INTRODUCTION
Inflammation is a complex biological response of tissue to noxious stimuli such as pathogens, damaged body cells, or irritants. These stimuli can activate nociceptors to release various chemical mediators, such as stimulating amino acids, vasoactive amines, proteins, peptides, nitric oxide, arachidonic acid, and cytokines, which act on specific receptors or ion channels and contribute to the induction of pain and inflammation. Inflammation is characterized by pain, redness, and tissue or organ dysfunction [1,2]. Uncontrolled inflammation is considered one of the pathophysiological causes of most chronic diseases. Increased vascular permeability is involved in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory disorders, for example, rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, periodontitis, inflammatory bowel disease, atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, diabetes, neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, and other life-threatening and debilitating diseases [3,4].
The inflammatory response in the body is characterized by the presence of various mediators, such as pro-inflammatory cytokines in the form of interleukin (IL)-1, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interferon (INF), IL-6, IL-12, and IL-18, and anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1Ra, IL-35Ra, Il-37, IL-38, and others [5]. These mediators initiate complex processes, such as activating many enzymes, releasing mediators, cell migration, fluid extravasation, increased protein denaturation, and membrane changes. IL-6 is a multifunctional homodimeric pleiotropic cytokine that regulates immune responses, acute phase responses, hematopoiesis, and inflammation [6]. Therefore, this pro-inflammatory mediator is an essential target in inflammation [7]. IL-12 is also the main stimulator of inflammation mediated by monocytes, macrophages, and antigen-presenting cells. It activates and regulates immune cells, including stimulating macrophages, T-cells, and natural killer cells to facilitate the killing of cancer cells and inhibiting tumor angiogenesis. IL-12 also induces TNF alpha (TNF-α) and IFN-γ by stimulating T helper (Th1) cells [8,9]. On the other hand, TNF-α induces the production of other inflammatory mediators and proteases that regulate inflammatory responses [10]. Tumors also produce TNF-α as an endogenous tumor promoter, which plays a role in tumorigenesis, including cellular transformation, promotion, survival, proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis [11]. Although inflammation can be treated using steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, many of these medications have significant side effects or adverse drug reactions (ADRs). Therefore, novel anti-inflammatory drugs with fewer side effects and ADRs are needed [12].
Among natural products that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory activity are those identified from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei from the Solomon Islands, for example, the perthamides, solomonamides, and solomonsterols. The cyclopeptide perthamide C significantly reduced carrageenan-induced paw edema in a dose-dependent manner, causing about 60% reduction of edema in mice at the dose of 300 µg/kg (ip) [13]. Perthamide C modulates the expression of several chaperons, for example, heat shock protein 90, implicated in the folding of proteins correlated to apoptosis [14,15]. The cyclopeptide solomonamide A showed in vivo dose-dependent anti-inflammatory activity causing about 60% reduction of edema in mice at the dose of 100 µg/kg (ip) [16]. Furthermore, the sulfated sterols, solomonsterols A and B, have been shown to regulate pregnene-X-receptor (PXR) and effectively increase the expression of CYP3A4 and MDR1 in the human hepatocyte cell line HepG2 [17]. Administration of synthetically prepared solomonsterol A to animal models of colitis reduced the generation of TNF-α, inhibited nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) activation by a PXR-dependent mechanism, and effectively protected against the development of clinical signs and symptoms of colitis [18].
Theonella sponges are widely recognized as prolific sources of bioactive secondary metabolites, many of which originate from their associated microbial symbionts [19]. However, most studies have focused on specimens collected from regions such as Japan, Palau, or Papua New Guinea [13–18]. In contrast, the chemical diversity and bioactivity of Theonella sp. from Indonesian waters remain largely unexplored, despite the country’s location within the Coral Triangle—a global hotspot of marine biodiversity. The unique ecological and environmental conditions of this region may influence the composition of sponge-associated microbial consortia [19], potentially leading to the production of novel or structurally distinct metabolites. Since microbial symbionts play a crucial role in secondary metabolite biosynthesis, geographic variation could significantly impact the pharmacological properties of sponge-derived compounds. To our knowledge, few studies have investigated the immunomodulatory or anti-inflammatory potential of Indonesian Theonella sp., particularly in relation to key cytokines such as IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α. Therefore, exploring Theonella from this region offers a promising opportunity to discover unique bioactive compounds with therapeutic potential.
Here, we report the in vitro and in vivo evaluations of the ethanol extract of Theonella sp. (TE) collected from waters around Southeast Sulawesi Province of Indonesia (Fig.1a and b) for its anti-inflammatory activity. We also evaluated the activity of the extract in decreasing the levels of IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α as pro-inflammatory cytokines in carrageenan-induced Wistar rats.
 | Figure 1. Theonella sp. taken from waters around Saponda Island, Konawe Regency, Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. (a) Map of Indonesia indicating the location of sponge collection (red dashed circle); (b) photograph of the collected sponge Theonella sp. [Click here to view] |
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
The materials used in this study were marine sponge Theonella sp., 96% ethanol (Bratachem®, Indonesia), CHCl3, NH4OH, H2SO4, Dragendorff’s reagent, and phosphate buffer saline (PBS) pH 7.4, (Merck Milipore, Germany), Liebermann–Burchard reagent and Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose (Na-CMC) 0.5% (Sigma Aldrich, USA), isosaline, hyposaline solution, diclofenac sodium solution, dexamethasone, EDTA, sodium citrate, and heparin.
Collection, determination, and preparation of the sponge
The marine sponge Theonella sp. was collected around Saponda Island and Bintang Samudra Marine Education Park, Konawe Regency, Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia, by SCUBA (self-contained underwater breathing apparatus) diving. Theonella sp. was classified by the Faculty of Fisheries and Marine Science, Halu Oleo University, Indonesia. The sponge was cleaned from dirt and animals that are attached to its surface, washed with clean water, and soaked with ice cubes for 24 hours. Subsequently, the sponge was cut into small pieces for compound extraction.
Extract preparation and preliminary identification of the chemical content
The sponge was macerated with 96% ethanol for 3 days in a tightly sealed container. Subsequently, the ethanolic extract was filtered and concentrated using a rotary evaporator at 50°C followed by a water bath [20]. The extract was analyzed for its chemical constituents according to methods reported in the literature [21,22]. Briefly, for the alkaloid test, the sample (0.1 g) was dissolved in CHCl3 (10 ml) and four drops of NH4OH were added. Then, 10 drops of 2M H2SO4 were added and shaken. The aqueous layer was separated into another test tube, and Dragendorff’s reagent was added [21]. The reaction produced a red-orange precipitate, indicating the presence of alkaloids or peptides. For the steroid test, 1 ml of the concentrated extract, reacted with Liebermann–Burchard reagent [20]. The blue-purple color that appeared indicates the presence of steroid compounds.
In vitro anti-inflammatory assay
Human red blood cell membrane stabilization method
Fresh blood from a healthy volunteer was collected and centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 10 minutes at 25°C, followed by washing the cell pellet with isosaline and resuspensing the cells in isosaline to obtain 10% v/v isosaline-red blood cells. Subsequently, the suspension (0.5 ml) was mixed with PBS pH 7.4 (1 ml), hyposaline solution (2 ml), and the ethanol extract (1 ml at concentrations of 25, 50, 75, 100, 125, 150, and 200 μg/ml), and the mixture was incubated at 56°C for 30 minutes. Diclofenac sodium solution (1 ml at concentrations of 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, and 70 μg/ml) was used as a positive control. The mixture was centrifuged at 5,000 rpm for 10 minutes. The supernatant was measured with a UV-Vis spectrophotometer at 560 nm. The hemolysis and stability of human red blood cell (HRBC) were calculated using the following formulas [23]:
Albumin protein denaturation
The ethanolic extract [1 ml at various concentrations (25, 50, 75, 100, 125, 150, and 200 μg/ml)] was mixed with 0.2% v/v bovine serum albumin (BSA) in Tris buffer saline (TBS) solution (5 ml). The mixture was incubated at 25°C for 30 minutes, followed by incubation at 72°C for 30 minutes, and cooled to 25°C for 25 minutes. Diclofenac sodium solution (1 ml) at various concentrations (10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, and 70 μg/ml) was used as a positive control. The absorbance was measured with UV-Vis spectrophotometer at 660 nm. The inflammatory activity was calculated using the formula below [24]:
In vivo anti-inflammatory test
The in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of the TE was evaluated using the carrageenan-induced paw edema model in male Wistar rats. All experimental procedures involving animals were conducted in accordance with institutional guidelines and approved by the Institute of Research and Community Service, Universitas Halu Oleo, with ethical clearance number 170/UN29.20.1.2/PG/2023. Male Wistar rats were acclimatized for 1 week in a controlled cage. The rats were fed with uniform food and drink ad libitum. Routine observations were made of the general condition, and the rats were regularly weighed. Unhealthy rats with standing fur, less activity, and unclear eyes were excluded. After acclimatization, the animals were grouped into six groups (n = 4), namely groups I–VI. After acclimatizing, the rats were induced with 1% of carrageenan (200 μl) by intraplantar injection. The rats were then treated according to groups: Group I (not receiving any treatment), group II (treated with Na-CMC 0.5% as a negative control), group III (treated with dexamethasone 0.45 mg/ml as a positive control), and groups IV–VI were treated with TE 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 mg/ml, respectively. The solutions were given orally 3.5–5 ml according to their body weight. The rats’ paw edema was measured at 0 and 24 hours after carrageenan induction. The edema volume was measured with a plethysmometer using the following calculation [25]:
Edema volume = π.r2.t(4)
whereas:
t = increased in volume of mercury (cm)
r = radius of the capillary tube of the modified plethysmometer (cm)
The use of a small sample size was based on ethical considerations to minimize animal use while ensuring scientific validity, in accordance with the principles of the 3Rs (replacement, reduction, and refinement) and international guidelines for animal experiments [26–28]. This approach is supported by previous studies and relevant recommendations. Bustos-Salgado et al. [29] employed n = 3 in their in vivo evaluation of modulated flavanones and reported consistent anti-inflammatory effects. Similarly, Festing and Altman [26] emphasized that small sample sizes (n = 3–6 per group) are commonly used in exploratory research where large effects are expected and reduction of animal use is prioritized.
Determinations of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α
The bloods of rats from the paw edema experiment were collected 1 hour after ethanol extract treatment to measure the levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α. The blood was placed in tubes containing EDTA, sodium citrate, and heparin. Then, the samples were processed according to the protocol provided in the kit [20] and the levels of IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α were analyzed using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit (Bioassay Technology Laboratory Cat. No. E0135Ra) [25].
Molecular docking studies
In this study, molecular docking simulations were performed using the Maestro Schrödinger Suite version 10.6 to evaluate the binding affinities of solomonamide A, solomonamide B, solomonsterol A, and solomonsterol B toward the pro-inflammatory targets IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α.
Since the specific chemical constituents of the ethanol extract were not fully elucidated using analytical techniques such as Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry or nuclear magnetic resonance, the docking approach employed known anti-inflammatory compounds previously isolated from Theonella sp. This strategy is commonly used in early-stage drug discovery to explore potential bioactivities of structurally related natural products and to provide a mechanistic rationale for observed in vivo or in vitro effects. By using well-characterized compounds from the same genus, the docking study supports the hypothesis that the extract of Theonella sp. may contain similar active constituents responsible for its anti-inflammatory activity.
Ligand preparation
Four compounds from Theonella sp., which were reportedly anti-inflammatory, were used. These compounds were downloaded in 2D form from PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) [30]. Next, the ligands were prepared using LigPrep in Maestro, and the OPLS3 force field was used. These compounds were also ionized under pH = 7 conditions using Epik [31].
Protein preparation
The 3D structures of IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α proteins were downloaded from the RCSB Protein Data Bank (https://www.rcsb.org/) with each successive PDB ID 1ALU [32], 5MJ3, and 6X81. The protein preparation was conducted with the Protein Preparation Wizard from Maestro 10.6. Hydrogen atoms and water compounds less than 5.00 Å away were removed. Protein optimization with PROPKA pH 7.0 and Force Field OPLS3 was used in this preparation process to check and correct missing atoms and side chains, unusual compound bonds, and so on.
Grid preparation was conducted to determine the active site of IL-6 [root mean square deviation (RMSD): 0.07 Å], IL-12 (Dscore: 1.046), and TNF-α (RMSD: 0.82 Å) proteins. This procedure involves the Protein Preparation Wizard and the SiteMap (Dscore) tool to predict protein active sites. In the comparative analysis of binding free energy values, dexamethasone was used as a standard immunosuppressant. The grids used for each target were the 19, 10, and 20 Å grids, respectively.
Molecular docking simulation
Molecular docking simulations were conducted by docking the 3D structure of the test compound to the target protein. The ligand docking module from Glide in Maestro 10.6 was used in this simulation process. The prepared Grid receptor and ligand 3D structures were imported into the ligand docking panel with a van der Waals scaling factor of 0.80 and a partial charge cutoff of 0.15. Docking was performed flexibly using the OPLS3 force field and XP (extra precision) mode. The GlideScore function was applied to evaluate the binding affinity of the ligands. The resulting binding free energies and protein–ligand interactions were analyzed using the pose viewer panel in Maestro [30].
Data analysis
The data obtained were analyzed using the IBM SPSS statistics program. The effects of the TE on the levels of IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α in all treatment and comparison groups were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. p < 0.05 indicates a significant difference in activity between the groups. In the figures, the following notation is used:* indicates p > 0.05 (not significant); ** indicates p < 0.05 (statistically significant).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Extraction and preliminary chemical Screening
The sponge Theonella sp. collected from waters around Southeast Sulawesi Province of Indonesia was macerated with 96% ethanol for 3 days and the ethanol extract was filtered and concentrated in vacuo. Preliminary chemical screening was performed using Dragendorff’s and Liebermann–Burchard reagents [21,22] to confirm its alkaloid (peptide) and steroid contents. The results showed that the TE is positive for alkaloids (peptides) and steroids, consistent with those reported in other Theonella spp. [33].
While the sponge Theonella sp. collected from the waters around Southeast Sulawesi Province of Indonesia has only been identified at the genus level, preliminary chemical screening of the ethanol extract of the sponge indicated the presence of alkaloids (peptides) and steroids, which are consistent with those commonly reported in other sponges [32]. These classes of compounds have been shown to have many important biological activities. Of particular interest are several cyclic peptides and sterols from T. swinhoei collected at the Solomon Islands which showed anti-inflammatory activity. However, whether other species of Theonella or those collected from other regions of the world can also provide compounds with anti-inflammatory activity is an open question, given that many bioactive compounds isolated from marine sponges are produced by microbial symbionts that live in those filter-feeders, not by the invertebrates themselves [19].
The ethanol extract of Theonella sp. stabilizes the HRBC membrane
To determine the anti-inflammatory activity of the TE in vitro, we performed an HRBC membrane stability assay. This assay is a commonly used method to evaluate anti-inflammatory activity in vitro, as the HRBC membrane has similar components with lysosomal membrane components. Once disrupted and lysed, the inflammatory markers cyclooxygenase enzymes, which convert arachidonic acid to prostaglandins, are released. The ability of agents to prevent lysis and stabilize the cell membrane may suggest their anti-inflammatory activity. In this experiment, red blood cells from a healthy volunteer and the TE in various concentrations were co-incubated in PBS pH 7.4 and hyposaline solution. The amount of hemoglobin released, measured at 560 nm, is quantified as a measure of HRBC lysis. Diclofenac sodium solution was used as a positive control. We found that the TE can reduce hemolysis and increase membrane stability in a dose dependent-manner similar to diclofenac sodium (Fig. 2).
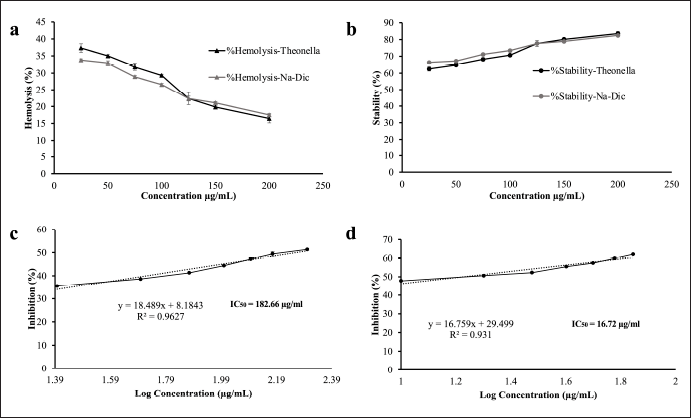 | Figure 2. In vitro anti-inflammatory activity tests of the ethanol extract of Theonella sp. (a) Hemolysis activity of the ethanol extract of Theonella sp. in HRBC. Diclofenac sodium was used as a positive control; (b) stability activity of the ethanol extract of Theonella sp. in HRBC. Diclofenac sodium was used as a positive control; (c) protein denaturation inhibition of the ethanol extract of Theonella sp.; and (d) protein denaturation inhibition of diclofenac sodium. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). [Click here to view] |
The ethanol extract of Theonella sp. prevents protein denaturation
Protein denaturation is considered a sign of inflammation; hence, agents that can prevent protein denaturation, characterized by protein aggregation and condensation, may have anti-inflammatory activity [34]. Therefore, we evaluated the TE for its inhibition of thermal-induced protein denaturation by co-incubating it with BSA in TBS at 72°C. The ability of the extract to prevent protein denaturation was determined based on its ability to reduce the turbidity of the solution after 30 minutes of incubation measured at 660 nm.
The extract demonstrated a dose-dependent inhibition of protein denaturation, with an IC50 value of 182.3 μg/ml, compared to 16.7 μg/ml for the positive control, diclofenac sodium (Fig. 2). While the extract is less potent than diclofenac, its measurable activity suggests that Theonella sp. ethanol extract possesses promising anti-inflammatory potential through the inhibition of protein denaturation. This result supports further investigation into its active constituents and mechanism of action.
The ethanol extract of Theonella sp. decreases the volume of rat paw edema
To investigate the effect of the TE in vivo, we performed paw edema experiments using male Wistar rats, whose edema was induced with intraplantar injection of carrageenan (200 μl, 1%). One hour after carrageenan induction, the rats were treated with the ethanol extract in three different concentrations (0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 mg/ml). Na-CMC (0.5%) was used as a negative control, whereas dexamethasone (0.45 mg/ml) was used as a positive control. They were administered orally with the volume ranging from 3.5 to 5 mL based on their body weight. The rat paw edema was measured at 0 and 24 hours after carrageenan induction. The results showed that treatment of the carrageenan-induced edema in the negative control group with Na-CMC did not decrease the volume of the rat paws, whereas those treated with dexamethasone showed a significant reduction of inflammation compared to the negative control (p < 0.05) (Fig. 3a, Table 1). The TE also reduced the carrageenan-induced edema in a dose-dependent manner with the most noticeable reduction observed in the 0.2 mg/ml group (p < 0.05) (Fig. 3a, Table 1). While edema reduction was also observed in the 0.05 and 0.1 mg/ml groups, it was not statistically significant (p > 0.05) compared to the negative control group.
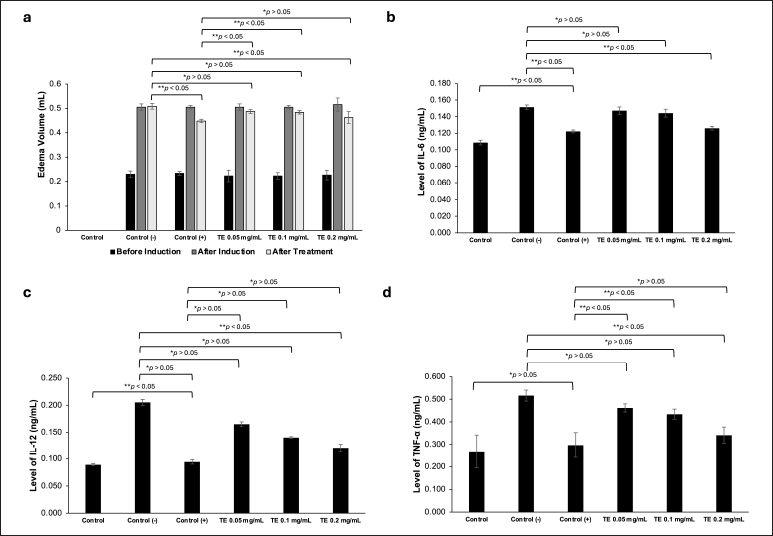 | Figure 3. In vivo anti-inflammatory activity tests of the ethanol extract of Theonella sp. (a) The edema volume of 1% carrageenan-induced rats before induction, after induction, and after treatment. Na-CMC (0.5%, 5 ml) was used as a negative control, dexamethasone (0.45 mg/ml, 5 ml) was used as a positive control; (b) The IL-6 levels of untreated rats (control group), negative control group, positive control group, TE 0.05, TE 0.1, and TE 0.2 mg/ml (5 ml each); (c) The IL-12 levels in all groups; (d) The TNF-α levels in all groups. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3), *p > 0.05 (not significant), **p < 0.05 (significant). [Click here to view] |
Table 1. Rat’s paw edema volume.
| Sample | Edema volume (ml) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-induction | Post-induction | Post-treatment | |
| Control (untreated) | - | - | - |
| Na-CMC (negative control) | 0.23 ± 0.014 | 0.51 ± 0.014 | 0.51 ± 0.012 |
| Dexamethasone (positive control) | 0.23 ± 0.008 | 0.51 ± 0.007 | 0.45 ± 0.007 |
| TE 0.05 mg/ml | 0.22 ± 0.024 | 0.51 ± 0.014 | 0.49 ± 0.008 |
| TE 0.1 mg/ml | 0.22 ± 0.014 | 0.51 ± 0.007 | 0.48 ± 0.007 |
| TE 0.2 mg/ml | 0.23 ± 0.020 | 0.52 ± 0.027 | 0.46 ± 0.024 |
The ethanol extract of Theonella sp. suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokine levels
To investigate the effect of the TE on the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, we collected the blood of the above-treated rats and measured the serum levels of IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α from each group (Fig. 3b–d, Table 2). The serum levels of IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α of the untreated control group were considered as the basal levels of the cytokines. Rats treated with Na-CMC (the negative control group) showed IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α levels significantly higher than the basal levels (p < 0.05). Treatment of the rats with dexamethasone (positive control) reduced the levels of IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α to nearly the basal levels. The TE also reduced the levels of IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α in a dose-dependent manner, where rats treated with 0.2 mg/ml of the extract showed significant reduction of the tested cytokines (p < 0.05). At this dose, the levels of IL-6 and TNF-α were very similar to those treated with dexamethasone (p > 0.05).
Table 2. IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α levels in each group.
| Sample | IL-6 level (ng/ml) | IL-12 level (ng/ml) | TNF-α level (ng/ml) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control (untreated) | 0.11 ± 0.003 | 0.09 ± 0.002 | 0.27 ± 0.073 |
| Na-CMC (negative control) | 0.15 ± 0.003 | 0.21 ± 0.006 | 0.52 ± 0.024 |
| Dexamethasone (positive control) | 0.12 ± 0.002 | 0.09 ± 0.004 | 0.30 ± 0.055 |
| TE 0.05 mg/ml | 0.15 ± 0.005 | 0.17 ± 0.004 | 0.46 ± 0.018 |
| TE 0.1 mg/ml | 0.14 ± 0.005 | 0.14 ± 0.002 | 0.43 ± 0.023 |
| TE 0.2 mg/ml | 0.13 ± 0.002 | 0.12 ± 0.007 | 0.34 ± 0.036 |
However, our in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity studies showed that the ethanol extract of the Indonesian Theonella sp. has anti-inflammatory activity. In the in vitro study, the extract reduced hemolysis, increased membrane stability, and prevented protein degradation in a dose-dependent manner. In the in vivo study, the extract reduced the volume of carrageenan-induced edema and serum levels of IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α in rats, also in a dose-dependent manner. The fact that the anti-inflammatory activity of the extract at 0.2 mg/ml is similar to that of dexamethasone at 0.45 mg/ml indicates that the extract contains highly potent anti-inflammatory agents.
Previous studies showed that the Solomonic T. swinhoei provided a number of cyclopeptides, for example, perthamides and solomonamides, with potent anti-inflammatory activity [13,16,17]. Perthamide C has been found to increase the expression of Hsp90 and reduce apoptosis, which is involved in a number of pathological processes, for example, cancer and inflammation [14,15]. Solomonamides A and B are proposed to inhibit the cascade response in inflammatory signaling pathways, including the toll-like receptor pathways. They inhibit the stimulation of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF receptors, which result in the inhibition of the NF-κB, the mitogen-activated protein kinase, the Janus kinase, and the signal transducer and activator of transcription pathways [35,36].
The extract also contained sulfated sterols, solomonsterols A and B, also with anti-inflammatory activity. The compounds were found to be selective agonists of the PXR, exerting immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory activity by inhibiting the function of NF-κB, a transcription factor that regulates the production of many genes related to innate and adaptive immunity such as cytokines, chemokines, adhesion proteins, and stress response genes [17,36]. The interaction of NF-κB with PXR leads to reciprocal regulation of these two factors, with PXR acting as a negative regulator of NF-κB activity. Additionally, PXR activation in T cells inhibits proliferation, reduces IFN expression, and thwarts MEK1/2 and NF-κB signaling [37]. While the active compounds in the ethanol extract of the Indonesian Theonella sp. reported here have not been determined, it is highly likely that the extract also contains peptides and/or sterols identical or similar to perthamides, solonamides, and/or solomonsterols. Further analysis of the chemical constituents of the extract is currently ongoing.
Molecular docking
The molecular docking results on the targets IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α show four Theonella sp. compounds, including Solomonamide A, Solomonamide B, Solomonsterol A, and Solomonsterol B, as shown in Figure 4. The interactions of amino acid residues with target receptors are shown in Table 4. Hydrophobic and hydrophilic analysis is also carried out in analyzing binding interactions and ligand-receptor behavior.
Table 3. The binding affinity of compounds from Theonella sp. against pro-inflammatory cytokines.
| No. | Compounds | Xp Gscore (Kcal/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL–6 | IL–12 | TNF–α | ||
| 1 | Solomonsterol A | –3.6 | –3.2 | –1.7 |
| 2 | Solomonsterol B | –3.4 | –3.0 | –1.3 |
| 3 | Solomonamide A | –6.1 | –7.2 | –2.4 |
| 4 | Solomonamide B | –4.6 | –8.3 | –4.0 |
| 5 | Dexamethasone | –3.2 | –5.4 | –4.0 |
 | Figure 4. The 3D visualization of dexamethasone and compounds from Theonella sp. [Click here to view] |
The binding free energy values in Table 3 show the ability of the compound to bind to the target protein. A molecular docking simulation of Theonella sp. examined compounds with the most significant potential to bind and predict their binding mode sites on IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α. Dexamethasone was used as a comparison compound with binding free energy values of –3.2, –5.4, and –4.0 Kcal/mol, respectively. Compounds 1, 2, 3, and 4 bind to IL-6 and have lower binding free energy values than the comparison compounds (Xp Gscore -3.6, -3.4, -6.1, and -4.6 Kcal/mol, respectively). Compounds 3 and 4 bind well with IL-12, with binding free energy values of –7.2 and –8.3 Kcal/mol, respectively, while compounds 1, 2, and 3 still show fairly good binding. However, compounds 1, 2, 3, and 4, which bind to TNF-α (Xp Gscore –1.7, –1.3, –2.4, and –4.0 Kcal/mol, respectively), do not have better binding energy values than the compound comparison.
The compound interacts with the active sites of target proteins listed in Table 4. The IL-6 complex with dexamethasone forms a hydrophobic bond at Leu 33 (bond length: 2.15 Å), a hydrogen bond with Asp 34 (bond length: 1.84 Å), Gln 175 (length bond: 2.08 Å), as well as Arg 189 (bond length: 2.64 Å), with a binding affinity of –3.2 Kcal/mol. Figure 5 shows a 3D visualization of the best compounds for each target displayed with Maestro 10.6. The best compound in binding free energy is IL-6 with solomonamide A, forming a hydrophobic bond on the backbone of Met 67 (bond length: 1.69 Å), two hydrogen bonds on the side chain of Soa 291 (bond length: 1.63 and 1.73 Å), Soa 290 (bond length: 1.85 Å), as well as two salt bridges in Soa 291 (bond length: 4.60 and 4.26 Å), with a bond affinity of –6.1 Kcal/mol. Potential amino acid residues for IL-6 binding are Arg, Asp, Gln, Met, Lys, and Leu. Meanwhile, the IL-12 complex with dexamethasone forms hydrophobic bonds in the backbone with Tyr 151 (bond length: 1.74 Å) and hydrogen bonds in the backbone (bond length: 2.19 Å), with a binding affinity of –5.4 Kcal/mol.
Table 4. Residue interaction compounds from Theonella sp. against pro-inflammatory cytokines.
| No. | Compounds | Residue interaction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | IL-12 | TNF-α | ||
| 1 | Solomonsterol A | H; Arg 182 Sb; Arg 179, Arg 182. Lys 171, Arg 30 R; Asp 26, Leu 33, Asp 34, Ile 36, Ser 37, Qrg 40, Leu 178, Gln 175 | R; Arg 230, Glu 204, Glu 203, Ala 202, Ala 201,Pro 200, Cys 199, Ser 270, Phe 269, Tyr 268, Ser 267, Asp 312, Tyr 314, Tyr 315, Tyr 136, Trp 262 | H; Tyr 151, Asn 34 R; Gly 148, Val 17, Leu 36, Hie 15, Ala 35, Ile 155, Ser 60, Tyr 59, Gln 61, Leu 120, Gly 121, Tyr 119, Leu 57, Ser 147 |
| 2 | Solomonsterol B | H; Arg 30, Arg 40, Arg 179 Sb; Arg 179, Arg 30 R; Ile 29, Leu 33, Asp 34, Ser 37, Ala 38, Lys 41, Lys 171, Gln 175, Leu 178, Arg 182 | Sb; Arg 160 R; Glu 204, Glu 203, Ala 202, Ala 201, Pro 200, Cys 199, Ala 198, Glu 195, Ser 270, Phe 269, Tyr 268 | H; Asn 34, Hie 15 R; Gln 61, Gln 149, Gly 148, Val 17, Tyr 151, Tyr 59, Ile 155, Leu 120, Gly 122, Ile 58, Gly 121, Leu 57 |
| 3 | Solomonamide A | H; Soa 291, Soa 290, Met 67 Sb; Soa 291, Soa 290 R; Glu 172, Gln 175, Ser 176, Arg 179, Phe 74, Lys 66, Ala 68, Glu 69 | H; Ala 202, Asp 312 Pi; Tyr 314 R; Glu 204, Glu 203, Ala 201, Pro 200, Tyr 136, Arg 230, Tyr 315, Arg 313, Trp 262, Ser 270, Phe 269, Tyr 268, Ser 267 | H; 2 Gln 61, 1 Tyr 151 R; Hie 15, Ile 155, Leu 57, Tyr 59, Gly 122, Gly 121, Leu 120, Tyr 119, Pro 117, Ser 60 |
| 4 | Solomonamide B | H; Soa 291, Soa 290 R; Met 67, Glu 69, Glu 172, Gln 175, Ser 176, Arg 179, Phe 74, Gln 75, Ser 76 | H; Glu 203, Ala 202 Sb; Glu 203 R; Glu 204, Ala 201, Pro 200, Cys199, Ser 270, Phe 269, Tyr 268, Tyr 315, Tyr 314, Asp 312, Tys 136, Trp 262 | H; 3 Gln 61, Tyr 151 R; Ile 155, Leu 57, Tyr 59, Gly 121, Ser 60, Leu 120, Tyr 119, Pro 117 |
| 5 | Dexamethasone | H; Arg 182, Asp 34, Gln 175, Leu 33 R; Arg 179, Leu 178, Ser 176, Arg 30, Lys 171, Ile 36, Ser 37 | H; Ala 202, Glu 204 R; Tyr 136, Glu 203, Ala 201, Pro 200, Tyr 268, Phe 269, Ser 270, Tyr 315, Tyr 314, Asp 312, Ile 229, Arg 230 | H; Gln 61, Tyr 151. R; Pro 117, Ser 60, Tyr 59, Leu 57, Gly 122, Ile 58, Gly 121, Leu 120, Tyr 119 |
The best compound in terms of binding free energy value is the IL12-solomonamide b complex, forming hydrophobic bonds on the backbone with Ala 202 (bond length: 1.66 Å) and hydrogen bonds on the side chain of Glu 203 (1.77Å) with a bond affinity value of –8.3 Kcal/mol. The potential amino acid residues for binding IL 12 are Ala, Glu, Asp, Tyr, and Arg. The TNF α–dexamethasone complex forms a hydrophobic bond in the side chain with tyr 151 (bond length: 2.09Å), forms a hydrogen bond in the side chain with Gln 61 (bond length: 1.97Å), with a bond affinity value of –4.0 Kcal/mol from Theonella sp. This target has a free energy value indicating activity towards this mediator (compounds 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively –1.7, –1.3, –2.4, and –4.0 Kcal/mol), but the binding free energy value is greater than the comparison compound could indicate that the compound’s binding interaction with the receptor is unstable. The data displayed also involve non-bonding interaction with the target. The 2D visualization of all compounds is in Figures 6–8.
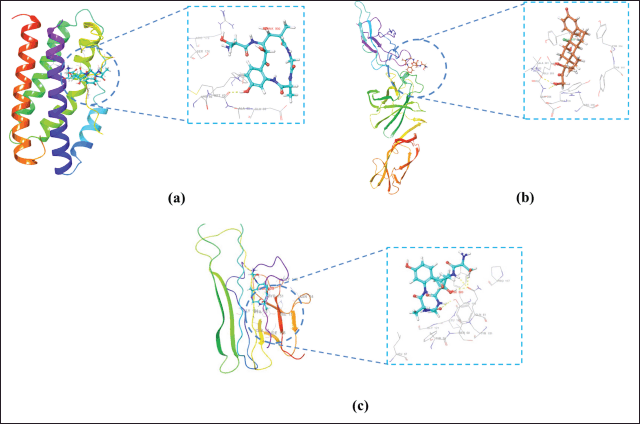 | Figure 5. Visualization of 3D ligand–receptor complex with binding free energy: (a) IL 6-Solonamide A, (b) IL-12-Solonamide B, and (c) TNF-α-Solomonamide B. Yellow dotted line: hydrogen bond. [Click here to view] |
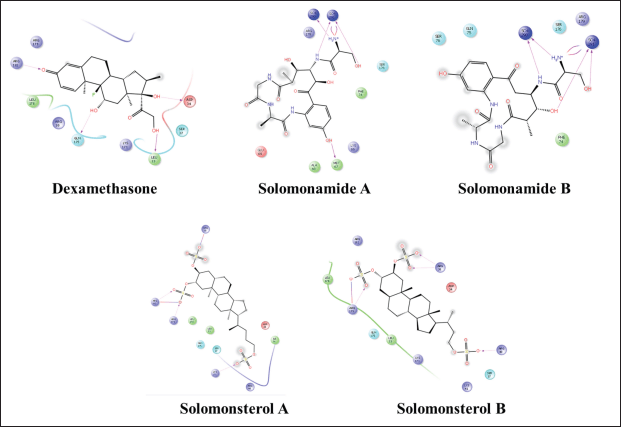 | Figure 6. 2D visualization of a compound that complexed with IL-6. [Click here to view] |
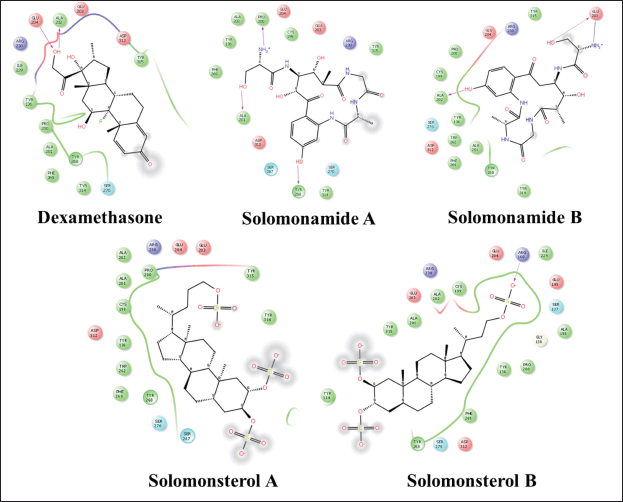 | Figure 7. 2D visualization of a compound that complexed with IL-12. [Click here to view] |
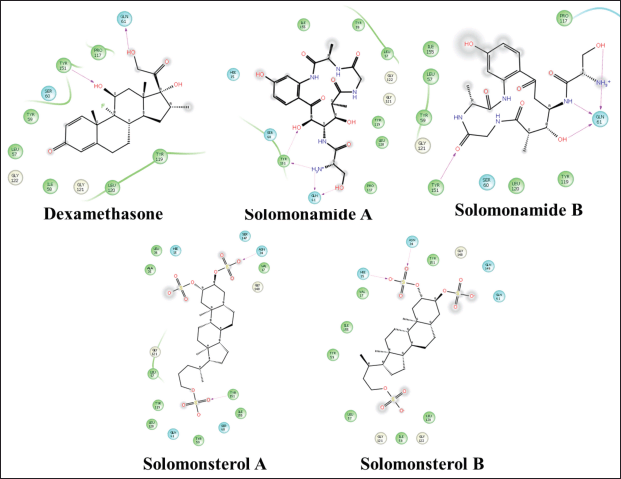 | Figure 8. 2D visualization of a compound that complexed with TNF-α. [Click here to view] |
The strong binding affinity of Solomonamide B toward IL-12 (–8.3 Kcal/mol), along with the formation of specific hydrophobic and hydrogen bonds with Ala202 and Glu203, suggests a structurally favorable interaction. The amphipathic nature of Solomonamide B likely contributes to its high binding propensity by enabling both polar and non-polar interactions within the IL-12 binding pocket. Given IL-12’s critical role in the pro-inflammatory signaling cascade, particularly in the differentiation of naive T cells into Th1 cells—this interaction implies that Solomonamide B may act as a potential modulator of IL-12 activity. Such modulation could translate into anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory effects, supporting its promise for further investigation in inflammatory or autoimmune disorders.
Molecular docking is the best molecular approach to explore the active site of a protein and the conformation position of the test compound in the binding pocket of the target protein. Ligand–protein complexes are studied based on binding affinity values (Kcal/mol), molecular interactions with active site amino acids, and binding interactions [32]. The smallest binding affinity value indicates the best conformational position in the protein’s active site. In general, ligand–protein complexes with low binding free energy values have a more extraordinary binding ability. The negativity of the free energy is essential, related to the ligand potential and the binding strength between the ligand–receptor [38].
The target structure is prepared to fix the structure; hence, it is ready for molecular docking. Target active site prediction was performed on IL-12 using SiteMap to search for potential protein active sites. Protein active sites were selected from the SiteMap results and used in Grid preparation. Prediction of the active site of this protein will require further analysis using crystal structures in the future. Meanwhile, for IL-6 and TNF-α, the Grid was prepared according to RMSD analysis, which had the lowest value (<2Å), shown in Table 5. The lower the RMSD value, the greater the probability of accurate binding site prediction.
Table 5. RMSD value from 1ALU.
| Grid | RMSD (Å) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 0.2442 |
| 11 | 0.1292 |
| 12 | 0.1450 |
| 13 | 0.1500 |
| 14 | 0.5062 |
| 15 | 0.3723 |
| 16 | 0.1468 |
| 17 | 0.1521 |
| 18 | 0.3286 |
| 19 | 0.0795 |
| 20 | 0.6267 |
The bold values showed lowest RMSD value.
The results of molecular docking show that four compounds from Theonella sp. (Fig. 5) have prominent activity. This molecular docking study is helpful in predicting the potential of compounds that can show activity when binding to the target protein’s active site. The target proteins IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α were docked with compounds 1, 2, 3, and 4 to evaluate the capabilities of these four compounds. The results of molecular docking show a negative free energy value, indicating these compounds’ potential activity towards these three targets. Solomonamide A has better binding ability than the reference compound to IL-6, and other compounds also have similar activity potential because they have lower binding free energy values than the reference ligand. The compound that binds to IL-12 best is Solomonamide B, while the Solomonamide A compound also has a lower free energy value than the comparison ligand. However, in contrast to Theonella sp.’s ability regarding TNF-α, none of the four compounds had a lower free energy value than the comparison compound. However, the results of a reasonably negative decrease in molecular energy can indicate the potential for these compounds to bind to IL-12. These differences in binding free energy values are strongly influenced by the interactions of these compounds with the active site of the target protein, including the number of hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and non-bonding interactions, all of which influence the binding free energy value and binding stability between the ligand and the target.
Compared to prior studies that emphasized the membrane-targeting and antifungal properties of compounds from T. swinhoei, particularly those from Pacific regions [13,16], the present study highlights a distinct interaction of Solomonamide B with a cytokine target (IL-12), suggesting an alternative mechanism of immunomodulatory action. These findings may reflect biogeographical differences, as Indonesian Theonella sponges inhabit a unique ecological niche within the Coral Triangle, potentially harboring symbiotic microbes that yield structurally distinct or more bioactive secondary metabolites [39]. This could explain the superior binding affinity observed in this study and underscores the need for regional bioprospecting to uncover novel therapeutic candidates.
Nevertheless, several limitations should be acknowledged. This study relied on secondary metabolites reported in previous literature without isolating or identifying compounds directly from Indonesian Theonella specimens. In addition, although molecular docking and dynamics simulations offer valuable predictive insights, they do not substitute for experimental validation. Therefore, further studies involving compound isolation, structural elucidation, and in vitro or in vivo immunological assays are needed to confirm the observed bioactivities and support the therapeutic potential of these marine-derived compounds.
CONCLUSION
The TE collected from waters around Southeast Sulawesi Province of Indonesia showed in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory properties. It was also supported form in silico model. It reduced hemolysis, increased membrane stability, and prevented protein degradation in a dose-dependent manner. The extract also reduced the volume of carrageenan-induced edema and serum levels of IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α in rats. Moreover, the in silico model of several compounds in Theonella sp. showed potency as anti-inflammatory agent. The results underscore the potential of Indonesian Theonella sp. as a source of new anti-inflammatory agents.
Although this study showed that the TE has anti-inflammatory properties, it is constrained by the lack of sophisticated phytochemical analysis techniques like TLC or LC-MS profiling. Subsequent research should incorporate comprehensive chemical fingerprinting to more accurately identify the bioactive compounds driving the observed effects.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Thank you to the 2023 World Class Professor Program from Directorate of Resources Affairs, Directorate General of Higher Education, Research, and Technology, Ministry of Education, Culture, Research and Technology, Republic of Indonesia (A.F. and T.M.). This study was supported by Penelitian Dasar Unggulan Perguruan Tinggi 2023, Contract No. 28/UN29.20/PG/2023 and 019/E5/PG.02.00.PL/2023 (A.F., I.S., and B.S.) and The 2023 World Class Professor Program from Directorate of Resources Affairs, Directorate General of Higher Education, Research, and Technology, Ministry of Education, Culture, Research and Technology, Republic of Indonesia (A.F. and T.M.).
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors report no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
All experimental procedures involving animals were conducted in accordance with institutional guidelines and approved by the Institute of Research and Community Service, Universitas Halu Oleo, with ethical clearance number 170/UN29.20.1.2/PG/2023.
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated and analyzed are included in this research article.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used artificial intelligence (AI)-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
REFERENCES
1. Stone WL, Basit H, Zubair M, Burns, B. Pathology, inflammation. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534820/
2. Serhan CN. Treating inflammation and infection in the 21st century: new hints from decoding resolution mediators and mechanisms. FASEB J. 2017;31(4):1273–88. CrossRef
3. Soares CLR, Wilairatana P, Silva LR, Moreira PS, Vilar Barbosa NMM, da Silva PR, et al. Biochemical aspects of the inflammatory process: a narrative review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;168:115764. CrossRef
4. Bulté D, Rigamonti C, Romano A, Mortellaro A. Inflammasomes: mechanisms of action and involvement in human diseases. Cells 2023;12(13):1766. CrossRef
5. Lee HM, Lee HJ, Chang JE. Inflammatory cytokine: an attractive target for cancer treatment. Biomedicines. 2022;10(9):2116. CrossRef
6. Gabay C. Interleukin-6 and chronic inflammation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(Suppl 2):S3. CrossRef
7. Akdis M, Aab A, Altunbulakli C, Azkur K, Costa RA, Crameri R, et al. Interleukins (from IL-1 to IL-38), interferons, transforming growth factor β, and TNF-α: receptors, functions, and roles in diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138(4):984–1010. CrossRef
8. Qiu N, Wang G, Wang J, Zhou Q, Guo M, Wang Y, et al. Tumor-associated macrophage and tumor-cell dually transfecting polyplexes for efficient interleukin-12 cancer gene therapy. Adv Mater. 2020;33(2):e2006189. CrossRef
9. Balasubbramanian D, Goodlett BL, Mitchell BM. Is IL-12 pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory? Depends on the blood pressure. Cardiovasc Res. 2019;115(6):998–9. CrossRef
10. Alzamil H. Elevated serum TNF-α is related to obesity in type 2 diabetes mellitus and is associated with glycemic control and insulin resistance. J Obes. 2020;2020:5076858. CrossRef
11. Sethi G, Sung B, Aggarwal BB. TNF: a master switch for inflammation to cancer. Front Biosci. 2008;13:5094–107. CrossRef
12. El-Shitany NA, Shaala LA, Abbas AT, Abdel-Dayem UA, Azhar EI, Ali SS, et al. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and immunomodulatory effects of the organic extract of the red sea marine sponge Xestospongia testudinaria against carrageenan induced rat paw inflammation. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0138917. CrossRef
13. Festa C, Marino SD, Sepe V, Monti MC, Luciano P, D’Auria MV, et al. Perthamides C and D, two new potent anti-inflammatory cyclopeptides from a Solomon Lithistid sponge Theonella swinhoei. Tetrahedron 2009;65:10424–9. CrossRef
14. Vilasi A, Monti MC, Tosco A, De Marino S, Margarucci L, Riccio R, et al. Differential in gel electrophoresis (DIGE) comparative proteomic analysis of macrophages cell cultures in response to perthamide C treatment. Mar Drugs. 2013;11(4):1288–99. CrossRef
15. Margarucci L, Monti MC, Mencarelli A, Cassiano C, Fiorucci S, Riccio R, et al. Heat shock proteins as key biological targets of the marine natural cyclopeptide perthamide C. Mol Biosyst. 2012;8(5):1412–7. CrossRef
16. Festa C, De Marino S, Sepe V, D’Auria MV, Bifulco G, Débitus C, et al. Solomonamides A and B, new anti-inflammatory peptides from Theonella swinhoei. Org Lett. 2011;13(6):1532–5. CrossRef
17. Festa C, De Marino S, D’Auria MV, Bifulco G, Renga B, Fiorucci S, et al. Solomonsterols A and B from Theonella swinhoei. The first example of C-24 and C-23 sulfated sterols from a marine source endowed with a PXR agonistic activity. J Med Chem. 2011;54(1):401–5. CrossRef
18. Sepe V, Ummarino R, D’Auria MV, Mencarelli A, D’Amore C, Renga B, et al. Total synthesis and pharmacological characterization of solomonsterol A, a potent marine pregnane-X-receptor agonist endowed with anti-inflammatory activity. J Med Chem. 2011;54(13):4590–9. CrossRef
19. Kogawa M, Miyaoka R, Hemmerling F, Ando M, Yura K, Ide K, et al. Single-cell metabolite detection and genomics reveals uncultivated talented producer. PNAS Nexus. 2022;1(1):pgab007. CrossRef
20. Hamsidi R, Wahyuni W, Sahidin I, Apriyani E, Harsono H, Azizah NA, et al. Suppression of proinflammatory cytokines by Etlingera alba (A.D.) poulsen rhizome extract and its antibacterial properties. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2021;2021:5570073. CrossRef
21. Raal A, Meos A, Hinrikus T, Heinämäki J, Romane E, Gudiene V, et al. Dragendorff’s reagent: historical perspectives and current status of a versatile reagent introduced over 150 years ago at the University of Dorpat, Tartu, Estonia. Pharmazie 2020;75(7):299–306. CrossRef
22. Nath MC, Chakravorty MK, Chowdhury SR. Liebermann-Burchard reaction for steroids. Nature 1946;157:103. CrossRef
23. Saleem TK, Azeem AK, Dilip C, Sankar C, Prasanth NV, Duraisami R. Anti-inflammatory activity of the leaf extacts of Gendarussa vulgaris Nees. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2011;1(2):147–9. CrossRef
24. Dharmadeva S, Galgamuwa LS, Prasadinie C, Kumarasinghe N. In vitro anti-inflammatory activity of Ficus racemosa L. bark using albumin denaturation method. Ayu 2018;39(4):239–42. CrossRef
25. Fristiohady A, Mahmud T, Maming JT, Arfan A, Jabbar A, Yusuf MI, et al. Safflower extract (Carthamus tinctorius Linn.) suppresses proinflammatory cytokines level in rheumatoid arthritis mice model stimulated by complete Freund’s adjuvants. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2024;5(2):189–99. CrossRef
26. Festing MF, Altman DG. Guidelines for the design and statistical analysis of experiments using laboratory animals. ILAR J. 2002;43(4):244–58. CrossRef
27. National Research Council (US) Committee. Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. 8th ed. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2011. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK54050/
28. OECD. Test No. 425: acute oral toxicity: up-and-down procedure. OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, section 4. Paris, France: OECD Publishing; 2008. CrossRef
29. Bustos-Salgado P, Rodríguez-Lagunas MJ, Domínguez-Villegas V, Andrade-Carrera B, Calpena-Campmany A, Garduño-Ramírez ML. Ex vivo and in vivo anti-inflammatory evaluations of modulated flavanones solutions. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Electronic Conference on Medicinal Chemistry, 2020, MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. p. 60(1). CrossRef
30. Chaudhary RK, Karoli SS, Dwivedi PSR, Bhandari R. Anti-diabetic potential of Corn silk (Stigma maydis): an in-silico approach. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022;21(1):445–54. CrossRef
31. Arba M, Ningsih AS, Bande LOS, Wahyudi ST, Bui-Linh C, Wu C, et al. Computational insights into the binding of pimodivir to the mutated PB2 subunit of the influenza A virus. Mol Simul. 2023;49(10):1031–43. CrossRef
32. Malik A, Naz A, Ahmad S, Hafeez M, Awan FM, Jafar TH, et al. Inhibitory potential of phytochemicals on interleukin-6-mediated T-cell reduction in COVID-19 patients: a computational approach. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2021;15:11779322211021430. CrossRef
33. Festa C, De Marino S, Zampella A, Fiorucci S. Theonella: a treasure trove of structurally unique and biologically active sterols. Mar Drugs. 2023;21(5):291. CrossRef
34. Khan MA, Khan H, Tariq SA, Pervez S. In vitro attenuation of thermal-induced protein denaturation by aerial parts of Artemisia scoparia. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2015;20(1):9–12. CrossRef
35. Liu W, Chen X, Li H, Zhang J, An J, Liu X. Anti-inflammatory function of plant-derived bioactive peptides: a review. Foods 2022;11(15):2361. CrossRef
36. Zhang K, Tang Y, Chen Q, Liu Y. The screening of therapeutic peptides for anti-inflammation through phage display technology. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15): 8554. CrossRef
37. Mencarelli A, D’Amore C, Renga B, Cipriani S, Carino A, Sepe V, et al. Solomonsterol A, a marine pregnane-X-receptor agonist, attenuates inflammation and immune dysfunction in a mouse model of arthritis. Mar Drugs. 2013;12(1):36–53. CrossRef
38. Pathak RK, Kim WI, Kim JM. Targeting the PEDV 3CL protease for identification of small molecule inhibitors: an insight from virtual screening, ADMET prediction, molecular dynamics, free energy landscape, and binding energy calculations. J Biol Eng. 2023;17(1):29. CrossRef
39. Sabdono A, Radjasa OK. Microbial symbionts in marine sponges: marine natural product factory. J Coast Dev. 2008;11(2):57–61. Available from: https://ejournal.undip.ac.id/index.php/coastdev/article/view/1221