INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a worldwide concern due to its high prevalence. According to the International Diabetes Federation data in 2021, Indonesia ranks 5th with the highest number of residents suffering from DM from all over the world. Diabetes is a chronic, metabolic disease characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose, which leads over time to serious damage to the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves [1]. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is the most common type of DM. The pathophysiology underlies that T2DM is insulin resistance, which involves various tissues, mainly muscle, adipose, and liver tissues [2]. The insulin resistance condition itself affects glucose absorption, especially the muscle tissue, which has an 80% role in the uptake of blood glucose after a meal [3].
GLUT4 is a transporter that helps the internalization of glucose into the cells. In order for GLUT4 to have this function, the insulin signaling pathway needs to be activated. The insulin signaling pathway starts when insulin binds to its receptor on the cell membrane, causing its downstream protein, insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) is phosphorylated on its tyrosine 612 residue, causing its full activation. The activated IRS-1 then binds to phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K), which phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) and eventually phosphorylates Akt/PKB on its serine 473 residue to be fully activated. This fully activated Akt/PKB then activates AS160, which is responsible for the GLUT4 translocation from cytosol to the cell membrane [4].
IRS-1 is crucial for regulating the intracellular insulin signaling cascade, as it is indeed the first step in dispersing the direction of insulin signaling by activating many other downstream proteins [5]. IRS-1 phosphorylation on serine residue inhibits the insulin signaling cascade as it interferes with the interaction between IRS-1 and PI3K, thus leading to an insulin resistance condition [6]. Akt/PKB activation is also needed to maintain the normal insulin signaling cascade. Disruption of this protein will result in decreasing GLUT4 translocation to the cell membrane, diminishing glucose uptake in insulin-sensitive tissues [7].
In Indonesia, many traditional herbs have been used by the locals to control blood sugar levels. One of the traditional herbs that has long been known for controlling blood sugar levels is Ciplukan (P. angulata). Several studies have proved that P. angulata contains bioactive components that have antidiabetic effects, such as withangulatin-A [8], quercetin [9], and rutin [10]. In vivo study about the effect of isolated compound of P. angulata, which was withangulatin-A on diabetic rats, showed that this compound was able to reduce blood sugar significantly [8]. In a separate study, quercetin was shown to improve glucose uptake in C2C12 insulin-resistant cells via IRS-1/Akt pathway [11]. Meanwhile, in other research, rutin was proven to exhibit glucose-lowering activities by inhibiting hepatic glucose production via Akt activation [12]. In a previous study regarding glucose absorption in the C2C12 cell line, the active fraction (AF) of P. angulata obtained from bioassay-guided fractionation was proved to increase the glucose absorption level by 26.47% [13]. Another study about the activity of this AF was conducted on insulin-resistant C2C12 cells, which showed that the optimal concentration to increase glucose absorption was at 100 μg/ml [14].
This study aims to observe the optimal incubation time for the AF of P. angulata at 100 μg/ml to increase the phosphorylation of IRS-1 Tyr-612 and Akt Ser-473.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Materials used in the study were DMEM (Gibco, Lot: 2512444), Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS, SIGMA, Lot: 001671877), Horse Serum (HS, SIGMA, Lot: 22B441), antibiotics (Elabscience, Lot: GY1142RN8913), BSA (Elabscience, Lot: DI02260R2362), GOD PAP (DSI, Lot: 60159945), p-IRS-1 Tyr-612 antibodies (Invitrogen, Lot: 2350459), p-Akt Ser-473 antibodies (ABClonal, Cat No: AP0140), and β-actin antibodies (Abclonal, Cat No: AC050). An AF of P. angulata was gained from the Department of Pharmacology and Therapy, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health, and Nursing, UGM.
Cell culture and differentiation
C2C12 cells were obtained from the Department of Pharmacology and Therapy, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health, and Nursing, UGM. The passage of the cells was 50. C2C12 cells were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS at 37°C and 5% CO2. Differentiation of C2C12 cells was induced by replacing the media with DMEM containing 2% HS [15]. Experiments were conducted after 6–8 days of differentiation.
Validation of insulin resistance
Insulin resistance condition was obtained by treating cells with palmitate (PA). Palmitate acts by reducing the phosphorylation of IRS-1 Tyr-612 and Akt Ser-473 [16,17]. An optimal concentration of palmitate was needed to induce insulin resistance in C2C12 cells. Therefore, we conducted validation of insulin resistance.
Validation of insulin resistance on C2C12 cells was done by the GOD PAP method. The 3 × 103 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate and then differentiated. The well-differentiated cells were divided into five groups: negative control, PA 0.25, PA 0.5, PA 0.75, and PA 1, which were treated without palmitate, with 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1-mM PA, respectively. After 16 hours of incubation [18], the media was tested with the GOD PAP method [19], read by an ELISA reader, and the result was analyzed by quantifying glucose concentration in the media.
Induction of insulin resistance and treatment with AF of P. angulata
On a 6-well plate, 2.5 × 105 of C2C12 cells were seeded. After differentiation, they were divided into four groups: K1, P1, P2, and P3 (Table 1 shows the distribution of groups). The optimal concentration of PA achieved from the validation’s result was used to treat the well-differentiated C2C12 cells. After 16 hours of PA incubation, the cells had become insulin-resistant and ready to be treated [18]. Treatments were done by replacing the media with 100-μg/ml AF of P. angulata and incubating each group according to its incubation time. This concentration was used as it was the optimal concentration for AF to increase glucose absorption in insulin-resistant C2C12 cells within the previous study [14].
 | Table 1. Distribution of groups. [Click here to view] |
Insulin induction and protein isolation
Induction of insulin was done to start the insulin signaling pathway of the C2C12 cells. Ten minutes before the end of induction time, each group was treated with 100 nM insulin [20]. After treatment with insulin, the media was retrieved and the cells were scrapped. The collected cells were stored at -80°C. Protein isolation was conducted to measure the expression of p-IRS-1 Tyr-612 and p-Akt Ser-473 with the western blot method [21].
Measuring expression p-IRS-1 Tyr-612 and p-Akt Ser-473
Western blot analyses were conducted to detect p-IRS-1 Tyr-612 and p-Akt Ser-473. After the isolation, proteins were normalized and subjected to SDS-PAGE. The stained proteins were loaded into SDS-PAGE gel and transferred to the PVDF membrane. After blocking with blocking buffer, the PVDF membrane was immunoblotted with a specific antibody (p-IRS-1 Tyr-612, p-Akt Ser-473, and β-actin) and the proteins were revealed by a chemiluminescence method [21]. The results were quantified with ImageJ and analyzed statistically.
Statistical analysis
Analysis of insulin resistance and western blot data was performed using GraphPad Prism version 9.3.1 on the Windows operating system. The data were evaluated through one-way ANOVA with a 95% confidence interval, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons, and the results were expressed as geometric mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05 [22].
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Cell culture and differentiation
Before treatment with AF of P. angulata, C2C12 myoblasts were differentiated into myotubes. Morphology changes of C2C12 cells during the differentiation process are shown in Figure 1. Fully differentiated myotubes were seen on day 8.
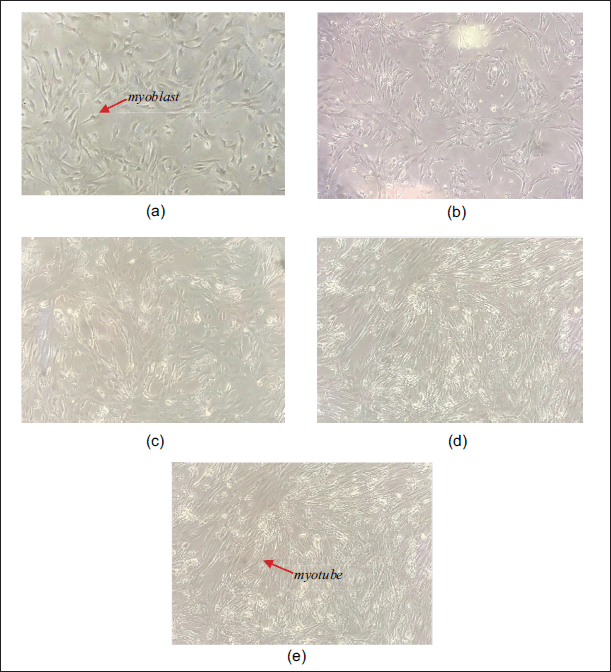 | Figure 1. Differentiation of C2C12 cells. (a–e) 0, 2nd, 4th, 6th, and 8th day differentiation. [Click here to view] |
Validation of insulin resistance
In order to present a diabetic state, these cells needed to undergo palmitate treatment to make them insulin-resistant. Palmitate is a saturated fatty acid that is often linked to insulin resistance. Palmitate is able to inhibit the phosphorylation of IRS-1 Tyr-612 and Akt Ser-473 through the formation of ceramide and diacylglycerol, which are metabolites derived from palmitate [16,17].
Validation of insulin resistance was conducted by observing the glucose concentration in media of the treatment group compared with the control group. The insulin-resistant cells were not able to absorb the glucose in the media, and therefore, the group with a significantly higher glucose concentration compared to the control group is considered insulin-resistant.
Figure 2 shows the result of the glucose consumption test with the GOD PAP method. According to the result, PA with a concentration of 0.75 mM could induce an insulin-resistant state in C2C12 myotubes (p < 0.05). Therefore, PA at this concentration was used to induce insulin resistance in C2C12 myotubes before treatment with AF of P. angulata.
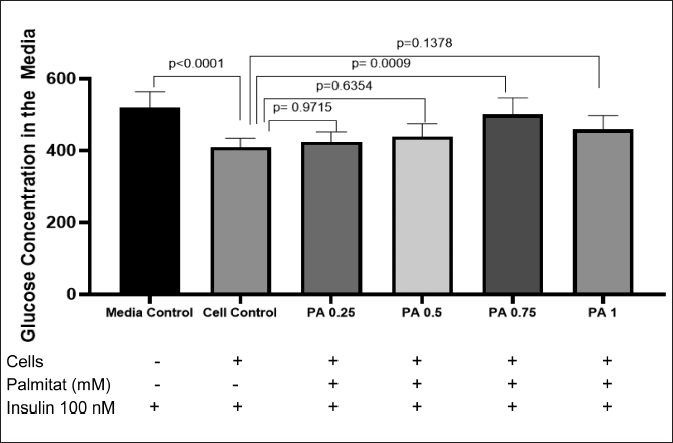 | Figure 2. Glucose concentration in the media. PA 0.75 shows a significantly higher level of glucose concentration in media compared with negative control group (p < 0.05) (n = 5, One way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey). [Click here to view] |
Effect of AF of P. angulata on the expression of p-IRS Tyr-612 on insulin-resistant C2C12 cells
The effect of AF of P. angulata was observed in every group. As seen in Figure 3, the highest phosphorylation of IRS-1 Tyr-612 was achieved in P3 (24-hour incubation time group), with a significant difference p < 0.05 compared with K1, the negative control group. Phosphorylation of IRS-1 Tyr-612 in P1 was also seen slightly higher than K1, but without any significant difference compared with the negative control (p > 0.05). Although the graph shows that P2 has the lowest expression of IRS-1 Tyr-612, it had no significant difference compared with P1 (p > 0.05).
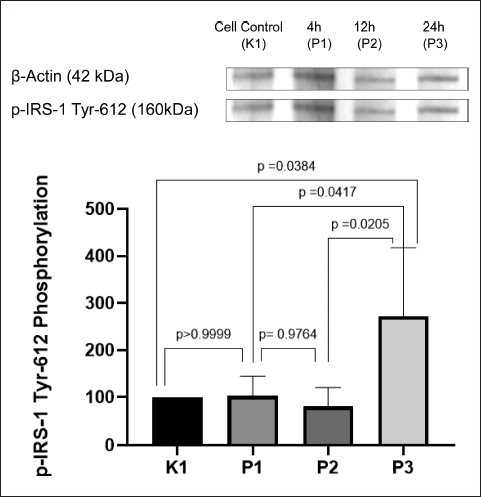 | Figure 3. Expression of p-IRS-1 Tyr-612 on insulin-resistant C2C12 cells after treatment with P. angulata AF. P3 has the highest expression of p-IRS-1 Tyr-612 (p < 0.05) (n = 4, One way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey). [Click here to view] |
IRS-1 is a downstream protein of insulin receptor. To be fully activated, IRS-1 needs to be phosphorylated on the right residue. In a resistant insulin model, increased phosphorylation of certain serine residue of IRS-1 is found. This corresponds to inhibition of insulin signaling pathway by preventing the interaction between IRS-1 and its downstream protein, which is PI3K [6]. On the other hand, phosphorylation on tyrosine residue of IRS-1 leads to the internalization of glucose through activation of insulin signaling pathway. Phosphorylation of IRS-1 on tyrosine 612 is very important to activate PI3K as its downstream protein [23].
Effect of AF of P. angulata on the expression of p-Akt Ser-473 on insulin-resistant C2C12 cells
The result of ImageJ quantification of p-Akt Ser-473 is presented in Figure 4. The highest expression of p-Akt Ser-473 is seen in the P3 group, with 24-hour incubation time (p < 0.05). P1 and P2 are shown to have higher expression of p-Akt Ser-473 than K1, the negative control, but with no significant difference (p > 0.05). Although P2 seems to have a slightly higher expression of p-Akt Ser-473 than P1, it had no significant difference (p > 0.05). Therefore, P1 and P2 can be considered to have the same level of expression of p-Akt Ser-473.
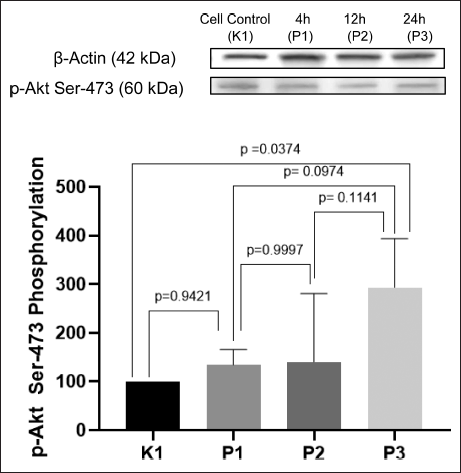 | Figure 4. Expression of p-Akt Ser-473 on insulin-resistant C2C12 cells after treatment with P. angulata AF. P3 has the highest expression of p-Akt Ser-473 (p < 0.05) (n = 4, One way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey). [Click here to view] |
Akt, also known as PKB, is a crucial protein that has functions related to cell survival and glucose metabolism. Similar to IRS-1, Akt also needs to be activated on its right residue to be fully activated. When Akt is fully activated, it will cause AS160 to translocate GLUT4 in the cytosol to the membrane cell [24]. When Akt is phosphorylated in threonine 308 and serine 473, it will be fully activated [25].
The AF of P. angulata used in this research was the methanol-insoluble partitioned resulted from the chloroform extract of the P. angulata herb, and therefore, the predicted compositions were semi-polar to nonpolar secondary metabolites. The secondary metabolites with these properties include alkaloids, terpenoids, and flavonoids [26]. Several studies have discovered that these compounds exert antidiabetic effects. Hirsutine, an alkaloid isolated from Uncaria rhynchophylla, was able to enhance glucose uptake by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in insulin-resistant HepG2 and H9c2 cells [27]. Along with this, another research also discovered that epiberberine, an alkaloid derived from Rhizoma coptidis, could increase GLUT4 protein expression and IRS-1/PI3K/Akt insulin signaling pathway in insulin-resistant HepG2 cells [28]. Eurocristatine, an alkaloid isolated from Eurotium cristatum, showed its antidiabetic effect also by increasing PI3K/IRS-1/Akt activation in vivo and in vitro [29].
Terpenoid constituent from Pinus spp. (Phyllostachys nigra and Pinus radiata), α-pinene, and essential oils derived from P. nigra could enhance the transcription of the GLUT4/Scl2a4 gene, leading to increased production of GLUT4 protein and its translocation to the plasma membrane in C2C12 cells [30]. A study about other terpenoids involved a terpenoid-rich extract from Dillenia indica L. bark, with findings indicating that the extract was able to enhance IRS-1/PDK1/Akt phosphorylation in insulin-resistant C2C12 cells [31]. Triterpenoid saponins extracted from Stauntonia chinensis were observed to be able to increase glucose uptake in insulin-resistant HepG2 cells via AMP-activated protein kinase and IR/IRS-1/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [32].
Flavonoid also has an antidiabetic effect, as seen in a study on kaempferol, flavonoids found Bauhinia for?cata in HepG2 cells. This study indicated that kaempferol had the capability to increase AKT phosphorylation in these cells [33]. Research on a different type of flavonoid was also carried out using Enicostema littorale. One of the plant’s flavonoid-rich fractions was able to upregulate glucose uptake rate via IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathway in insulin-resistant HepG2 cells [34]. Poncirin, a flavone glycoside found in many citrus fruits, was proven to improve glucose uptake by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in insulin-resistant C2C12 cells [35].
According to the results, the treatment of 100-μg/ml AF of P. angulata was shown to have a positive effect on phosphorylation of IRS-1 Tyr-612 and Akt Ser-473 in 24-hour incubation time, which was inhibited beforehand with PA 0.75 mM. This effect worked in a time-dependent manner. The 24-hour incubation was considered the optimum time for compounds in AF of P. angulata to exert the antidiabetic effect. This effect was probably because the longer the incubation time, the better the absorption level of AF into the cells, so that it could cause a higher effect of phosphorylation.
In brief, this study showed that the AF of P. angulata increased IRS-1 Tyr-612 and Akt Ser-473 phosphorylation in 24-hour incubation time. This study could be further investigated by exploring the mechanism of action of P. angulata’s AF in other parameters of insulin signaling pathways, either using the same cell line or different types of cell lines. Furthermore, in vivo studies could be conducted to further investigate the potential of P. angulata’s AF to enhance understanding of this herb’s potential as an alternative treatment for DM.
CONCLUSION
The results of this study demonstrate that 100-μg/ml AF of P. angulata was able to increase phosphorylation of IRS-1 Tyr-612 and Akt Ser-473 in 24-hour incubation time. Since IRS-1/Akt phosphorylation is essential for addressing insulin resistance, as seen in DM, therefore this discovery offered insight into future alternative treatments for DM utilizing an AF of P. angulata.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors would like to thank dr. Dwi Aris Agung Nugrahaningsih, M.Sc, Ph.D for the support, all the laboratory technicians for the assistance and Jessica Gita Batoteng for the partnership during this research.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
This research was funded by Hibah Dana Masyarakat (DAMAS) Project, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada, 2023. Article Processsing Charge (APC) of this article was funded by Universitas Kristen Duta Wacana.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors report no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Faculty of Medicine, Public Health, and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Indonesia (Approval No.: KE/ FK/1731/EC/2023).
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated and analyzed are included in this research article.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used artificial intelligence (AI)-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
REFERENCES
1. World Health Organization. Classification of diabetes mellitus 2019. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2019.
2. Freeman AM, Acevedo LA, Pennings N. Insulin resistance. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2023. [cited 2023 March 19]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507839/
3. Merz KE, Thurmond DC. Role of skeletal muscle in insulin resistance and glucose uptake. Compr Physiol. 2020;10(3):785–809. CrossRef
4. ?widerska E, Strycharz J, Wróblewski A, Szemraj J, Drzewoski J, ?liwi?ska A. Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in insulin-mediated glucose uptake. In: Szablewski L, editor. Blood glucose levels. London, UK: IntechOpen [Internet]; 2020 [cited 2023 March 17]. CrossRef
5. Draznin B. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance: serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 and increased expression of p85α: the two sides of a coin. Diabetes. 2006;55(8):2392–7. CrossRef
6. Langlais P, Yi Z, Finlayson J, Luo M, Mapes R, De Filippis E, et al. Global IRS-1 phosphorylation analysis in insulin resistance. Diabetologia. 2011;54(11):2878–89. CrossRef
7. Rajendiran D, Packirisamy S, Kanna De N. The PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Current advances in biosciences. Namakkal, India: Thanuj International Publishers; 2024. 9–19 pp.
8. Raju P, Mamidala E. Anti diabetic activity of compound isolated from Physalis angulata fruit extracts in alloxan induced diabetic rats. Am J Sci Med Res. 2015;1(2):40–3. CrossRef
9. Iwansyah AC, Luthfiyanti R, Ardiansyah RCE, Rahman N, Andriana Y, Hamid HA. Antidiabetic activity of Physalis angulata L. fruit juice on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. S Afr J Bot. 2022;145:313–31. CrossRef
10. Nguyen KNH, Nguyen NVT, Kim KH. Determination of phenolic acids and flavonoids in leaves, calyces, and fruits of Physalis angulata L. in Viet Nam. Pharmacia. 2021;68(2):501–9. CrossRef
11. Jiao Y, Williams A, Wei N. Quercetin ameliorated insulin resistance via regulating METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of PRKD2 mRNA in skeletal muscle and C2C12 myocyte cell line. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2022;32(11):2655–68. CrossRef
12. Luo K, Huang W, Qiao L, Zhang X, Yan D, Ning Z, et al. Dendrocalamus latiflorus and its component rutin exhibit glucose-lowering activities by inhibiting hepatic glucose production via AKT activation. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12(5):2239–51. CrossRef
13. Wahyuningsih MSH, Ketut SSW, Aurelia PRP, Nugrahaningsih DAA, Yuniyanti MM. Bioassay-guided fractionation of ciplukan (Physalis angulata L.) monitored by glucose consumption assay and thin layer chromatography on myoblast cells. Majalah Obat Tradis. 2023;28(1):22–30. CrossRef
14. Prasetyo YC. Efek fraksi aktif herba ciplukan (Physalis angulata Linn) terhadap konsumsi glukosa Sel C2C12 myotube resisten insulin [Magister’s thesis]. Yogyakarta, Indonesia: Universitas Gadjah Mada; 2023.
15. American Type Culture Collection. C2C12 CRL-1772. Manassas, VA: American Type Culture Collection; 2021.
16. Pinel A, Morio-Liondore B, Capel F. n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids modulate metabolism of insulin-sensitive tissues: implication for the prevention of type 2 diabetes. J Physiol Biochem. 2014;70(2):647–58. CrossRef
17. Boucher J, Kleinridders A, Kahn CR. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014;6:a009191. CrossRef
18. Ayeleso TB, Ramachela K, Mukwevho E. Aqueous-methanol extracts of orange-fleshed sweet potato (ipomoea batatas) ameliorate oxidative stress and modulate type 2 diabetes associated genes in insulin resistant C2C12 cells. Molecules. 2018;23(8):2058. CrossRef
19. Rezekiyah S, Lestari WS, Fitriana E, Karwiti W, Riska DM. Reagent temperature variations affect for stability of natrium fluorid (Naf) plasma blood glucoselevels using enzymatic (God-Pap) methods. Jambura. 2021;3(2):10225. CrossRef
20. Li Z, Zhu Y, Li C, Tang Y, Jiang Z, Yang M, et al. Liraglutide ameliorates palmitate?induced insulin resistance through inhibiting the IRS?1 serine phosphorylation in mouse skeletal muscle cells. J Endocrinol Invest. 2018;41(9):1097–102. CrossRef
21. Sule R, Rivera G, Gomes AV. Western blotting (immunoblotting): history, theory, uses, protocol and problems. BioTechniques. 2023;75:99–114. CrossRef
22. Lee S, Lee DK. What is the proper way to apply the multiple comparison test? Korean J Anesthesiol. 2018;71(5):353–60. CrossRef
23. Song BR, Alam MB, Lee SH. Terpenoid-rich extract of Dillenia indica L. bark displays antidiabetic action in insulin-resistant C2C12 cells and STZ-induced diabetic mice by attenuation of oxidative stress. Antioxidants. 2022;11(7):1227. CrossRef
24. Egawa T, Tsuda S, Ma X, Hamada T, Hayashi T. Caffeine modulates phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 and impairs insulin signal transduction in rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol. 2011;111(6):1629–36. CrossRef
25. Mackenzie R, Elliott B. Akt/PKB activation and insulin signaling: a novel insulin signaling pathway in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2014;7:55–64. CrossRef
26. Song G, Ouyang G, Bao S. The activation of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med. 2005;9(1):59–71. CrossRef
27. Crozier A, Clifford MN, Ashihara H. Plant secondary metabolites. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley; 2006. CrossRef
28. Hu W, Li M, Sun W, Li Q, Xi H, Qiu Y, et al. Hirsutine ameliorates hepatic and cardiac insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice and in vitro models. Pharmacol Res. 2022;177:105917. CrossRef
29. Zhang S, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Wang H, Chen Y, Lu H. Activation of NRF2 by epiberberine improves oxidative stress and insulin resistance in T2DM mice and IR-HepG2 cells in an AMPK dependent manner. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;327:117931. CrossRef
30. Zhang H, Hui J, Yang J, Deng J, Fan D. Eurocristatine, a plant alkaloid from Eurotium cristatum, alleviates insulin resistance in db/db diabetic mice via activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;887:173557. CrossRef
31. Feriotto G, Tagliati F, Costa V, Monesi M, Tabolacci C, Beninati S, et al. α-Pinene, a main component of Pinus essential oils, enhances the expression of insulin-sensitive glucose transporter type 4 in murine skeletal muscle cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(2):1252. CrossRef
32. Hu X, Wang S, Xu J, Wang DB, Chen Y, Yang GZ. Triterpenoid saponins from Stauntonia chinensis ameliorate insulin resistance via the AMP-activated protein kinase and IR/IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathways in insulin-resistant HepG2 cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(6):10446–58. CrossRef
33. Santana-Lima B, Belaunde LHZ, de Souza KD, Rosa ME, de Carvalho JE, Machado-Jr J, et al. Acute kaempferol stimulation induces AKT phosphorylation in HepG2 cells. Life. 2024;14(6):764. CrossRef
34. Mokashi P, Khanna A, Pandita N. Flavonoids from Enicostema littorale blume enhances glucose uptake of cells in insulin resistant human liver cancer (HepG2) cell line via IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;90:268–77. CrossRef
35. Yousof Ali M, Zaib S, Mizanur Rahman M, Jannat S, Iqbal J, Kyu Park S, et al. Poncirin, an orally active flavonoid exerts antidiabetic complications and improves glucose uptake activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in insulin resistant C2C12 cells with anti-glycation capacities. Bioorganic Chem. 2020;102:104061. CrossRef