C-18, 4.0 mm, Methanol: Water = 70:30, 0.8 ml/minutes, 220 nm, 9.3 MPa, 308 K): tR = 10.11 minutes (78.4% peak area).
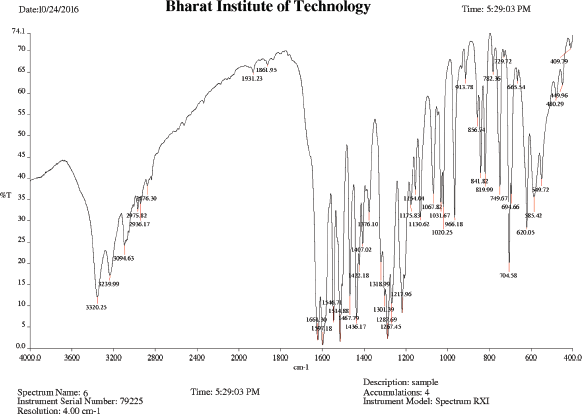
IR (KBr), cm−1: 3,320.25 (N−H asym stretching amide), 3,239.99 (N–H stretching amine), 2,975.82 (C−H asym. stretching CH2), 2,936.17 (C−H sym. stretching CH2), 1,661.30 (C=O stretching amide), 1,597.18 (N−H bend amide), 1,514.88 (C−C stretching skeletal bands), 1,267.45 (CH bend isopropyl), and 749.67 (C−N bending amide).
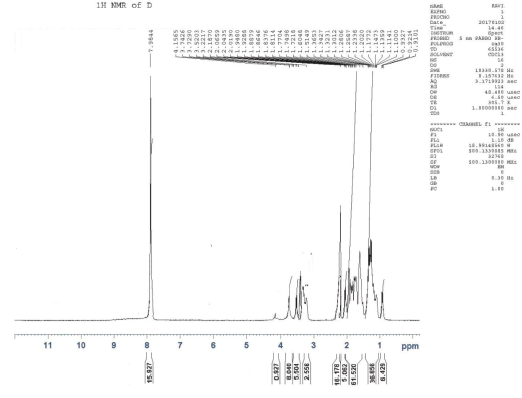
1H NMR (CDCl3), δ: 0.921 (t, 6H, J= 3.47Hz, γ-H, Ile), 1.107 (d, 18H, J = 4.3Hz, ββ′-H, Val) 1.218 (d, 6H, J = 9.54Hz, α-H, Ala), 1.270 (d, 6H, J = 6.6Hz, γ γ′-H, Leu), 1.312 (d, 6H, J = 6.6Hz, β′-H, Ile), 1.3427–1.6048 (m, 16H, β-H, Lys, β-H, Ile), 1.7218–1.7704 (m, 15H, γ-H, Lys, β-H Arg, β-H, Leu), 1.838 (t, 14H, J= 8.2 Hz, α-H, Lys, α-H Arg), 1.929 (t, 16H, J= 5.8 Hz, γ-H, Arg, δ-H, Lys, α- H, Leu), 2.0190–2.0659 (m, 5H, α-H, Ile, α-H, Val), 2.1870 (s, 16H, NH2, Lys, NH2, NH, Arg), 3.2217–3.7426 (m, 15H, N-CH-CO), and 7.9844 ppm (s, 15H, NH , amide).
Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance (13C NMR) (CDCl3), δ: 175.2 (2C, C=O, Ala-2), 174.5 (6C, C=O, Lys-6), 173.9 (C, C=O, Leu), 172.6 (C, C=O, Arg), 171.6 (2C, C=O, Ile-2), 168.7 (3C, C=O, Val-3), 160.2 (C, C=NH, Arg), 63.8 (3C, C-α, Val-3), 58.8 (2C, C-α, C-Ile-2), 56.8 (6C, C-α, Lys-6), 55.6 (C,C-α, C-Arg), 54.3 (C, C-α, Leu), 51.8 (2C, C-α, Ala-2) 44.4 (6C, C-ε, Lys-6), 43.7 (C, C-α, Leu), 39.7 (C, C-δ, C-Arg), 37.4 (2C, C-β, Ile-2), 35.6 (6C, C-ε, Lys-6 ), 33.1 (6C, C-β, Lys-6) 32.2 (3C, C-β, Val-3), 31.6 (C, C-β, Arg), 28.4 (2C, C-γ, Ile-2), 26.8 (C, C-γ, C-Arg), 24.8 (2C, C-γγ′, Leu), 23.6 (C, C-β, Leu), 22.7 (6C, C-γ, Lys-6), 19.8 (2C, C-β, Ala-2), 18.5 (6C, C-γγ′, Val-3), 17.2 (2C, C-γ, Ile-2), and 11.1 (2C, C-δ, Ile-2).
Fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry (m/z, rel. int.): 1704.2 [(M + H)+, 100], 1676.3 [(1704.2 – CO)+, 23], 1633.2 [(1704.2–A)+, 32], 1576.4 [(1704.2–K)+, 29], 1520.1 [(1704.2–LA)+, 17], 1448.0 [(1704.2–KK)+, 39], 1421.0 [(1704.2–VLA)+, 44], 1349.9 [(1704.2–AVLA)+, 52], 1348.9 [(1704.2–VKK)+, 67], 1236.8 [(1707.2– IAVLA)+, 79], 1220.8 [(1704.2–KVKK)+, 44], 1108.8 [(1704.2–KIAVLA)+, 32], 1092.8 [(1704.2–KKVKK)+, 47], 1009.7 [(1704.2–VKIAVLA)+, 41], 979.6 [(1704.1–IKKVKK)+, 19], 853.6 [(1707.2–RVKIAVLA)+, 41], 851.5 [(1704.2–KIKKVKK)+, 27], 725.5 [(1704.2– KRVKIAVLA)+, 26], 695.4 [(ALVAIKV)+, 24], 612.4 [(KKVKK)+, 46], 596.3 [(ALVAIK)+,38], 484.3 [(KKVK)+, 34], 468.3[(ALVAI)+, 46], 356.2 [(KKV)+, 51], 355.2 [(ALVA)+,38], 284.2 [(VLA)+, 34], 257.2 [(KK)+, 24], 185.1 [(VL)+, 46], 129.1 [(K)+, 34], 72.2 [(V)+, 51], 86.2 [(C 5H 12N)+, 22], 44.1 [(C 2H 6N)+, 16], 31.0 [(CH 3O)+, 9], 30.1 [(CH 4N)+, 12], 29.1 [(C 2H 5)+, 11], and 15.0 [(CH 3)+, 10].
In-vitro cytotoxic activity for synthesized peptide
The cytotoxic activity of synthesized compound 10 and 12 was carried out using 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltratrazolium bromide (MTT) assay in vitro against Dalton’slymphoma ascites (DLA), Ehrlich’s ascites carcinoma (EAC), and Breast Cancer cell line Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 (MCF-7) by 1 × 104 cells in 96-well plates. The plates were seeded and incubated with serially fourfold diluted concentration (21.33–170.70 μg/ml) of different peptides for 48 hours at 37°C. Standard drug 5-fluorouracil was also used as positive control. 200 ml, 5 mg/ml of MTT solution in phosphate buffered saline was added to cells and left for 4 hours at 37°C followed by addition of 150 ml dimethyl sulfoxide, which was added for dissolving formazan crystals. The absorbance was determined at 490 nm. The results were expressed as IC50, representing the concentration at which cell viability was reduced by 50%. The cytotoxicity assays were repeated in quadruplicates.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Chemistry
Disconnection strategy was used to carry out the synthesis of designed compounds. The designed compounds were split into three tetrapeptide units Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-OH (1) K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-OCH3 (2), Boc-V- K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-OH (3), and a tripeptide unit V-L-A–OCH3 (4). To obtain tetrapeptide Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-OH, Boc-V- OH was coupled with K(2-Cl-Z)-OCH3.HCl to give Boc-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-OCH3 by employing DCC as coupling agents and TEA/NMM as bases. Trifluoroacetic acid was used for removing Boc group of Boc-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-OCH3 to give V-K(2-Cl-Z)-OCH3. Dipeptide V-K(2-Cl-Z)-OCH3 was coupled with Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-OH to give Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-OCH3 by employing DCC as coupling agents and TEA/NMM as bases. Trifluoroacetic acid was used for removing Boc group of Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-OCH3 to give K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-OCH3. Tripeptide K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-OCH3 was coupled with Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-OH to give Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-OCH3 by employing DCC/DIPC as coupling agents and TEA/NMM as bases. Lithium hydroxide (LiOH) was used for removing ester group of Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-OCH3 to give Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-OH (1). Other tetrapeptide units K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-OCH3 (2), Boc-V- K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-OH (3) and tripeptide V-L-A –OCH3 (4) were prepared by coupling of Boc-amino acids with corresponding amino acid methyl ester hydrochlorides as above. Tetrapeptide Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-OH (1) and K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-OCH3 (2) were coupled to get the octapeptide unit Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-OCH3. Lithium hydroxide (LiOH) was used for removing ester group of Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-OCH3 to give Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-OH (5). Tetrapeptide Boc-V- K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-OH (3) and tripeptide V-L-A –OCH3 (4) were then coupled to get the heptapeptide Boc-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-V-L-A –OCH3 . Trifluoroacetic acid was used for removing Boc group of Boc-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-V-L-A –OCH3 to give V-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-V-L-A-OCH3 (6). Octaapeptide Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-OH (5) and heptapeptide V-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-V-L-A-OCH3 (6) units were coupled to get the linear pentadecapeptide unit Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-V-L-A-OCH3 (7). The Compound Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-V-L-A-OCH3 (7) was deprotected at carboxyl end to give Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-V-L-A-OH (8) by using lithium hydroxide (LiOH) and amino terminal by using CF3COOH to give K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-R-I-K(2-Cl-`Z)-A-A-V-A-A-T-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-A-OH (9). Hydrogen bromide in glacial acetic acid (36%) was used for deprotection of 2-chloro-Benzyloxycarbonyl of peptide K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-R-I-K(2-Cl-`Z)-A-A-V-A-A-T-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-A-OH (9) at amino terminal of side chain to get KKVKKIKRVKIAVLA (10) peptide (Fig. 1). The linear peptide Boc-K(2-Cl-Z)-K(2-Cl-Z)-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-Q-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-K(2-Cl-Z)-R-V-K(2-Cl-Z)-I-A-V-L-A-OH (8) was coupled with p-nitrophenyl to give BocK(2-Cl-Z)K(2-Cl-Z)VK(2-Cl-Z)K(2-Cl-Z)IK(2-Cl-Z)RVK(2-Cl-Z)IAVLAOPNP (8a) followed by deprotection of Boc group by using TFA to give K(2-Cl-Z)K(2-Cl-Z)VK(2-Cl-Z)K(2-Cl-Z)IK(2-Cl-Z)RVK(2-Cl-Z)IAVLAOPNP (8b). Linear peptide K(2-Cl-Z)K(2-Cl-Z)VK(2-Cl-Z)K(2-Cl-Z)IK(2-Cl-Z)RVK(2-Cl-Z)IAVLAOPNP (8b) was allowed to stand with catalytic amount of NMM at 0áµ’C for 7 days to get cyclicpeptide K(2-Cl-Z)K(2-Cl-Z)VK(2-Cl-Z)K(2-Cl-Z)IK(2-Cl-Z)RVK(2-Cl-Z)IAVLA (11). Hydrogen bromide in glacial acetic acid (36%) was used for deprotection of 2-chloro-Benzyloxycarbonyl of Cylic-K(2-Cl-Z)K(2-Cl-Z)VK(2-Cl-Z)K(2-Cl-Z)IK(2-Cl-Z)RVK(2-Cl-Z)IAVLA (11) at amino terminal of side chain to get compound KKVKKIKRVKIAVLA (12) (Fig. 2). Characterization of newly synthesized peptide was accomplished by elemental analysis as well as spectral analysis. Solution phase technique (Bodanzsky and Bodanzsky, 1984) was used for synthesis of designed peptides. For this DCC was used as a coupling agents and TEA/NMM as bases. Compound 12 was synthesized with 77 % yield. Absence of absorption bands at 1722.63 cm-1 (C=O stretching of acid) in IR spectra of compound 12 proved the cyclization of linear peptide 10. Cyclization was further confirmed by absence of singlets at 9.153 ppm for one protons of free carboxylic acid group in 1H NMR of compound 12 and M+1 peak at m/z 1704.2 in mass spectrum is compatible with the moecular formula C77H143N25O18. Physical characterization of synthesized compounds is shown in Table 2.
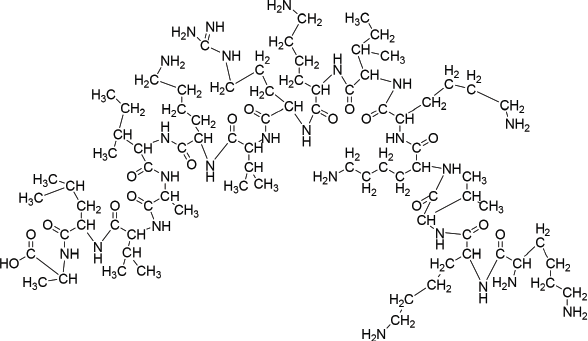 | Figure 1. Structure of compound 10. [Click here to view] |
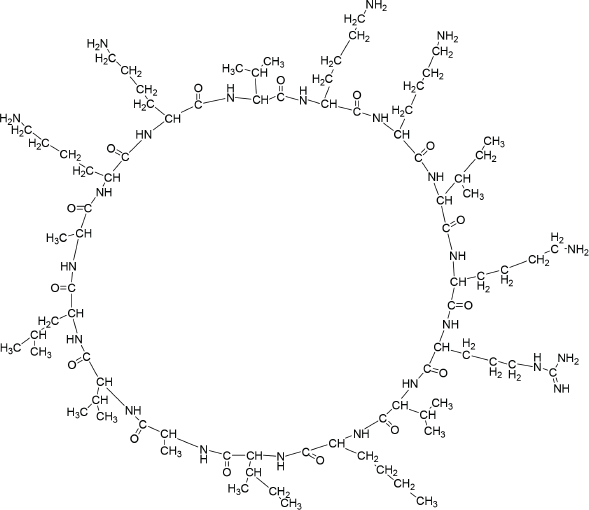 | Figure 2. Structure of compound 12. [Click here to view] |
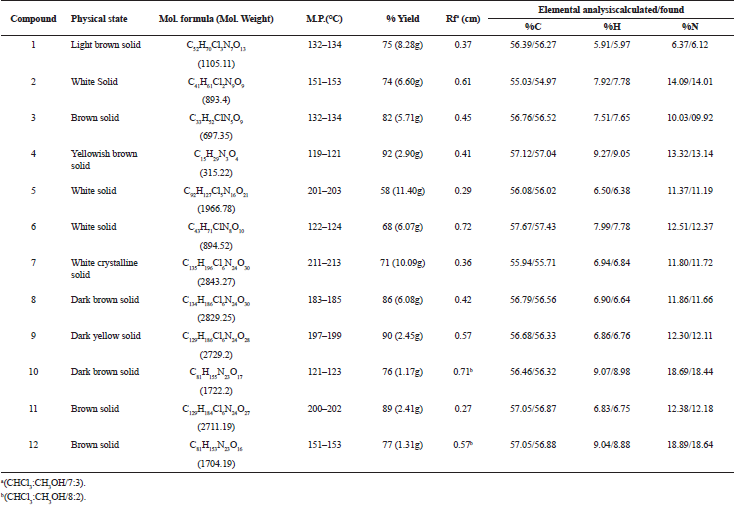 | Table 2. Physical Characterization for Synthesized Compounds 1–12. [Click here to view] |
In-vitro cytotoxic activity
IC50 values of synthesized linear peptide 10 were 59.52, 76.25, and 94.24 μg, respectively, and IC50 values of synthesized cyclopeptide 12 were 52.19, 62.27, and 86.88 μg, respectively, in comparison to standard drug (5-FU) which exhibited IC50 values of 51.77, 61.31, and 81.72 μg against DLA (Fig. 3), EAC (Fig. 4) and MCF-7 (Fig. 5) cell lines, respectively. The IC50 values of synthesized compound 12 were found much lower than compound 10 but almost equal potency to that of standard drug 5-FU against DLA and EAC cell lines. The Comparison of IC50 values of synthesized compound and 5-FU against all cell lines is shown in Figure 6.
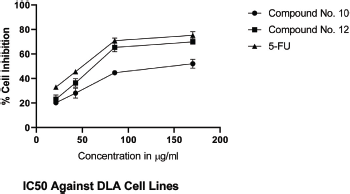 | Figure 3. IC50 against DLA cell lines. [Click here to view] |
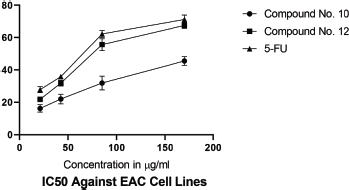 | Figure 4. IC50 against EAC cell lines. [Click here to view] |
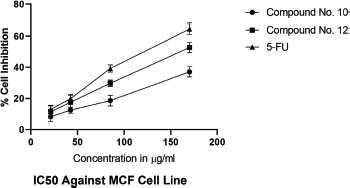 | Figure 5. IC50 against MCF-7 cell lines. [Click here to view] |
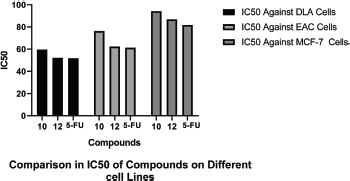 | Figure 6. Comparison of IC50 of compounds on different cell lines. [Click here to view] |
CONCLUSION
We were able to evolve short chain linear and cyclic peptides having same charge and hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity with improved activity by utilizing a structure-based rational approach. Based on removing of amino acid of the peptide at non-polar/polar face of the amphipathic α-helical cationic anticancer peptide cecropin B, the desired peptides were designed. We were able to retain peptide charge and hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity in linear and cyclic peptide by systematically removing amino acids which resulted in optimize anticancer activity against DLA and EAC cell lines.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
Ben-Ishai D, Berger A. Cleavage of N-Carbobenzoxy groups by dry hydrogen bromide and hydrogen chloride. J Org Chem, 1952; 17(12):1564–70. CrossRef
Bodanzsky M, Bodanzsky A. The practice of peptide synthesis. Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, 1984.
Brooks SA, Lomax-Browne HJ, Carter TM, Kinch CE, Hall DM. Molecular interactions in cancer cell metastasis. Acta Histochem, 2010; 112(1):3–25. CrossRef
Bush JA, Li G. Cancer chemoresistance: the relationship between p53 and multidrug transporters. Int J Cancer, 2002; 98(3):323–30. CrossRef
Chou HT, Kuo TY, Chiang JC, Pei MJ, Yang WT, Yu HC, Lin SB, Chen SW. Design and synthesis of cationic antimicrobial peptides with improved activity and selectivity against Vibrio spp. Int J Antimicrob Agents, 2008; 32(2):130–38. CrossRef
Dahiya R, Kumar A, Gupta R. Synthesis, cytotoxic and antimicrobial screening of a proline-rich cyclopolypeptide. Chem Pharm Bull, 2009; 57(2):214–17.
Dahiya R, Mourya R, Agrawal SC. Synthesis and antimicrobial screening of peptidyl derivatives of bromocoumarins/methylimidazoles. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol, 2010; 4(5):214–25.
Dahiya R, Pathak D. First total synthesis and biological evaluation of halolitoralin A. J Serb Chem Soc, 2007; 72(2):101–07. CrossRef
Dahiya R, Sharma RD. Synthesis and bioactivity of a novel cyclic hexapeptide from Stellaria Delavayi. Eur J Sci Res, 2008; 21(2):277–87.
Dennison SR, Whittaker M, Harris F, Phoenix DA. Anticancer alpha-helical peptides and structure/function relationships underpinning their interactions with tumour cell membranes. Curr Protein Pept Sci, 2006; 7(6):487–99. CrossRef
Donnelly JG. Pharmacogenetics in cancer chemotherapy: balancing toxicity and response. Ther Drug Monit, 2004; 26(2):231–35.
Harris F, Dennison SR, Singh J, Phoenix DA. On the selectivity and efficacy of defense peptides with respect to cancer cells. Med Res Rev, 2013; 33(1):190–234. CrossRef
Hoskin DW, Ramamoorthy A. Studies on anticancer activities of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr, 2008; 1778(2):357–75. CrossRef
Huang Y, Feng Q, Yan Q, Hao X, Chen Y. Alpha-helical cationic anticancer peptides: a promising candidate for novel anticancer drugs. Mini Rev Med Chem, 2015; 15(1):73–81. CrossRef
Hui L, Leung K, Chen HM. The combined effects of antibacterial peptide cecropin A and anti-cancer agents on leukemia cells. Anticancer Res, 2002; 22(5):2811–16.
Kosaku N, Shigeyuki T, Nobuo I. Modified benzyloxycarbonyl group for protection of ε-amino groups of lysine. Bull Chem Soc Jpn, 1970; 43(6):1883–85. CrossRef
Kreeger PK, Lauffenburger DA. Cancer systems biology: a network modeling perspective. Carcinogenesis, 2009; 31(1):2–8. CrossRef
Liberio MS, Joanitti GA, Fontes W, Castro M.S. Anticancer peptides and proteins: a panoramic view. Protein Pept Lett, 2013; 20(4):380–91. CrossRef
Mader JS, Hoskin DW. Cationic antimicrobial peptides as novel cytotoxic agents for cancer treatment. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2006; 15(8):933–46. CrossRef
Marusyk A, Polyak K. Tumor heterogeneity: causes and consequences. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2010; 1805(1):105–17. CrossRef
Naumov GN, Townson JL, MacDonald IC, Wilson SM, Bramwell VHC, Groom AC, Chambers AF. Ineffectiveness of doxorubicin treatment on solitary dormant mammary carcinoma cells or late—developing metastases. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2003; 82(3):199–206. CrossRef
Riedl S, Zweytick D, Lohner K. Membrane-active host defense peptides—challenges and perspectives for the development of novel anticancer drugs. Chem Phys Lipids, 2011; 164(8):766–81. CrossRef
Srisailam S, Arunkumar AI, Wang W, Yu C, Chen HM. Conformational study of a custom antibacterial peptide cecropin B1: implications of the lytic activity. Biochim Biophys Acta Protein Struct Mol Enzymol, 2000; 1479(1–2):275–85. CrossRef
Sung SY, Hsieh CL, Wu D, Chung LW, Johnstone PA. Tumor microenvironment promotes cancer progression, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance. Curr Probl Cancer 2007; 31(2):36–100. CrossRef
Thun MJ, DeLancey JO, Center MM, Jemal A, Ward EM. The global burden of cancer: priorities for prevention. Carcinogenesis 2010; 31(1):100–10. CrossRef
Zelezetsky I, Tossi A. Alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides—using a sequence template to guide structure-activity relationship studies. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr, 2006; 1758(9):1436–49. CrossRef