INTRODUCTION
An inhibitor of calcium ion influx called diltiazem hydrochloride is used in the treatment of hypertension, angina pectoris, coronary artery disease, and cardiac arrhythmias [1,2]. It is an orally as well as intravenously administered drug and has a short duration of action [3,4]. Additionally, diltiazem also has weak negative chronotropic and ionotropic effects (Fig. 1) [5]. Citrus fruits naturally contain a flavanone-7-O-glycoside called naringin [6]. It has various pharmacological effects such as antioxidant activity, anti-carcinogenic activity, and anti-diabetic activity. It also inhibits a few cytochrome P450 enzymes, such as CYP3A4 and CYP1A2, that may in-vitro cause a number of medication interactions [7]. Naringin may possibly function as a dual CYP3A4 and P-gp inhibitor (Fig. 2) [8].
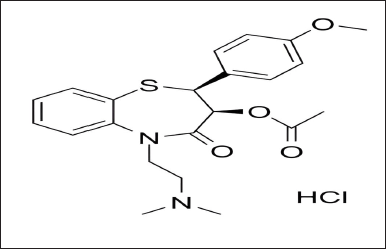 | Figure 1. Diltiazem HCl. [Click here to view] |
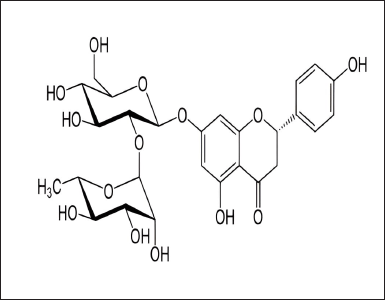 | Figure 2. Naringin. [Click here to view] |
Diltiazem has been analyzed by various methods like reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography [9], high performance thin liquid chromatography (HPTLC) [10], Flourescence spectroscopic studies [11], GC [12], FT-Raman spectroscopy [13], liquid chromatography-ultraviolet spectroscopy [14], RP-UPLC [15], thin layer chromatography (TLC), and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) [16]. Similarly, Naringin has also been estimated by various methods such as Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry [17], Capillary electrophoresis [18], HPLC [19], HPTLC [20], ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry [21], TLC, and fourier transform infrared spectroscopy [22].
By reviewing many literatures, it has been found that many analytical methods are available to analyze Diltiazem and Naringin separately. Simultaneously, we also found literatures indicating the increase in oral bioavailability of Diltiazem by the presence of Naringin. There also exists a high probability of concomitant use of Diltiazem and Naringin in hypertensive patients, but there is a lack of simple and suitable methods for their routine analysis. Thus, there is a need for an analytical method development for their routine quality control evaluation. Hence, two novel and advanced spectrophotometric methods were developed and validated to simultaneously estimate the accurate amount of Diltiazem and Naringin. As recently, there are no such spectrophotometric methods available to analyze Diltiazem and Naringin simultaneously so, further any such methods can be developed for simultaneous estimation of Diltiazem and Naringin.
During the development phase, many of the pharmaceuticals generate impurities that must be detected and quantitated. The pharmaceutical analysis thus plays an important role in identifying and preventing errors for the safety or to improve the bioperformance of the drugs.
Q-ratio method
The simultaneous equations approach has been modified by the “absorption ratio method,” as well. A constant value unaffected by the concentration or path length is known as “Hufner’s Quotient” or Q-value. It entails determining absorbance at two different wavelengths, one of which is the iso-absorptive point and the other which is the maximum of one of the components [23].
Equations in mathematics can be used to determine each component’s concentration:
Cx = (QM-QY/QX-QY)*A/a1 (1)
Cy = (QM-QX/QY-QX)*A/a2 (2)
where,
Cx = Concentrations of x
Cy = Concentrations of y
A = Absorbance of sample at isoabsorpitive wavelength and
a1 and a2 = Absorptivity of x and y, respectively, at iso-absorptive wavelength.
Absorptivity factor method
The concentration of two medications in binary mixes is determined using the modified absorption method for UV spectroscopy, where the maximum difference in the absorptivity values of the two drugs must exist and an iso-absorptive point must not exist [24].
For the drugs in a binary mixture X and Y, where the drug Y’s concentration can be found by using any well-established spectrophotometric methods or using a linear regression equation between its concentration and absorbance at the wavelength where the maximum absorption has occurred, and also where there is no drug interference. Utilizing the absorptivity factor approach, the concentration of drug X is determined. The absorptivity factor method is used to determine the ratio between the two absorbtivities (aX, aY) at the crossing point with the same absorbance value. This is termed as absorptivity factor point (F). This can be summed up as follows:
AX = AY
aX bX cX = aY bY cY (Where, bX = bY = 1 cm)
? aX cX = aY cY ? aX/aY = cY/cX
aX/aY = F ? aX = FaY
where,
F = Absorptivity factor
AX and aY = The absorptivities of X and Y, respectively.
A regression equation describing the linear relationship between the absorbance of Y and its corresponding concentration at the absorptivity factor point can be used to determine the total concentration of the combination (FcX + cY). The concentration of drug X also can be determined from the concentration of Y using the following equation:
cX = [(FcX + cY ) – cY ] / F
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The suppliers of Diltiazem HCl and Naringin were Yarrow Chem Products in Mumbai, India. Methanol was used as a solvent and was purchased from S.D Fine Chemicals Ltd, in Mumbai, India. A twin-beam Shimadzu UV-1800 spectrophotometer was used for spectrophotometric measurements at a wavelength range of 200–500 nm. Weighing was done using a Shimadzu ATY224R electronic analytical balance.
Preparation of standard solutions
Q-ratio method: Placed 10.0 mg of Diltiazem in a 10.0 ml volumetric flask after weighing it precisely. It was dissolved in methanol, and the same solvent was used to increase the volume to the appropriate level. This was regarded as the stock solution. A 10.0 ml of volumetric flask was filled with methanol after pipetting 1.0 ml from the stock solution into it. A pipette was used to transfer 1.0 ml of this solution to a 10.0 ml of volumetric flask and the remaining capacity was filled with methanol. In the UV visible spectrophotometer, this solution was scanned between 200 and 500 nm. Similarly, for the preparation of Naringin also same process was followed to that of Diltiazem.
Absorptivity factor method: Diltiazem and Naringin were prepared in a similar manner to that of the Q-ratio method. However, for the preparation of Naringin, a concentration of 42 µg/ml was extracted from the stock solution.
Preparation of sample solution
Weighed precisely 103.3 mg of the artificial mixture of Diltiazem and Naringin and deposited it into a volumetric flask with a volume of 100.0 ml. Methanol was used to dissolve it, and the same solvent was also used to increase the volume to the appropriate level. This was considered as the stock solution. 5.0 ml of stock solution was pipetted into a volumetric flask with a capacity of 50.0 ml, and the remaining volume was filled with methanol. In the UV-visible spectrophotometer, this solution was scanned between 200 and 500 nm.
Development of Q-ratio method for Diltiazem and Naringin
The individual spectrum of Diltiazem and Naringin were overlaid to determine the iso-absorptive point which is selected as λ1, 257 nm (Fig. 3). Many experiments were performed using λmax values of both Diltiazem and Naringin. From the results obtained, λ2 is selected as λmax value of Naringin, i.e., 275 nm. The absorbance was measured for the two standard drug solutions along with their synthetic mixtures taking the wavelength of iso-absorptive point as λ1 and λmax of Naringin as λ2.
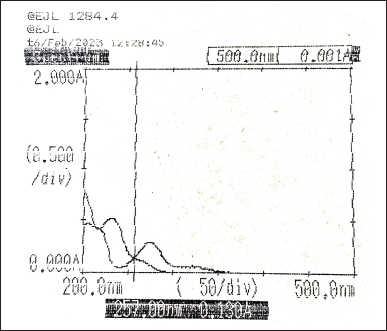 | Figure 3. Overlay spectra of Diltiazem and Naringin (10 µg/ml). [Click here to view] |
Development of absorptivity factor method for Diltiazem and Naringin
Taking different concentrations of Diltiazem and Naringin, the individual spectra were obtained and overlaid to determine their absorptivity factor points. The absorptivity values were obtained at 229 nm (Fig. 4) and 247 nm (Fig. 5). Then, the absorbance of the two drugs was measured and recorded along with the synthetic mixture.
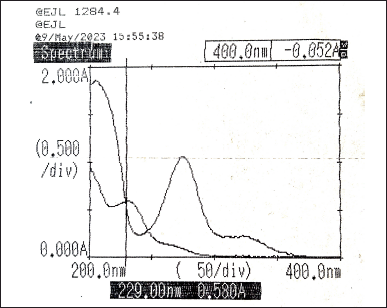 | Figure 4. Overlay spectra of Diltiazem and Naringin showing absorptivity factor point at 229 nm. [Click here to view] |
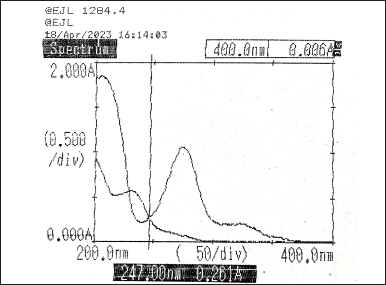 | Figure 5. Overlay spectra of Diltiazem and Naringin showing absorptivity factor point at 247 nm. [Click here to view] |
Naringin was synthesized in a series of concentrations ranging from 5 to 50 µg/ml, and its first derivative spectra at 226 nm were used to monitor it. The calibration curve for the first derivative of the Naringin spectra was then constructed at 226 nm. The concentration of the naringin was now calculated using the regression equation obtained from the curve. The concentration of Diltiazem was then calculated by substituting those values with the zero-order values at 229 or 257 nm using the formula for the absorptivity factor technique.
Spectrophotometric methods validation
Linearity
For the Q-ratio method, a series of concentrations was prepared from 0.2 to 80 µg/ml for Diltiazem and 0.1–50 µg/ml for Naringin. Similarly, for the absorptivity factor method, a series of concentrations was prepared from 5 to 50 µg/ml for Diltiazem and Naringin. Each concentration was then measured under the UV-visible spectrophotometer at their respective wavelengths. With the recorded absorbance, a graph was plotted between concentrations versus absorbance. From this graph, the regression equation and correlation coefficient value were noted down (Table 2).
Precision
The precision of the method was evaluated on the basis of intra day and inter day precision. The absorbance of Diltiazem, Naringin, and sample were measured at their respective wavelengths for both methods. The process was repeated six times. Absorbance was recorded for all six solutions and the calculations were made to determine the relative standard deviation, the mean, and the standard deviation (Table 2).
Accuracy
In the accuracy parameter, a recovery study was performed for both methods.
The standard addition approach was used to conduct recovery tests using synthetic combination solutions for both Diltiazem and Naringin which involves preparing three different concentrations of Diltiazem and Naringin separately and adding those solutions individually to the pre-analyzed sample solutions that are prepared at six different 50 ml volumetric flask. The volume was raised to the proper level using the same solvent. The absorbances at the chosen wavelengths were measured, and the amount and percentage of recoveries were computed (Table 1).
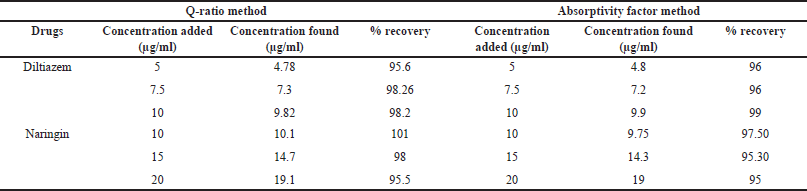 | Table 1. Recovery studies of the proposed methods. [Click here to view] |
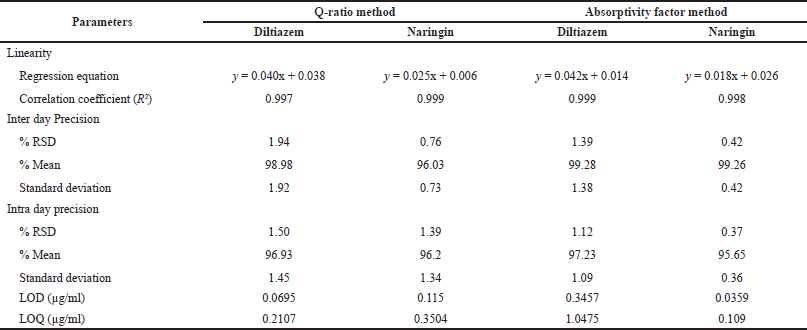 | Table 2. Summary table of validation parameters for both the method. [Click here to view] |
Limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantitation (LOQ)
Concentrations ranging from 0.2 to 80 µg/ml and 0.1 to 50 µg/ml were prepared for Diltiazem and Naringin for the Q-ratio method. Similarly, a concentration range from 0.5 to 50 µg/ml was prepared for Diltiazem and Naringin for the absorptivity factor method. Their absorbance was recorded at their respective wavelengths.
The following equations were used to mathematically compute the LOD and LOQ (Table 2):
RESULT AND DISCUSSION:
Q-Ratio method
With correlation coefficient values of 0.997 and 0.999 for Diltiazem and Naringin, respectively, the method demonstrated good linearity over the ranges of 0.2–80 and 0.1–50 µg/ml. The intra-day RSD for precision was reported to be 1.50 and 1.39, whereas the inter-day RSD was reported to be 1.94 and 0.76. The recovery percentages for accuracy criteria were 95.6%–98.26% and 95.5%–101%. For Diltiazem and Naringin, the LOD was determined to be 0.0695 and 0.115 µg/ml, and the LOQ was determined to be 0.2107 and 0.3504 µg/ml, respectively.
Absorptivity factor method
With correlation coefficient values of 0.999 and 0.998 for Diltiazem and 0.998 and 0.997 for Naringin at wavelengths of 229 and 247 nm, respectively, the technique demonstrated good linearity over the range of 5–50 µg/ml. The intra-day RSD for precision was reported to be 1.12 and 0.37, whereas the inter-day RSD was reported to be 1.39 and 0.42. The recovery percentages for accuracy parameters were 96%–99% and 95%–97.50%. For Diltiazem and Naringin, the LOD was determined to be 0.3457 µg/ml and 0.0359 µg/ml, and the LOQ was determined to be 1.0475 and 0.109 µg/ml, respectively.
For the quantification of Diltiazem and Naringin in synthetic mixtures, two UV spectrophotometric techniques were created and verified. In the first approach, the analysis was done at the iso-absorptive point of Diltiazem and Naringin as well as the maximum concentration of Naringin. With the second method, you can use a straightforward mathematical equation to determine the concentration of two medications in a binary mixture. When the developed procedures were validated, it was discovered that they were exact, accurate, and repeatable. These spectrophotometric methods are so easy to use, repeatable, accurate, and affordable. Consequently, a combined formulation analysis of Diltiazem and Naringin is possible.
CONCLUSION
Two simple, sensitive, novel, and reproducible methods, i.e., the Q-ratio method and absorptivity factor method, were developed for the determination of the mixtures of Diltiazem and Naringin in a synthetic mixture. The methods used were validated in accordance with the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) recommendations, and the results for the validation parameters met the requirements outlined by the ICH guidelines. As a result, the approach has been validated and is suitable for use in regular quality control analyses of synthetic mixtures containing Diltiazem and Naringin.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors would like to give their warmest thanks to Dr. Nihar Ranjan Bhuyan, Principal, for the support and encouragement. The authors also want to convey their sincere gratitude to Dr. H.P. Chhetri, Director, Himalayan Pharmacy Institute, Majhitar, Sikkim, India, for providing the facilities needed to effectively finish the research work.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
There is no funding to report.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors report no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
This study does not involve experiments on animals or human subjects.
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated and analyzed are included in this research article.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used artificial intelligence (AI)-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
REFERENCES
1. Mazzo DJ, Obetz CL, Shuster J. Diltiazem hydrochloride. In: Brittain HG, editor. Analytical profiles of drug substances and excipients. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press; 1994. pp 53–98.
2. Akbari J, Saeedi M, Semnani KM, Ghasemi M, Eshaghi M, Eghbali M, et al. An ecofriendly and hopeful promise platform for delivering hydrophilic wound healing agents in topical administration for wound disorder: diltiazemloaded niosomes. J Pharm Innov. 2023;18:1111–27.
3. Samaha D, Shehayeb R, Kyriacos S. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles of diltiazem modified-release formulations. Dissolution Technol. 2009;16(2):41–6.
4. Arafat MO. Simple HPLC validated method for the determination of diltiazem hydrochloride in human plasma. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2014;6(9):213–6.
5. Rovei V, Mitchard M, Morselli PL. Simple, sensitive and specific gas chromatographic method for quantification of diltiazem in human body fluids. J Chromatogr A. 1977;138(2):391–8.
6. Iswariya T, Pradesh A, Gupta S. Bioavailability enhancers: an overview. IJARIIT. 2019;5(2):825–9.
7. PubChem. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US). National Center for Biotechnology Information [Internet]; 2004 [cited 2024 Dec 21]. Available from: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Naringin
8. Choi JS, Han HK. Enhanced oral exposure of diltiazem by the concomitant use of naringin in rats. Int J Pharm. 2005;305(1-2):122–8.
9. Patil BR, Bhusnure OG, Paul BN, Ghodke AY, Mulaje SS. Analytical method development and validation for the estimation of diltiazem hydrochloride in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form by RP-HPLC. Int J drug Regul Aff. 2014;2(2):78–84.
10. Devarajan PV, Dhavse VV. High-performance thin-layer chromatographic determination of diltiazem hydrochloride as bulk drug and in pharmaceutical preparations. J Chromatogr B. 1998;706(2):362–6.
11. Bao C, Wang J, Tong X, Tang X, Wang Q. The fluorescence spectroscopic studies on the interaction of diltiazem hydrochloride with bovine serum albumin. J Appl Life Sci Int. 2018;18(3):1–9.
12. Alebi?-Kolbah T, Plavši? F. Determination of serum diltiazem concentrations in a pharmacokinetic study using gas chromatography with electron capture detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1990;8(8-12):915–8.
13. Vergote GJ, Vervaet C, Remon JP, Haemers T, Verpoort F. Near-infrared FT-raman spectroscopy as a rapid analytical tool for the determination of diltiazem hydrochloride in tablets. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2002;16(1-2):63–7.
14. Sultana N, Arayne MS, Ali SN. An ultra-sensitive and selective LC-UV method for the simultaneous determination of pravastatin, diltiazem, naproxen sodium and meloxicam in API, pharmaceutical formulations and human serum. Am J Appl Chem. 2013;1(1):1–8.
15. Bajetha D, Mangla B, Joshi SK. Method development and validation for the quantitation estimation of diltiazem hcl in tablet dosage form by RP-UPLC. Int J Innov Pharm Sci Res. 2016;4(4):340–52.
16. Sugihara J, Sugawara Y, Ando H, Harigaya S, Etoh A, Kohno K. Studies on the metabolism of diltiazem in man. J Pharmacobio-Dyn. 1984;7(1):24–32.
17. Xiong X, Jiang J, Duan J, Xie Y, Wang J, Zhai S. Development and validation of a sensitive liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of naringin and its metabolite, naringenin, in human plasma. J Chromatogr Sci. 2014;52(7):654–60.
18. Akiyama T, Yamada T, Maitani T. Analysis of enzymatically glucosylated flavonoids by capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A. 2000;895(1-2):279–83.
19. Ishii K, Furuta T, Kasuya Y. Determination of naringin and naringenin in human urine by high performance liquid chromatography utilizing solid-phase extraction. J Chromatogr B. 1997;704(1-2):299–305.
20. Alam P, Siddiqui NA, Al-Rehaily AJ, Alajmi MF, Basudan OA, Khan TH. Stability-indicating densitometric high-performance thin-layer chromatographic method for the quantitative analysis of biomarker naringin in the leaves and stems of Rumex vesicarius L. JPC-J Planar Chromat. 2014;27(3):204–9.
21. Wen J, Qiao Y, Yang J, Liu X, Song Y, Liu Z, et al. UPLC–MS/MS determination of paeoniflorin, naringin, naringenin and glycyrrhetinic acid in rat plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Si-Ni-San decoction. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012;66:271–7.
22. Hakim A, Loka IN, Prastiwi NW. New method for isolation of naringin compound from citrus maxima. Nat Resour. 2019;10(8):299–304.
23. Patel D, Panchal D, Patel K, Dalwadi M, Upadhyay U. A review on UV visible spectroscopy. IJCRT. 2022;10(10):399–411.
24. Samir A, Salem H, Abdelkawy M. New developed spectrophotometric method for simultaneous determination of salmeterol xinafoate and fluticasone propionate in bulk powder and seritide® diskus inhalation. Bull Fac Pharm Cairo Univ. 2012;50(2):121–6.