INTRODUCTION
The genus Paeonia of the family Paeoniaceae consists of 33 species and 26 sub-species worldwide [1,2]. Paeonia is currently divided into three sections. Moutan includes 11 species and two sub-species of shrubs that are native to China and countries of East Asia. Oanepia includes two species of herbs distributed in America. Paeonia includes 22 species and 13 subspecies of herbs occurring from Europe to East Asia [1,2]. Traditional uses of Paeonia species have been recorded in plant parts such as the root, root bark, seed, leaf, flower, and whole plant [3]. In traditional Chinese medicine, the roots of Paeonia species such as P. lactiflora, P. suffruticosa, P. emodi, and P. obovata have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and sedative properties [3−5]. They have also been used for inflammation, aches, cardiovascular disorders, neurological diseases, hypertension, asthma, hypertension, asthma, urinary diseases, female genital diseases, skin ailments, and trauma.
In Paeonia species, a total of 153 monoterpene glycosides have been reported. They are well-known for having cage-like pinane skeletons [3,6]. These cage-like compounds are hollow cage molecules having 3-D structures and a wide range of bioactivities [7]. Other classes of metabolites of Paeonia species reported include flavonoids, tannins, stilbenes, triterpenoids, steroids, and phenols [3,8].
Belonging to the family Paeoniaceae, Paeonia lactiflora Pall. (syn. P. albiflora ) or Bai Shao is a stout and erect perennial herb [2,12]. Leaves are alternate and oblique-ovate to lanceolate in shape. Flowers of P. lactiflora are one to three per shoot, fragrant, and terminal or axillary. Petals of wild plants are single and white, red or pink in color, and those of cultivated plants are double and of varying colors (Fig. 1a). Flowers bear many stamens having yellow anthers and filaments. Fruits are oblong-ellipsoid follicles, dehisce when ripe, showing the seeds [2,12]. Roots of P. lactiflora are cylindrical and pale brown in color (Fig. 1b) without flavor and with a slight bitter taste. Paeonia suffruticosa (Andr.) or Mu Dan is a 1−4 m tall shrub. Leaves are ovate, lobed with an acuminate apex. Flowers of P. suffruticosa are large and are in colors of white, pink, red, or purple (Fig. 1c). Roots are cylindrical and yellowish–brown (Fig. 1d).
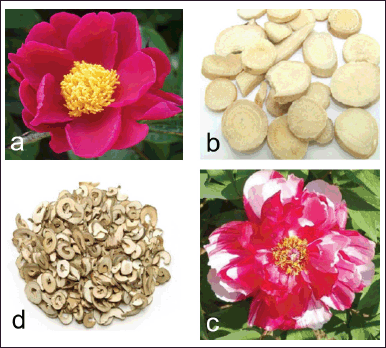 | Figure 1. Red flower (a) [9] and root slices (b) [10] of P. lactiflora, and pink flower (c) [9] and root slices (d) [11] of P. suffruticosa. [Click here to view] |
Species such as P. lactiflora and P. suffruticosa are rich in chemical constituents responsible for a wide range of bioactivities. The major groups of secondary metabolites are polyphenols such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, terpenoids, polyphenols, stilbenes, tannins, and monoterpene glycosides [13,14]. Paeoniflorin (PF) from the root of P. lactiflora and paeonol (PN) from the root bark of P. suffruticosa are among the major compounds. From the aqueous ethanol root extract of P. suffruticosa, the content of PF and PN has been reported to be 1.18% and 2.12%, respectively [15].
PF AND PN
Chemistry
PF or peonidin is a monoterpene glucoside or an iridoid glycoside having a molecular formula and molecular weight of C23H28O11 and 480 g/mol, respectively [16]. It is a β-glucoside of paeoniflorigenin. Important components of PF are a glucose moiety (C6H12O6), a benzoyl moiety (COC6H5), and a pinane skeleton that is cage-like (Fig. 2a). The glucose moiety and the benzoyl moiety are connected to the pinane skeleton at C1 and C8, respectively. The cage-like pinane skeleton has a methyl unit and a hydroxyl unit at C2 and C4, respectively. Without the glucose and benzoyl moieties, PF loses its bioactivity [17]. These compounds are hollow cage molecules having a three-dimensional structure [7]. PF is a dominant monoterpene glucoside with cage-like structures isolated from P. lactiflora. Other compounds include albiflorin, benzoyl PF, benzoyl oxypaeoniflorin, PF sulfonate, dibenzoyl PF, and oxypaeoniflorin [7]. PF was first isolated from the root of P. lactiflora by Shibata and Nakahara in 1963 [18] and its chemical structure was rectified by Kaneda et al. only in 1972 [19].
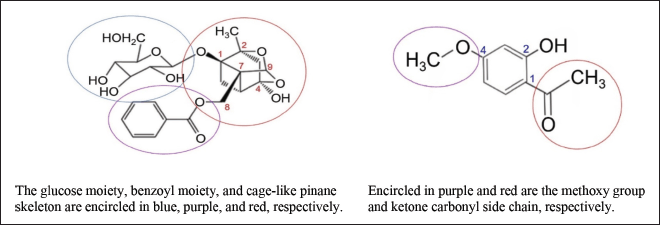 | Figure 2. Chemical structures of PF (left) and PN (right). [Click here to view] |
PN or 2’-hydroxy-4’-methoxyacetophenone is a phenolic compound having a molecular formula of C9H10O3 and a molecular weight of 166 g/mol [20]. The 4-methoxy component of PN is a functional group associated with anticancer activity while the ketone carbonyl side chain is a bioactive functional group at C1 (Fig. 2b) [21]. There is an OH group at C2. PN was first isolated from the root bark of Paeonia moutan by Harada and Yamashita in 1969 [22].
Anticancer properties
The anticancer properties of PF based on the types of cancer, cell lines, effects, molecular processes, and references are shown in Table 1. The five most reported types of cancer have been selected for review. Glioma (9) is the most reported cancer type followed by gastric (6), liver (6), breast (5), and colorectal (5). In the literature, there are three reviews on the anticancer properties of PF. They include the anticancer effects and underlying molecular mechanisms of PF [23], the diverse anticancer activities of PF [24], and the multi-faceted activities of PF in the treatment of tumors [25]. Other cancer types affected by PF are bladder, cervical, endometrial, leukemia, lung, myeloma, nasopharyngeal, osteosarcoma, ovarian, and renal [24,25].
 | Table 1. Anticancer properties of PF. [Click here to view] |
The anticancer properties of PN with information on cancer types, cell lines, effects, molecular processes, and references are shown in Table 2. Liver (8) and lung (7) are the most reported cancer type followed by colorectal (5), gastric (5), and ovarian (4). The mechanisms and clinical prospects of PN for cancer therapy [21], and the effects and mechanisms of PN on anti-tumor and cancer therapy [57] are two recent reviews on the anticancer properties of PN. Other cancer types affected by PN are bladder, breast, cervical, esophageal, melanoma, osteosarcoma, ovarian, pancreatic, and renal [21,57].
 | Table 2. Anticancer properties of PN. [Click here to view] |
Other pharmacological properties
Besides anticancer properties, PF possesses anti-inflammatory, analgesic, immuno-modulatory, neuroprotective, anti-depression, anti-platelet aggregation, reducing dyslipidemia, and vascular dilatory effects [88]. The prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases are among its neuroprotective effects [89]. Beneficial effects of PF toward the nervous system include subarachnoid hemorrhage, on pathogenesis related to cognition, learning, and memory impairment, on Parkinson’s disease, on post-traumatic stress, on neuro-inflammatory pain, on epilepsy, on depression, and on glioblastoma [90].
In the review of the neuroprotective functions and anti-depressive properties of PF [91], the following aspects included: (a) upregulation of the levels of neurotransmitters, (b) inhibition of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, (c) promotion of neuroprotection, (d) modulation of hippocampus neurogenesis, (e) up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor level, (f) inhibition of inflammatory reaction, and (g) down-regulation of nitric oxide level.
Besides anticancer properties, PN is endowed with anti-inflammatory effects against osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, periodontitis, skin inflammation, osteoporosis, organ injury, and colitis [92]. It also possesses neuroprotective activities against diabetic encephalopathy, cerebral ischemic injury, aging, depression, and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. It protects the cardiovascular system via suppression of angiogenesis and metastasis, treatment of myocardial infarction, and protection of vascular endothelial dysfunction [92]. Against atherosclerotic and cardiovascular disorders, PN confers protection against inflammation, lipid metabolism, autophagy, mitochondria damage, platelet aggregation, and endoplasmic reticulum stress.
PF and PN possess the following pharmacological properties such as anti-allergic effect in mice [93], attenuation of myelosuppression in mice [94], attenuation of neuropathic pain in mice [95], and protection of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats [96]. In traditional Chinese medicine, PF and PN possess various pharmacological properties. They are used to treat diabetic nephropathy [97], dysmenorrhea [98], and endometriosis [99].
CONCLUSION
In many Chinese herbal medicines, PF and PN are the main active ingredients possessing a wide spectrum of bioactivities. They include significant and potent in vitro and in vivo anticancer effects. Notably, PF is effective against glioma, and against various types of cancer cells such as those of gastric, liver, breast, and colorectal. PN has anticancer properties against liver, colorectal, gastric, lung, and ovarian cancer cells. In clinical practice, the synergic use of PF and PN as combination drug therapy has been widely reported. PF and PN have reinforced the effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents such as cisplatin, erlotinib, doxorubicin, and 5-fluorouracil. Similarly, their complementary use with other anticancer plant species has also been tested. In combination with PF and PN, their anticancer effects are more effective than chemotherapeutic agents when used alone. Toxicity is an important issue with regard to PF and PN. It is worthwhile to synthesize derivatives that are more effective, selective, and yield less toxic side effects in cancer therapy. Studies on the pharmacokinetic profiles of PF and PN, involving absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, would generate useful information. Currently, research on the effects of PF and PN on tumor prevention and therapy is mainly based on in vitro experiments and lacks clinical evidence to support research findings. Another suggested field of research is to synthesize and evaluate derivatives that are more potent in anticancer activities. Finally, properly designed and randomized controlled clinical trials are necessary to assess the safety and efficacy of PF and PN in tumor patients before they can be developed into commercial cancer drugs.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
There is no funding to report.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The author reports no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this paper.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
This study does not involve experiments on animals or human subjects.
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated and analyzed are included in this research article.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used artificial intelligence (AI)-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
REFERENCES
1. Hong DY. Peonies of the world: taxonomy and phytogeography. London, UK: Royal Botanic Garden, Kew; 2010. pp 300.
2. Hong DY. Peonies of the world: polymorphism and diversity. London, UK: Royal Botanic Garden, Kew; 2011. pp 94.
3. Li P, Shen J, Wang Z, Liu S, Liu Q, Li Y, et al. Genus Paeonia: a comprehensive review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, clinical application, and toxicology. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;269:113708. doi: CrossRef
4. Wu S, Wu D, Chen Y. Chemical constituents and bioactivities of plants from the genus Paeonia. Chem Biodivers. 2010;7(1):90−104. doi: CrossRef
5. Kumar S, Ratha KK, Rao MM, Acharya R. A comprehensive review on the phytochemistry, pharmacological, ethnobotany, and traditional uses of Paeonia species. J Herbmed Pharmacol. 2023;12(1):13−24. doi: CrossRef
6. He CN, Peng Y, Zhang YC, Xu LJ, Gu J, Xiao PG. Phytochemical and biological studies of Paeoniaceae. Chem Biodivers. 2010;7(4):805−38.
7. Li Y, Zhang L, Wang W, Liu Y, Sun D, Li H, et al. A review on natural products with cage-like structure. Bioorg Chem. 2022; 128:106106. doi: CrossRef
8. Parker S, May B, Zhang C, Zhang AL, Lu C, Xue CC. A pharmacological review of bioactive constituents of Paeonia lactiflora Pallas and Paeonia veitchii Lynch. Phytother Res. 2016;30(9):1445−73. doi: CrossRef
9. Zhang K, Yao L, Zhang Y, Baskin JM, Baskin CC, Xiong Z, et al. A review of the seed biology of Paeonia species (Paeoniaceae), with particular reference to dormancy and germination. Planta. 2019;249:291−303. doi: CrossRef
10. Du GH, Yuan TY, Zhang YX. The potential of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment and modulation of pain. Adv Pharmacol. 2016;75:325−61. doi: CrossRef
11. Wu M, Yu Z, Li X, Zhang X, Wang S, Yang S, et al. Paeonol for the treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: a pharmacological and mechanistic overview. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:690116. doi: CrossRef
12. Lim TK. Paeonia lactiflora. In: Edible medicinal and non-medicinal plants: Volume 8, Flowers. Dordrecht: Springer Science & Business Media; 2014. pp. 559−96. doi: CrossRef
13. Kim J, Choi J, Kang SS, Lee S. Simultaneous determination of phytochemical constituents in Paeonia lactiflora extracts using the HPLC-UV method. J Appl Biol Chem. 2021;64(1):13−7. doi: CrossRef
14. Ekiert H, Klimek-Szczykutowicz M, Szopa A. Paeonia × suffruticosa (Moutan Peony)—a review of the chemical composition, traditional and professional use in medicine, position in cosmetics industries, and biotechnological studies. Plants. 2022;11(23):3379. doi: CrossRef
15. Seo CS, Kim JH, Shin HK, Kim BS. Quantitative analysis of (+)-catechin, paeoniflorin, and paeonol in moutan radicis cortex and its processed products. Kor J Pharmacogn. 2016;47(3):237−45.
16. Zhao C, Luo C, Ling W, Yin M, Qin S. Modern research progress on pharmacological effects of paeoniflorin. IOP Conf EES. 2020;559(1):12015. doi: CrossRef
17. Abdel-Hafez AA, Meselhy MR, Nakamura N, Hattori M, Watanabe H, Mukarami Y, et al. Effects of paeoniflorin derivatives on scopolamine-induced amnesia using a passive avoidance task in mice; structure-activity relationship. Biol Pharm Bull. 1998;21(11):1174−9. doi: CrossRef
18. Shibata S, Nakahara M. Studies on the constituents of Japanese and Chinese crude drugs. VIII. Paeoniflorin, a glucoside of Chinese paeony root. Chem Pharm Bull. 1963;11(3): 372−8.
19. Kaneda M, Iitaka Y, Shibata S. The absolute structures of paeoniflorin, albiflorin, oxypaeoniflorin and benzoylpaeoniflorin isolated from Chinese paeony root. Tetrahedron. 1972; 28(16):4309−17. doi: CrossRef
20. Adki KM, Kulkarni YA. Chemistry, pharmacokinetics, pharmacology and recent novel drug delivery systems of paeonol. Life Sci. 2020;250:117544. doi: CrossRef
21. Wang Y, Li BS, Zhang ZH, Wang Z, Wan YT, Wu FW, et al. Paeonol repurposing for cancer therapy: from mechanism to clinical translation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165:115277. doi: CrossRef
22. Harada M, Yamashita A. Pharmacological studies on the root bark of Paeonia moutan. I. Central effects of paeonol. J Pharm Soc Jpn. 1969;89(9):1205−11. doi: CrossRef
23. Deng LJ, Lei YH, Chiu TF, Qi M, Gan H, Zhang G, et al. The anticancer effects of paeoniflorin and its underlying mechanisms. Nat Prod Commun. 2019;14(9):1−8. doi: CrossRef
24. Xiang Y, Zhang Q, Wei S, Huang C, Li Z, Gao Y. Paeoniflorin: a monoterpene glycoside from plants of Paeoniaceae family with diverse anticancer activities. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2020;72(4):483−95. doi: CrossRef
25. Wang XZ, Xia L, Zhang XY, Chen Q, Li X, Mou Y, et al. The multifaceted mechanisms of paeoniflorin in the treatment of tumors: state-of-the-art. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;149:112800. doi: CrossRef
26. Li W, Qi Z, Wei Z, Liu S, Wang P, Chen Y, et al. Paeoniflorin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human glioma cells via microRNA-16 up-regulation and matrix metalloproteinase-9 downregulation. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(2):2735−40. doi: .org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3718
27. Nie XH, Ou-Yang J, Xing Y, Li DY, Dong XY, Liu RE, et al. Paeoniflorin inhibits human glioma cells via STAT3 degradation by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:5611−22. doi: CrossRef
28. Ouyang J, Xu H, Li M, Dai X, Fu F, Zhang X, et al. Paeoniflorin exerts antitumor effects by inactivating S phase kinase-associated protein 2 in glioma cells. Oncol Rep. 2018;39(3):1052−62. doi: CrossRef
29. Wang Z, Liu Z, Yu G, Nie X, Jia W, Liu RE, et al. Paeoniflorin inhibits migration and invasion of human glioblastoma cells via suppression transforming growth factor β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Neurochem Res. 2018;43:760−74. doi: CrossRef
30. Wang Z, Yu G, Liu Z, Zhu J, Chen C, Liu RE, et al. Paeoniflorin inhibits glioblastoma growth in vivo and in vitro: a role for the Triad3A-dependent ubiquitin proteasome pathway in TLR4 degradation. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10:887. doi: CrossRef
31. Yu G, Wang Z, Zeng S, Liu S, Zhu C, Xu R, et al. Paeoniflorin inhibits hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced migration and invasion and actin rearrangement via suppression of c-Met-mediated RhoA/ROCK signaling in glioblastoma. BioMed Res Int. 2019;2019:9053295. doi: CrossRef
32. Gao ZW, Huang YY, Zhang JQ, Rong JY, Qiao GY, Chen N, et al. Paeoniflorin elicits the anti-proliferative effects on glioma cell via targeting translocator protein 18 KDa. J Pharmacol Sci. 2021;145(1):115−21. doi: CrossRef
33. Liu Z, Wang Z, Chen D, Liu X, Yu G, Zhang Y, et al. Paeoniflorin inhibits EMT and angiogenesis in human glioblastoma via K63-linked C-Met polyubiquitination-dependent autophagic degradation. Front Oncol. 2022;12:785345. doi: CrossRef
34. Nie XH, Qiu S, Xing Y, Xu J, Lu B, Zhao SF, et al. Paeoniflorin regulates NEDD4L/STAT3 pathway to induce ferroptosis in human glioma cells. J Oncol. 2022;2022:6093216. doi: CrossRef
35. Wu H, Li W, Wang T, Shu Y, Liu P. Paeoniflorin suppresses NF-κB activation through modulation of IκBα and enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2008;62(9):659−66. doi: CrossRef
36. Fang S, Zhu W, Zhang Y, Shu Y, Liu P. Paeoniflorin modulates multidrug resistance of a human gastric cancer cell line via the inhibition of NF-κB activation. Mol Med Rep. 2012;5(2):351−6. doi: CrossRef
37. Zheng YB, Xiao GC, Tong SL, Ding Y, Wang QS, Li SB, et al. Paeoniflorin inhibits human gastric carcinoma cell proliferation through up-regulation of microRNA-124 and suppression of PI3K/Akt and STAT3 signaling. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(23): 7197−207. doi: CrossRef
38. Wang ZF, Ma DG, Wang L, Feng L, Fu JW, Li Y, et al. Paeoniflorin inhibits migration-and invasion-promoting capacities of gastric cancer associated fibroblasts. Chin J Integr Med. 2019;25:837−44. doi: CrossRef
39. Niu K, Liu Y, Zhou Z, Wu X, Wang H, Yan J. Antitumor effects of paeoniflorin on hippo signaling pathway in gastric cancer cells. J Oncol. 2021;2021:4724938. doi: CrossRef
40. Kim TW. Paeoniflorin induces ER stress-mediated apoptotic cell death by generating Nox4-derived ROS under radiation in gastric cancer. Nutrients. 2023;15(24):5092. doi: CrossRef
41. Hu S, Sun W, Wei W, Wang D, Jin J, Wu J, et al. Involvement of the prostaglandin E receptor EP2 in paeoniflorin-induced human hepatoma cell apoptosis. Anticancer Drugs. 2013;24(2):140−9. doi: CrossRef
42. Lu JT, He W, Song SS, Wei W. Paeoniflorin inhibited the tumor invasion and metastasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2014;115(7):427−33. doi: CrossRef
43. Liu H, Zang L, Zhao J, Wang Z, Li L. Paeoniflorin inhibits cell viability and invasion of liver cancer cells via inhibition of Skp2. Oncol Lett. 2020;19(4):3165−72. doi: .org/10.3892/ol.2020.11424
44. Zhou Y, Liu X, Gao Y, Tan R, Wu Z, Zhong Q, et al. Paeoniflorin affects hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway through downregulation of 5-HT1D. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021;22(9):1246−53. doi: CrossRef
45. Gao M, Zhang D, Jiang C, Jin Q, Zhang J. Paeoniflorin inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth by reducing PD-L1 expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;166:115317. doi: CrossRef
46. Li J, Zhu C, Zhang Z, Zheng X, Wang C, Zhang H. Paeoniflorin increases the anti-tumor efficacy of sorafenib in tumor-bearing mice with liver cancer via suppressing the NF-κB/PD-l1 axis. Heliyon. 2024;10:e24461. doi: CrossRef
47. Zhang Q, Yuan Y, Cui J, Xiao T, Jiang D. Paeoniflorin inhibits proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells through suppressing the Notch-1 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;78:197−203. doi: CrossRef
48. Zhou Z, Wang S, Song C, Hu Z. Paeoniflorin prevents hypoxia-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer cells. Oncol Targets Ther. 2016;9: 2511−8. doi: CrossRef
49. Zhang J, Yu K, Han X, Zhen L, Liu M, Zhang X, et al. Paeoniflorin influences breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion via inhibition of the Notch?1 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(1):1321−5. doi: CrossRef
50. Wang Y, Wang Q, Li X, Luo G, Shen M, Shi J, et al. Paeoniflorin sensitizes breast cancer cells to tamoxifen by downregulating microRNA-15b via the FOXO1/CCND1/β-catenin axis. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021;15:245−57. doi: CrossRef
51. Zhang P, Wu N, Song ZJ, Tai ZF. Paeoniflorin enhances the sensitivity of ER-positive breast cancer cells to tamoxifen through promoting sirtuin 4. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:6730559. doi: CrossRef
52. Wang H, Zhou H, Wang CX, Li YS, Xie HY, Luo JD, et al. Paeoniflorin inhibits growth of human colorectal carcinoma HT 29 cells in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012;50(5):1560−7. doi: CrossRef
53. Yue M, Li S, Yan G, Li C, Kang Z. Paeoniflorin inhibits cell growth and induces cell cycle arrest through inhibition of FoxM1 in colorectal cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 2018;17(2):240−9. doi: CrossRef
54. Zhang JW, Li LX, Wu WZ, Pan TJ, Yang ZS, Yang YK. Anti-tumor effects of paeoniflorin on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human colorectal cancer cells. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:6405−13. doi: CrossRef
55. Wang Y, Zhou Y, Lin H, Chen H, Wang S. Paeoniflorin inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of ulcerative colitis-associated colon cancer by targeting EGFL7. J Oncol. 2022;2022:7498771. doi: CrossRef
56. Su Z, Hu B, Li J, Zeng Z, Chen H, Guo Y, et al. Paeoniflorin inhibits colorectal cancer cell stemness through the miR-3194-5p/catenin beta-interacting protein 1 axis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2023;39:1011−21. doi: CrossRef
57. Chang X, Feng X, Du M, Li S, Wang J, Wang Y, et al. Pharmacological effects and mechanisms of paeonol on antitumor and prevention of side effects of cancer therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1194861. doi: CrossRef
58. Xu SP, Sun GP, Shen YX, Wei W, Peng WR, Wang H. Antiproliferation and apoptosis induction of paeonol in HepG2 cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13(2):250. doi: CrossRef
59. Xu SP, Sun GP, Shen YX, Peng WR, Wang H, Wei W. Synergistic effect of combining paeonol and cisplatin on apoptotic induction of human hepatoma cell lines. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007;28(6):869−78. doi: CrossRef
60. Sun GP, Wang H, Xu SP, Shen YX, Wu Q, Chen ZD, et al. Anti-tumor effects of paeonol in a HepA-hepatoma bearing mouse model via induction of tumor cell apoptosis and stimulation of IL-2 and TNF-α production. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;584:246−52. doi: CrossRef
61. Zhang C, Hu S, Cao M, Xiao G, Li Y. Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of paeonol on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2008;19(4):401−9. doi: CrossRef
62. Chen B, Ning M, Yang G. Effect of paeonol on antioxidant and immune regulatory activity in hepatocellular carcinoma rats. Molecules. 2012;17(4):4672−83. doi: CrossRef
63. Li Q, Zhang Y, Sun J, Bo Q. Paeonol?mediated apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by NF?κB pathway. Oncol Lett. 2019;17(2):1761−7. doi: CrossRef
64. Cai M, Shao W, Yu H, Hong Y, Shi L. Paeonol inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion and induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating miR-21-5p/KLF6 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:5931−43. doi: CrossRef
65. Liu H, Zhang C. Paeonol induces antitumor effects in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through survivin via the cyclooxygenase-2/prostaglandin E2 signaling pathway. Translat Cancer Res. 2020;9(11):7183. doi: CrossRef
66. Lei Y, Li HX, Jin WS, Peng WR, Zhang CJ, Bu LJ, et al. The radio-sensitizing effect of paeonol on lung adenocarcinoma by augmentation of radiation-induced apoptosis and inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Radiat Biol. 2013;89(12):1079−86. doi: CrossRef
67. Tian Y, Chen C, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Xie H. Paeonol inhibits migration, invasion and bone adhesion of small cell lung cancer cells. Curr Signal Transduct Ther. 2015;10(2):126−30.
68. Jiang Y, Li Y, Yang T, Shi X, Suo H, Zhang W, et al. Design, synthesis, and anti-lung adenocarcinoma activity research of novel paeonol Schiff base derivatives containing a 1,2,3-triazole moiety. J Chin Chem Soc. 2020;67(1):165−71. doi: CrossRef
69. Zhang L, Chen WX, Li LL, Cao YZ, Geng YD, Feng XJ, et al. Paeonol suppresses proliferation and motility of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by disrupting STAT3/NF-κB signaling. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:572616. doi: CrossRef
70. Fan Y, Chen X, Zhang G. Paeonol enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis of human lung cancer cells by upregulating death receptors-4 and -5 via ROS-JNK/ERK-CHOP signaling. Trop J Pharm Res. 2021;20(3):467−73. doi: CrossRef
71. Lv J, Zhu S, Chen H, Xu Y, Su Q, Yu G, et al. Paeonol inhibits human lung cancer cell viability and metastasis in vitro via miR-126-5p/ZEB2 axis. Drug Dev Res. 2022;83(2): 432−46. doi: CrossRef
72. Zhang L, Wu L, Zhu X, Mei J, Chen Y. Paeonol represses A549 cell glycolytic reprogramming and proliferation by decreasing m6A modification of Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. J Physiol Investig. 2023;66(4):248−56. doi: CrossRef
73. Zhang C, Zhang J, Guo K. Paeonol upregulates expression of tumor suppressors TNNC1 and SCARA5, exerting anti-tumor activity in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Naunyn Schmiedeberg Arch Pharmacol. 2024;397:1−11. doi: CrossRef
74. Ye JM, Deng T, Zhang JB. Influence of paeonol on expression of COX-2 and p27 in HT-29 cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(35):4410. doi: CrossRef
75. Li M, Tan SY, Zhang J, You HX. Effects of paeonol on intracellular calcium concentration and expression of RUNX3 in LoVo human colon cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7(5):1425−30. doi: CrossRef
76. Li M, Tan SY, Wang XF. Paeonol exerts an anticancer effect on human colorectal cancer cells through inhibition of PGE2 synthesis and COX-2 expression. Oncol Rep. 2014;32(6):2845−53. doi: CrossRef
77. Li M, Tan SY, Yu YJ. Paeonol suppresses invasion, migration, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells through inhibition of COX-2 and PGE2. Res Sq. 2020 [Preprint]. doi: CrossRef
78. Liu LH, Shi RJ, Chen ZC. Paeonol exerts anti?tumor activity against colorectal cancer cells by inducing G0/G1 phase arrest and cell apoptosis via inhibiting the Wnt/β?catenin signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2020;46(2):675−84. doi: CrossRef
79. Li N, Fan LL, Sun GP, Wan XA, Wang ZG, Wu Q, et al. Paeonol inhibits tumor growth in gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(35):4483. doi: CrossRef
80. Yang S, Wang X, Zhong G. Paeonol inhibits the growth of gastric cancer cells via suppressing HULC expression. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2016;9(7):13900−8.
81. Fu J, Yu L, Luo J, Huo R, Zhu B. Paeonol induces the apoptosis of the SGC?7901 gastric cancer cell line by downregulating ERBB2 and inhibiting the NF?κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(3):1473−83. doi: CrossRef
82. Li M, Cai O, Yu Y, Tan S. Paeonol inhibits the malignancy of apatinib-resistant gastric cancer cells via LINC00665/miR-665/MAPK1 axis. Phytomedicine. 2022;96:153903. doi: CrossRef
83. Lyu ZK, Li CL, Jin Y, Liu YZ, Zhang X, Zhang F, et al. Paeonol exerts potential activities to inhibit the growth, migration and invasion of human gastric cancer BGC823 cells via downregulating MMP?2 and MMP?9. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(5):7513−9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7576
84. Yin J, Wu N, Zeng F, Cheng C, Kang K, Yang H. Paeonol induces apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells. Acta Histochem. 2013;115(8):835−9. doi: CrossRef
85. Li B, Yang J, Hong L, Tang J, Li Q, Fu Q. Paeonol induces apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells through the AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2017;10(7): 10170−8.
86. Zhou HM, Sun QX, Cheng Y. Paeonol enhances the sensitivity of human ovarian cancer cells to radiotherapy-induced apoptosis due to down-regulation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt/phosphatase and tensin homolog pathway and inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(4):3213−20. doi: CrossRef
87. Gao L, Wang Z, Lu D, Huang J, Liu J, Hong L. Paeonol induces cytoprotective autophagy via blocking the Akt/mTOR pathway in ovarian cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(8):609. doi: CrossRef
88. Zhou YX, Gong XH, Zhang H, Peng C. A review on the pharmacokinetics of paeoniflorin and its anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;130:110505. doi: CrossRef
89. Manayi A, Omidpanah S, Barreca D, Ficarra S, Daglia M, Nabavi SF, et al. Neuroprotective effects of paeoniflorin in neurodegenerative diseases of the central nervous system. Phytochem Rev. 2017;16:1173−81. doi: CrossRef
90. Hong H, Lu X, Wu C, Chen J, Chen C, Zhang J, et al. A review for the pharmacological effects of paeoniflorin in the nervous system. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:898955. doi: CrossRef
91. Wang XL, Feng ST, Wang YT, Chen NH, Wang ZZ, Zhang Y. Paeoniflorin: a neuroprotective monoterpenoid glycoside with promising anti-depressive properties. Phytomedicine. 2021;90:153669. doi: CrossRef
92. Zhang L, Li DC, Liu LF. Paeonol: pharmacological effects and mechanisms of action. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;72:413−21. doi: CrossRef
93. Lee B, Shin YW, Bae EA, Han SJ, Kim JS, Kang SS, et al. Antiallergic effect of the root of Paeonia lactiflora and its constituents paeoniflorin and paeonol. Arch Pharm Res. 2008;31:445−50. doi: CrossRef
94. Zhu YL, Wang LY, Wang JX, Wang C, Wang CL, Zhao DP, et al. Protective effects of paeoniflorin and albiflorin on chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression in mice. Chin J Nat Med. 2016;14(8):599−606. doi: CrossRef
95. Zhou J, Wang L, Wang J, Wang C, Yang Z, Wang C, et al. Paeoniflorin and albiflorin attenuate neuropathic pain via MAPK pathway in chronic constriction injury rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016: 8082753. doi: CrossRef
96. Nizamutdinova IT, Jin YC, Kim JS, Yean MH, Kang SS, Kim YS, et al. Paeonol and paeoniflorin, the main active principles of Paeonia albiflora, protect the heart from myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Planta Med. 2008;74(1):14−8. doi: CrossRef
97. Sun M, Huang L, Zhu J, Bu W, Sun J, Fang Z. Screening nephroprotective compounds from cortex Moutan by mesangial cell extraction and UPLC. Arch Pharm Res. 2015;38:1044−53. doi: CrossRef
98. Sun L, Liu L, Zong S, Wang Z, Zhou J, Xu Z, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine Guizhi Fuling capsule used for therapy of dysmenorrhea via attenuating uterus contraction. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;191:273−9. doi: CrossRef
99. Wang X, Shi Y, Xu L, Wang Z, Wang Y, Shi W, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine prescription Guizhi Fuling pills in the treatment of endometriosis. Int J Med Sci. 2021;18(11):2401. doi: CrossRef