INTRODUCTION
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second-most prevalent cancer among men. GLOBOCAN 2022 estimates that PCa accounts for 7.3% of new cases and 4.1% of deaths out of all cancer types worldwide [1]. It is a complex and heterogeneous disease, displaying an extensive array of clinical signs that can range from mild to highly aggressive symptoms. As the disease advances, a significant number of patients develop distant metastases, resulting in 0.4 million fatalities each year this is anticipated to increase by more than double by 2040 [2]. To date, androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT) which targets androgen receptors remains a primary care for individuals diagnosed with locally advanced and metastatic prostate cancer (mPCa) [3]. Unfortunately, remissions are temporary because patients with mPCa will eventually show significant rates of post-treatment recurrence and become insensitive to ADT to form castration-resistant PCa [4–6]. The transition from epithelial to mesenchymal cells and their plasticity are key factors in driving the metastatic growth of PCa. Moreover, the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) may play crucial roles in the initiation and progression of PCa. EGFR may play a role in regulating epithelial to mesenchymal transition, cell differentiation, cell proliferation, and angiogenesis, and eventually, promoting the dissemination and spread of cancer cells the dissemination, thus serving as a potential marker for heightened metastatic potential. PCa with elevated EGFR expression is associated with higher grade tumors, advanced stages, an increased likelihood of prostate-specific antigen recurrence, a poor prognosis, a higher incidence of castration-resistant phenotype, and cancer metastasis. Therefore, understanding the key mechanisms driving the growth and metastasis of PCa cells is essential. On the other hand, in-depth studies on EGFR expression in PCa with respect to tumor characteristics and tumor stages are limited [7–10].
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have recently emerged as key regulators of gene expression and signal transduction in both normal biological processes and disease development, especially in PCa [3]. Several studies have reported various ncRNA types that play crucial roles in PCa pathogenesis. These ncRNAs include microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs, and circular RNAs (circRNAs) [11,12]. The association between miRNA dysregulation and PCa, is not surprising, given the importance of miRNAs in regulating gene expression and influencing diverse cellular processes [13,14]. CircRNAs primarily serve as sponges for miRNAs, along with which, it controls alternative splicing, influences parental genes, sequesters proteins, and acts as scaffolds. These circRNAs have been established as crucial components in the development and advancement of human diseases, particularly cancer. Recent research has also suggested that they hold promise as diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers of cancer [15,16]. The primary cause of the progression to mPCa may be attributed to the deprivation of various tumor suppressor miRNAs [17]. Several studies have indicated the key regulatory role of the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in controlling various cellular processes essential for cancer progression [18]. However, the underlying molecular mechanism of EGFR-circRNA, miRNA and mRNA mediated regulation of PCa development and progression remains unexplored. In an effort to better understand the factors influencing the differential expression of EGFR in PCa, the current study focused on miRNAs and circRNAs associated with EGFR that are crucial for the transition from hormone dependency to a metastatic phenotype in PCa. In the current study, we investigated miR-936-mediated regulation of EGFR, as well as other miRNAs involved in EGFR regulation among PCa patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Analysis of EGFR expression and determination of percent survival
The relationship between EGFR expression levels and overall survival (OS) in prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD) was assessed using the GEPIA database (http://gepia2.cancer-pku.cn/) [19]. The database uses a log-rank test to compare the survival outcomes between high and low EGFR-expressed groups and Cox regression analysis to give the hazards on OS.
Identification of EGFR targeting miRNAs in-silico
MiRWalk 3.0 (http://mirwalk.umm.uni-heidelberg.de/), a freely accessible, user-friendly, online database that predicts the miRNA targets precisely, was queried using the official gene symbol “EGFR” to search for miRNAs that potentially bind to its sequence, including regions like 5′-UTR, CDS, or 3′-UTR. The predicted miRNAs were subsequently cross-checked with other databases such as miRTarbase and TargetScan to confirm and validate their binding.
Determination of miRNA expression in prostate cancer and their in-silico validation
The expression pattern of miRNAs targeting EGFR was queried in NCBI’s data repository, the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Briefly, each miRNA was queried in the “GEO profiles” with the specific keyword “PCa” to retrieve the datasets. Among the datasets, those containing hormone-dependent PCa tissue samples and/or metastatic PCa tissue, as well as those including PCa cell lines such as LNCaP and DU-145, were selected for further analysis. The selected datasets comprised the expression profiles of both miRNA and EGFR mRNA. Prior to analysis, all datasets underwent normalization using the Min–max normalization method to ensure consistency and reliability of the results. Subsequently, the raw data of the queried miRNAs, EGFR, and their respective reference housekeeping gene, U6 snRNA for miRNAs and GAPDH for EGFR, were noted and determined the expression pattern. Furthermore, validation of the differential expression of these miRNAs was performed through a comprehensive literature review via PubMed. This involved searching for studies containing western blotting, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, or immunohistochemistry (IHC) data related to each miRNA in both prostate cancer tissue and cell lines.
Cell culture and transfection
PCa cell lines, LNCaP, DU145, and PC-3, were procured from NCCS Pune (India) and grown in RPMI-1640 medium (HiMedia, India) supplemented with fetal bovine serum (10%), 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 mg/ml streptomycin. The cells were incubated at 37°C in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere. As described previously, for transfection, a transfection mixture was prepared in a 150 mM NaCl solution, incubated at room temperature, and added to the culture medium in a dropwise manner [8]. Furthermore, to generate stable PC-3 cell lines, a miRNAs expression vector, pCMV-MIR (M1005758 (#SC400690), Origene Technology Inc, USA), was used to construct the hsa-miR-936 plasmid vector for transfection. The transfected cells were then named as miR-PC-3 cells and selected using G-418.
Immunohistochemistry
The paraffin-embedded PCa tissue slices were acquired from the Department of Pathology of a tertiary care hospital in accordance with established core procedures after obtaining ethical approval. EGFR expression in hormone-dependent and metastatic tissues collected from PCa patients, and from animal studies, was measured using IHC staining as per a previous study [8]. The clinicopathological data is provided in a supplementary file (Table S1). Briefly, tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin–eosin to evaluate the histological structures and tumor grades before performing the IHC. After deparaffinization and blocking endogenous peroxidase, the sections were heated in 0.01 M citrate buffer solution (pH 6.0) in a water bath at 98°C for 20 minutes; subsequently, they were incubated with a diluted monoclonal antibody (1:100) to EGFR (sc-28385, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, TX, USA) overnight at 4°C and visualized using a 3,3′-diaminobenzidine detection kit (Vector labs). The intensity of EGFR staining was assessed through Image J (IJ 1.46r).
Western blot analysis
The proteins from the PCa cells were extracted, quantified, and separated on 10% Bis–Tris PAGE, and western blotting was carried out as described previously [20]. EGFR, p-Src, and GAPDH proteins were identified with specific monoclonal antibodies. The appropriate secondary antibodies conjugated with horseradish peroxidase were treated with the corresponding membranes for 2 hours at room temperature. The enhanced chemiluminescence system (MJEA13553, UVITEC, UK) was used to capture the images, and Image J (IJ 1.46 r) was used for densitometry analysis to quantify the protein bands. All primary antibodies were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, and were used at a dilution of 1:1000. The catalogue numbers for the primary antibodies are as follows: EGFR (sc-03-G), GAPDH (sc-25778), and p-Src (sc-101802). The secondary antibody was procured from Bio-Rad, USA, and was used at a dilution of 1:3000. The catalogue numbers for the secondary antibodies are as follows: Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H/L): HRP (#5178-2504), Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H/L): HRP (#5196-2504).
Total RNA extraction and quantitative reverse transcription?polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from the PCa cells using the TRIzol reagent (ThermoFisher Scientific Inc., USA) and the amount of RNA was measured using a Biospectrophotometer. Then, 1 μg of total RNA was used for the synthesis of cDNA (iScript cDNA synthesis kit, BioRAD, India) as directed by the manufacturer. qRT-PCR was performed as previously described [20] using TB Green Premix Ex Taq II kit (#RR820A, Takara, Japan) in QuantStudio QS3 (ThermoFisher Scientifc Inc., USA). The gene-specific primers were designed using Primer3 software and procured from Barcode Biosciences, India. The relative expression levels were determined using the 2−ΔΔCT method, with the expression of GAPDH and U6 snRNA serving as endogenous controls.
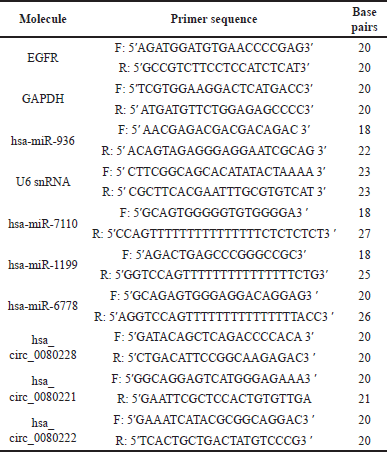 | [Click here to view] |
Statistical analysis
To analyze our data, we used GraphPad Prism 9.3.1, employing Mann–Whitney U test, Cohens d, effect size, and Two-way ANOVA test. p-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
In-silico identification of circRNAs and their binding with EGFR-associated miRNA
Three publicly available repositories of human circRNAs, circBank, circBase, and circinteractome were employed to identify EGFR-circRNA and Annexin A2 (ANXA2)-circRNA. By querying the official gene symbols “EGFR” and “ANXA2”, a list of its circRNAs was obtained. To eliminate redundancy, the lists were merged and duplicate entries were removed. Then, each circRNA from the final list was screened further using the “miRNA” section of circBank database to explore its potential binding with the miRNAs that target only EGFR.
RESULTS
EGFR is highly expressed in hormone-independent PCa
IHC analysis revealed the differential expression pattern of EGFR in both hormone-dependent and hormone-independent PCa tissue samples. Furthermore, it demonstrated that there is a significantly higher expression of EGFR in a higher Gleason score (3+ staining) and poorly differentiated PCa. However, the EGFR is very low or null in early PCa incidence, which has 0 or 1+ staining intensity (Fig. 1a and b). Moreover, an in-silico data-based UALCAN analysis also showed a gradual increase in EGFR expression with an increase in the Gleason score of PRAD (Fig. S1a). Furthermore, the OS analysis showed a correlation between high EGFR expression with poor survival of PRAD patients compared to low/medium expression of EGFR (Fig. S1b). Additionally, the expression pattern of EGFR was ascertained in PCa cell lines LNCaP and DU145 by qRT-PCR and western blot analysis (Table 2, Fig. 2a–c). This increased expression pattern of EGFR in mPCa was also observed in in-silico analysis of PCa cell lines and tissue microarray data (Table S2, Fig. S2a and b).
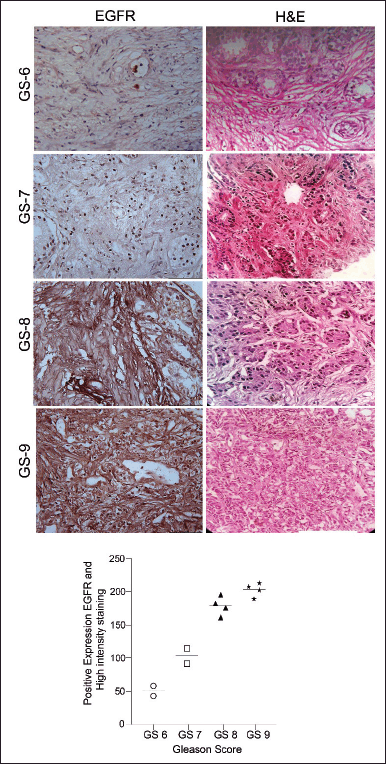 | Figure 1. Representative immunohistochemical (a) and its analytical data (b) demonstrating EGFR expression pattern in clinical PCa specimens with different Gleason Score. [Click here to view] |
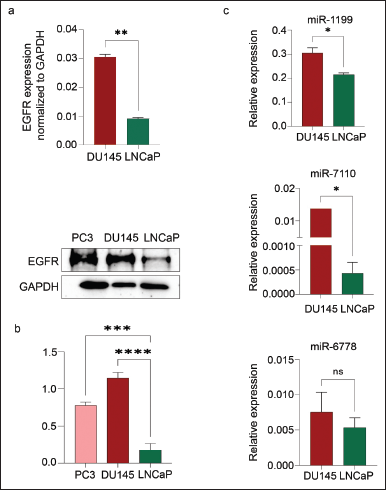 | Figure 2. qRT-PCR analysis shows the EGFR mRNA expression in DU-145 and LNCaP cells (a); protein expression in DU145, PC-3, and LNCaP (b); and the expression of miR-1190, miR-7110, and miR-6778 in DU-145 and LNCaP cells. [Click here to view] |
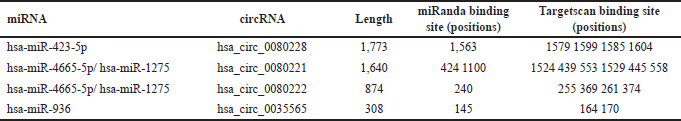 | Table 1. circBank analysis for binding of tumor suppressor miRNAs with EGFR-circRNAs and ANXA2 circRNA. [Click here to view] |
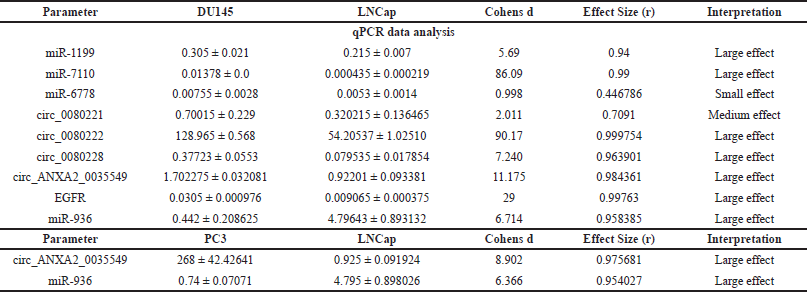 | Table 2. Comparison of qPCR expression data of various miRNA, CircRNA, and EGFR in DU145, LNCap, and PC3 cell lines using effect size. [Click here to view] |
EGFR-associated miRNAs and circRNAs are differentially expressed in PCa
MiRWalk 3.0 analysis revealed the 1,678 potential miRNAs binding to various regions of the EGFR gene, of which, 55 miRNAs binding to the 5′UTR, 731 to the 3′UTR, and 892 to the CDS region. Further validation for miRNA binding using miRDB and TargetScan revealed that only 29 miRNAs binding EGFR were then scrutinized for experimental validation through a literature survey (Table S4). Finally, only six miRNAs, hsa-miR-1275, hsa-miR-423-5p, hsa-miR-493-5p, hsa-miR-1199, hsa-miR-7110, and hsa-miR-6778 had experimental evidence reported and were thus selected and further assessed for their expression patterns in early hormone-dependent PCa cells (LNCaP) and mPCa cells (DU145), as well as tissue samples (Table S3). Among the six miRNAs that were differentially expressed, miR-1275, miR-423-5p, and miR-493-5p were downregulated in DU145 and highly expressed in LNCaP cells (Table S1, Fig. S3a). However, miR-1275/4665-5p, miR-423-5p, and miR-493-5p were observed in the early neoplastic stage, as these tumor suppressor miRNAs have a seed sequence complementary to the EGFR 3′-UTR region that destabilizes mature mRNA synthesis post-transcriptionally (Fig. S4a). On the contrary, oncomiRs miR-1199 (p = 0.078), miR-7110 (p = 0.003), and miR-6778 (p = 0.027) have shown higher expression in mPCa compared to hormone-dependent PCa, and these miRNAs also have a complementary seed sequence in the 5′-UTR of EGFR (Table S2, Figs. S3b and S4d). Our qRT-PCR data is consistent with these observations, showing higher expression patterns of miR-1199, miR-7110, and miR-6778 in DU-145 cells compared to LNCaP (Table 2, Fig. 2c).
Furthermore, we investigated the exact reason behind the loss of EGFR-associated tumor suppressor miRNA in PCa. The in-silico analysis identified three EGFR-circRNAs namely, hsa_circ_0080228, hsa_circ_0080221, hsa_circ_0080222, and one ANXA2-circRNA, hsa_circ_0035549 (Table S5) that have the higher expression levels in mPCa cells DU-145, compared to hormone-dependent LNCaP (Table 2, Fig. 3b and c). It was found that the hsa_circ_0080228 and hsa_circ_0080221 seed sequences are complementary to the tumor suppressor hsa-miR-423-5p, while the hsa_circ_0080222 seed sequence is complementary to hsa-miR-1275/4665-5p (Table 1). The hsa-miR-936 had seed sequence complementarity with hsa_circ_0035549 (Fig. S5b and Table 1). Unfortunately, we could not find any EGFR-circRNA against hsa-miR-493-5p (Table 1). Also, we could not find any suitable datasets as per our study’s requirement in the GEO database for the analysis of the differential expression of these circRNAs.
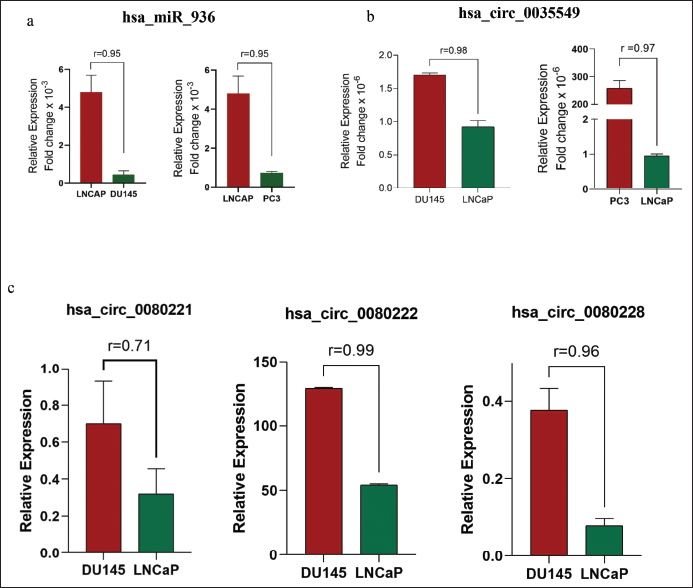 | Figure 3. qRT-PCR analysis shows a significant expression of hsa-miR-936 in LNCaP cells, compared to PC-3, and DU145 (a). Also, qRTPCR analysis showing expression of ANXA2-circRNA (hsa_circ_0035565), (b) and EGFR-circRNAs, hsa_circ_0080228, hsa_circ_0080221, and hsa_circ_0080222, and (c) in mPCa and HDPCa cell lines. [Click here to view] |
hsa-miR-936 regulates EGFR expression and signaling axis
In our previous study, we delved into the interaction of a tumor suppressor miRNA, hsa-miR-936, with ANXA2 and identified its binding sites in coding as well as 3′-UTR sections [8]. Considering the multifaceted regulatory potential of miRNAs, the present study further explored the interaction of hsa-miR-936 with EGFR mRNA. The in-silico investigation revealed that hsa-miR-936 seed sequences are complementary to EGFR’s coding as well as 3’UTR regions suggesting the potential existence of a significant interaction between hsa-miR-936 and EGFR. (Fig. S5a). In PC-3 cells, the loss of hsa-miR-936 is shown to increase tumorigenicity through EGFR expression. Its effects on EGFR-mediated downstream signaling were further investigated. EGFR expression was significantly reduced at the protein level in PC-3 cells following miR-936 vector transfection, as demonstrated by a gain-of-function assay. The reduction in EGFR and pSrc expression (Fig. 4a) in our study demonstrates that miR-936’s ectopic expression influenced EGFR’s downstream effectors such as VEGF, HIF-1α, vimentin, and MMP-9. The results also showed an increase in E-cadherin levels. Additionally, the protein expressions of pEGFR and other downstream signaling molecules, such as pAKT, pSTAT-3, and pERK, were downregulated following the overexpression of miR-936.
As per the previous report, xenografts of PC-3 cells with hsa-miR-936 have shown reduced tumor size compared to vector control [8]. The results indicated that the ectopic expression of hsa-miR-936 markedly inhibited tumor growth. Additionally, our immunohistochemical analysis showed a decrease in EGFR expression in the xenografts of PC-3 cells that expressed miR-936 in male BALB/c nude mice, in comparison to the vector control (Fig. 4b).
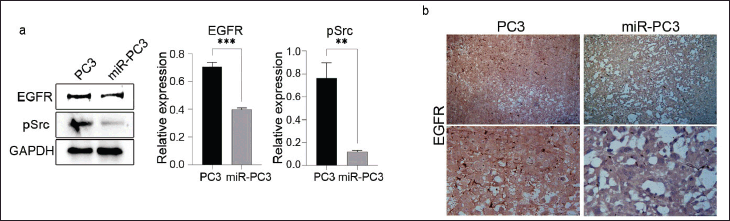 | Figure 4. (a) Western blot data showing the expression of EGFR and its downstream signaling molecule pSrc upon stable transfection of pre-miR-936 in PC-3 cells and GAPDH was used as a loading control. (b) Immunohistochemical data demonstrating reduced EGFR expression in xenografts of PC-3 cells expressing miR-936 in male BALB/c nude mice compared to vector control. [Click here to view] |
DISCUSSION
Prostate carcinomas showcase a notable degree of heterogeneity and can either stay confined within the prostate or metastasize to nearby lymph nodes and other organs [21,22]. The development of PCa unfolds in stages, with most tumors initially reliant on androgens for growth, leading to the primary treatment modality of androgen ablation [23]. Nonetheless, in numerous cases, tumor cells progress to a hormone-resistant state, resulting in androgen-independent tumors with heightened proliferation and invasion capabilities. Although there are many different ways for metastasis, the molecular mechanisms responsible for PCa development, progression, and hormone-independence are not clear yet [24,25]. This has resulted in a therapeutic bottleneck for PCa. Thus, it is crucial to identify and investigate the key molecules involved in the process of PCa development.
Several studies indicate that changes in various pathways involving growth factor receptors contribute to this multistep process. Notably, EGFR is often overexpressed in advanced PCa and is linked to a more aggressive clinical outcome [7,26,27]. The present in-silico analysis revealed that PCa patients with elevated EGFR expression and a high Gleason score (>6.0) have a poorer survival rate (Fig. S1). Androgens decrease EGFR levels in the normal prostate, but not in prostate cancer. Similarly, our IHC data and western blot analysis also suggested higher expression of EGFR in mPCa compared to hormone-dependent PCa (Figs 1a and 2b). These findings suggest the loss of EGFR regulation and alterations in its signaling pathways might help in the phenotypic shifting of prostate tumors from androgen dependent to androgen independent [27]. However, the precise molecular mechanism responsible for the varying expression of EGFR in PCa remains inadequately understood.
Several studies indicate that aberrant miRNA expression contributes to the initiation and advancement of cancer by dysregulating the target gene’s expression [28,29]. Modulating the miRNA expression has the major advantage of targeting several genes and pathways simultaneously which is not possible with the genes [30]. Similar to other malignancies, PCa has a distinctive miRNA expression profile, which has been the basis for the functional study of miRNA in PCa. Accumulated evidence suggests that miRNAs serve as tumor suppressors or oncogenes depending on the target gene. Dysregulation of miRNAs may serve important roles in the initiation and progression of cancer of various tissue origins including PCa [31–33]. In this context, our study delved into the possibility of using miRNA to regulate EGFR in PCa to identify the underlying reason for the varying levels of EGFR expression. The investigation revealed an inverse correlation in the levels of expression between EGFR and hsa-miR-423-5p, hsa-miR-1275/4665-5p, as well as hsa-miR-493-5p. Similarly, a study by Wang et al. [34] has demonstrated that hsa-miR-493-5p is not highly expressed in the mPCa cell lines PC-3 and DU-145, whereas functional research has substantiated that the overexpression of miR-493-5p leads to a decrease in the expression of EGFR in PC-3 and DU-145 cells. Moreover, miR-423-5p inhibits the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of PCa [35]. The miRNA has the potential to impact cellular processes and gene expression in a context-dependent manner [24]. For example, the miR-1275 has been shown to have the ability to foster or impede the progression of human cancer by regulating the levels of various targets in distinct cellular pathways such as PI3-AKT, Wnt, and a few others [36,37]. Han et al. [38] has revealed that miR-1275 serves as a tumor suppressor, and this miRNA induces apoptosis in breast cancer by inhibiting cell proliferation, differentiation, tumor development, invasion, and migration. Through bioinformatics analysis, we have gathered additional evidence to support this assertion. Our findings indicate a reduced expression of miR-1275 in mPCa in comparison to HDPCa. Additionally, binding studies have revealed specific binding sites for this miRNA in the EGFR gene. In contrast to the aforementioned tumor suppressor miRNAs, in-silico investigations and qRT-PCR findings have revealed that hsa-miR-1199-5p, hsa-miR-7110, and hsa-miR-6778-5p exhibit similar expression patterns to EGFR in both HDPCa and mPCa. In oral squamous cell carcinoma and gastric cancer, miR-7110 and miR-6778-5p demonstrated increased expression levels, respectively, in comparison to their corresponding normal tissue, providing additional evidence for our study [39,40]. Some studies reported miR-1199-5p as a tumor suppressor [41,42], but in this study, hsa-miR-1199-5p showed higher expression in mPCa compared to HDPCa. These EGFR-associated miRNAs, when considered as a whole, could have a significant impact on the varying expression patterns of EGFR in PCa.
The impact of hsa-miR-936 on the progression of PCa has been outlined in a recent study published by our team. The absence of hsa-miR-936 plays a crucial role in the shift from HDPCa to mPCa. Additionally, our research indicates that hsa-miR-936 acts as a distinct post-transcriptional regulator of the calcium-dependent phospholipid binding protein ANXA2 in both hormone-dependent and hormone-independent PCa [8]. Given that one miRNA may control several genes, we hypothesized that hsa-miR-936 could also regulate EGFR since EGFR and ANXA2 interact with each other and are on the same signaling pathway [20]. By directly binding to the 3′-UTR of EGFR, miR-936 affects the expression of EGFR in PCa. Furthermore, hsa-miR-936 showed a differential expression pattern in DU-145 and LNCaP, demonstrating a negative correlation with EGFR levels. Functional studies have additionally illustrated that elevated levels of hsa-miR-936 overexpressed PC-3 cells lead to decreased EGFR expression. Moreover, low expression of EGFR is also observed in xenograft tissue derived from hsa-miR-936 overexpressing PC3 cells, underscoring the role of hsa-miR-936 in regulating EGFR alongside other EGFR-associated miRNAs in PCa.
The reduced accumulation of miR-936 along with miR-1275, miR-423-5p, and miR-493-5p may reflect diminished levels of EGFR expression in HDPCa and loss of all these EGFR-associated tumor suppressor miRNAs may be the reason behind the transition from HDPCa to mPCa. In mPCa, miR-1199-5p, miR-7110, and miR-6778-5p are upregulated, supporting their oncogenic role. On the other hand, these oncomirs are not highly expressed in HDPCa, and their binding affinity to the EGFR 5′-UTR position may also be a strong reason for the abundant expression of EGFR in mPCa. All of this evidence clearly implies that instead of targeting a single miRNA, upregulating tumor suppressor miRNAs such as miR-1275, miR-423-5p, and miR-493-5p while downregulating a trio of oncomirs (miR-1199-5p, miR-7110, and miR-6778-5p) might result in a better clinical outcome in PCa. As the loss of expression of tumor suppressor miRNAs tends to be both the cause and the outcome of metastasis in PCa [8,43,44], we looked into the possibility of circRNA-mediated regulation of these miRNAs in PCa.
Although the biological functions of most circRNAs remain unclear, growing evidence suggests that circRNAs regulate gene expression by acting as sponges for miRNAs, interacting with RNA-binding proteins, and even directly translating into proteins [18,45,46]. To the best of our knowledge, we demonstrated for the first time, three EGFR-circRNAs: hsa_circ_0080228, hsa_circ_0080221, and hsa_circ_0080222 expressions in PCa. These EGFR-circRNAs exhibited similar expression patterns as EGFR in both HDPCa and mPCa cell lines. Additionally, their expression levels demonstrate a reciprocal relationship with miR-1275, miR-423-5p, miR-493-5p, and miR-936. In-silico analysis showed that there are miRNA-responsive elements of these anti-oncomirs (miR-1275, miR-423-5p) in both EGFR-circRNAs and 3′-UTR of EGFR. Therefore, we assume that the loss of miR-1275/4665-5p in mPCa may be due to the binding of hsa_circ_0080221, hsa_circ_0080222, and miR-423-5p by hsa_circ_0080228. Similar to our observation in PCa, a recent study using TNBC also reported that hsa_circ_0080222 promotes cancer progression [47]. Despite the regulatory function of hsa-miR-493-5p and hsa-miR-936 on EGFR expression, no EGFR-circRNAs were found to bind to both of these miRNAs. The hsa-miR-936 also regulates ANXA2 which is upstream to EGFR [20], we checked into the possibility of ANXA2-circRNAs binding to hsa-miR-936 and, to our surprise, only one ANXA2-circRNA, hsa_circ_0035549 was found. As we suspected this, ANXA2-circRNA has shown very low expression as like ANXA2 and EGFR in LNCaP cells allowed miR-936 to suppress ANXA2 and EGFR mRNA expression. The loss of hsa-miR-936 is one of the main reasons for the transition to the metastatic stage from HDPCa [8]. To date, no study has reported hsa_circ_0035549 and its regulatory relationship with miR-936. By considering a higher expression of hsa_circ_0035549 in mPCa and their binding towards hsa-miR-936, this study endeavors to unravel the underlying reasons behind the loss of this tumor-suppressing miRNA. Through the outcomes of the present study, we could build a linkage between EGFR-mRNA, EGFR- and ANXA2-circRNA, and EGFR-associated miRNAs. Owing to that these circRNAs can perform their function as a sponge of tumor suppressor miRNAs, we came to the conclusion that the trio of EGFR-circRNA and ANXA2-circRNA may decoy these miRNAs, resulting in the positive regulation of EGFR, thus accelerating metastasis in PCa. More importantly, silencing ANXA2-circRNA along with EGFR-circRNAs may downregulate the functions of EGFR in mPCa by restating tumor suppressor miRNAs expression that supresses EGFR.
To recapitulate briefly, EGFR-circRNAs (hsa_circ_0080228, hsa_circ_0080221, and hsa_circ_0080222) and ANXA2-circRNA (hsa_circ_0035549) were highly expressed in mPCa DU-145 cells compared to HDPCa cell line LNCaP and accelerated the transition from HDPCa to mPCa through upregulation EGFR by functioning as a molecular sponge for hsa-miR-1275/4665-5p, hsa-miR-423-5p, and hsa-miR-936. These EGFR-circRNAs and ANXA2-circRNA, which exerts a cancer-promoting role in mPCa may serve as a potential therapeutic target against the PCa transition. Consequently, we identified six noteworthy miRNAs, of which, hsa-miR-1275/4665-5p, hsa-miR-423-5p, and hsa-miR-493-5p showed similar expression patterns like hsa-miR-936; conversely, hsa-miR-1199, hsa-miR-7110, and hsa-miR-6778 showed reciprocal expression pattern in PCa. These miRNAs hold potential as key players in bridging the transition from hormone dependence to a metastatic phenotype in PCa. Three EGFR-circRNAs, hsa_circ_0080228, hsa_circ_0080221, and hsa_circ_0080222, were found to sponge tumor suppressor miRNAs such as hsa-miR-1275/4665-5p, hsa-miR-423-5p, and hsa-miR-493-5p. Unfortunately, no EGFR-circRNA was identified to bind to hsa-miR-936. Given the significance of the ANXA2-EGFR signaling axis in PCa and the role of hsa-miR-936 in regulating ANXA2 expression, we investigated the potential of ANXA2-circRNAs as sponges for hsa-miR-936. Only one ANXA2-circRNA, hsa_circ_0035565, exhibited seed sequence complementarity and reciprocal expression with hsa-miR-936. Unlike conventional molecular-targeted drugs and antibody drugs that control ANXA2-EGFR signaling axis, replacement therapy using antisense EGFR-circRNAs against hsa_circ_0080228, hsa_circ_0080221, and hsa_circ_0080222 along with hsa_circ_0035565 may control the expression of EGFR and ANXA2 by restating the expression of tumor suppressor miRNA in mPCa. Therefore, this therapeutic strategy is a next-generation drug modality that can treat prostate cancer patients with high unmet medical needs. Previously, our research focused on investigating the role of hsa-miR-936 in PCa, demonstrating its significance as a tumor suppressor miRNA that targets the calcium-dependent phospholipid binding protein ANXA2, when knocked down contributes to the development of a metastatic phenotype [8].
Despite the reliability and accuracy of our in-silico methods and results, further molecular biology investigations, including dual luciferase assays, are required to elucidate the interplay between these miRNAs and the EGFR gene in driving the phenotypic shift in PCa. Additionally, in-vitro experimental validations are crucial to substantiate the relationship between EGFR-circRNAs and ANXA2-circRNA in the PCa progression. However, though our findings provide a scope and molecular basis for future studies aimed at combating the progression of PCa, they need further experimental support to fully validate the proposed mechanisms.
CONCLUSION
The current study demonstrates that the differential expression of EGFR plays a crucial role in the transition from HDPCa to mPCa. The differential expression pattern of EGFR-associated miRNAs and circRNAs in HDPCa and mPCa could be a major reason for the altered expression of EGFR and can provide new insights into the specific mechanisms of PCa progression. Furthermore, elevating hsa-miR-936, hsa-miR-1275, hsa-miR-423-5p, and hsa-miR-493-5p expression by regulating hsa_circ_0035549, hsa_circ_0080228, hsa_circ_0080221, and hsa_circ_0080222 could be a key factor in improving patient prognosis. Nonetheless, these discoveries could act as a catalyst for future investigations aimed at unraveling the precise role of EGFR and ANXA2-circRNA and EGFR-associated miRNAs in PCa.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like to acknowledge the support by the CSIR-SRF (DIRECT2021/10881) for funding the employment of S. Edachery. We extend our gratitude for using the instrumentation facility available in the Department of Biochemistry, Kuvempu University, established under the DST-FIST programme (Grant No. FIST-No. SR/FST/ LS-1/2018/175(C)) to complete this research. We also express our heartfelt gratitude to Ms. Mahima Rachel Thomas for her invaluable suggestions and insights.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors report no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of SDM College of Medical Sciences and Hospital (SDM-IEC-54/Ext-2016, and 08-07-2016) for studies involving humans. The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of SDM College of Medical Sciences and Hospital (SDM-IAEC-53/Ext-2016, and 08-07-2016) for studies involving animals.
CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated and analyzed are included in this research article.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used artificial intelligence (AI)-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
REFERENCES
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229–63. CrossRef
2. Tao LJ, Pan XY, Wang JW, Zhang L, Tao LS, Liang CZ. Circular RNA circANKS1B acts as a sponge for miR-152-3p and promotes prostate cancer progression by upregulating TGF-α expression. Prostate. 2021;81(5):271–8. CrossRef
3. Bu T, Li L, Tian J. Unlocking the role of non-coding RNAs in prostate cancer progression: exploring the interplay with the Wnt signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1269233. CrossRef
4. Cheng L, He Q, Liu B, Chen L, Lv F, Li X, et al. SGK2 promotes prostate cancer metastasis by inhibiting ferroptosis via upregulating GPX4. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(1):74. CrossRef
5. Caggia S, Johnston A, Walunj DT, Moore AR, Peer BH, Everett RW, et al. Gαi2 protein inhibition blocks chemotherapy-and anti-androgen-induced prostate cancer cell migration. Cancers. 2024;16(2):296. CrossRef
6. Soares S, Aires F, Monteiro A, Pinto G, Faria I, Sales G, et al. Radiotherapy metastatic prostate cancer cell lines treated with gold nanorods modulate miRNA signatures. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(5):2754. CrossRef
7. Nasta?y P, Stoupiec S, Pop?da M, Smentoch J, Schlomm T, Morrissey C, et al. EGFR as a stable marker of prostate cancer dissemination to bones. Br J Cancer. 2020;123(12):1767–74. CrossRef
8. Edachery S, Patil P, Mohan R, Aradhya B, Shetty J, Kabekkodu SP, et al. Loss of miR-936 leads to acquisition of androgen-independent metastatic phenotype in prostate cancer. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):17070. CrossRef
9. Sun C, Lu C, Li X, Li R, Wen Z, Ge Z, et al. The value of a panel of circulating microRNAs in screening prostate cancer. Transl Cancer Res. 2024;13(2):687. CrossRef
10. Tseng JC, Wang BJ, Wang YP, Kuo YY, Chen JK, Hour TC, et al. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester suppresses EGFR/FAK/Akt signaling, migration, and tumor growth of prostate cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 2023;116:154860. CrossRef
11. Zhao P, Han P, Ma Y, Tian P, Li J. Circ_0082878 contributes to prostate cancer progression via the miR-455-3p/WTAP axis. Environ Toxicol. 2024;39(2):979–90. CrossRef
12. Xu W, Zhong Z, Gu L, Xiao Y, Chen B, Hu W. circCPA4 induces malignant behaviors of prostate cancer via miR-491-5p/SHOC2 feedback loop. Clinics. 2024;79:100314. CrossRef
13. Ghamlouche F, Yehya A, Zeid Y, Fakhereddine H, Fawaz J, Liu YN, et al. MicroRNAs as clinical tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in prostate cancer. Transl Oncol. 2023;28:101613. CrossRef
14. Mazzetti S, Defeudis A, Nicoletti G, Chiorino G, De Luca S, Faletti R, et al. Development and validation of a clinical decision support system based on PSA, microRNAs, and MRI for the detection of prostate cancer. Eur Radiol. 2024;34(8):1–10. CrossRef
15. Wu YP, Lin XD, Chen SH, Ke ZB, Lin F, Chen DN, et al. Identification of prostate cancer-related circular RNA through bioinformatics analysis. Front Genet. 2020;11:892. CrossRef
16. Wang X, Wang R, Wu Z, Bai P. Circular RNA ITCH suppressed prostate cancer progression by increasing HOXB13 expression via spongy miR-17-5p. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:1–11. CrossRef
17. Choi S, Lee S, Han YH, Choi J, Kim I, Lee J, et al. miR-31-3p functions as a tumor suppressor by directly targeting GABBR2 in prostate cancer. Front Oncol. 2022;12:945057. CrossRef
18. Khan S, Jha A, Panda AC, Dixit A. Cancer-associated circRNA–miRNA–mRNA regulatory networks: a meta-analysis. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:671309. CrossRef
19. Tang Z, Kang B, Li C, Chen T, Zhang Z. GEPIA2: an enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):W556–60. CrossRef
20. Shetty PK, Thamake SI, Biswas S, Johansson SL, Vishwanatha JK. Reciprocal regulation of annexin A2 and EGFR with Her-2 in Her-2 negative and herceptin-resistant breast cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44299. CrossRef
21. Xin S, Liu X, Li Z, Sun X, Wang R, Zhang Z, et al. ScRNA-seq revealed an immunosuppression state and tumor microenvironment heterogeneity related to lymph node metastasis in prostate cancer. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023;12(1):49. CrossRef
22. Cussenot O, Valeri A, Berthon P, Fournier G, Mangin P. Hereditary prostate cancer and other genetic predispositions to prostate cancer. Urol Int. 1998;60(Suppl. 2):30–4. CrossRef
23. Carrion-Salip D, Panosa C, Menendez JA, Puig T, Oliveras G, Pandiella A, et al. Androgen-independent prostate cancer cells circumvent EGFR inhibition by overexpression of alternative HER receptors and ligands. Int J Oncol. 2012;41(3):1128–38. CrossRef
24. Sidorova EA, Zhernov YV, Antsupova MA, Khadzhieva KR, Izmailova AA, Kraskevich DA, et al. The role of different types of microRNA in the pathogenesis of breast and prostate cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(3):1980. CrossRef
25. Zhang P, Chen L, Zhou F, He Z, Wang G, Luo Y. NRP1 promotes prostate cancer progression via modulating EGFR-dependent AKT pathway activation. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(2):159. CrossRef
26. Höti N, Lih TS, Pan J, Zhou Y, Yang G, Deng A, et al. A comprehensive analysis of FUT8 overexpressing prostate cancer cells reveals the role of EGFR in castration resistance. Cancers. 2020;12(2):468. CrossRef
27. Traish A, Morgentaler A. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression escapes androgen regulation in prostate cancer: a potential molecular switch for tumour growth. Br J Cancer. 2009;101(12):1949–56. CrossRef
28. Inoue J, Inazawa J. Cancer-associated miRNAs and their therapeutic potential. J Hum Genet. 2021;66(9):937–45. CrossRef
29. Palanichamy JK, Rao DS. miRNA dysregulation in cancer: towards a mechanistic understanding. Front Genet. 2014;5:54. CrossRef
30. Hussen BM, Hidayat HJ, Salihi A, Sabir DK, Taheri M, Ghafouri-Fard S. MicroRNA: a signature for cancer progression. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;138:111528. CrossRef
31. Jiang FN, Liang YX, Wei W, Zou CY, Chen GX, Wan YP, et al. Functional classification of prostate cancer?associated miRNAs through CRISPR/Cas9?mediated gene knockout. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(5):3777–84. CrossRef
32. Massillo C, Dalton GN, Farré PL, De Luca P, De Siervi A. Implications of microRNA dysregulation in the development of prostate cancer. Reproduction. 2017;154(4):R81–97. CrossRef
33. Fang Y, Gao W. Roles of microRNAs during prostatic tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Oncogene. 2014;33(2):135–47. CrossRef
34. Wang S, Wang X, Li J, Meng S, Liang Z, Xu X, et al. c-Met, CREB1 and EGFR are involved in miR-493-5p inhibition of EMT via AKT/GSK-3β/Snail signaling in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(47):82303. CrossRef
35. Ferri C, Di Biase A, Bocchetti M, Zappavigna S, Wagner S, Le Vu P, et al. MiR-423-5p prevents MALAT1-mediated proliferation and metastasis in prostate cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41(1):1–16. CrossRef
36. Chong ZX, Yeap SK, Ho WY, Fang CM. Unveiling the tumour-regulatory roles of miR-1275 in cancer. Pathol-Res Pract. 2022;230:153745. CrossRef
37. Xie C, Wu Y, Fei Z, Fang Y, Xiao S, Su H. MicroRNA-1275 induces radiosensitization in oesophageal cancer by regulating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(1):747–59. CrossRef
38. Han X, Li M, Xu J, Fu J, Wang X, Wang J, et al. miR-1275 targets MDK/AKT signaling to inhibit breast cancer chemoresistance by lessening the properties of cancer stem cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19(1):89. CrossRef
39. Neralla M, Preethi A, Selvakumar S, Sekar D. Expression levels of microRNA-7110 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Minerva Dent Oral Sci. 2024;73(3):155–60. CrossRef
40. Zhao M, Hou Y, Du YE, Yang L, Qin Y, Peng M, et al. Drosha-independent miR-6778–5p strengthens gastric cancer stem cell stemness via regulation of cytosolic one-carbon folate metabolism. Cancer Lett. 2020;478:8–21. CrossRef
41. Diepenbruck M, Tiede S, Saxena M, Ivanek R, Kalathur RKR, Lüönd F, et al. miR-1199-5p and Zeb1 function in a double-negative feedback loop potentially coordinating EMT and tumour metastasis. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1168. CrossRef
42. Sato A, Yamamoto A, Shimotsuma A, Ogino Y, Funayama N, Takahashi Y, et al. Intracellular microRNA expression patterns influence cell death fates for both necrosis and apoptosis. FEBS Open Bio. 2020;10(11):2417–26. CrossRef
43. Olivan M, Garcia M, Suárez L, Guiu M, Gros L, Méndez O, et al. Loss of microRNA-135b enhances bone metastasis in prostate cancer and predicts aggressiveness in human prostate samples. Cancers. 2021;13(24):6202. CrossRef
44. Ru P, Steele R, Newhall P, Phillips NJ, Toth K, Ray RB. miRNA-29b suppresses prostate cancer metastasis by regulating epithelial–mesenchymal transition signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(5):1166–73. CrossRef
45. Ikeda Y, Morikawa S, Nakashima M, Yoshikawa S, Taniguchi K, Sawamura H, et al. CircRNAs and RNA-binding proteins involved in the pathogenesis of cancers or central nervous system disorders. Non-coding RNA. 2023;9(2):23. CrossRef
46. Dudekula DB, Panda AC, Grammatikakis I, De S, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M. CircInteractome: a web tool for exploring circular RNAs and their interacting proteins and microRNAs. RNA Biol. 2016;13(1):34–42. CrossRef
47. Song H, Zhao Z, Ma L, Zhao W, Hu Y, Song Y. Novel exosomal circEGFR facilitates triple negative breast cancer autophagy via promoting TFEB nuclear trafficking and modulating miR-224-5p/ATG13/ULK1 feedback loop. Oncogene. 2024;43(11):821–36. CrossRef