INTRODUCTION
Cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitors help manage pain, inflammation, and fever by inhibiting the cyclooxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2), which are involved in prostaglandin formation [1]. These enzymes convert arachidonic acid into prostaglandins, which play significant roles in inflammation, pain, and fever. COX-1 is expressed constitutively in most tissues and controls normal cellular activities such as gastric mucosal lining maintenance and platelet aggregation [2,3]. In contrast, COX-2 is activated during inflammatory processes [4]. Because prostaglandins are important mediators of inflammation and pain, COX inhibitors are critical in the treatment of a variety of inflammatory disorders [5,6]. Recent research has identified selective inhibition of COX-2 lowers the gastrointestinal adverse effects frequently seen with non-selective COX inhibitors that inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 [7].
Beyond pain and inflammation, COX inhibitors have received interest in their involvement in cancer prevention and treatment. COX-2 overexpression has been associated with carcinogenesis in several malignancies, including colorectal, breast, liver, and lung cancer [8,9]. Several studies and clinical trials have shown that inhibiting COX-2 reduces tumor development and improves patient outcomes [8]. Furthermore, continuing research indicates that COX-2 inhibitors may improve the efficacy of chemotherapy, making them a promising adjuvant therapy in cancer treatment [10]. However, the potential cardiovascular hazards of long-term COX-2 suppression demand thorough patient monitoring and risk-benefit analysis [11,12]. Aspirin, a nonselective COX inhibitor, is also used in low doses for its antiplatelet effects, which reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events including heart attacks and strokes by inhibiting COX-1-mediated thromboxane A2 production [13].
This study seeks to evaluate the current scientific output of the COX inhibitors, comprising an overview of important metrics, research areas, authorship patterns, and the structure of cooperation in this area of study. Emphasis on the history of research into COX inhibitors, its use in inflammatory diseases, cancer, and molecular modeling, while also interest into nascent areas of research and gaps in the existing literature.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data source and search strategy
The data used in this bibliometric analysis were retrieved from Scopus, an extensive and highly regarded database of academic articles. Starting on August 15th, 2024, all relevant research for COX inhibitors was located using the search thread (Fig. 1). Article titles were combed through using a search approach that targeted specific keywords and the following search strings “(TITLE(((cyclooxygenase OR cox) AND (inhibitor OR inhibitors OR drugs))) AND (EXCLUDE (PREFNAMEAUID, “Undefined”)) AND (LIMIT-TO ( DOCTYPE, “ar”)) AND (EXCLUDE (AFFILCOUNTRY, “Undefined”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (LANGUAGE, “English”))).”
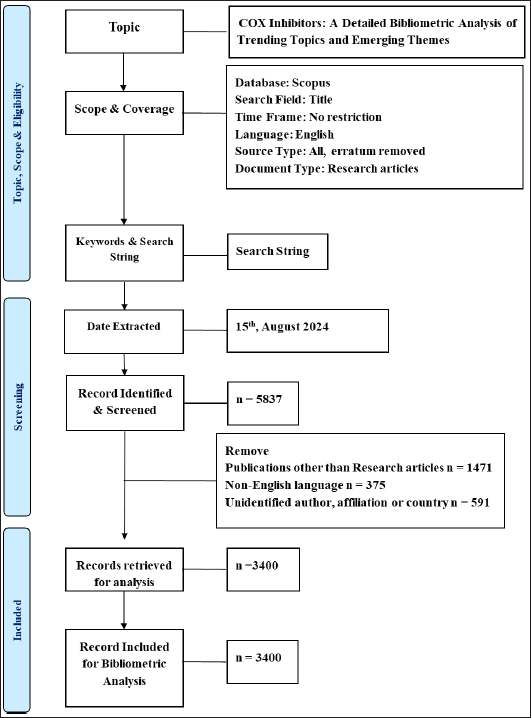 | Figure 1. PRISMA flowchart for the bibliometric analysis of cyclooxygenase inhibitors. [Click here to view] |
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
All publications selected for inclusion in the study had to be indexed in Scopus. To ensure uniformity, only English-language articles were used to draw findings. Because the study did not limit the time period, patterns throughout time could be thoroughly examined. Errata and non-research articles, such as reviews, editorials, and letters, were excluded, as they do not contribute original data or findings. Publications in languages other than English were removed to ensure uniformity and accessibility of data interpretation. Additionally, entries lacking critical metadata, such as author names, affiliations, or country of origin, were excluded to maintain the accuracy of bibliometric analyses. Through these criteria, the dataset was refined from an initial 5,837 records to 3,400 records.
Data cleaning and preprocessing
After data was exported from Scopus, the file was checked and cleaned using the Bibliometrix package data report. Duplicates were checked and removed and articles missing details were excluded.
Bibliometric analysis
Bibliometric analysis was conducted as previously described [14–16]. The study was carried out by VOSviewer using “version 1.6.18” and the Bibliometrix package in R Studio “version 3.1.4.” VosViewer software was employed to generate the maps of the co-occurrence of keywords while the software R Bibliometrix packages generated the annual scientific output, publication growth rates, citation impacts, emerging themes, and thematic map of the data [17,18]. The key output comprised documents, authors, countries, keywords, maps, and collaboration metrics.
RESULTS
Search strategy and results
Figure 1 depicts the processes followed to conduct a bibliometric analysis of COX inhibitors. The Scopus database was queried for the analysis, with search parameters limited to titles and no time limits. The extraction method was completed on August 15, 2024, with carefully selected keywords and search strings that thoroughly covered the issue. In the beginning, this search yielded 5,837 documents.
Following a rigorous screening process, records that did not meet the inclusion criteria were excluded. These included non-research articles (1,471), publications in languages other than English (375), and entries lacking sufficient metadata such as author, affiliation, or country information (591). This refinement resulted in 3,400 records deemed suitable for analysis, all of which were subsequently included in the bibliometric analysis.
Datasets characteristics
The bibliometric analysis of cyclooxygenase inhibitors over the past two decades from 2000 to 2024 reveals several important trends and insights (Fig. 2). The analysis spans 24 years with 1219 sources. The research output is notable, with 3,400 documents published. The number of authors involved is impressive, with 13,993 contributors in total. However, only 104 of these documents are single-authored. This collaboration is further reflected in the 17.82% international co-authorship rate. One particularly notable aspect is the annual growth rate of 4.15%. There was an average of 5.76 co-authors per document. In terms of keywords, there are 5,640 distinct author’s keywords. The document’s average age is 13.7 years. Finally, the average citation per document receives an impressive 34.96 citations.
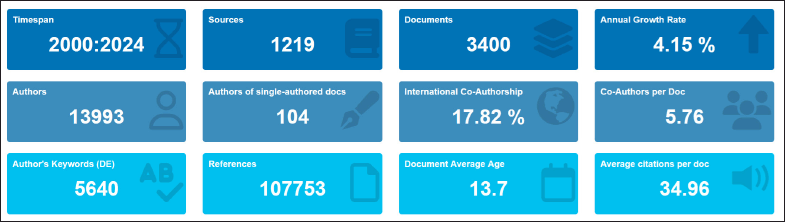 | Figure 2. A Bibliometrix platform of the key bibliometric indicators for research on cyclooxygenase inhibitors from 2000 to 2024. [Click here to view] |
Annual scientific production
The annual scientific production of research on COX inhibitors has shown a dynamic pattern. In the early 2000s, research in this field skyrocketed (Fig. 3). The number of research published peaked around the mid-2000s. However, this peak is followed by a slow fall through 2017. This pattern has been steady over decades, with minor swings. In recent years, research production has remained stable, albeit at a lower level.
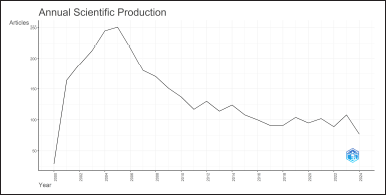 | Figure 3. Annual scientific production of cyclooxygenase inhibitors research. The graph tracks the number of articles published each year along the Y-axis, while the X-axis represents the years, ranging from around 2000 to 2024. [Click here to view] |
Author’s impact
Figure 4 shows that KNAUS EE is the most active researcher in this discipline, with an impressive H-index of 24. ZARGHI A follows closely with an H-index of 19, while MARNETT LJ and RAO PNP have H-indexes of 17. Other notable contributions are KULKARNI SK and LI W with H-indices of 16.
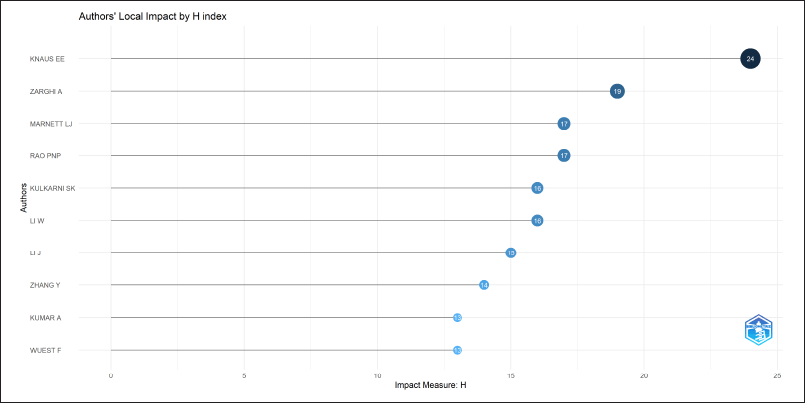 | Figure 4. Authors’ local impact by H-Index in the field of cyclooxygenase inhibitors research. The Y-axis lists the authors, while the X-axis measures their H-index. [Click here to view] |
Average article citations per year
Figure 5 demonstrates a considerable shift in the average annual citation count for COX inhibitor research over the last 20 years. With an average of more than four citations per publication, the research was well-known in the early 2000s. However, citations began to decline rapidly in 2001, and by the mid-2000s, the average number of citations per article had decreased to roughly two. The citation rate fluctuated minimally between 2005 and 2015. There was a modest recovery from 2017 and 2020. However, the citation rate fell dramatically again after 2020.
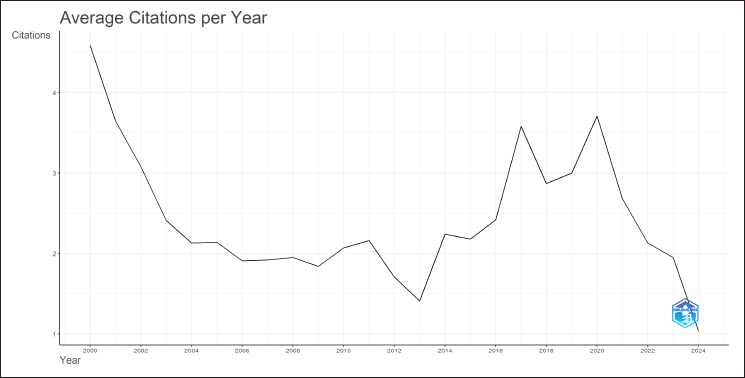 | Figure 5. The trend of average citations received by articles on cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitors research from around 2000 to 2024. The Y-axis represents the average number of citations per article, while the X-axis shows the years. [Click here to view] |
Core sources by Bradford’s law
Figure 6 reveals journals such as Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, European Journal of Pharmacology, Bioorganic Chemistry, and Journal of Medicinal Chemistry are key sources. Beyond these core journals, the number of articles drops down, reflecting Bradford’s Law’s principle that a small number of journals will account for the bulk of the research output, while many other journals will contribute far fewer articles.
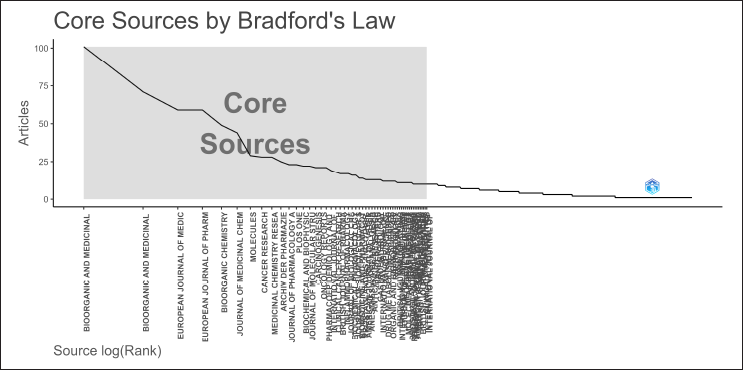 | Figure 6. “Core Sources by Bradford’s Law” demonstrates the distribution of articles across various journals in the field of COX inhibitors research. [Click here to view] |
Country collaboration map
In Figure 7, the United States emerges as a major research hub, with strong ties to Europe, Asia, and Australia. European countries, such as the UK, Germany, France, and Italy play major roles, with extensive collaboration networks both within Europe and with North America. Australia is also well-connected, collaborating with the United States and Europe. Japan, China, and India represent Asia’s active participation. Although African countries are less visible, they continue to participate with links with European and Asian countries and the USA.
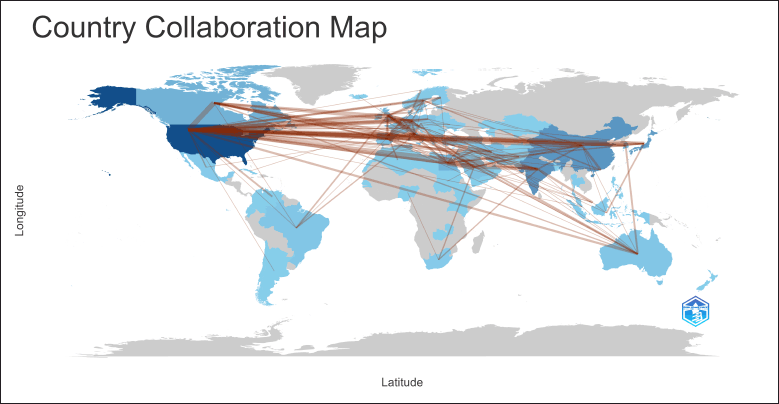 | Figure 7. Country Collaboration Map of research on COX inhibitors. The lines connect countries that are engaged in co-authored research, with the intensity of the color reflecting the frequency and strength of these collaborations. [Click here to view] |
Country scientific production
The United States in Figure 8 shows its top contribution, depicted by the darkest shade of blue. China also plays an essential role, with a large amount of research activity. European countries, particularly Germany and Italy, make important contributions, albeit to a smaller extent than the United States and China. Asia also receives major contributions from India and Japan. Meanwhile, countries in Africa and South America use lighter blues, reflecting lower levels of research productivity in this field with Egypt being the most prominent contributor.
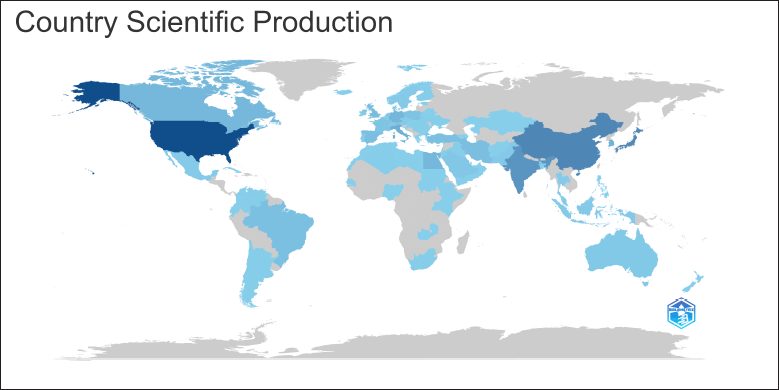 | Figure 8. The Country Scientific Production map of the global distribution of scientific research output on cyclooxygenase inhibitors. [Click here to view] |
Most globally cited documents
Figure 9 shows that the most influential paper is Chandrasekharan NV, 2002 (PNAS), with 1740 citations [19]. Mukherjee et al. [20] (JAMA) follow closely behind with 1718 citations. Other highly cited publications are Catella-Lawson et al. [21] (New England Journal of Medicine), with 1349 citations, and Serhan et al. [22] (J Exp Med), with 1012 citations. These papers, along with others such as Nussmeier et al. [23] (New England Journal of Medicine) [23] and Bhardwaj et al. [24] (Nat Commun) [24], have earned 1003 and 977 citations, respectively.
 | Figure 9. The most globally cited documents graph of the top research papers in the field of cyclooxygenase inhibitors. The Y-axis lists the documents by author, year, and journal, while the X-axis represents the number of citations. [Click here to view] |
Most relevant authors
ZARGHI A is the most prolific author, with 45 publications (Fig. 10). KNAUS EE closely tracks 37 articles. Other prominent authors are LI J and ZHANG Y, who have 32 and 28 publications, respectively. Furthermore, LI W, RAO PNP, and WANG Y have each submitted over 20 documents. KUMAR A, MARNETT LJ, and KULKARNI SK, all of whom have roughly 19–20 publications.
 | Figure 10. The most relevant authors graph of the leading contributors in COX inhibitors research. The Y-axis lists the authors, while the X-axis represents the number of documents produced by each. [Click here to view] |
Corresponding authors’ countries
The United States tops the field in terms of document count, with the vast majority of them being single-country publications (SCPs) (Fig. 11). India and China are close behind, with large output primarily made up of SCPs. Countries like Japan, Egypt, and Canada make considerable contributions, with Egypt having a disproportionate amount of SCPs.
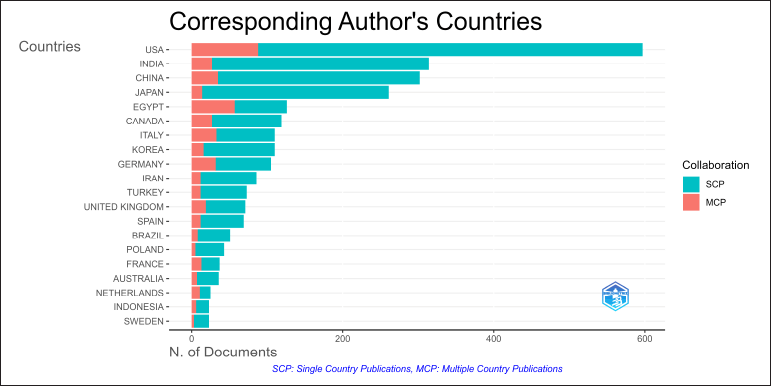 | Figure 11. The corresponding author’s countries graph of the number of documents published by corresponding authors from various countries in the field of COX inhibitors research. The Y-axis lists the countries, while the X-axis shows the number of documents. SCP: Single Country Publications and MCP: Multiple Country Publications, with SCPs represented in teal and MCPs in red. [Click here to view] |
Most relevant sources
In Figure 12, the Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters is the most prolific journal, with 101 publications. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry is constantly monitored, with 71 publications. The European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry and the European Journal of Pharmacology have each contributed 59 documents. Other noteworthy sources are Bioorganic Chemistry (49 publications) and Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (44 publications). Journals such as Molecules, Cancer Research, and Medicinal Chemistry Research also play an important role, contributing 28–29 documents.
 | Figure 12. The most relevant sources graph of the top journals and sources that have published the highest number of documents on COX inhibitors research. The Y-axis lists the sources, while the X-axis shows the number of documents contributed by each source. [Click here to view] |
Most relevant keywords
COX-2 is the most frequently used keyword, with 345 occurrences. Celecoxib, a well-studied COX-2 inhibitor, has 268 occurrences. Other keywords, such as cyclooxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2, appear 261 and 251 times, respectively. Keywords such as COX-2 inhibitors and COX-2 inhibitor stress the importance of this enzyme inhibition, whilst broader terms such as inflammation (164 occurrences) and NSAIDs (151 occurrences). On the other hand, certain words, such as anti-inflammatory and molecular docking were also commonly used.
Sources local impact by H-index
The Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters has the highest H-index at 38. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry is a close second, with an H-index of 37, followed by Journal of Medicinal Chemistry at 35. The European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry and Cancer Research, both with H-indices of 30 and 26. Other noteworthy publications are the European Journal of Pharmacology (H-index of 25) and Bioorganic Chemistry (H-index of 22).
Thematic map
Research on COX inhibitors has evolved into distinct thematic areas that reflect both the current state of development and their relevance to the broader scientific field (Fig. 13A). In the niche themes, we find topics such as cox inhibition, epilepsy, and benzodiazepine. These are well-developed areas but remain relatively isolated from the core of COX inhibitor research. Their presence indicates that specific neurological aspects, such as how COX inhibition relates to epilepsy and the role of microglia (the immune cells in the brain), are being explored but remain specialized.
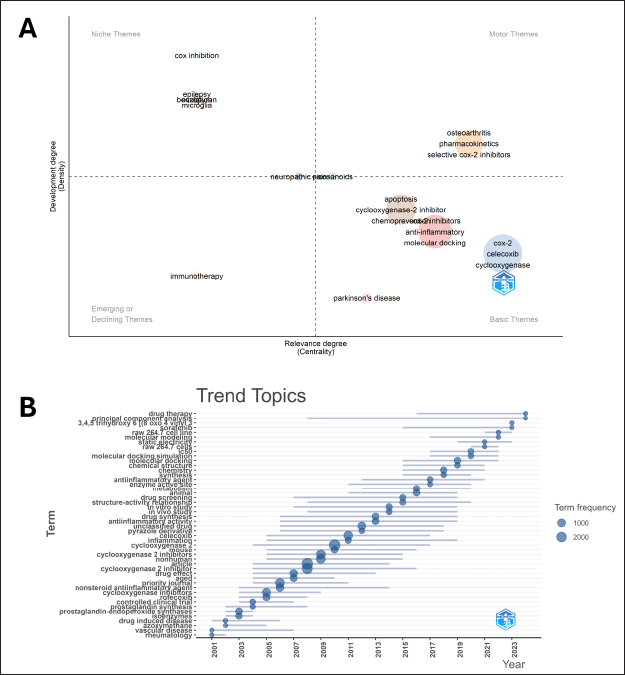 | Figure 13. Thematic map and trend topics. A) Thematic map related to cyclooxygenase inhibitors divided into four quadrants based on their development degree (density) and relevance degree (centrality). B) The trend Topics graph of the evolution of key terms over time in COX inhibitors research. The Y-axis lists the terms, while the X-axis shows the years, starting from 2001 through 2024. The size of the bubbles represents the term frequency, with larger bubbles indicating higher usage. [Click here to view] |
The motor themes quadrant includes central and well-developed topics that are driving the field forward. Osteoarthritis, pharmacokinetics, and selective COX-2 inhibitors dominate this space. Basic themes, located in the lower right quadrant, represent foundational aspects of COX inhibitor research. Themes such as COX-2, celecoxib, cyclooxygenase, and anti-inflammatory dominate this space. Emerging or decreasing themes, such as immunotherapy, indicate fields of research that are underdeveloped or losing prominence. Central themes comprised neuropathic pain and eicosanoids. These topics are relevant to the field but not fully developed in terms of their depth of study.
Trend topics
The timeline of research on COX inhibitors reveals clear shifts in focus over the years, starting with foundational studies in pharmacology and moving toward more complex molecular and computational methods (Fig. 13B). In the early 2000s, terms like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, prostaglandin synthase, cyclooxygenase inhibitors, and controlled clinical trials were prevalent. Between 2005 and 2010, the focus shifted to selective COX-2 inhibitors, with terms like celecoxib, rofecoxib, and COX-2 inhibitors becoming more prominent. From 2020 to 2023, terms like drug therapy, principal component analysis, and IC50 suggest a continuing emphasis on computational tools and statistical methods in COX inhibitor research.
Word cloud
The largest terms, such as cyclooxygenase, cyclooxygenase-2, and COX-2 appeared clearly in Figure 14A. The term celecoxib, a well-studied COX-2 inhibitor, also comes up. Terms such as inflammation, anti-inflammatory, and NSAIDs are documented. Furthermore, phrases such as molecular docking, apoptosis, and prostaglandins are present.
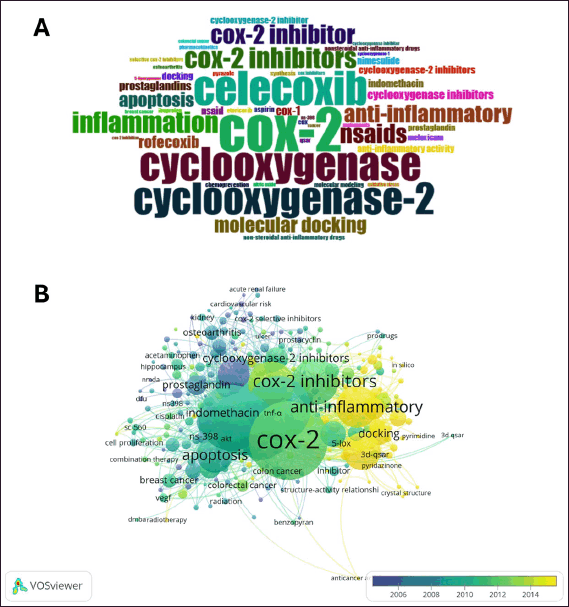 | Figure 14. The keywords patterns. A) The word cloud of the most frequently occurring terms in COX inhibitors research. Larger words indicate higher frequency and importance within the field. B) Keyword co-occurrence overlay network of cyclooxygenase inhibitors over the years. [Click here to view] |
Keywords overlay
The overlay visualization of keywords related to cyclooxygenase inhibitors highlights the progression of research topics from 2006 to 2014 (Fig. 14B). Central terms like COX-2, COX-2 inhibitors, and anti-inflammatory remain key areas of focus throughout the timeline, as indicated by their green color. More recent studies, represented by yellow shades, focus on topics such as docking and structure-activity relationships, showing a shift towards molecular modeling, 3D-QSAR, and drug design. Earlier research, in blue, focused on areas like prostaglandins, COX-2 inhibitors, and selective inhibitors.
Three-field plot
Figure 15A shows that on the left side, countries like the USA, Japan, India, and China are shown as major contributors to the research field. The middle column lists highly contributing authors such as Vane J.R., Smith W.L., and Tsuji M. The right side displays keywords like COX-2, celecoxib, inflammation, and apoptosis. The lines connecting these fields illustrate the relationships between countries, influential authors, and key research areas. For example, the USA shows a strong connection to influential authors and core topics like COX-2 inhibitors and anti-inflammatory research. Similarly, Japan and other countries contribute to significant research topics.
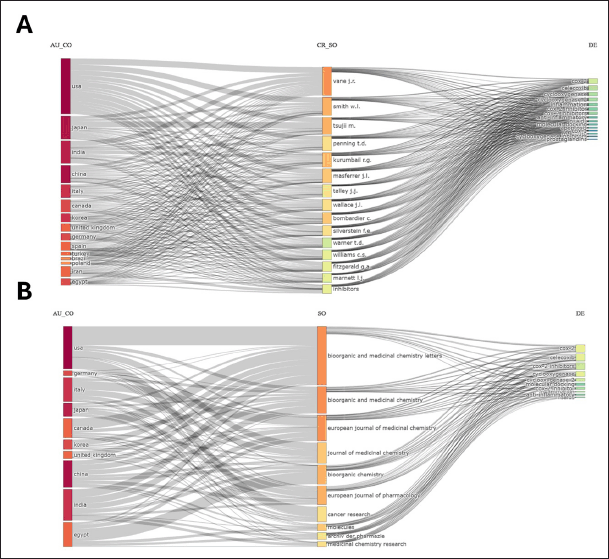 | Figure 15. Three field plots. A) The three-field plot linking countries (AU_CO), cited authors (CR_SO), and keywords (DE) in the research on cyclooxygenase inhibitors. B) Three-field plot visualizes the connections between contributing countries (AU_CO), major journals (SO), and relevant keywords (DE) in the field of cyclooxygenase inhibitors. [Click here to view] |
Figure 15B shows countries like the USA, Germany, Italy, and Japan emerge as the leading contributors, with their research being published in major journals such as Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, the European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, and the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. These journals are strongly linked to central research topics like COX-2, celecoxib, cyclooxygenase-2, and anti-inflammatory mechanisms, which are pivotal in the study of cyclooxygenase inhibitors.
DISCUSSION
The publication trends of COX inhibitor research exhibit a biphasic pattern, with a peak in the mid-2000s driven by interest in COX-2 inhibitors. Notably, the bibliometric trends revealed a decline in COX-2-related publications following the mid-2000s, coinciding with heightened concerns over the cardiovascular risks of selective COX-2 inhibitors like celecoxib. This shift reflects how safety controversies have influenced research directions, with several highly cited studies from that period focusing on adverse effects and regulatory responses.
The field of COX inhibitors benefited from several key scientific advancements. Our knowledge of the mechanisms behind the management of pain and fever was greatly enhanced by the discovery of COX-3, a cyclooxygenase variation that is targeted by acetaminophen and related medicines [19]. Another significant milestone has been the cardiovascular risks associated with selective COX-2 inhibitors [20]. Another milestone was the relationship between COX inhibitors and aspirin’s antiplatelet effects [21]. The discovery of novel lipid-derived mediators with anti-inflammatory properties generated via COX-2 pathways was also a new therapeutic approach [22]. Additionally, the complications associated with COX-2 inhibitors in postoperative cardiac patients have been thoroughly explored [23]. An analysis of the top five most cited papers revealed that all originated from research teams based in the United States, highlighting the influential role of geographic origin and strong research infrastructure in shaping citation impact.
Recent studies have used a range of sophisticated artificial intelligence models—including four supervised machine learning algorithms, including support vector machine, random forest, deep neural networks, and eXtreme Gradient Boosting, as well as ensemble learning—to accurately forecast COX-2 and microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase inhibitory activity as well as to facilitate cascade virtual screening of large molecular libraries [25]. Furthermore, strong classifiers for drug-likeness assessment have come from methods including QSAR modeling and deep learning [26]. While compound screening from Tinospora cordifolia using machine learning combined with molecular docking and dynamic simulations emphasizes the practical use of artificial intelligence in finding dual COX-1/2 inhibitors [27], hybrid deep learning systems like UNet and enhanced Laguerre neural networks have also been used to find COX-2 suppression in cancer environments [28]. These developments show the rising integration of artificial intelligence in rational anti-inflammatory drug creation, which is becoming clearer in the new keywords and topics exposed by our bibliometric study.
The strengths of this work include an extensive bibliometric study regarding COX inhibitors. The application of advanced analytical programs VOSviewer and Bibliometrix enables a complete analysis of publication trends, major issues in research, and the most important contributors and journals in the domain. The analysis also covers the co-authorship relationships by countries and institutions. It encompasses a vast Scopus dataset, which enhances understanding of the research landscape and identifies new themes in literature and gaps with respect to existing literature, hence, strengthening this work with regard to the next steps in the research.
Although the main goal of this paper was to investigate the scientific landscape of COX inhibitor research, clinical milestones shown in citation patterns emphasize the practical influence of this domain. The increase and fall in publications on selective COX-2 inhibitors, for instance, mirror worries about cardiovascular safety and draw attention to how clinical changes influence research paths. The regular use of words like cancer prevention and aspirin in trend studies further shows the translational value of COX inhibitors in cardiology and oncology.
However, it is vital to note the study’s limitations. The analysis is based on data from the Scopus database, which may leave out major research indexed in other databases. Furthermore, the study’s concentration on quantitative data may mask qualitative aspects of research, such as the therapeutic or societal implications of certain findings. Despite bibliometric analysis offers useful quantitative insights into publication patterns, authorship trends, research impact, and citation metrics, it naturally lacks the capacity to evaluate the qualitative aspects of scientific contributions. High citation totals, for example, may not always imply therapeutic relevance, commercialization, or innovative success. Furthermore, bibliometric measures can ignore contextual elements such as policy influence, patient outcomes, or the application of findings in actual environments. When analyzing the findings, we should take these restrictions into account since they emphasize the need to augment bibliometric studies with qualitative evaluations for a more complete knowledge of research influence.
The study on COX inhibitors identifies some research gaps that present opportunities for future investigation. One notable gap is the need for additional research into the long-term effects and safety profiles of COX-2 inhibitors, particularly in terms of cardiovascular risk and gastrointestinal side effects. While many studies have focused on short-term outcomes, long-term evidence is scarce. Furthermore, studies on selective COX-2 inhibitors for certain ailments, such as cancer and neurological diseases, are still in their early phases. There is also a dearth of understanding of the molecular mechanisms underpinning COX-1 and COX-2 inhibition, as well as their diverse effects on different tissues, which could lead to the development of more targeted treatments with fewer side effects.
CONCLUSION
COX inhibitors were the focus of the research output around the year 2000, but lately, that rate of publications has considerably decreased. On the other hand, the work on COX inhibitors keeps being relevant due to continuous optimization by computational tools. The recent advancements in computational methods as well as the new molecular docking techniques and the personalized medicine have made it more appealing for researchers. This study offers a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of COX inhibitor research, highlighting important publication patterns, cooperative networks, and classical and emerging scientific trends. While the study could be further enriched by a deeper exploration of AI methodologies, clinical implications, and the inherent limitations of bibliometric analysis, it nonetheless offers important insights.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia (Project# KFU242652). The authors extend their appreciation to Abdulmonem Alrashed Humanitarian Foundation (FSP-2-0015).
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The author reports no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
This study does not involve experiments on animals or human subjects.
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
Data can be requested from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used AI-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
REFERENCES
1. Wautier JL, Wautier MP. Pro-and anti-inflammatory prostaglandins and cytokines in humans: a mini review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(11):9647. CrossRef
2. Faki Y, Er A. Different chemical structures and physiological/pathological roles of cyclooxygenases. Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2021;12(1):e0003. CrossRef
3. Rius B, Claria J. Principles, mechanisms of action, and future prospects of anti-inflammatory drugs. In: NSAIDS and aspirin: recent advances and implications for clinical management. Cham, Switzerland: Springer; 2016. pp. 17–34. CrossRef
4. Gilroy DW, Colville-Nash P, Willis D, Chivers J, Paul Clark M, Willoughby D. Inducible cyclooxygenase may have anti-inflammatory properties. Nat Med. 1999;5(6):698–701. CrossRef
5. Ali KA, Maity A, Roy SD, Pramanik SD, Das PP, Shaharyar MA. Insight into the mechanism of steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. How synthetic drugs work. Elsevier; Cambridge, MA: Academic Press; 2023. pp. 61–94.
6. Burayk S, Oh Hashi K, Kandeel M. Drug discovery of new anti-inflammatory compounds by targeting cyclooxygenases. Pharmaceuticals. 2022;15(3):282. CrossRef
7. Sohail R, Mathew M, Patel KK, Reddy SA, Haider Z, Naria M, et al. Effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and gastroprotective NSAIDs on the gastrointestinal tract: a narrative review. Cureus. 2023;15(4):e37080. CrossRef
8. Kolawole OR, Kashfi K. NSAIDs and cancer resolution: new paradigms beyond cyclooxygenase. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1432. CrossRef
9. Ozleyen A, Yilmaz YB, Donmez S, Atalay HN, Antika G, Tumer TB. Looking at NSAIDs from a historical perspective and their current status in drug repurposing for cancer treatment and prevention. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023;149(5):2095–113. CrossRef
10. Bell CR, Pelly VS, Moeini A, Chiang SC, Flanagan E, Bromley CP, et al. Chemotherapy-induced COX-2 upregulation by cancer cells defines their inflammatory properties and limits the efficacy of chemoimmunotherapy combinations. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):2063. CrossRef
11. Fanelli A, Ghisi D, Aprile PL, Lapi F. Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular risk with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors: latest evidence and clinical implications. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2017;8(6):173–82. CrossRef
12. Minhas D, Nidhaan A, Husni ME. Recommendations for the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and cardiovascular disease risk: decades later, any new lessons learned? Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2023;49(1):179–91. CrossRef
13. Hohlfeld T, Saxena A, Schrör K. High on treatment platelet reactivity against aspirin by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs--pharmacological mechanisms and clinical relevance. Thromb Haemost. 2013;109(5):825–33. CrossRef
14. Kandeel M. Trends in camel research in South Asia: a bibliometric approach. Vet World. 2024;17(12):2763–73. CrossRef
15. Kandeel MK. Bibliometric analysis of camel research in China: research trends and thematic evolution. Egypt J Vet Sci. 2024:1–16. CrossRef
16. Naji R, Kandeel M, Mahmoud M. A bibliometric analysis of six decades of camel research in North Africa: trends, collaboration, and emerging themes. Open Vet J. 2024;14(12):3505–24. CrossRef
17. Guleria D, Kaur G. Bibliometric analysis of ecopreneurship using VOSviewer and RStudio Bibliometrix, 1989–2019. Library Hi Tech. 2021;39(4):1001–24. CrossRef
18. Arruda H, Silva ER, Lessa M, Proença Jr D, Bartholo R. VOSviewer and bibliometrix. J Med Libr Assoc. 2022;110(3):392. CrossRef
19. Chandrasekharan NV, Dai H, Roos KL, Evanson NK, Tomsik J, Elton TS, et al. COX-3, a cyclooxygenase-1 variant inhibited by acetaminophen and other analgesic/antipyretic drugs: cloning, structure, and expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(21):13926–31. CrossRef
20. Mukherjee D, Nissen SE, Topol EJ. Risk of cardiovascular events associated with selective COX-2 inhibitors. JAMA. 2001;286(8):954–9. CrossRef
21. Catella-Lawson F, Reilly MP, Kapoor SC, Cucchiara AJ, DeMarco S, Tournier B, et al. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors and the antiplatelet effects of aspirin. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(25):1809–17. CrossRef
22. Serhan CN, Clish CB, Brannon J, Colgan SP, Chiang N, Gronert K. Novel functional sets of lipid-derived mediators with antiinflammatory actions generated from omega-3 fatty acids via cyclooxygenase 2-nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and transcellular processing. J Exp Med. 2000;192(8):1197–204. CrossRef
23. Nussmeier NA, Whelton AA, Brown MT, Langford RM, Hoeft A, Parlow JL, et al. Complications of the COX-2 inhibitors parecoxib and valdecoxib after cardiac surgery. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(11):1081–91. CrossRef
24. Bhardwaj A, Kaur J, Wuest M, Wuest F. In situ click chemistry generation of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1. CrossRef
25. Tian Y, Zhang Z, Yan A. Discovering the active ingredients of medicine and food homologous substances for inhibiting the cyclooxygenase-2 metabolic pathway by machine learning algorithms. Molecules. 2023;28(19):6782. CrossRef
26. Dibia KT, Igbokwe PK, Ezemagu GI, Asadu CO. Exploration of the quantitative structure-activity relationships for predicting Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition bioactivity by Machine learning approaches. Res Chem. 2022;4:100272. CrossRef
27. Mathe A, Mulpuru V, Katari SK, Karlapudi AP, T CV. Virtual screening and in vitro evaluation of cyclooxygenase inhibitors from Tinospora cordifolia using the machine learning tool. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024;42(23):13275–89. CrossRef
28. Pawar SB, Deshmukh NK, Jadhav SB. Hybrid deep learning technique for COX-2 inhibition bioactivity detection against breast cancer disease. Biomed Eng Lett. 2024;14(4):631–47. CrossRef