INTRODUCTION
Cancer is a main community health problem all over the globe because of its significantly high rate of morbidity and mortality. It is the next most important reason for death in the present society after cardiovascular disease (De Martel et al., 2012). There are various types of cancers, the maximum of these types are treatable leaving behind a number of serious side effects. Now, the area of interest is to develop new anticancer drug candidate with fewer side effects and a more potent drug profile (Pisani, 2009). There are various categories of drugs, such as antimetabolites (Peter et al., 2000), alkylating agent (Singh et al., 2018), anthracyclines (Takimoto and Calvo, 2008), plant alkaloids, epipodophyllotoxins, and topoisomerase (Glam et al., 2005) inhibitor which are used in a cancer chemotherapy but they all show several adverse effects, such as infertility, cardiotoxicity (Jarkowski et al., 2011), hepatotoxicity (Perry, 2010), nephrotoxicity (Kintzel, 2001), encephalopathy (Schacht et al., 2012), bone marrow depression, alopecia, drug-induced cancer, and many more (Finley and Volpp, 1969). Other than chemotherapy, radiation therapy, laser therapy, hormone therapy, hyperthermia, and surgery had also emerged as a treatment but they also carry many side effects (Frankish, 2013).
In the past few years, many researchers had revealed the synthesis, structure–activity relationships, and pharmacological activities [such as antitumor (Ingale et al., 2018), anti-inflammatory, and anti-bacterial (Karrouchi, 2018)] of the pyrazole nucleus (Bernatowicz et al., 1992). This potential activity profile of pyrazole motivated us to synthesize some new pyrazole derivatives (Fustero et al., 2009). So, in this research, we have been synthesized some protected pyrazole derivatives which are characterized by various spectral techniques (Chankeswara and Chakraborti, 2006; Nadia et al., 2004).
EXPERIMENTAL
Materials and methodology
All chemicals were procured from Aldrich, Fluka, and HIMEDIA companies in the pure form. Melting point was measured with VMP-D melting point apparatus and uncorrected. The changes in the reaction were observed with the help of silica gel-G coated thin-layer chromatography (TLC) plates with a suitable visualizing agent. 1H NMR, 13C NMR spectra were measured with Bruker-Avance-II (400 MHz) spectrometer in CDCl3 solvent and tetramethylsilane as an internal reference and chemical shifts are in δ (ppm). IR spectra were measured with Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)-9050S-CE (SHIMADZU) and FTIR (CARY-660) Agilent. Elemental analyses were measured with Perkin Elmer CHNS/O Analyzer series-II Model 2400.
Synthesis of 4-acetylpyrazole derivative (2)
3, 5-dimethyl pyrazole (0.1 moles, 8.16 g) was slowly added into the solution of acetic anhydride (0.1 moles, 3.02 g) and then two drops of 96% sulfuric acid. The reaction mixture was condensed for 15 hours and checked by TLC to determine reaction proceeding. Excess acetic anhydride was distilled off by rotary evaporator. After evaporation residue was obtained, this was again refluxed for 20 minutes after the addition of 40 ml concentrated hydrochloric acid and 2 g charcoal. The reaction mixture was cooled and filtered to take away the charcoal. The filtrate was concentrated on a rotary evaporator. The dry residue thus obtained was solubilized in 10 ml of water and slowly made alkaline with 15 g of sodium acetate trihydrate. The crude product precipitate was separated off. The excess solvent was evacuated on a rotary evaporator and purified with column chromatography (Silica Gel, 10% Ethanol/Hexane) to the desired compound. Yield: 98%; Melting Point: 109°C–110°C.
Synthesis of Boc-protected pyrazole derivative (3)
In the present research work, we have adopted five methods for the synthesis of compound 3.
CONVENTIONAL METHOD-A
The mixture of substituted pyrazole (2) (1.0 mmol), (Boc)2O (1.4 mmol), and PEG-400 (1.0 ml) was continuously stirred at room temperature for 2.5 hours followed by the TLC until it shows total reactant consumption. After reaction completion, the solution was drained into the water and extracted with dry ether. The organic layer with anhydrous Na2So4 was dried, concentrated on a rotary evaporator, and purified with column chromatography (benzene/methanol, 8:2) to give a purified product. The PEG-400 was recovered with the extracted aqueous layer and reused without loss of chemical and physical properties. Yield: 95%; Melting Point: 110°C–111°C.
CONVENTIONAL METHOD-B
In 50 ml round bottom flask, substituted pyrazole (2) (1 mmol) was dissolved in dichloromethane on magnetic stirrer to obtain a clear yellow solution. In this clear solution, add N, N-diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) (1 mmol) and 4-dimethylamino pyridine (DMAP) in a catalytic amount at 0°C temperature. After 15 minutes, (Boc)2O (1 mmol) was added and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours till TLC shows the total disappearance of the reactant. After completion, dichloromethane was evaporated and the remaining raw product was purified with column chromatography (20% Ethanol/Hexane) to give the desired product. Yield: 85%; Melting Point: 112°C–114°C.
CONVENTIONAL METHOD-C
In an RBF, the solution of substituted pyrazole (2) (1 mmol), (Boc)2O (1 mmol) and a catalytic quantity of iodine (10 mol%) were mixed through stirring without any solvent at room temperature. After reaction completion, dry ether (10 ml) was added and washed by using Na2SO4. The reaming solvent was concentrated on a rotary evaporator and the crude product was purified with column chromatography (10% Ethanol/Hexane) to give the pure product. Yield: 20%; Melting Point: 113°C–114°C.
CONVENTIONAL METHOD-D
In 50 ml RBF, the solution of distilled water (9.5 ml), acetone (0.5 ml), and substituted pyrazole (2) (1 mmol) were mixed with stirring at room temperature for 30 minutes and dichloromethane (5 ml) was added. After completion of the reaction, the organic layer was dried on anhydrous Na2SO4 and reduced under vacuum. The precipitate was purified with column chromatography (CH2Cl2/ MeOH, 9:1). Yield: 50%; Melting Point: 100°C–110°C.
CONVENTIONAL METHOD-E
In 250 ml RBF, the solution of tetrahydrofuran (40 ml) and substituted pyrazole (2) (14.4 mmol) were mixed at 20°C temperature to give a transparent solution. In this solution, formaldehyde (1.0 eq., 3% water solution) was added and stirred for 4 hours to obtain a uniform solution. The solvent was removed with a rotary evaporator. Yield: 60%; Melting Point: 105°C–108°C.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In the present research work, we try to develop an eco-friendly, novel, and efficient methods for the protection of secondary amine of 4-acetyl-3, 5-dimethylpyrazole (2) with the help of protecting agent. To the finest of our information, this is the first report of the use of PEG-400 and DMAP, DIPEA catalyst for the protection of secondary amine of pyrazole nucleus using Boc. PEG-400 has been found to be an adequate and eco-friendly reaction medium for the chemoselective transformation of amines to N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl) amines. Correlated to the previously reported methods, these both protocols (method A and B) offer several advantages such as mild reaction circumstances, easy operation, small reaction period, and high yield (Agami and Couty, 2003; Kelly and Mcneil, 1994; Pisár et al., 2018; Raju et al., 2009; Sharma et al., 2004; Varela et al., 2006).
Some various procedures apply for the protection of secondary amine in pyrazole but only two methods (A and B) was succeeded and the other three (C, D, and E) were failed (Fig. 1). For the use of method A, the product (3) was obtained in good to excellent yield (95%) when reproduced again and again, and in the case of method (B), the product (4) yield was 85% with no formation of any side product (Scheme1). Method A product was obtained with higher impurity as compared to another one, so the melting point of the same structured product but with different synthetic procedures (Chankeswara, 2006; Giampietra, 2007; Heydari et al., 2007; Krystof, 2006; Sook Hoo, 2007) is different from each other.
1-(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-yl) ethanone (2): Pale yellow amorphous solid, Yield: 98%,m.p 112°C–115°C; FTIR (KBr) cm−1: 3,242 cm−1 (N-H), 2,985 CH3 (str.), 1,769 C=O, 1,667 C=C (str.); 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ 13.7 (s,1H,NH), 2.79 (s, 6H, CH3), 2.55 (s, 3H,CH3); 13C NMR: δ 148.0, 114.5, 199.8 (C), 11.0, 11.2, 29.3 (CH3); anal. calcd. for C7H10N2O (139.09): C, 60.41; H, 7.97; N, 20.13. Found: C, 60.65; H, 7.30; N, 20.28.
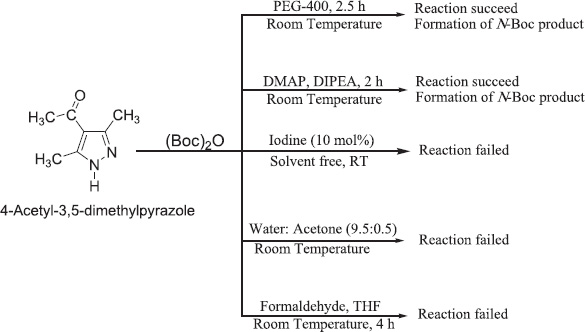 | Figure 1. Procedures applied for the protection of secondary amine in substituted pyrazole. [Click here to view] |
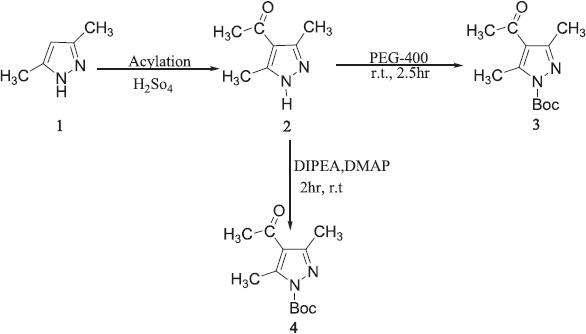 | Scheme 1. N-Boc protection of secondary amine by PEG-400 and DIPEA, DMAP. [Click here to view] |
tert-butyl-4-acetyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-1-carboxylate (3): Pale yellow amorphous solid, Yield: 95%, m.p 68°C–70°C; FTIR (KBr) cm-1: 2,985 CH3 (str.), 1,769 C=O, 1,667 C=C (str.);1H NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.40 (s, 9H, Boc), δ 2.55 (s, 3H, CH3), δ 2.79 (s, 9H, CH3); 13C NMR: δ 28.5 (CH3, Boc), 79.6 (Cq, Boc), 149.2 (C=O), 29.3, 11.0, 4.2 (CH3), 199.8, 147, 106, 144.2; anal. calcd. for C12H18N2O2 (222.14): C, 64.84; H, 8.16; N, 12.60. Found: C, 60.49; H, 7.61; N, 12.01.
tert-butyl-4-acetyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-1-carboxylate (4): Pale yellow amorphous solid, Yield: 85%, m.p 70°C–75°C; FTIR (KBr) cm-1: 2,985 CH3 (str.), 1,769 C=O, 1,667 C=C (str.);1H NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.40 (s, 9H, Boc), δ 2.55 (s, 3H, CH3), δ 2.79 (s, 9H, CH3); 13C NMR: δ 28.5 (CH3, Boc), 79.6 (Cq, Boc), 149.2 (C=O), 29.3, 11.0, 4.2 (CH3), 199.8, 147, 106, 144.2; anal. calcd. for C12H18N2O2 (222.14): C, 64.84; H, 8.16; N, 12.60. Found: C, 60.49; H, 7.61; N, 12.01.
CONCLUSION
In summary, protected pyrazole has been synthesized and characterized. In the present research work on the use of PEG-400, it is a green and eco-friendly approach. This method was easy and adequate for the N-Boc protection of amines because of eco-friendly reaction medium at room temperature (Scheme1) (3) to obtain good to excellent yield. No side product such as isocyanate, urea, or N, N-di-Boc derivatives were showed in TLC, infrared spectroscopy (IR), 1H NMR, and 13C NMR analysis.
We also apply a conventional method of Boc protection of secondary amine in pyrazole. This reaction was performed at room temperature in the presence of catalyst DMAP and DIPEA (Scheme1) (4). This reaction completed very fast with pyrazole moiety as compared to other nucleus and formation of side product is less in number.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to Punjab University, Chandigarh, for spectral analysis and “Consolidation of University Research for Innovation and Excellence in Women Universities” (CURIE) of the Department of Science & Technology (DST), India, for providing research instrument to fulfill the research work. Research work was funded by the DST, Rajasthan (student project) and Banasthali Vidyapith, India.
CONFLICT OF INTERSET
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
Agami C, Couty F. The reactivity of the N-Boc protecting group: an underrated feature. Tetrahedron Lett, 2003; 58:8113–5. CrossRef
Bernatowicz MS, Matsueda GR. 1H-Pyrazole-1-carboxamidine hydrochloride an attractive reagent for guanylation of amines and its application to peptide synthesis. J Org Chem, 1992; 57:2497–502. CrossRef
Chankeswara VS. Catalyst-free chemoselective N-tert Butyloxycarbonylation of amines in water. ARKIVOC, 2006; 12:220–31. CrossRef
Chankeswara SV, Chakraborti AK. Catalyst-free chemoselective N-tert butyloxycarbonylation of amines in water. Org Lett, 2006; 8:3259–62. CrossRef
De Martel C, Ferlay J, Franceschi S, Vignat J, Bray F, Forman D, Plummer M. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2008: a review and synthetic analysis. Lancet Oncol, 2012; 13:607. CrossRef
Finley JH, Volpp GP. Aromatic substitution of 4-phenylisothiazole. J Heterocycl Chem, 1969; 6:841–5. CrossRef
Frankish H. 15 million new cancer cases per year by 2020. Lancet, 2003; 12:361. CrossRef
Jarkowski A, Glode AE, Spangenthal EJ, Wong MK. Heart failure caused by molecularly targeted therapies for cancer. Pharmacotherapy, 2011; 31:92. CrossRef
Fustero S, Simón-Fuentes A, Sanz-Cervera JF. Recent advances in the synthesis of pyrazoles: a review. Org Prep Proc Int, 2009; 41(4):253–90. CrossRef
Giampietro CN. Synthesis cis- or trans-3, 5-disubstituted pyrazolidines via pd-catalyzed carboamination reactions. J Med Chem, 2007; 23:345–59.
Glam U, Hager MH, Van Lanen SG, Ju J, Thorson JS, Shen B. Antitumor antibiotics: bleomycin, enediyens and mitomycin. Chem Rev, 2005; 105:739. CrossRef
Heydari A, Shiroodi RK, Hamadi H, Esfandyari M, Pourayoubi M. N-tert-Butoxycarbonylation of amines using H3PW12O40 as an efficient heterogeneous and recyclable catalyst. Tetrahedron Lett, 2007; 48:5865–8. CrossRef
Ingale AP, More VK, Gangarde US, Shinde SV. Chemoselective N-tert-butyloxycarbonylation of amines in glycerol. New J Chem. 2018; 42:10142–7. CrossRef
Kintzel PE. Anticancer drug-induced kidney disorders. Drugs Saf, 2001; 24:19. CrossRef
Karrouchi K, Radi S, Ramli Y, Taoufik J, Mabkhot YN, Al-Aizari FA, Ansar M. Synthesis and pharmacological activities of pyrazole derivatives: a review. Molecules, 2018; 23:134. CrossRef
Kelly TW, McNeil DWA. A simple method for the protection of arylamines as their t-butylcarbomyl (BOC) derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett, 1994; 35:9003–6. CrossRef
Krystof V. Synthesis 3-Arylazo-3, 5-diamino-1H-pyrazole as a novel group of ATP antagonists with potency against CDK2-Cyclin. E J Med Chem, 2006; 23:6891.
Nadia K, Malika B, Nawel K, Yazid BM, Zine R, Aouf N-E. Simple and efficient cleavage reaction of the Boc group in heterocyclic compounds. J Heterocycl Chem, 2004; 41:57–60. CrossRef
Perry MC. Chemotherapy hepatotoxicity and dose modification in patients with liver disease. Up To Date, 2010; CA371.
Peter GJ, van der Wilt CL, van Moorsel CJ, Kroep JR, Bergman AM, Ackland SP. Basis for effective combination cancer chemotherapy with antimetabolites. Pharmacol Ther, 2000; 87:227. CrossRef
Pisani P. The cancer burden and cancer control in developing countries. Environ Health, 2011; 10:2–4. CrossRef
Pisár M, Schütznerová E, HanÄík F, Popa I, TrávníÄek Z, CankaÅ™ P.. Modification of Boc-Protected CAN508 via Acylation and Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling. Molecules, 2018; 23:149. CrossRef
Raju M, Mäeorg S, Tšubrik O, Mäeorg U An efficient solventless technique for Boc-protection of hydrazines and amines. ARKIVOC, 2009; 4:291–7. CrossRef
Schacht J, Talaska A E, Rybak LP. Cisplatin and aminoglycoside antibiotics: Hearing loss and its prevention. Anat Rec. 2012; 295(11):1837–50. CrossRef
Sharma GVS, Janardhan Reddy J, Sree Lakshmi P, Krishna PR. Rapid and facile lewis acid catalyzed boc protection of amines. Tetrahedron Lett, 2004; 45:6963–5. CrossRef
Singh RK, Kumar S, Prasad DN, Bharadwaj TR. Therapeutic journery of nitrogen mustard as alkylating anticancer agents: historic to future perspectives. Eur J Med Chem, 2018; 151:401–33. CrossRef
Sook Hoo K. Synthesis of 1,3,4-trisubstituted pyrazole from Baylis-Hillman adducts. Bull Korean Chem Soc, 2007; 28:1841. CrossRef
Principles of oncologic pharmacotherapy. Ch 3 Appendix 3. In: Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (eds.). Cancer management: a multidisciplinary approach. 11th edition. Available via http://www.cancernetwork.com/cancermanag?ement-11.
Varela R, Nuvula S, Adapa SR. Molecular iodine-catalyzed facile procedure for N-Boc protection of amines. J Org Chem, 2006; 71:8283–6. CrossRef
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
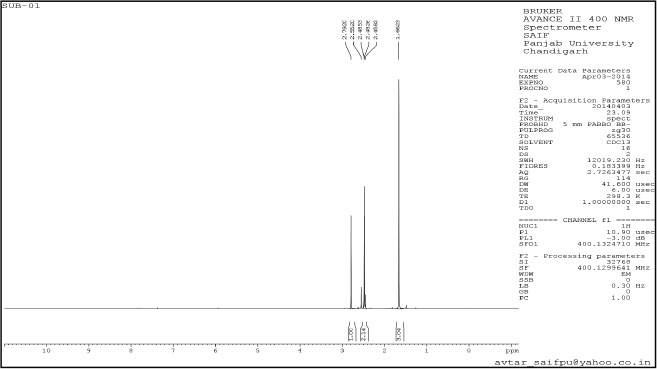
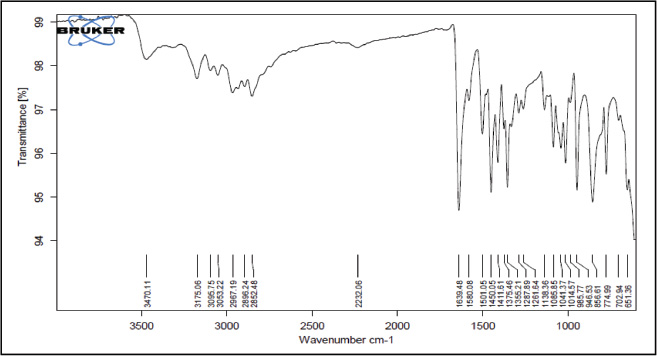 | Supplementary Figure 1. 1H NMR Spectra. [Click here to view] |
 | Supplementary Figure 2. 13C NMR spectra. [Click here to view] |
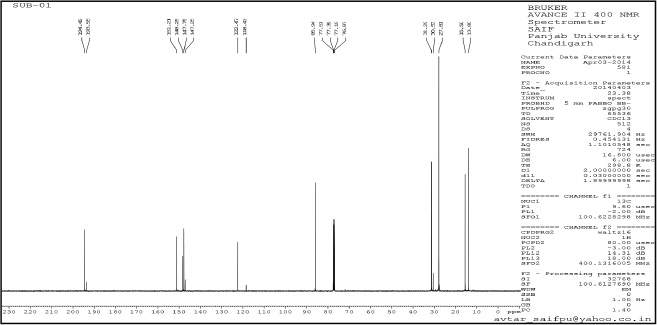 | Supplementary Figure 3. tert-butyl-4-acetyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-1-carboxylate (3). [Click here to view] |
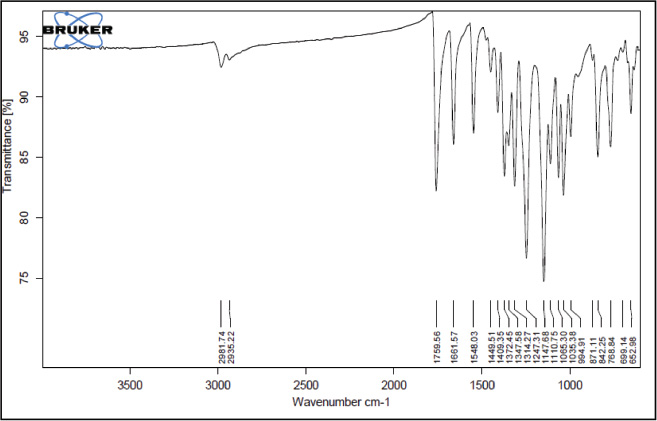 | Supplementary Figure 4. 1H NMR Spectra. [Click here to view] |
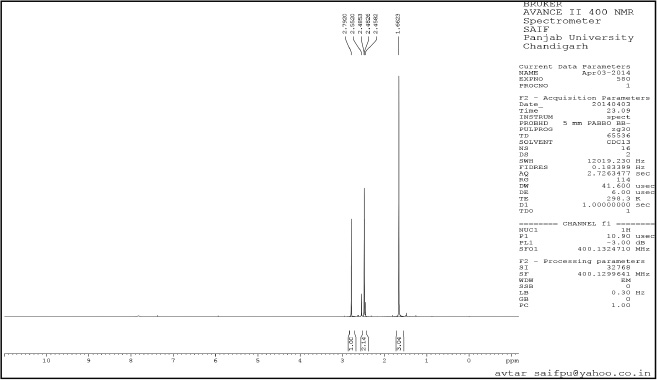 | Supplementary Figure 5. 13C NMR Spectra. [Click here to view] |
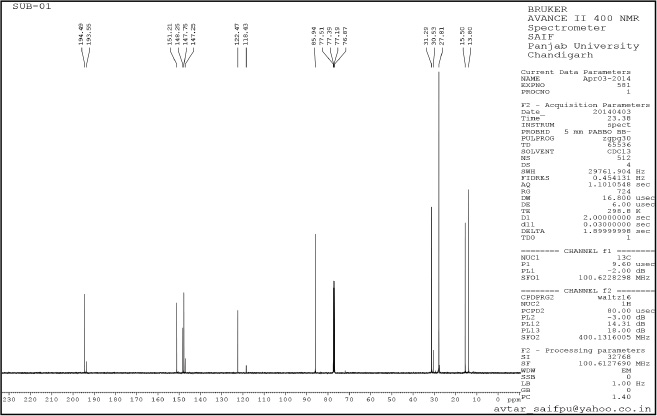 | Supplementary Figure 6. tert-butyl-4-acetyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-1-carboxylate (4). [Click here to view] |
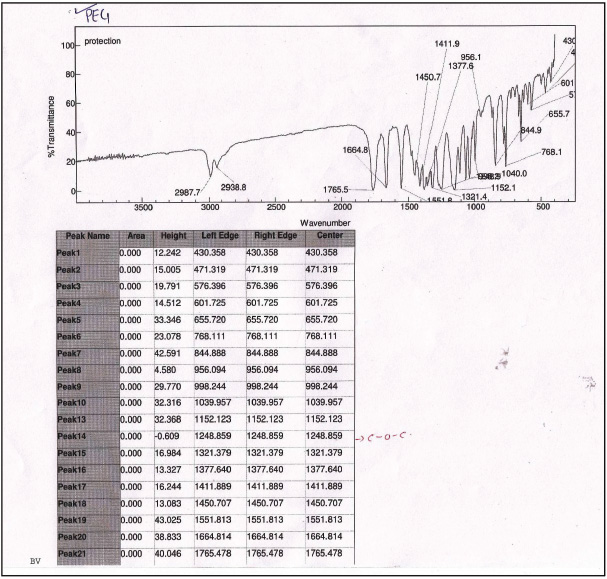 | Supplementary Figure 7. 1H NMR. [Click here to view] |
 | Supplementary Figure 8. 13C NMR. [Click here to view] |
 | Supplementary Figure 9. 1H NMR. [Click here to view] |