INTRODUCTION
Bone-related disorders encompass a wide spectrum of conditions that significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. These include osteoporosis, arthritis, Paget’s disease, osteonecrosis, bone cancer, rickets, scoliosis, and gout, affecting millions worldwide [1]. In India, osteoporosis and arthritis are the most prevalent, with osteoporosis showing a higher incidence among the elderly and postmenopausal women [2]. According to the World Health Organization, 30% of postmenopausal women globally suffer from osteoporosis. Reports indicate that in India, 61 million individuals are affected, with women comprising 80% of cases. Notably, osteoporosis manifests 10–20 years earlier in the Indian population compared to Western countries, posing a significant public health and economic burden [3]. Osteoporosis, a metabolic bone disorder, is characterized by impaired microarchitecture, reduced bone mineral density (BMD), trabecular thinning, cortical deterioration, and increased porosity [4]. It is classified into primary and secondary forms, with primary osteoporosis further subdivided into age-related and postmenopausal types [5,6]. Secondary osteoporosis, on the other hand, arises from underlying medical conditions or medications that impair bone regeneration [7]. In both sexes, hypogonadism accelerates bone loss and increases fracture risk [8]. Additionally, genetic variations, such as mutations in the vitamin D receptor gene, influence bone metabolism and susceptibility to osteoporosis [9]. The pathophysiology of osteoporosis revolves around dysregulated bone remodeling, a dynamic process essential for maintaining skeletal integrity. Similarly, arthritis, a group of inflammatory conditions primarily affecting the joints, disrupts normal joint homeostasis, leading to pain, stiffness, swelling, and restricted mobility. The most prevalent form is osteoarthritis, characterized by cartilage degeneration, while rheumatoid arthritis represents a secondary autoimmune-driven variant [10,11].
Psoriatic arthritis is associated with the skin disorder psoriasis [12], whereas gout results from uric acid crystal deposition in joints [13]. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis manifests as chronic arthritis in young individuals [14]. Furthermore, obesity has been strongly correlated with the onset and progression of arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis [15]. In addition, smoking has been identified as a significant risk factor for the development and progression of rheumatoid arthritis [16]. It is fundamental to possess a more profound understanding of the pathophysiology of arthritis so as to develop targeted treatment methods. When the immune system attacks the synovium, B cells and T cells become activated, and enzymatic mediators like cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) are elevated in the inflammatory synovium [11]. The bone is renovated, and osteophytes appear as a result of the cartilage’s degradation, which reveals the underlying bone [17]. The management of osteoporosis remains challenging due to underdiagnosis, inadequate risk assessment, and high treatment costs, which limit accessibility to effective therapies [18]. While rheumatoid arthritis and gout are less common, osteoarthritis affects approximately 22% of the population. The lack of awareness, delayed diagnosis, and absence of standardized treatment protocols further hinder arthritis management [19]. Existing pharmacological interventions, such as bisphosphonates and hormone replacement therapy, have potential adverse effects, underscoring the need for alternative therapeutic strategies. Traditional medicinal plants with pharmacological properties may serve as promising interventions for bone health [20].
One such plant is Cissus quadrangularis Linn (CQ), which features four-winged internodes on a fleshy, fibrous stem. Known for its antioxidant and antibacterial properties, CQ is rich in calcium, phosphorus, and anabolic steroidal compounds, contributing to bone metabolism and regeneration [21].
Numerous phytochemical investigations of CQ have identified a wide spectrum of bioactive constituents, including carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, ascorbic acid, alkaloids, saponins, glycosides, triterpenoids, phytosterols, tannins, and flavonoids. The aerial stem has been reported to contain both primary metabolites (cyclic and acyclic fatty acids, methyl esters, iridoids, amino acids, gums, and mucilages) and secondary metabolites (alkaloids, flavones, saponins, steroids, stilbenes, cardiac glycosides, carotene, and ascorbic acid). The underground parts share many of these compounds, though typically lack vitamins, proteins, and fatty acids. Traditionally, CQ is known for its fracture-healing and analgesic properties. Additionally, its extracts exhibit antioxidant, antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-hemorrhoidal activities [22]. This review aims to critically evaluate the therapeutic potential of CQ in the management of osteoporosis and arthritis, with a focus on its mechanisms of action, effective dosage ranges, and long-term efficacy as evidenced by in vivo studies.
Addressing osteoporosis and arthritis, especially within the Indian context, is critical. Given CQ’s multifaceted benefits—enhanced bone regeneration, improved fracture healing, reduced fracture risk, joint tissue protection, and alleviation of pain and inflammation—its integration into mainstream healthcare warrants exploration. This review seeks to bridge the gap between traditional medicine and modern therapeutic strategies by elucidating CQ’s medicinal properties and potential clinical applications with the aim of understanding CQ’s role in bone health, highlighting its potential as a natural therapeutic agent for osteoporosis and arthritis management.
The phytochemicals present in CQ demonstrate significant therapeutic potential in managing bone-related disorders. Understanding the mechanisms by which these phytonutrients influence bone metabolism is critical, predominantly their interaction with key cellular signaling pathways. These include RANKL-OPG, estrogen, MAPK, inflammatory response, Wnt, calcium, and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) pathways, all of which regulate gene expression essential for bone remodeling. Vital to this process is the NF-κB pathway, comprising RANK, its ligand RANKL, and the decoy receptor OPG, which together maintain bone homeostasis. Osteoblast differentiation is principally governed by RUNX2, a transcription factor that modulates osteogenic markers such as collagen type I, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), osteopontin, osteocalcin, and bone sialoproteins. RUNX2 expression is, in turn, upregulated by BMP, TGF-β, IGF, and Wnt signaling, promoting osteoblast maturation. Increased ALP activity during this process further reflects active bone metabolism [23].
Osteoporosis results from excessive bone resorption surpassing bone formation, principally driven by RANKL-RANK interactions that stimulate osteoclast activity and pro-inflammatory cytokine release tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-7), along with OPG downregulation. Osteoblast differentiation is regulated by signaling pathways such as Wnt, PTH, BMPs, and FGF. In postmenopausal women, estrogen deficiency disturbs bone homeostasis, further aggravated by oxidative stress, raised homocysteine, and reduced folate and SOD levels. Conventional therapies (e.g., bisphosphonates, PTH analogs, and calcitonin) stimulate bone formation but carry risks of adverse effects and cost-related barriers. In contrast, herbal medicines offer a promising, potentially safer alternative for managing osteoporosis and osteoarthritis [24].
Figure 1 presents a schematic representation of bone remodeling, highlighting key regulatory mechanisms [25]. The RANK/RANKL/OPG signaling pathway, which governs osteoclast differentiation and activation, is disrupted in osteoporosis, leading to excessive bone resorption. Additionally, impairment of the β-catenin signaling pathway compromises optimal osteoblast function, further contributing to bone loss [8].
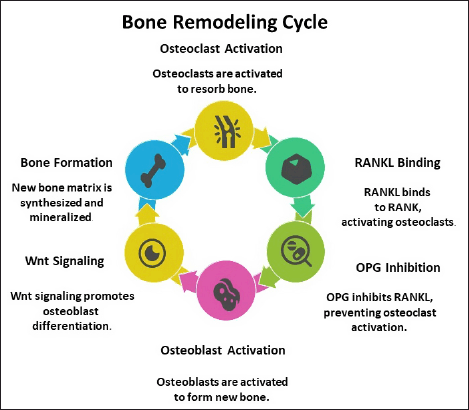 | Figure 1. Schematic representation of bone remodelling cycle. [Click here to view] |
Botanical profile and traditional uses of CQ
CQ, or Veldt grape, belongs to the Vitaceae family. Table 1 depicts the scientific classification of CQ [26]. It is an uncultivated and fast-growing succulent plant with tendrils. It is native to India, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka, and is found in Africa. Figure 2 shows the distribution of CQ based on data from the CABI Digital Library, indicating its native regions in green and countries of introduction in pink.
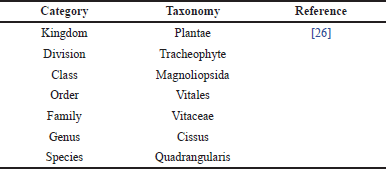 | Table 1. Scientific classification of CQ. [Click here to view] |
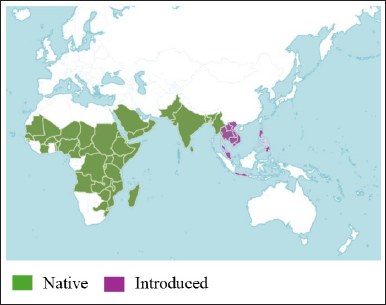 | Figure 2. Geographical distribution of CQ, showing its native range (green) and introduced regions (pink). Source: CABI Digital Library [28] . [Click here to view] |
The name “quadrangularis” is owing to the distinctive characteristic quadrangular shape of the stem, which is visible in Figure 3, which shows the foliage and stem of CQ [27,28]. It belongs to arid habitats and subtropical areas with low rainfall and high temperatures. Its common English name is ‘Veldt grape’. Different parts of the CQ plant are used as medicines. Traditionally, CQ is known as a bonesetter, and is used for bone regeneration and for skin infections [29]. Every part of the plant has its own unique therapeutic analgesic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-microbial applications. As a general tonic, it was used in folk medicine for joint pain, fractures, and osteoporosis [29,30].
 | Figure 3. Foliage and stem of CQ. Source: CABI Digital Library [27] . [Click here to view] |
Pharmacological properties of CQ
CQ comprises various phytochemicals such as quercetin and kaempferol that contribute to its pharmacological properties. These significant bioactive flavonoids, in addition to other compounds present, such as sterols, carotenoids, triterpenoids, and vitamin C, are responsible for the diverse pharmacological characteristics of CQ [31,32]. CQ offers a wide range of health benefits. It exhibits anti-ulcer, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory properties, making it effective for gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions. Additionally, it shows diuretic, anabolic, and androgenic activities suggest potential benefits in enhancing physical performance, muscle growth, and recovery [33]. Additionally, CQ has demonstrated potential in managing metabolic disorders, including diabetes, by improving insulin sensitivity and regulating blood sugar levels. Studies also suggest that it may support weight management by reducing fat accumulation and enhancing fat metabolism. Moreover, CQ’s antimicrobial properties contribute to boosting immunity and fighting infections, further establishing its therapeutic potential in various health conditions [21].
CQ offers significant benefits for bone health, with studies showing its potential to enhance bone healing and reduce the risk of fractures [33]. Additionally, CQ’s anti-inflammatory properties help reduce bone-related pain and inflammation, making it useful for conditions like osteoporosis and fractures [35].?
Elevated osteoclastic activity in bone increases serum levels of C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX), a key biomarker used to assess bone resorption in conditions like osteoporosis. Studies on CQ have shown its osteogenic potential, as demonstrated through enhanced ALP activity (a positive marker of bone formation) and reduced CTX levels, thus contributing to bone homeostasis and mitigating bone loss in osteoporosis [36].
CQ contains a diverse range of bioactive phytochemicals—including flavonoids (kaempferol, quercetin), phytosterols, triterpenoids, glycosides, tannins, saponins, alkaloids, proteins, calcium, and vitamin C, that contribute to bone healing. CQ promotes osteoblast proliferation and enhances mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into osteoblastic lineages. It upregulates RUNX2 expression, activating MAPK and Wnt signaling pathways essential for bone remodeling. CQ also stimulates osteogenic markers such as NF-κB, AP-1, survivin, and ALP, while exerting anti-inflammatory, anti-clastogenic, and anti-osteoporotic effects that support bone regeneration and cartilage repair [31,34].
Anti-osteoporotic and anti-arthritic potential of CQ
Studies have demonstrated that CQ extracts stimulate osteoblast differentiation and enhance bone matrix mineralization. In vitro experiments using human osteoblast-like cells treated with the extract showed a significant increase in ALP activity [34]. Furthermore, animal models indicated that supplementation elevated serum osteocalcin levels [35]. CQ exhibits inhibitory effects on osteoclastogenesis and osteoclast activity. In an ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis model, its supplementation significantly reduced osteoclast activity, suggesting a potential role in mitigating excessive bone resorption [37,38].
In a case-control study, supplementation with petroleum ether extracts of CQ improved bone strength and mineralization in ovariectomized rats [39]. CQ enhanced callus formation and increased bone remodeling activity, suggesting a synergistic effect of its phytocompounds rather than the action of β-sitosterol alone [38]. However, its effects on BMD in clinical settings remain inadequately explored. A randomized double-blind study reported a significant increase in lumbar spine BMD after 24 months, while a trial in postmenopausal women demonstrated improvements in spinal BMD. Although current clinical data do not conclusively establish it as a direct fracture prevention agent, evidence suggests an indirect role in reducing fracture risk by improving BMD [40]. Despite these promising findings, further well-designed clinical trials are essential to validate its efficacy as a supplemental treatment for osteoporosis and fracture prevention.
The anti-arthritic effectiveness of CQ is attributed to multiple mechanisms of action. Notably, its antioxidant properties play a crucial role in protecting joint tissues from oxidative stress and damage [31]. Additionally, it modulates immune responses associated with arthritis onset by regulating inflammatory pathways.
Studies indicate that the extract inhibits the production of key pro-inflammatory mediators, including TNF-α, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-6, which contribute to inflammation and tissue damage in arthritic conditions. Suppression of these mediators suggests its potential for alleviating arthritis symptoms [41]. Furthermore, its ability to promote collagen synthesis enhances cartilage integrity and joint function, while also stimulating glycosaminoglycan production—an essential component for joint lubrication and cushioning [40,41]. These mechanisms collectively support joint preservation and may slow disease progression. In animal models of arthritis, supplementation led to increased pain thresholds and reduced pain perception. The extract has demonstrated inhibitory effects on cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and 5-LOX, enzymes responsible for synthesizing inflammatory prostaglandins and leukotrienes, respectively [21]. This dual inhibition suggests its role as a natural analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent.
Although limited clinical studies have explored its efficacy in human arthritis management, existing evidence points to therapeutic potential. A randomized controlled trial reported improvements in pain relief, joint inflammation, and physical function in individuals with knee osteoarthritis following supplementation [29]. However, further clinical investigations are required to validate these findings and assess long-term efficacy in arthritis treatment.
METHODOLOGY
Study design
This study employed a scoping review design to systematically explore the therapeutic potential of CQ in osteoporosis and arthritis. The review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines. A comprehensive literature search was conducted across PubMed, SCOPUS, JSTOR, EBSCO Web of Science, and Google Scholar databases for relevant studies published between 2003 and 2024 for osteoporosis and 2010–2024 for arthritis, respectively. The search phrases CQ AND osteoporosis and CQ AND arthritis were chosen for the analysis.
Inclusion criteria
Studies assessing bone health following CQ administration in preclinical (animal) models, in vivo studies on CQ administration, studies on bone health, osteoporosis, arthritis after CQ administration, English studies, and animal subjects.
Exclusion criteria
The review’s exclusion criteria included review articles, studies on unintentional fractures, non-English studies, and human studies.
Data screening and extraction
Data screening and selection were conducted using a systematic approach that ensured a streamlined and transparent review process. Two authors independently screened the abstracts, followed by a full-text evaluation of studies that met the inclusion criteria. A PRISMA flow diagram was used to depict study selection, illustrating the number of records identified, screened, included, and excluded at each stage. Key variables, including dosage, administration route, and outcome measures, were extracted and synthesized to assess CQ efficacy in bone health management. This approach ensured a structured evaluation of the available evidence, highlighting gaps and future research directions. Figure 4 displays the PRISMA flow diagram of the study selection process.
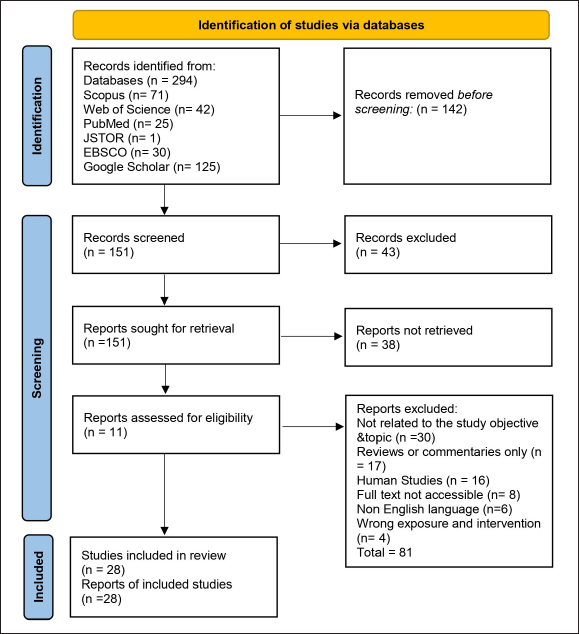 | Figure 4. PRISMA flow diagram of the study selection process. [Click here to view] |
RESULTS
A total of 294 studies were initially identified through database searches. After the removal of 142 duplicates, 151 unique studies remained for screening. Following a title and abstract assessment, 113 studies proceeded to full-text review. Based on the predefined selection criteria, 28 studies were included, while 72 were excluded. Among the selected studies, 18 focused on osteoporosis, and 10 specifically addressed arthritis. The subsequent tables synthesize the extracted data to align with the objectives of this review. Table 2 provides a detailed analysis of osteoporosis studies, including those that evaluate long-term effects. While, Table 3 summarizes the therapeutic effects of CQ on arthritis, detailing its mechanisms of action, effective dosages, long-term impacts, and comparative efficacy with standard treatments.
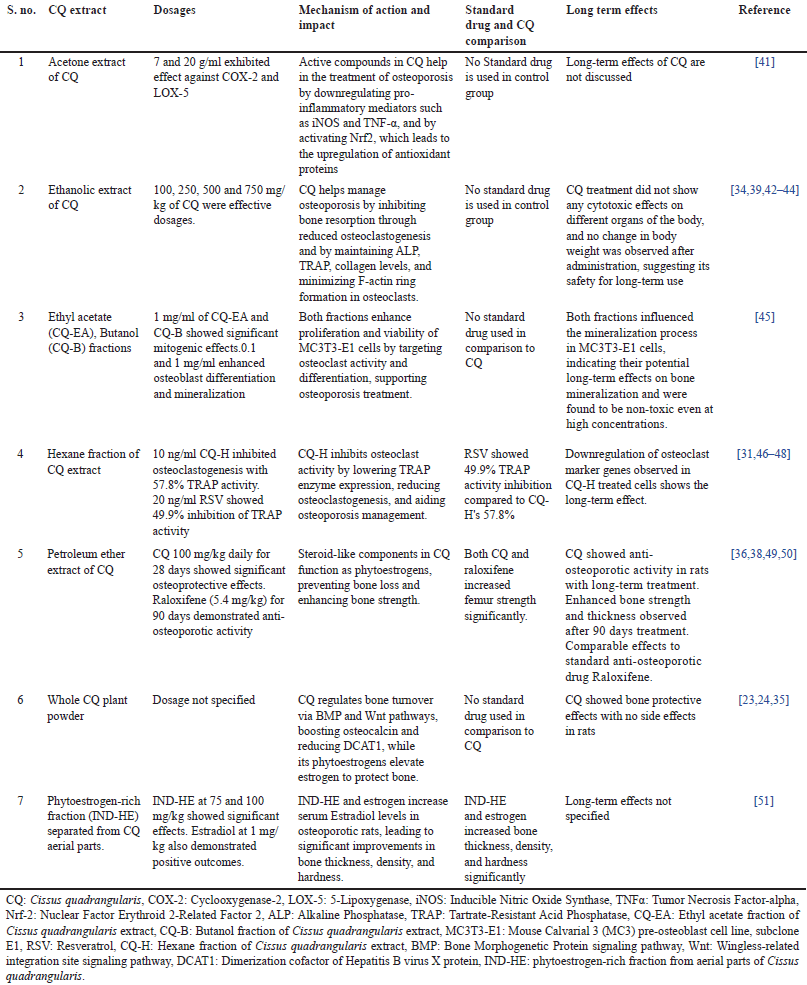 | Table 2. Effects of CQ on osteoporosis: dosages, mechanism, impact, and long-term outcomes. [Click here to view] |
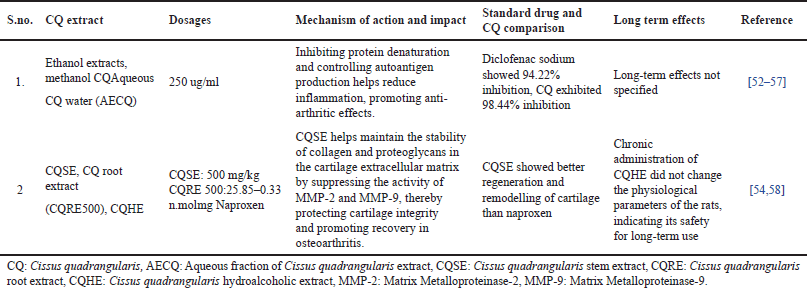 | Table 3. Summary of CQ effects on arthritis: mechanisms, dosages, long-term impact, and comparisons with standard treatments. [Click here to view] |
Table 4 outlines the pharmacological activities of CQ emphasizing its bioactive components and their therapeutic roles. Complementing this, Figures 5–7 illustrates the chemical structures of these key bioactive compounds, providing a visual representation of their molecular composition [60–62]. Additionally, Table 5 presents the classical formulations of CQ highlighting its traditional medicinal applications.
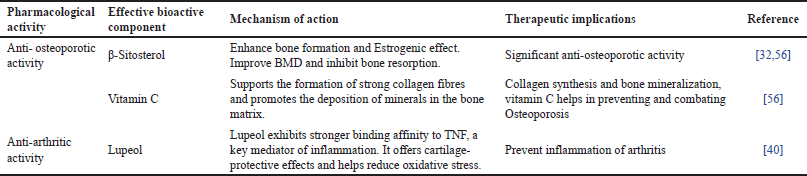 | Table 4. Pharmacological activities of CQ: bioactive components, mechanisms and therapeutic implications. [Click here to view] |
 | Figure 5. Chemical structure of bioactive component of CQ: ascorbic acid. [Click here to view] |
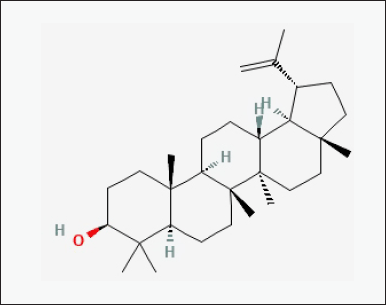 | Figure 6. Chemical structure of bioactive component of CQ: Lupeol. [Click here to view] |
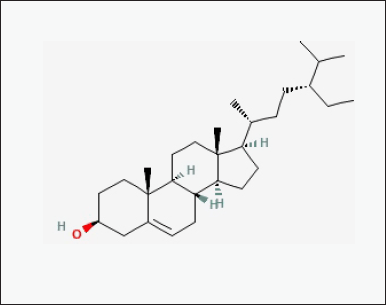 | Figure 7. Chemical structure of bioactive component of CQ: beta-sitosterol. [Click here to view] |
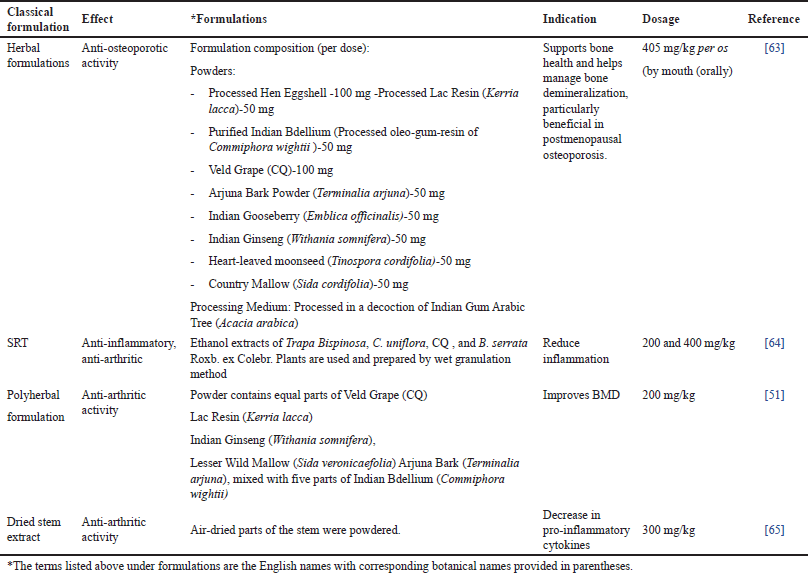 | Table 5. Classical and contemporary formulations of CQ: therapeutic potential and pharmacological insights. [Click here to view] |
DISCUSSION
CQ has been shown through a literature review to possess anti-inflammatory, bone-healing, and bone-mineral density properties that help manage bone illnesses like osteoporosis and arthritis [49]. The anabolic steroid from the CQ plant showed a marked influence on the rate of fracture healing by the early generation of all connective tissue [67].
The therapeutic effects of CQ in treating bone diseases have been well-recognized in ancient Indian traditional medicine [68]. Traditionally, in folk as well as Ayurvedic medicine, its extracts were used as oral and topical applications to treat fractures and sprains, to speed up the healing process. The studies brief in Table 2 provide substantial evidence for the anti-osteoporotic potential of CQ through several mechanisms of action. The therapeutic effects of CQ cannot solely be attributed to individual phytoconstituents but are likely a result of synergistic interactions among flavonoids, triterpenoids, and steroidal compounds, enhancing bioavailability and biological activity beyond what isolated constituents achieve. The extracts of CQ, prepared using diverse solvents such as acetone, ethanol, ethyl acetate, butanol, hexane, and petroleum ether, have been examined for their impact on bone health. CQ has confirmed its efficacy in osteoporosis management by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis, reducing bone resorption, and stimulating osteoblast differentiation and mineralization. The acetone extract demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects through COX-2 and LOX-5 inhibition, while ethanolic and ethyl acetate extracts efficiently inhibited osteoclastogenesis and enhanced osteoblast activity, assisting bone regeneration. Predominantly, the petroleum ether extract showed steroid-like phytoestrogenic activity, which amended bone mineralization and strength, similar to the standard anti-osteoporotic drug raloxifene. Likewise, a phytoestrogen-rich fraction (IND-HE) improved estrogen levels, mirroring the beneficial effects of estradiol on bone density and thickness. Prominently, the long-term safety of CQ was emphasized in select studies, where no cytotoxic effects or conflicting changes in body weight were observed, indicating its potential as a safe therapeutic intervention [52]. The downregulation of osteoclast markers and the modulation of key signaling pathways, such as BMP and Wnt, further back its role in bone healing and protection. However, some studies lacked data on long-term effects and standard drug comparisons, necessitating further investigation into CQ’s sustained efficacy and clinical significance. The fundamental concept of these research studies is that the plant contains unidentified anabolic steroids that work by binding to the bone’s estrogenic receptor. The plant’s ability to promote early bone ossification and remodeling can also improve metabolism and osteoblasts’ rapid uptake of minerals such as calcium, sulfur, and strontium [22].
Overall, the findings strengthen CQ’s potential as a natural alternative for osteoporosis management. Upcoming studies should focus on clinical trials to establish optimal dosages, long-term effects, and comparative efficacy besides the conventional osteoporosis treatments. The studies summarized in Table 3 highlight the credibility of CQ in managing arthritis through various bioactive extracts. The ethanol, methanol, and aqueous extracts of CQ demonstrated significant anti-arthritic activity by inhibiting protein denaturation and regulating autoantigen production. Notably, CQ showed a higher inhibition rate (98.44%) compared to diclofenac sodium (94.22%), signifying its robust anti-inflammatory potential. Furthermore, CQ stem extract (CQSE) and hydroalcoholic extract (CQHE) contributed to osteoarthritis management by conserving collagen and proteoglycan stability in cartilage, suppressing matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-2 and MMP-9), and encouraging cartilage regeneration. CQSE displayed better cartilage remodeling compared to naproxen, suggesting its therapeutic advantage. Moreover, long-term administration of CQHE did not modify physiological parameters in animal models, reinforcing its safety for sustained use [59]. Overall, these findings suggest that CQ holds anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective properties, making it a likely natural alternative for arthritis management. Further clinical studies are essential to establish its optimal dosage, long-term efficacy, and comparative benefits over standard pharmacological treatments. The pharmacological activities of CQ are accredited to its bioactive components, which play a crucial role in bone health and arthritis management. For osteoporosis, β-Sitosterol has established significant osteoprotective properties by enhancing bone formation, exerting estrogenic effects, and inhibiting bone resorption [33,63]. These mechanisms contribute to enhanced BMD, making it beneficial for osteoporosis prevention and management. Additionally, vitamin C plays a critical role in bone metabolism by supporting collagen synthesis and promoting mineral deposition in the bone matrix, further reinforcing its anti-osteoporotic potential. Regarding arthritis, Lupeol, a key bioactive compound, has revealed strong anti-inflammatory effects by effectively binding to TNF receptors, which are involved in the inflammatory response. It also provides cartilage protection and reduces oxidative stress, thereby preventing the progression of arthritis. Overall, the presence of these bioactive components in CQ highlights its therapeutic potential in managing osteoporosis and arthritis [41]. More in-depth studies are required to discover their precise mechanisms, clinical efficacy, and long-term benefits in human populations. Various formulations have been developed, integrating CQ with other bioactive herbal components to enhance its efficacy.
These bone-strengthening formulations, incorporate CQ along with a combination of herbal and mineral ingredients traditionally used to support bone health. These include Hen Eggshell Ash—rich in calcium carbonate, Lac Resin, Indian Bdellium, and Arjuna Tree Bark (Terminalia arjuna) among others. These formulations have demonstrated osteoprotective effects, particularly in postmenopausal osteoporosis, by enhancing bone remineralization and density [63]. The sustained-release tablet (SRT) formulation, which includes CQ along with Water chestnut, Cassia uniflora, and Boswellia serrata, has been developed to provide prolonged anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects. This formulation efficiently reduces inflammation, making it a promising option for arthritis management [59]. Likewise, there are polyherbal preparations that combine CQ with Lac resin, Indian Ginseng, Country Mallow, and Arjun Tree Bark, all known for their bone-strengthening properties. Such formulations have shown efficacy in improving BMD, reinforcing its role in osteoporosis and arthritis treatment [56]. Furthermore, the dried CQSE has demonstrated anti-arthritic activity by decreasing pro-inflammatory cytokines, supporting its use in inflammatory joint conditions [66]. These formulations underline the pharmacological versatility of CQ in skeletal health and inflammatory disorders. Future research should focus on clinical validation, optimized dosages, and long-term safety to enhance its therapeutic applications.
The literature has suggested CQ’s effectiveness in bone regeneration and pain alleviation as a valuable remedy in traditional medical practices [57]. To enhance the exploration and integration of traditional knowledge concerning CQ into clinical practice, its standardized plant extracts are being incorporated into formulations for nutraceuticals and dietary supplements that target bone health [68]. It clearly shows the potential to enhance bone formation, implying that it might prevent the loss of bone mass and the possibility of fractures. In line with a collaborative study of results focusing on both diseases, CQ has shown effects similar to those of typical synthetic medicines in terms of efficacy [48]. Furthermore, one research study on CQ-fortified raw rice and rice flour demonstrated promising effects on osteoporosis and osteoarthritis that have been documented. The increased content of CQ fortificant in the products enhanced BMD, decreased systemic inflammation, and averted articular degeneration and micro-architectural damages in experimental models of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. The results imply that dietary modifications can be vital in preventing and managing bone-related disorders [68].
Although CQ is linked to therapeutic benefits through compounds like β-sitosterol, lupeol, and vitamin C, its precise molecular mechanisms remain inadequately understood. Most studies lack dose-response data and direct validation of these bioactives in bone or joint tissues, highlighting a major gap in phytopharmacological evidence.
Key knowledge gaps include the absence of standardized phytochemical profiling, limited pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics data, inadequate dose-response and long-term safety evidence, and few comparative studies with standard treatments like bisphosphonates or NSAIDs. Future research should focus on isolating active constituents via bioassay-guided fractionation and validating mechanisms using pathway-specific models while also conducting clinical trials to assess efficacy, safety, and dosing. Until more robust evidence emerges, CQ should be viewed as a complementary therapy. Its use in functional foods or nutraceuticals such as CQ-fortified rice may offer preventive benefits in bone health, as early in vivo studies indicate.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, this review revealed the potential pharmacological actions of CQ for its diverse bioactive components, classical formulations, mechanisms of action, dosages, and impacts in managing osteoporosis and arthritis. Vitamin C and β-sitosterol prevent osteoporosis by promoting bone formation and inhibiting resorption. Lupeol’s anti-arthritic qualities include reduced inflammation, cartilage protection, and immune regulation. Bone-strengthening herbal supplements containing CQ, SRT, polyherbal formulations, and Stem Powder have all been shown to promote joint health and lower pro-inflammatory cytokines.
In animal models, the CQ dosage of 200 mg/kg body weight to 400 mg/kg body weight was found effective in managing the ailments.
Despite its promising pharmacological profile, further clinical studies are necessary to establish standardized dosages, evaluate long-term effects, and ensure safety for therapeutic use. Future research should focus on clinical validation, mechanistic insights, and formulation optimization to fully harness the medicinal potential of CQ in musculoskeletal disorders.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors would like to thank Ms. Anushthi Singh and Ms. Surabhi Singh Yadav for their support during the preparation of the manuscript.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
There is no funding to report.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors report no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
This study does not involve experiments on animals or human subjects.
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated and analyzed are included in this research article.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used artificial intelligence (AI)-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
REFERENCES
1. Office of the Surgeon General (US). Bone health and osteoporosis: a report of the surgeon general. Rockville, MD: Office of the Surgeon General (US); 2004 [cited 2025 May 16]. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20945569/
2. Babhulkar S, Seth S. Prevalence of osteoporosis in India: an observation of 31,238 adults. Int J Res Orthop. 2021;7(2):362–8. CrossRef
3. Khinda R, Valecha S, Kumar N, Walia JPS, Singh K, Sethi S, et al. Prevalence and predictors of osteoporosis and osteopenia in postmenopausal women of Punjab, India. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(5):2999. CrossRef
4. Cooper C, Ferrari S. IOF compendium of osteoporosis [Internet]. 2nd ed. Nyon, Switzerland: International Osteoporosis Foundation; 2019 [cited 2025 May 16]. Available from: https://www.osteoporosis.foundation/
5. Demontiero O, Vidal C, Duque G. Aging and bone loss: new insights for the clinician. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2012;4(2):61–76. CrossRef
6. Ji M, Yu Q. Primary osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2015;1(1):9–13. CrossRef
7. Van Staa TP, Leufkens HG, Abenhaim L, Zhang B, Cooper C. Use of oral corticosteroids and risk of fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15(6):993–1000. CrossRef
8. Manolagas SC. From estrogen-centric to aging and oxidative stress: a revised perspective of the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2010;31(3):266–300. CrossRef
9. Ralston SH. Genetic control of susceptibility to osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87(6):2460–6. CrossRef
10. Bijlsma JW, Berenbaum F, Lafeber FP. Osteoarthritis: an update with relevance for clinical practice. Lancet. 2011;377(9783):2115–26. CrossRef
11. Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423(6937):356–61. CrossRef
12. Ritchlin CT, Colbert RA, Gladman DD. Psoriatic arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(10):957–70. CrossRef
13. Perez-Ruiz F, Dalbeth N, Bardin T. A review of uric acid, crystal deposition disease, and gout. Adv Ther. 2015;32(1):31–41. CrossRef
14. Martini A, Lovell DJ. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis: state of the art and future perspectives. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(7):1260–3. CrossRef
15. Messier SP. Obesity and osteoarthritis: disease genesis and nonpharmacologic weight management. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2008;34(3):713–29. CrossRef
16. Klareskog L, Malmström V, Lundberg K, Padyukov L, Alfredsson L. Smoking, citrullination and genetic variability in the immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Immunol. 2011;23(2):92–8. CrossRef
17. Goldring MB, Goldring SR. Articular cartilage and subchondral bone in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192(1):230–7. CrossRef
18. Lips P, van Schoor NM. Quality of life in patients with osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16(5):447–55. CrossRef
19. Pal CP, Singh P, Chaturvedi S, Pruthi KK, Vij A. Epidemiology of knee osteoarthritis in India and related factors. Indian J Orthop. 2016;50(5):518–22. CrossRef
20. Kennel KA, Drake MT. Adverse effects of bisphosphonates: implications for osteoporosis management. Mayo Clin Proc. 2009;84(7):632–8. CrossRef
21. Tiwari M, Gupta PS, Sharma N. Ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and pharmacological review of plant Cissus quadrangularis L. Res J Pharmac Phytoch. 2018;10(1):81. CrossRef
22. Hamid HS, Patil S. A phytochemical and pharmacological review of an Indian plant: Cissus quadrangularis. Med Sci Forum. 2023;21(1):20. CrossRef
23. Singh P, Gupta A, Qayoom I, Singh S, Kumar A. Orthobiologics with phytobioactive cues: a paradigm in bone regeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;130:110754. CrossRef
24. Sharma A, Sharma C, Shah OP, Chigurupati S, Ashokan B, Meerasa SS, et al. Understanding the mechanistic potential of plant-based phytochemicals in management of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;163:114850. CrossRef
25. Raggatt LJ, Partridge NC. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of bone remodeling. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(33):25103–8. CrossRef
26. Bhat S, Chowdhary R. Effect of Cissus quadrangularis hydrogel on enhancing osseointegration of titanium implant to bone: an in vivo study. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2022;23(6):582–8. Available from: https://www.thejcdp.com/doi/pdf/10.5005/jp-journals-10024-3363
27. CABI. Cissus quadrangularis (treebine): foliage and stem [Internet]. Wallingford, UK: CABI Compendium; 2022 [cited 2025 May 16]. Available from: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.1079/cabicompendium.13396
28. CABI. Cissus quadrangularis [Internet]. Wallingford, UK: CABI Digital Library; 2023 [cited 2025 Jun 3]. Available from: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.1079/cabicompendium.13396
29. Thakur P, Kuriakose C, Cherian KE, Asha HS, Kapoor N, Paul TV. Knowledge gap regarding osteoporosis among medical professionals in Southern India. J Eval Clin Pract. 2020;26(1):272–80. CrossRef
30. Shukla R, Pathak A, Kambuja S, Sachan S, Mishra A, Kumar S. Pharmacognostical, phytochemical and pharmacological overview: Cissus quadrangularis Linn. Int J Pharm Biol Res. 2015;3(3):59–65. CrossRef
31. Farjana HN, Valiathan GM. Cissus quadrangularis: a comprehensive review as an emerging biomaterial for periodontal regeneration. J Oral Res Rev. 2025;17(1):87–92. CrossRef
32. Pathomwichaiwat T, Ochareon P, Soonthornchareonnon N, Ali Z, Khan IA, Prathanturarug S. Alkaline phosphatase activity-guided isolation of active compounds and new dammarane-type triterpenes from Cissus quadrangularis hexane extract. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;160:52–60. CrossRef
33. Bhadada SK, Chadha M, Sriram U, Pal R, Paul TV, Khadgawat R, et al. The Indian Society for Bone and Mineral Research (ISBMR) position statement for the diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis in adults. Arch Osteoporos. 2021;16(1):1–12. CrossRef
34. Parisuthiman D, Singhatanadgit W, Dechatiwongse T, Koontongkaew S. Cissus quadrangularis extract enhances biomineralization through up-regulation of MAPK-dependent alkaline phosphatase activity in osteoblasts. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2009;45(3-4):194–200. CrossRef
35. Siddiqui S, Ahmad E, Gupta M, Rawat V, Shivnath N, Banerjee M, et al. Cissus quadrangularis Linn exerts dose-dependent biphasic effects: osteogenic and anti-proliferative, through modulating ROS, cell cycle and Runx2 gene expression in primary rat osteoblasts. Cell Prolif. 2015;48(4):443–54. CrossRef
36. Guerra JM, Hanes MA, Rasa C, Loganathan N, Innis-Whitehouse W, Gutierrez E, et al. Modulation of bone turnover by Cissus quadrangularis after ovariectomy in rats. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019;37(5):780–95. CrossRef
37. Potu BK, Rao MS, Nampurath GK, Bhat KM, Chamallamudi MR, Nayak SR. Petroleum ether extract of Cissus quadrangularis (LINN) stimulates the growth of fetal bone during intrauterine developmental period: a morphometric analysis. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2008;63(6):815–20. CrossRef
38. Nath R, Kar BK, Dhadiwal RK, Daftary GV, Khemnar BM, Patil NN. Role of Cissus quadrangularis in bone loss pathologies. Int J Orthop Sci. 2024;10(1):196–201. CrossRef
39. Potu BK, Bhat KM, Rao MS, Nampurath GK, Chamallamudi MR, Nayak SR, et al. Petroleum ether extract of Cissus quadrangularis (Linn.) enhances bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and facilitates osteoblastogenesis. Clinics. 2009;64(10):993–8. CrossRef
40. Shirwaikar A, Khan S, Malini S. Antiosteoporotic effect of ethanol extract of Cissus quadrangularis Linn. on ovariectomized rat. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003;89(2-3):245–50. CrossRef
41. Hatai J, Banerjee SK. Study the molecular docking for established phytochemicals of Cissus quadrangularis against tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) for the prevention of inflammation of arthritis as a major risk of urinary incontinence. J Pharmacogn Phytochem. 2019;8(3):2094–8.
42. Bhujade AM, Talmale S, Kumar N, Gupta G, Reddanna P, Das SK, et al. Evaluation of Cissus quadrangularis extracts as an inhibitor of COX, 5-LOX, and proinflammatory mediators. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;141(3):989–96. CrossRef
43. Tasadduq R, Gordon J, Al-Ghanim KA, Lian JB, Van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, et al. Ethanol extract of Cissus quadrangularis enhances osteoblast differentiation and mineralization of murine pre-osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(3):540–7. CrossRef
44. Muthusami S, Gopalakrishnan V, Stanley JA, Krishnamoorthy S, Ilangovan R, Gopalakrishnan VK, et al. Cissus quadrangularis prevented the ovariectomy induced oxidative stress in the femur of adult albino rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;81:416–23. CrossRef
45. Azam Z, Sapra L, Baghel K, Sinha N, Gupta RK, Soni V, et al. Cissus quadrangularis (Hadjod) inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and augments bone health in an estrogen-deficient preclinical model of osteoporosis via modulating the host osteoimmune system. Cells. 2023;12(2):216. CrossRef
46. Toor RH, Tasadduq R, Adhikari A, Chaudhary MI, Lian JB, Stein JL, et al. Ethyl acetate and n-butanol fraction of Cissus quadrangularis promotes the mineralization potential of murine pre-osteoblast cell line MC3T3-E1 (sub-clone 4). J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(7):10300–14. CrossRef
47. Toor RH, Tasadduq R, Lian JB, Stein JL, Stein GS, Shakoori AR. Cissus quadrangularis (hexane fraction) inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation of murine macrophage RAW264.7 cell line. Pak J Zool. 2023;55(6):2707–15. CrossRef
48. Toor RH, Malik S, Qamar H, Batool F, Tariq M, Nasir Z, et al. Osteogenic potential of hexane and dichloromethane fraction of Cissus quadrangularis on murine preosteoblast cell line MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4). J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):23082–96. CrossRef
49. Potu BK, Rao MS, Nampurath GK, Chamallamudi MR, Nayak SR, Thomas H. Anti-osteoporotic activity of the petroleum ether extract of Cissus quadrangularis Linn. in ovariectomized Wistar rats. Chang Gung Med J. 2010;33(3):252–7.
50. Sirasanagandla SR, Karkala RP, Potu BK, Bhat KM. Beneficial effect of Cissus quadrangularis Linn. on osteopenia associated with streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus in male Wistar rats. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2014;2014:483051. CrossRef
51. Bodhankar S, Aswar U, Mohan V. Antiosteoporotic activity of phytoestrogen-rich fraction separated from ethanol extract of aerial parts of Cissus quadrangularis in ovariectomized rats. Indian J Pharmacol. 2012;44(3):345. CrossRef
52. Shamina S, Anjana A, Suja S. Haematological assessment of methanolic stem extract of Cissus quadrangularis Linn. against Freund’s complete adjuvant induced female albino arthritic rats. Int J Pharma Bio Sci. 2020;10(4):L155–63. CrossRef
53. Vaijayanthimala P, Sakthipriya M, Sangameswaran B. In vitro anti-arthritic activity of Cissus quadrangularis stem extract. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2019;12(1):250. CrossRef
54. Lakshmanan DK, Ravichandran G, Elangovan A, Jeyapaul P, Murugesan S, Thilagar S. Cissus quadrangularis (veldt grape) attenuates disease progression and anatomical changes in mono sodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced knee osteoarthritis in the rat model. Food Funct. 2020;11(9):7842–55. CrossRef
55. Samarasinghe RM, Kanwar RK, Kumar K, Kanwar JR. Antiarthritic and chondroprotective activity of Lakshadi Guggul in novel alginate-enclosed chitosan calcium phosphate nanocarriers. Nanomedicine. 2014;9(6):819–37. CrossRef
56. Gopinathan N, Harish G, Kumar GA, Chitra K, Reddy CU in vitro anti-arthritic, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant activity of Cissus quadrangularis Linn. Indian J Res Pharm Biotechnol. 2015;3(1):24.
57. Bhujade A, Talmale S. In vivo studies on antiarthritic activity of Cissus quadrangularis against adjuvant induced arthritis. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2015;6:3. CrossRef
58. Kumar R, Gupta YK, Singh S, Arunraja S. Cissus quadrangularis attenuates the adjuvant-induced arthritis by downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokine and inhibiting angiogenesis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;175:346–55. CrossRef
59. Sayers EW, Beck J, Bolton EE, Brister JR, Chan J, Comeau DC, et al. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024;52(D1):D33–43. CrossRef
60. PubChem. Ascorbic acid [Internet]. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2004 [cited 2025 May 29]. Available from: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Ascorbic-Acid
61. PubChem. Beta-sitosterol [Internet]. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2004 [cited 2025 May 29]. Available from: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Beta-Sitosterol
62. Singh N, Singh V, Singh R, Pant A, Pal U, Malkunje L, et al. Osteogenic potential of Cissus quadrangularis assessed with osteopontin expression. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2013;4(1):52–6. CrossRef
63. Sanaye M, Bora B, Chawda M, Kshirsagar V. Evaluation of anti-osteoporotic activity of asthiposhak tablets in ovariectomized rats. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2021;12(6):3498–507. CrossRef
64. Dongare AB, Jadhav DRK. Investigation of anti-arthritic activity of sustained release tablet of different herbal plants by using in vivo and in vitro models. J Pharm Negat Results. 2023;14(2):S02.105. CrossRef
65. Nawghare CG, Taur AT, Sawate AR. Studies on the physico-phytochemical and anti-arthritic properties of Hadjod (Cissus quadrangularis) stem powder. J Pharmacogn Phytochem. 2017;6(5):443–5.
66. Sundaran J, Begum R, Vasanthi M, Kamalapathy M, Bupesh G, Sahoo U. A short review on pharmacological activity of Cissus quadrangularis. Bioinformation. 2020;16(8):579–85. CrossRef
67. Patel BDP, Tiwari NN, and Upadhayaya A. discuss binomial nomenclature and its relationship to the nomenclature of medicinal plants in Ayurveda Classics. J Ayurveda Campus. 2022;1(1):33–44. Available from: http://jacjournal.org/jac/index.php/jac/article/view/6
68. Lakshmanan DK, Ravichandran G, Elangovan A, Thilagar S. Fortification of raw rice and rice flour using Cissus quadrangularis L. (veldt grape) stem powder to overcome osteoporosis and its associated skeletal complications through staple diet. J Food Biochem. 2021;45(10):e13918. CrossRef