INTRODUCTION
Fungal infections are prevalent, particularly in the tropics, and are often associated with other health problems such as asthma, AIDS, cancer, organ transplantation, and also corticosteroid therapies [1]. Candida albicans is the most prevalent fungal species causing mucosal disease candidiasis, which can be divided into mouth, throat, and esophagus, vaginal candidiasis, and invasive candidiasis [2]. Invasive candidiasis is associated with infection of the blood, heart, brain, eye, bone, and other organs. Nearly 95% of invasive candidiasis is caused due to the presence of C. albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, Candida tropicalis, and Candida krusei [1]. Besides candidiasis, aspergillosis is an infectious disease caused by Aspergillus, such as allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, allergic Aspergillus sinusitis, aspergilloma, chronic pulmonary aspergillosis, invasive aspergillosis, and cutaneous (skin) aspergillosis. A recent study reported that Aspergillus fumigatus caused around 60% of infections, followed by Aspergillus flavus [3].
Antifungal therapeutics have long been used to manage fungal infections, although some resistance has been reported, for instance, azole antifungal against Candida and Aspergillus species and echinocandin multidrug against C. glabrata [4]. Therefore, the attempts to identify new antifungal therapeutics are constantly increasing, such as natural products such as well-known antifungal drugs, polyenes, and echinocandins [5].
Lagerstromia speciosa is a medicinal plant widely distributed in Asia, including China, India, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Indonesia. The plant is commonly used as an ingredient, spice, or traditional medicine [6,7]. Various parts of the plant, such as the bark, flower, and leaves are commonly used for disease prevention and treatment, especially diabetes mellitus [8,9]. Lagerstreomia speciosa contains corosolic acid as a key marker compound [10], ellagitannin (lagerstannins A, B, and C), monomeric and dimeric ellagitannins (flosins A and B and reginins A, B, C, and D), ellagic acid, quercetin, isoquercetin, coumarin, β-sitosterol, neolignan, and ursolic acid, all of which are responsible for the biological and pharmacological activity [7,9,11]. Antifungal activities, especially from the fruit and flower of L. speciosa, have been reported [12,13]. However, little is known about how the leaf and bark extracts may also inhibit fungal growth.
Previously, our group reported that corosolic acid, methanolic leaf, and bark extracts of L. speciosa exhibited profound antibacterial activity and showed that corosolic acid enhanced the antibacterial activity of cefotaxime. This study was extended to investigate whether corosolic acid, methanolic bark, and leaf extracts of L. speciosa possess antifungal activity against three different clinical fungal isolates that commonly caused candidiasis and aspergillosis.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Preparation of drug
The positive control fluconazole (Pharmaceutical product, Indonesia) was diluted in sterile aquadest and medium according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) M27-A2 to obtain a working concentration of 2 mg/ml for the antifungal assay [14].
Plant extraction
The plant material was a kind gift from Professor Fitmawati, Department of Biology, University of Riau, and had been previously identified using ITS coding region [8]. The voucher specimen was deposited in the Department of Pharmacy, Atma Jaya Catholic University of Indonesia, for the current study. The leaves and bark were separately cleaned and ground before methanolic maceration. Excess methanol solvent was evaporated using a rotary evaporator to obtain dry extracts, which were then diluted in dimethylsulfoxide (PAN-Biotech, Aidenbach, Germany) to obtain a working concentration of 80 mg/ml. Determination of the test concentration was previously described in several studies [15,16].
Antifungal activity
Microorganisms and culture
The three microorganisms used were C. albicans, A. fumigatus, and A. flavus obtained as a clinical isolate from the Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Indonesia. The fungal isolates were confirmed using HiCHROM Agar for C. albicans with a blue/green appearance (Fig. S1) and the slide culture technique for A. fumigatus and A. flavus (Fig. S2-S3). For the assay, one inoculating loop of 24 hours C. albicans was suspended in 10 ml NaCl (0.9%) and homogenized using a bench vortex for 15 s. The absorbance of the homogenized C. albicans suspension was measured at 530 nm to reach the turbidity of McFarland 0.5 (Absorbance of 0.5–0.6), equivalent to 0.5–2.5 × 103 CFU/ml. One inoculating loop of 72 hours A. fumigatus or A. flavus was suspended in 10 ml NaCl (0.9%) to obtain A. fumigatus suspension according to the previously mentioned procedure.
Well-diffusion antifungal assay
Well-diffusion antifungal assay was performed according to CLSI guidelines and previous studies [14,17]. Briefly, 20 ml of Mueller Hinton Agar (MHA, Oxoid, United Kingdom) was poured onto a 20 cm diameter Petri dish and allowed to dry for 30 minutes. The C. albicans suspension was then evenly spread on the top of the MHA before 8 mm diameter wells were made in the agar at a distance of approximately 2.5 cm between wells. Then, 50 μl of 2 mg/ml fluconazole, 80 mg/ml, and 40 mg/ml of extract were placed in each well. The same procedure was applied to A. fumigatus and A. flavus. The petri dishes with C. albicans were incubated at 35°C for 24 hours and 48 hours for A. fumigatus or A. flavus. The inhibitory zone was then determined based on the diameter of the inhibitory zone against C. albicans as susceptible when the inhibitory zone ≥ 19 mm, dose-dependently susceptible if the inhibitory zone was 18–13 mm, and resistant if the inhibitory zone ≤12 mm [18].
Broth microdilution antifungal assay
The method was adopted from CLSI guidelines and previous studies [14,17]. Twofold serial dilutions of fluconazole with 100 μl media RPMI 1640 (PAN Biotech, Germany) were performed in a 96-well plate to obtain serial dilutions in a range of 0.0155–32 μg/ml [14]. Plant extracts were prepared similarly to obtain serial dilutions in a range of 0.020–40 mg/ml. Afterward, 100 μl of C. albicans suspension was added to each well and incubated at 35°C for 24 hours. Similar procedures were applied for A. fumigatus and A. flavus, but the incubation time was 48–72 hours. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was determined for each tested drug and extract. The percentage of fungal growth was calculated based on the absorbance reading at 600 nm before and after incubation according to the formula:
% Inhibitory fungal growth = 100%−% fungal growth.
Statistical analysis
The number of replications was determined according to Federer (t(r– 1)> 15), n = 3. The data were analyzed using Microsoft Office Excel and presented as the average inhibitory zone ± SD and the average MIC ± SD for each tested strain.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Lagerstreomia speciosa, as a medicinal plant, contains some important bioactive compounds, including corosolic acid [10]. Previously, we showed that L. speciosa methanolic leaves extract and corosolic acid profoundly exhibits antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, including the methicillin-resistant S. aureus. The current study investigated how L. speciosa extracts inhibit fungal growth. Methanol has been considered the universal organic solvent that can extract various phytochemicals, often with high antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, resulting in higher extraction efficiency. It is, therefore, appropriate to screen for bioactivity before further fractionation guided by a bioassay of active compounds [19,20]. In our current study, besides the extract, we also tested 0.125 mg/ml of corosolic acid against all fungal strains; however, no inhibitory fungal growth was observed (data not shown). In the well-diffusion method, C. albicans showed sensitivity to leaf and bark L. speciosa extracts at concentrations of 2 and 4 mg/ml. In contrast, A. flavus and A. fumigatus resisted the bark extract and were dose-dependently susceptible to the leaf extract (Table 1, Fig. 1). A previous study by [12] showed that C. albicans was susceptible dose-dependent to L. speciosa flower extract (2 mg/ml) [12], whereas [13] reported that the extract was inactive against A. niger
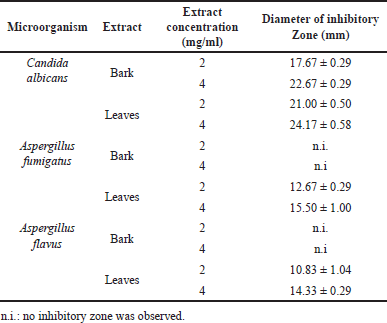 | Table 1. Diameter of the inhibitory zone of the leaf and bark extracts of L. speciosa against C. albicans and Aspergillus. [Click here to view] |
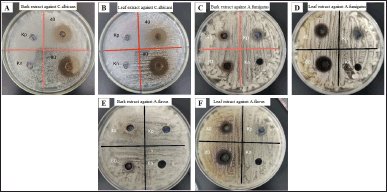 | Figure 1. Inhibitory zone of the bark (A, C, E) and leaf (B, D, F) extracts of L. speciosa against C. albicans (A, B), Aspergillus fumigatus (C, D), and A. flavus (E, F) tested using the well diffusion method.Kp: positive control (Fluconazole 0,1 mg/ml), Kn: negative control (DMSO 2.5%), 40: concentration of extract in test (2 mg/ml), 80: concentration of extract in test (4 mg/ml). [Click here to view] |
Using broth microdilution, C. albicans, A. flavus, and A. fumigatus were dose-dependently susceptible to the positive control fluconazole [21]. Fluconazole (16 μg/ml) inhibited 54.15% ± 0.007% of C. albicans growth, 36.86% ± 0.003% of A. fumigatus, and 27.60% ± 0.003% of A. flavus at 32 μg/ml. No study was conducted previously on the antifungal activity of leaf and bark extracts of L. speciosa using the microdilution method. In the current study, the MIC of L. speciosa bark extract against C. albicans was 10.867 ± 0.822 mg/ml, against A. fumigatus was 7.747 ± 0.322 mg/ml, and against A. flavus was 12.65 ± 0.32 mg/ml, whereas the MIC of the L. speciosa leaf extract against C. albicans was 4.69 ± 0.034 mg/ml, against A. fumigatus was 9.462 ± 0.231 mg/ml, and against A. flavus was 23.872 ± 0.338 mg/ml (Table 2). Based on the microdilution test, the bark extract was more potent than the leaf extract in inhibiting the growth of the Aspergillus strains, while the leaf extract was more potent against C. albicans than Aspergillus.
 | Table 2. MIC of the bark and leaf extracts of L. speciosa against C. albicans and Aspergillus. [Click here to view] |
Nasrin and Ahmad [22] reported that the antifungal activity of L. speciosa bark extract was slightly more potent than the leaf extract based on the disc diffusion method containing 500 μg extract/disc against clinical C. albicans and A. niger cultures . In contrast, low fungal inhibitory activity was observed from L. speciosa flowers against A. niger using the disc diffusion method [13]. A review reported that corosolic acid possesses antifungal activity, although the mechanism of action remains unclear [6]. It was also not in accordance with the current study. Polyphenol compounds contained in L. speciosa, such as tannin, ellagitannin, flavonoid, and flavonols, may also play important roles in the antifungal activity of the extract, as exhibited in several studies [23–25]. The possible mechanism of action of polyphenols against fungi includes plasma membrane disruption, mitochondrial dysfunction, inhibition of cell wall formation, and inhibition of RNA and DNA or protein synthesis [26].
Besides polyphenols, the L. speciosa extract also contains steroids and triterpenoids with phenolic –OH group that may bind to the sulfhydryl group via non-specific interaction with protein and inhibit fungal biochemical process [27] as well as disturb the membrane integrity [28]. Those chemical compounds can work synergistically to inhibit microbial growth compared to the single active compound, corosolic acid, with no fungal inhibitory activity. The L. speciosa extract (2,000 mg/ml) showed no toxicity/mortality or morbidity in the acute toxicity study using the Sprague-Dawley rat based on movement, physical parameters, behavior, and overall appearance [29], indicating that the extract is safe as a novel antifungal candidate.
CONCLUSION
The leaf and bark extracts of L. speciosa demonstrated inhibitory activity against C. albicans, A. fumigatus, and A. flavus based on two antifungal test methods, thus are potential novel antifungals. Bioassay-guided fractionation of both extracts is warranted to identify the novel antifungal fractions and/or compounds.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Authors are grateful to the technical support staffs from Department of Pharmacy and Department of Parasitology, School of Medicine and Health Sciences.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
All authors made intellectual and substantial contributions to the conception and design of the work; acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data; drafting the manuscript and revising it critically; and all authors have approved the final version.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
This work was supported by Atma Jaya Catholic University of Indonesia.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors report no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
This study does not involve direct experiments on animals or human subjects.
DATA AVAILABILITY
All data generated and analyzed are included in this research article.
REFERENCES
1. Bongomin F, Gago S, Oladele RO, Denning DW. Global and multi-national prevalence of fungal diseases—estimate precision. J Fungi. 2017;3:57. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/JOF3040057
2. Shields BE, Rosenbach M, Brown-Joel Z, Berger AP, Ford BA, Wanat KA. Angioinvasive fungal infections impacting the skin: background, epidemiology, and clinical presentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:869–80.e5. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JAAD.2018.04.059
3. Bandres MV, Modi P, Sharma S. Aspergillus Fumigatus. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing, 2022.
4. Perlin DS, Rautemaa-Richardson R, Alastruey-Izquierdo A. The global problem of antifungal resistance: prevalence, mechanisms, and management. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:e383–92. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30316-X
5. Dorsaz S, Snäkä T, Favre-Godal Q, Maudens P, Boulens N, Furrer P. Identification and mode of action of a plant natural product targeting human fungal pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:e00829–17. doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00829-17
6. Stohs SJ, Miller H, Kaats GR. A review of the efficacy and safety of banaba (Lagerstroemia speciosa L.) and corosolic acid. Phytother Res. 2012;26(3):317–24. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/PTR.3664
7. Tripathi SK, Behera S, Panda M, Zengin G, Biswal BK. A comprehensive review on pharmacology and toxicology of bioactive compounds of Lagerstroemia speciosa (L.) Pers. Curr Tradit Med. 2020;7:504–13. doi: https://doi.org/10.2174/2215083806999201211213931
8. Nurcahyanti AD, Arieselia Z, Kurniawan SV, Sofyan F, Wink M. Revisiting Bungur (Lagerstroemia speciosa) from Indonesia as an antidiabetic agent, its mode of action, and phylogenetic position. Pharm Rev. 2018;12:40–5. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/phrev.phrev_20_17
9. Chan EW, Tan LN, Wong SK. Phytochemistry and pharmacology of Lagerstroemia speciosa: a natural remedy for diabetes. Int J Herb Med. 2014;2:100–5.
10. Kim MO, Lee SU, Yuk HJ, Jang HJ, Lee JW, Kwon EB, et al. Metabolomics approach to identify the active substances influencing the antidiabetic activity of Lagerstroemia species. J Funct Food. 2020;64:1–7. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JFF.2019.103684
11. Huang GH, Zhan Q, Li JL, Chen C, Huang DD, Chen WS, et al. Chemical constituents from leaves of Lagerstroemia speciosa L. Biochem Syst Ecol. 2013;51:109–12. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BSE.2013.08.029
12. Pavithra GM, Rakesh KN, Dileep N, Junaid S, Kumar RK, Kekuda PT. Elemental analysis, antimicrobial and radical scavenging activity of Lagerstroemia speciosa (L.) flower. J Chem Pharm Res. 2013;5:215–22.
13. Sharmin T, Rahman MS, Mohammadi H. Investigation of biological activities of the flowers of Lagerstroemia speciosa, the Jarul flower of Bangladesh. BMC Complementary Altern Med. 2018;181–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/S12906-018-2286-6/TABLES/9
14. Alexander B, Procop G, Dufresne P, Fuller J, Ghannoum M, Hanson K, et al. M27: Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of yeasts. 4th ed. Wayne (PA): Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute; 2017.
15. Okla MK, Alatar AA, Al-Amri SS, Soufan WH, Ahmad A, Abdel-Maksoud MA. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of the extracts of different parts of Avicennia marina (Forssk.) Vierh. Plants. 2021;10:252. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/PLANTS10020252
16. Suurbaar J, Mosobil R, Donkor AM. Antibacterial and antifungal activities and phytochemical profile of leaf extract from different extractants of Ricinus communis against selected pathogens. BMC Res Notes. 2017;10:1–6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/S13104-017-3001-2/FIGURES/1
17. Sharaf EF, Al-Zaidi HS. In vitro antifungal activity of some indigenous medicinal plant extracts against five isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2021;83:695–700.
18. Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: a review. J Pharm Anal. 2016;(2):71–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPHA.2015.11.005
19. Truong DH, Nguyen DH, Ta NT, Bui AV, Do TH, Nguyen HC. Evaluation of the use of different solvents for phytochemical constituents, antioxidants, and in vitro anti-inflammatory activities of Severinia buxifolia. J Food Qual. 2019;2019:1–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8178294
20. Zhang QW, Lin LG, Ye WC. Techniques for extraction and isolation of natural products: a comprehensive review. Chin Med. 2018;13:20. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/S13020-018-0177-X
21. Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ, Sheehan DJ. Interpretive breakpoints for fluconazole and Candida revisited: a blueprint for the future of antifungal susceptibility testing. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19:435. doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.19.2.435-447.2006
22. Nasrin F, Ahmad S. Evaluation of antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of methanolic extracts of Lagerstroemia speciosa leaves and barks. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2012;2:142–7. doi: https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2012.21028
23. Latté KP, Kolodziej H. Antifungal effects of hydrolysable tannins and related compounds on dermatophytes, mould fungi and yeasts. Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung. C J Biosci. 2000;55:467–72. doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/ZNC-2000-5-625
24. Salih EYA, Julkunen-Tiitto R, Luukkanen O, Fyhrqvist P. Anti-Candida activity of extracts containing ellagitannins, triterpenes and flavonoids of Terminalia brownii, a medicinal plant growing in semi-arid and Savannah Woodland in Sudan. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14:2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/PHARMACEUTICS14112469
25. Yamaguchi MU, Garcia FP, Cortez DA, Ueda-Nakamura T, Filho BP, Nakamura CV, et al. Antifungal effects of Ellagitannin isolated from leaves of Ocotea odorifera (Lauraceae). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2011;99:507–14. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/S10482-010-9516-3
26. Aboody MSA, Mickymaray S. Anti-fungal efficacy and mechanisms of flavonoids. Antibiotics. 2020;9(2):45. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIBIOTICS9020045
27. Rao A, Zhang Y, Muend S, Rao R. Mechanism of antifungal activity of terpenoid phenols resembles calcium stress and inhibition of the TOR pathway. Antimicrobl Agents Chemother. 2010;54:5062–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01050-10
28. Konuk HB, Ergüden B. Phenolic -OH group is crucial for the antifungal activity of terpenoids via disruption of cell membrane integrity. Folia Microbiol. 2020:65:775–83. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/S12223-020-00787-4
29. Alkahtani S, Hasnain MS, Algamdy H, Aljarba NH, AlKahtane A. Acute and sub-acute oral toxicity Lagerstroemia speciosa in sprague-dawley rats. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022;(3):1585–91. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SJBS.2021.11.005